FINAL SUMMATIVE REVIEW
1/658
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
659 Terms
(leukopenia/leukocytosis) is increased WBCs from infection, inflammation, or tissue necrosis
(leukopenia/leukocytosis) is decreased WBCs from bone marrow failure or infection
leukocytosis
leukopenia
(hemoglobin/hematocrit) is the measure of the total amount in the peripheral blood and correlates to the amount of RBCs present
(hemoglobin/hematocrit) is "packed cell volume" that is a measure of the % of total blood that is made of RBCs
hemoglobin
hematocrit
(MCHC/MCH/MCV) is the volume of a single RBC that is the best thing to use to classify anemias
(MCHC/MCH/MCV) is the amount of Hgb in each RBC
(MCHC/MCH/MCV) is the average concentration of Hgb in RBCs
MCV (mean corpuscular volume)
MCH (mean corpuscular Hgb)
MCHC (mean corpuscular Hgb concentration)
when imaging bone & intrarticular/complex fractures, a(n) (CT scan/MRI) is better
when imaging soft tissue & spinal cord, a(n) (CT scan/MRI) is better
CT scan
MRI (more detail for SOFT tissue)
sinusitis classification
ACUTE is less than ____ weeks
SUBACUTE is ____ to ____ weeks
CHRONIC is greater than _____ weeks
4
4-12
12
which of the following is most commonly affected by acute sinusitis?
a. maxillary sinus
b. frontal sinus
a. maxillary sinus
Pt is presenting with throbbing facial pain and a runny nose for the past 3 weeks. Their nasal cavity is inflamed.
Before you can dx this pt with acute sinusitis, what plain XR view do you need to order?
what do you expect to see on this XR?
besides an XR, what is the MOST diagnostic (but not routinely used)?
Water's view... will show opacities
CT scan... will show air fluid levels & mucosal edema
which of the following is NOT part of the "bacterial triad" of acute sinusitis?
a. headache
b. fever
c. facial pain
d. runny nose
d. runny nose
If a pt is presenting with acute sinusitis, we consider it to be viral. After how many days of symptoms can we consider giving abx?
a. 3 days
b. 5 days
c. 10 days
d. 14 days
c. 10 days
supportive care until then though!
what is the GOLD standard for dx of acute bacterial sinusitis (ARBS)?
a. Water's view plain XR
b. CT scan
c. MRI
d. echo
b. CT scan
T/F: a longer course of abx is needed in pts with chronic sinusitis than acute sinusitis
TRUE
pts need 3-6 weeks of AUGMENTIN or other abx
which of the following is NOT part of ASA (Samter's) Traid?
a. severe bronchial asthma or rash
b. upper respiratory infection
c. nasal polyps
d. aspirin sensitivity
b. upper respiratory infection
Tx:
- ASA desensitization
- PO or topical steroid
- polypectomy
- AVOID ASA & NSAIDS
Pt presents with deterioration of central vision without pain or redness. Fundascopic exam shows orange drusen bodies. What is the dx?
