Agribusiness Management Midterm
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Operating Profit:
Gross Profit - Operating Expenses
1) Considering Idea Feasibility
a) 1. Strength of Business Idea - We do not want idea to have a fatal flaw
b) 2. Size of Target Market and Customers - Bigger is better! We must meet a definitive market need!
c) Industry and Competitive Advantage - Less competition is better!
d) Capability of Founders - Do our founders have the skills needed for the business to excel?
e) Capital Requirements - Lower capital requirements is better!
4Ps of Marketing
i) product (what you're selling), place (location), pricing (how you are pricing the product), promotion (how you are advertising)
Return on owners equity:
Net profits / Total Owners Equity
Debt ratio:
Total Liabilities / Total Assets
Total asset turnover:
Sales / Total Assets
Return on Assets:
Operating Profits / Total Assets
Debt-to-Asset Ratio:
Total Liabilities / Total Assets
Basis points:
100 basis points = 1%.
1) Definition of Small Business
a) No universal definition of small business
a) Typically categorize small businesses as
i) Microbusiness: provides minimal profits to owner
ii) Attractive Small firm: substantial profits to owner, but not scale-able.
iii) High Potential Venture: small firm with great prospects for growth.
1) Entrepreneurship process:
a) Identify an opportunity
b) Acquire critical resources
c) Execute the plan
d) Harvest the plan
1) Reasons for Starting Your Own Business
a) Personal Fulfillment - doing something for more than yourself
b) Personal Satisfaction - doing something that makes you feel good
c) Independence - being your own boss
d) Financial rewards - generating wealth
1) Entrepreneur Legacy
material assets and intangible qualities passed on to both heirs and society.
1) Types of Startup Ideas
a) New Market: start up idea focused around providing customers with a product not available in their market.
b) New Technology: startup idea focused around a new or relatively new technology.
c) New Benefit: startup idea focused on providing customers with a new or improved product
1) Sources of Startup Ideas
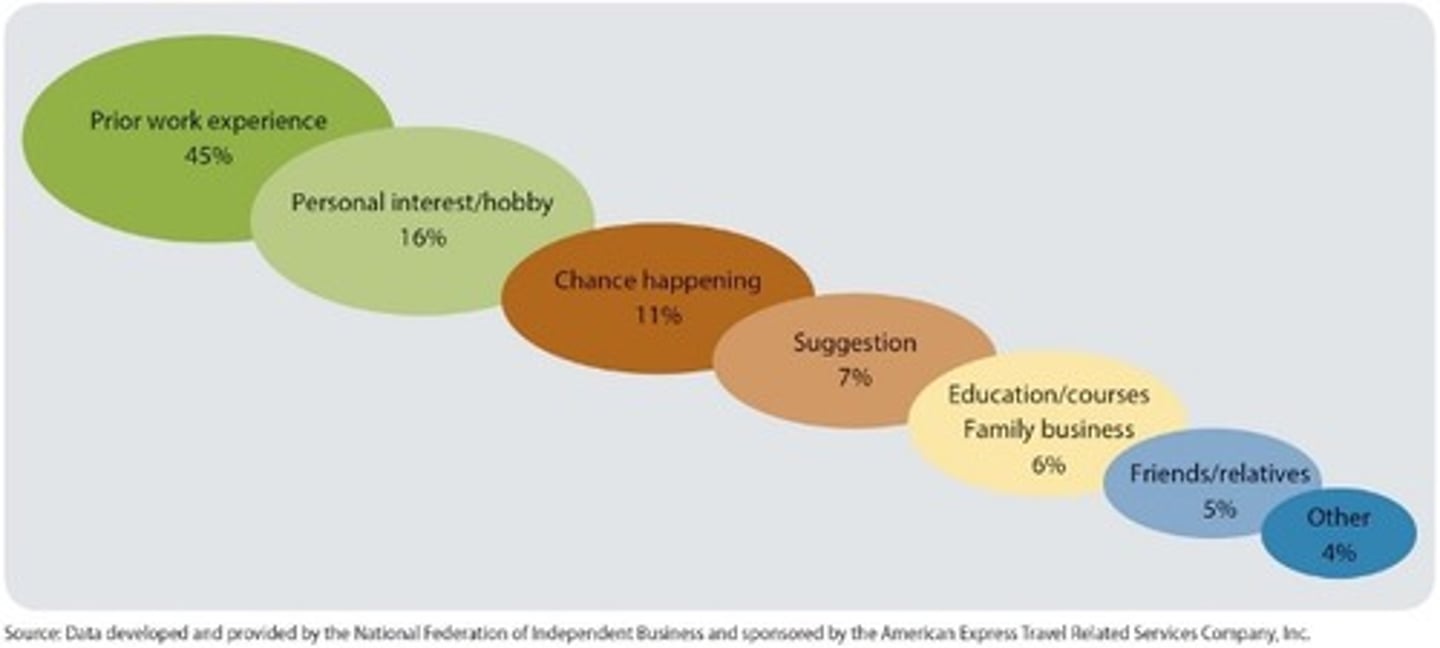
i) We use Porters 5 Forces to Analyze Industry Environment. 5 Forces Include
(1) Threat from New Competition
(2) Threat of Substitute Products
(3) Threat of Rivalry Among Existing Firms
Bargaining Power from Suppliers
Core competency
i) The capabilities that distinguish a firm competitively and reflects its focus and personality.
Cost-based Strategy:
: keeping costs down
Differentiation-based Strategy
a) Providing extra attributes that are valued by customer, so product can be sold for higher price and make profit.