a. central artery occlusion
b. central vein occlusion
c. vitreous hemorrhage
d. age-related macular degeneration (ARMD)
d. age-related macular degeneration (ARMD)
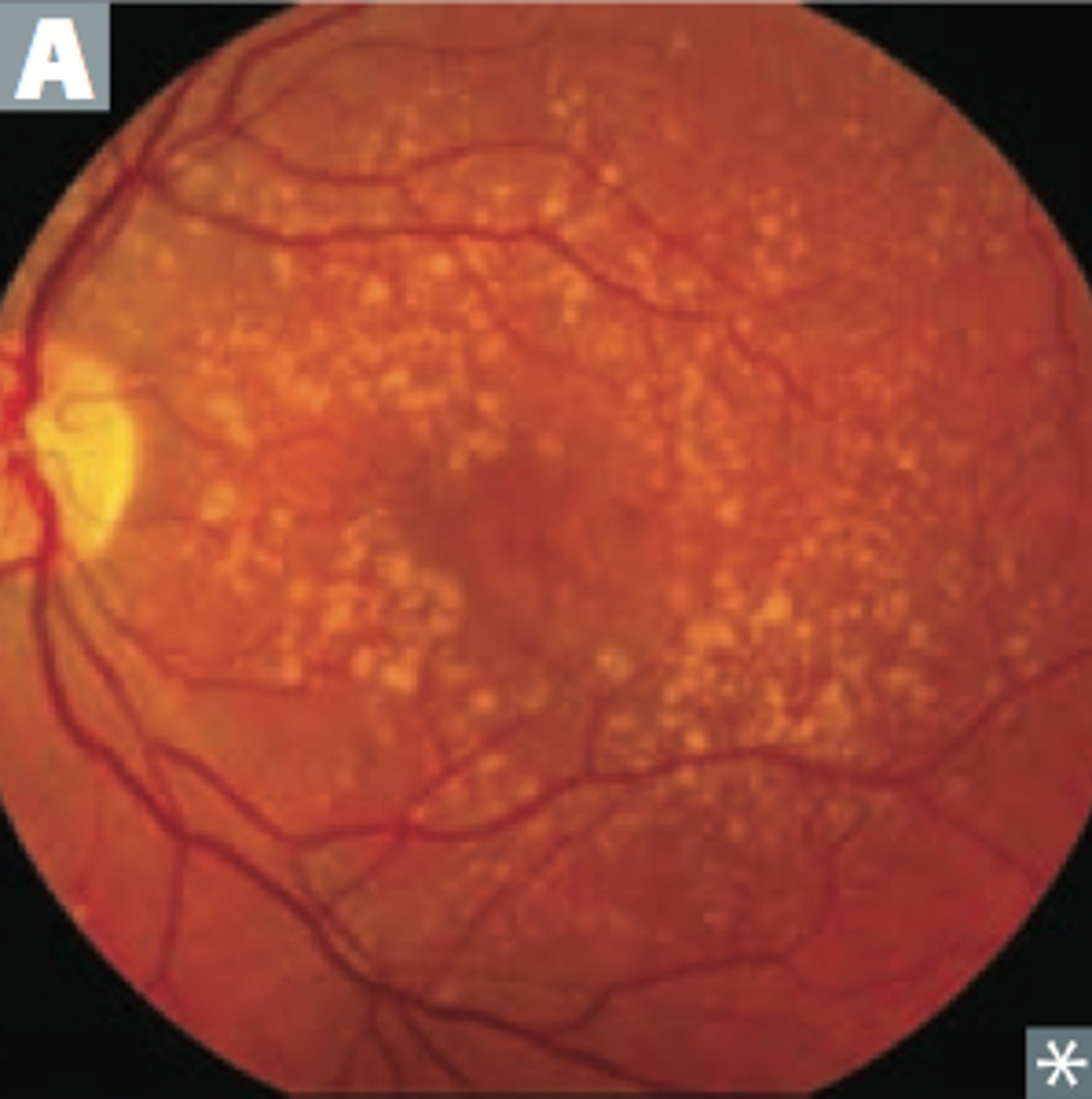
Pt is a 55 yo male presenting with the rapid loss of vision in one eye. They state that it was like a "curtain" spread across their vision. They admit to recent cataract surgery. What is the dx?
a. retinal detachment
b. CMV retinopathy
c. diabetic retinopathy
d. retinoblastoma
a. retinal detachment
transport pt with the head of the bed so that gravity will cause the retina to fall back
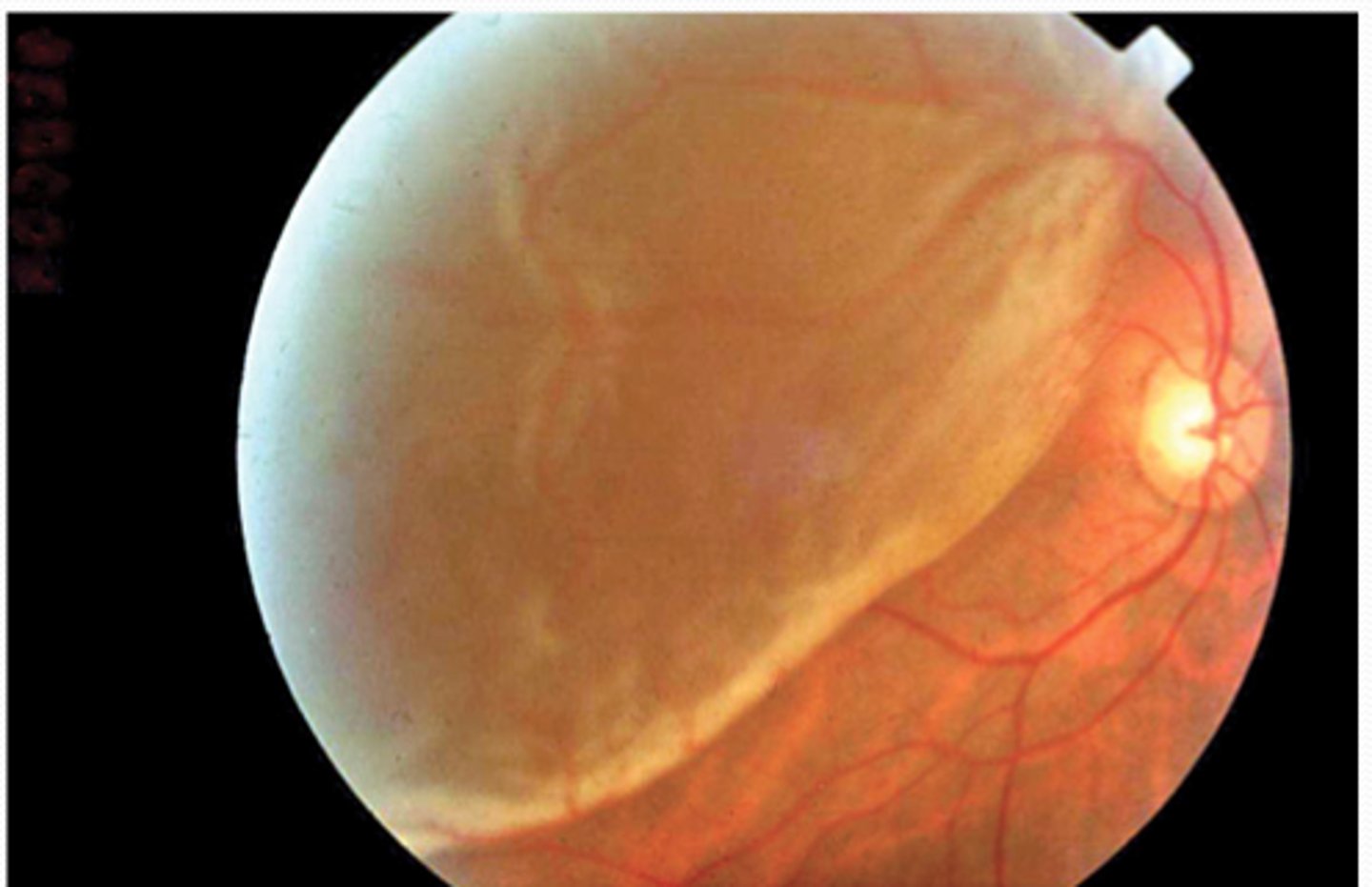
which of the following will present as yellow-white patches on a fundascopic exam in a pt with a CD4 count < 50?