Extensive
The full plan.
1) What is Marketing
a) Business activities that direct the creation, development, and delivery of a bundle of satisfaction from the creator to the targeted customer.
1) Market Research
i) Identify the informational need
ii) Search for secondary data
iii) Collect primary data
iv) Interpret the data gathered
Observational methods:
i) Collecting data while avoiding interpersonal contact with the subject and the researcher
Questioning methods
Collecting data via interaction with respondents
Single-segment approach:
a) A strategy that recognized the existence of several segments but focuses only on one segment. (example: Carters (only sells kids clothes)
B2B (Business to business)
) Hewlett Packard
B2C
Amazon
C2C
online auctions
Transaction based model
(1) website provides mechanism for buying/selling products online. (Amazon)
Operating Profit Margin:
Operating profits / Sales
Current Ratio:
Current Assets / Current Liabilities
Net Profits:
Profit Before Taxes - Income Tax Expense
Profit Before Taxes:
Operating Profit - Interest Expense
Gross Profit:
Sales - Cost of Goods Sold (sales is same thing as revenue
1) Steps in forecasting an income statement
a) Amount of sales
b) Cost of goods sold
c) Operating expenses
d) Interest expense
e) Taxes
Percentage of sales technique
a) a method to forecasting asset requirements using a ratio of assets to sales.
1) 5 C's of Credit
a) Character, capacity, capital, collateral, and conditions
1) Analyzing Business Ideas
i) Outside - In: First evaluate the marketplace and then determine how to use their ability to pursue an opportunity.
ii) Inside - Out: First evaluate their abilities and then identify new products that they might be able to offer the market.
short plan
: Best to make when market conditions are changing rapidly,
a) Bundle of satisfaction includes -
i) Core product - the benefit you get from the product/service.
ii) Actual product - physical commodity/service
iii) Augmented product - ex. Customer service
a) Market Analysis
i) Customer profile: a description of potential customers in target market
ii) Sales forecast: forecast of the volume of sales to expect for one firm (expressed in $)
a) Unsegmented approach:
defines the total market as the target market (example: coca cola)
a) Multi-segment approach:
strategy that recognized different preferences of indivdaul market segments and develops a unique market strategy for each (example: JCPenny selling men's and women's clothing)
information based
information only
content based
(1) provides information, with the hope of generating revenue through advertising (Facebook)
Still learning (30)
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!