a. retinal detachment
b. CMV retinopathy
c. diabetic retinopathy
d. retinoblastoma
b. CMV retinopathy
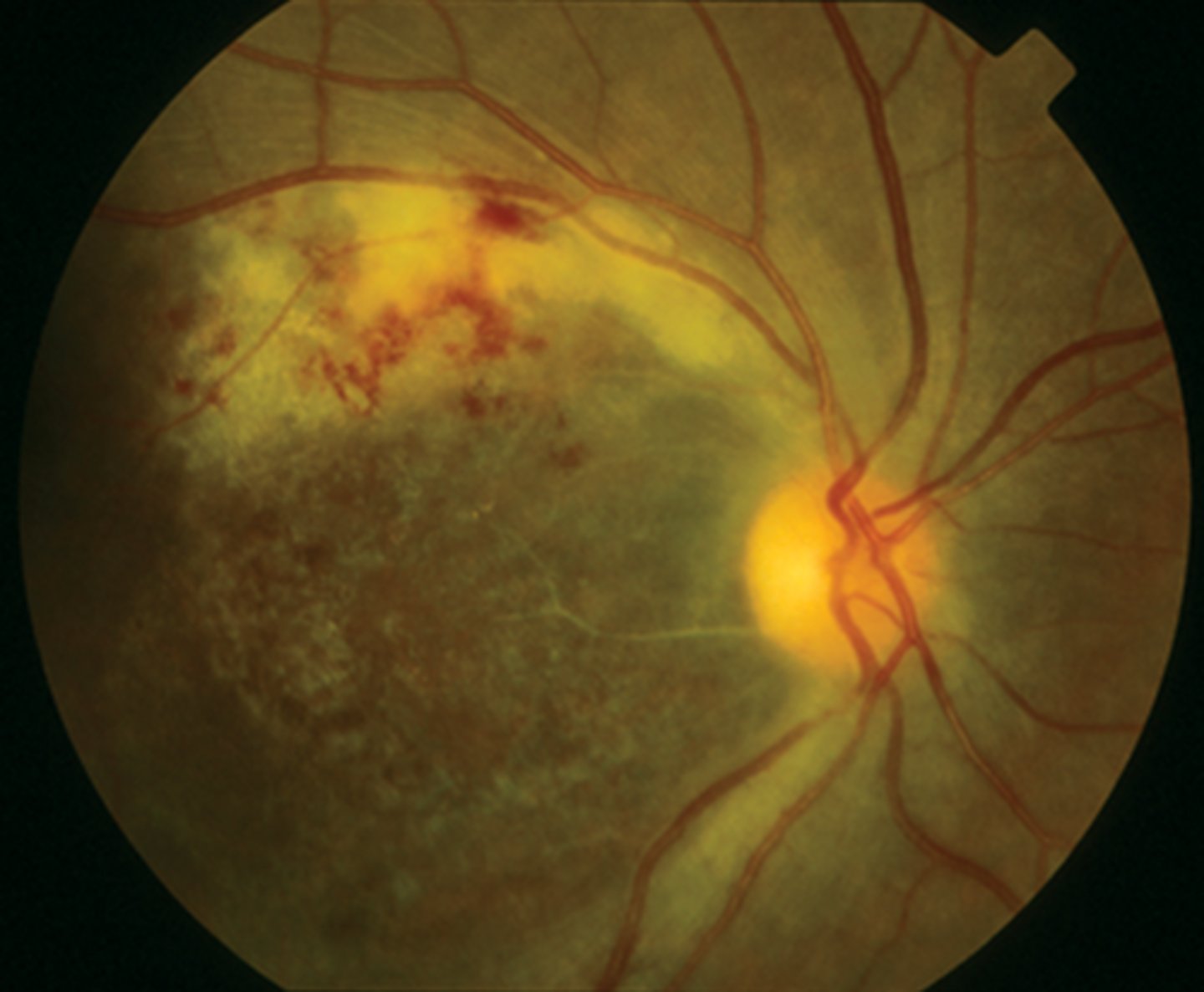
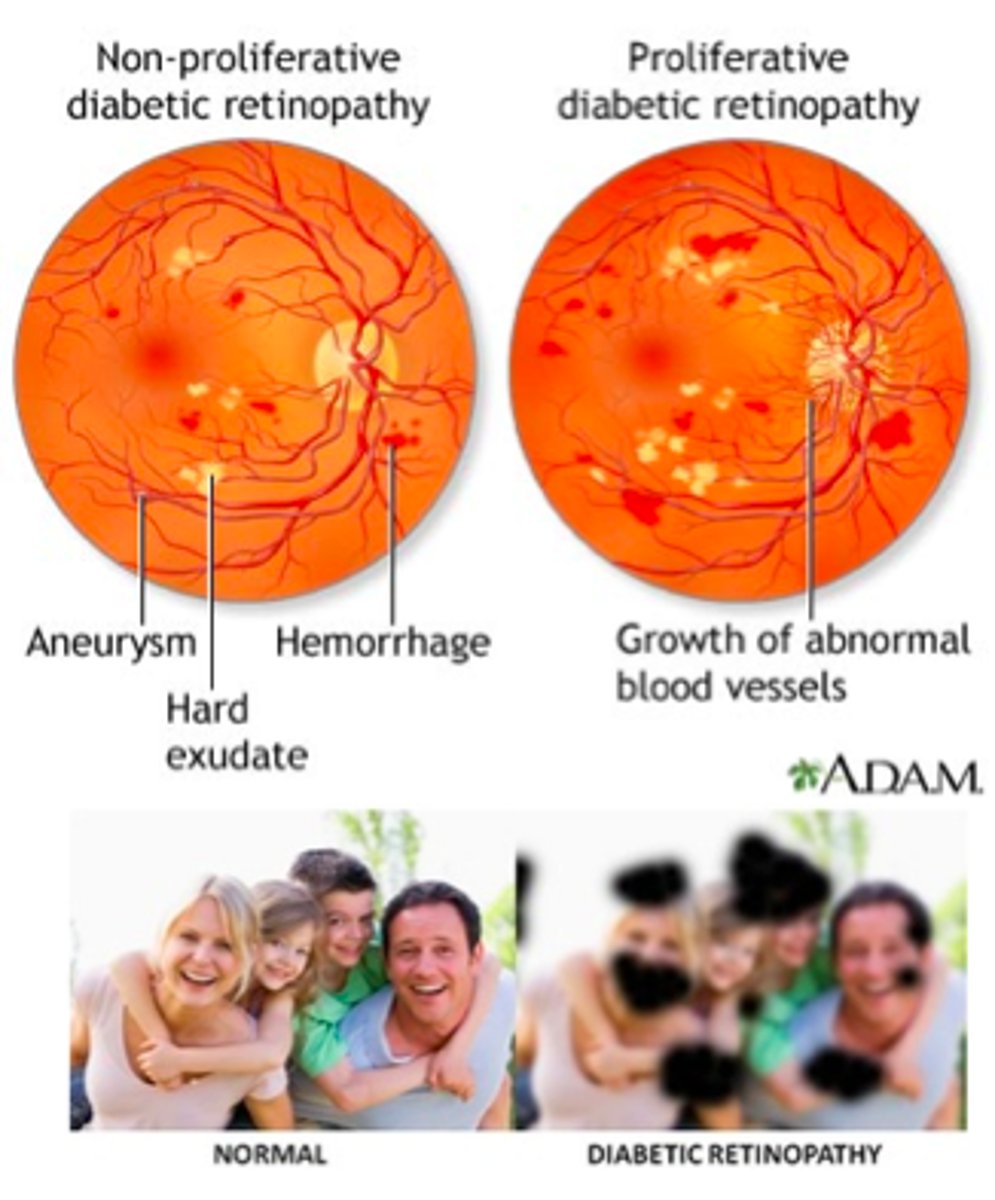
diabetic retinopathy:
(proliferative/non-proliferative) will have hemorrhaging, cotton wool spots, & hard exudates present on fundascopic exam
(proliferative/non-proliferative) will have neovascularization, vitreous hemorrhaging, & possible retinal detachment present on fundascopic exam
non-proliferative
proliferative
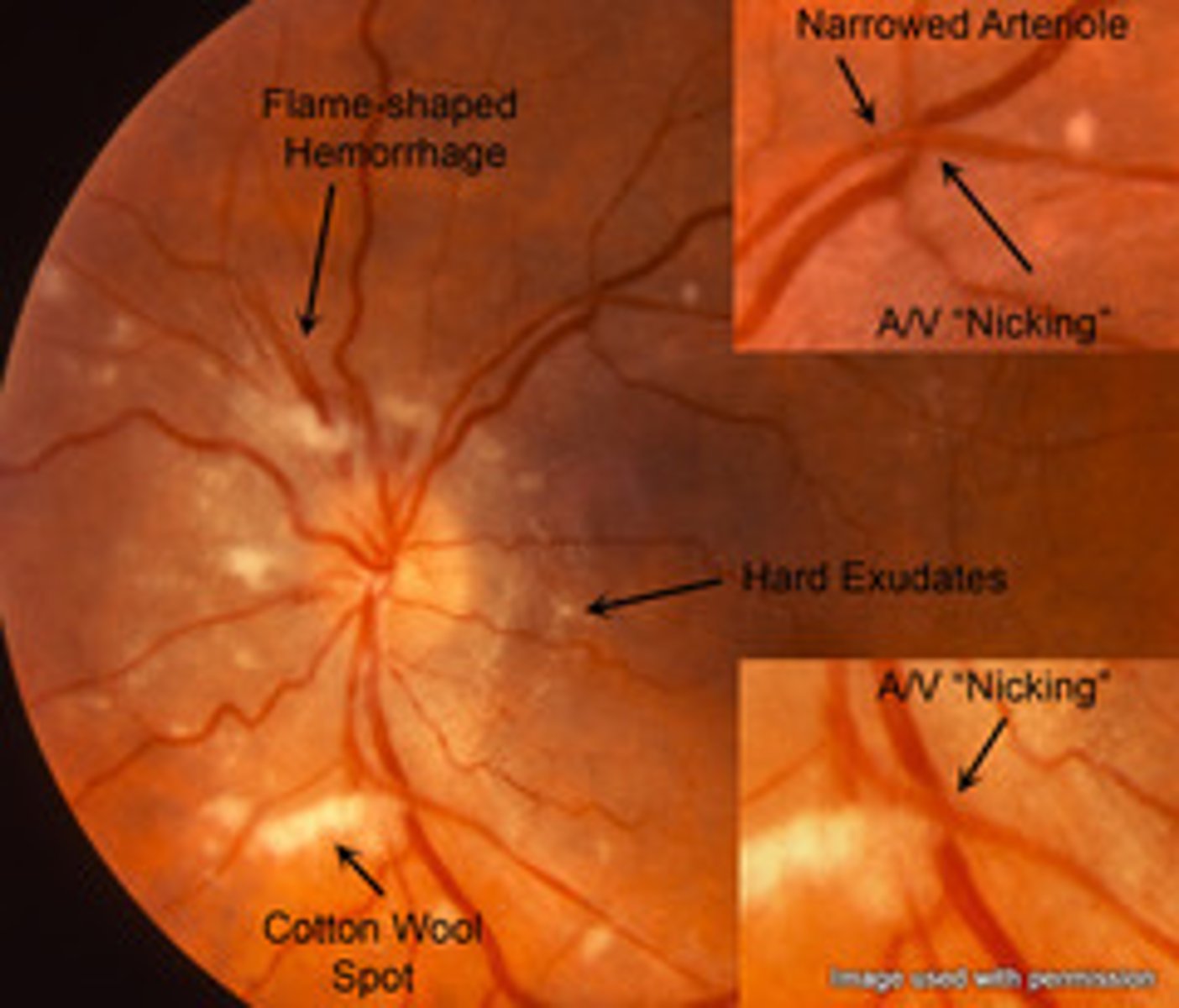
which of the following will result in AV nicking, flame hemorrhages, copper wire, silver wire, cotton wool spots, & hard exudates present on fundascopic exam?
a. HTN retinopathy
b. CMV retinopathy
c. diabetic retinopathy
d. sickle cell retinopathy
a. HTN retinopathy
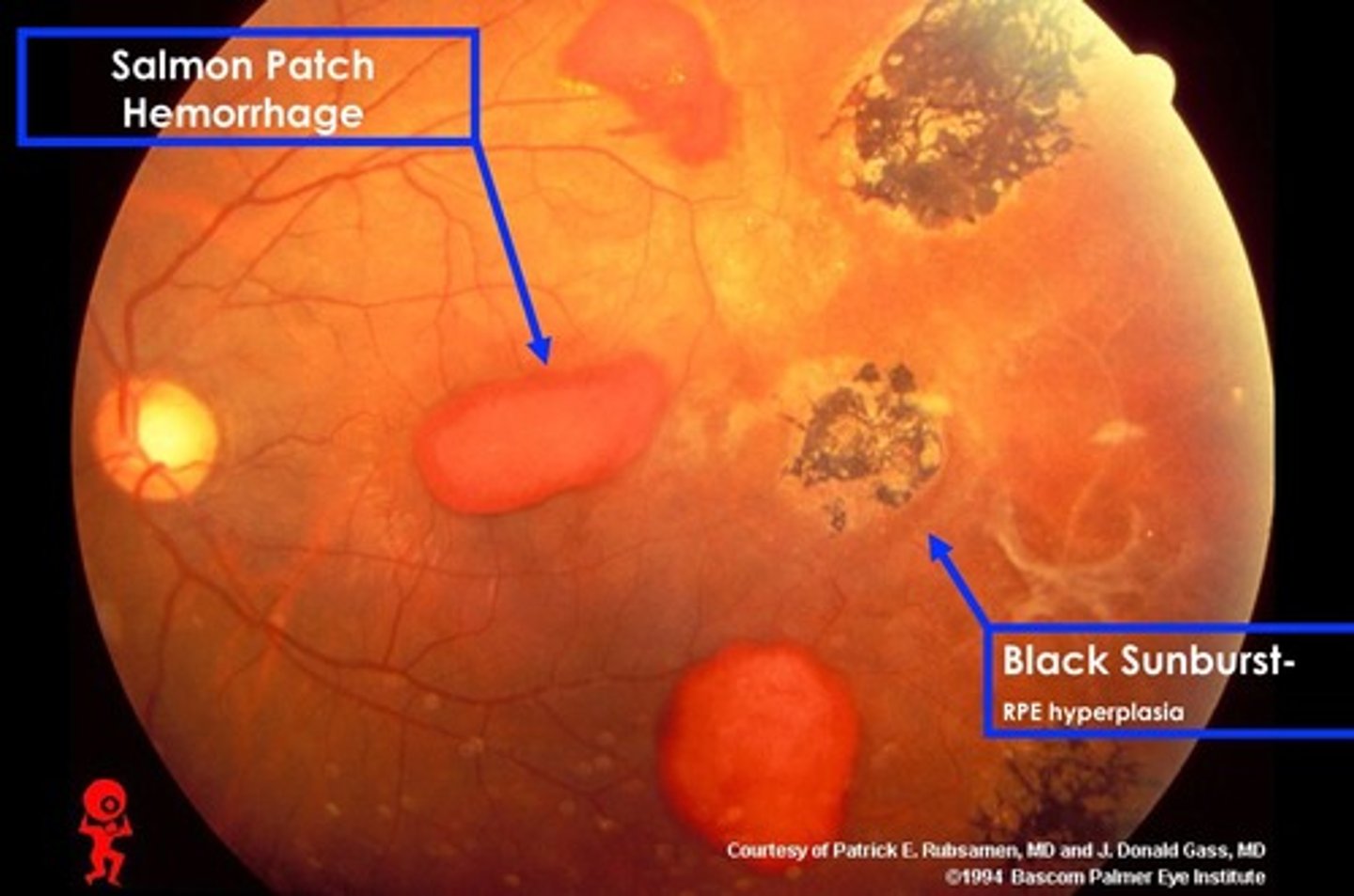
Which of the following is associated with sea fans, salmon patches, & black sunbursts present on a fundascopic exam?
a. HTN retinopathy
b. HIV retinopathy
c. DM retinopathy
d. sickle cell retinopathy
d. sickle cell retinopathy
all start with "S"
which of the following is the most common intraocular malignancy?
a. rhabdomyosarcoma
b. retinoblastoma
c. meningioma
d. optic neuritis
b. retinoblastoma
S/S:
- NO RED REFLEX... eye will appear white
- unilateral leukocoria
- CT = tumor present
Pt is presenting with unilateral proptosis, lid edema, and vision loss. PE reveals a non-tender mass on their eye. What is the dx?
a. rhabdomyosarcoma
b. retinoblastoma
c. meningioma
d. optic neuritis
a. rhabdomyosarcoma
Pt is a 25 yo pt previously dx with multiple sclerosis presenting with unilateral vision loss and blurred vision. PE reveals pupils that are slow to react and a scotomata noted on visual field testing. Fundascopic exam shows a swollen optic disc. What is the tx?
a. abx
b. steroids
c. diet modification, quit smoking, decrease caffeine intake
d. IV acetazolamide followed by PO pilocarpine or timolol
b. steroids
this is optic neuritis - inflammation of the optic nerve
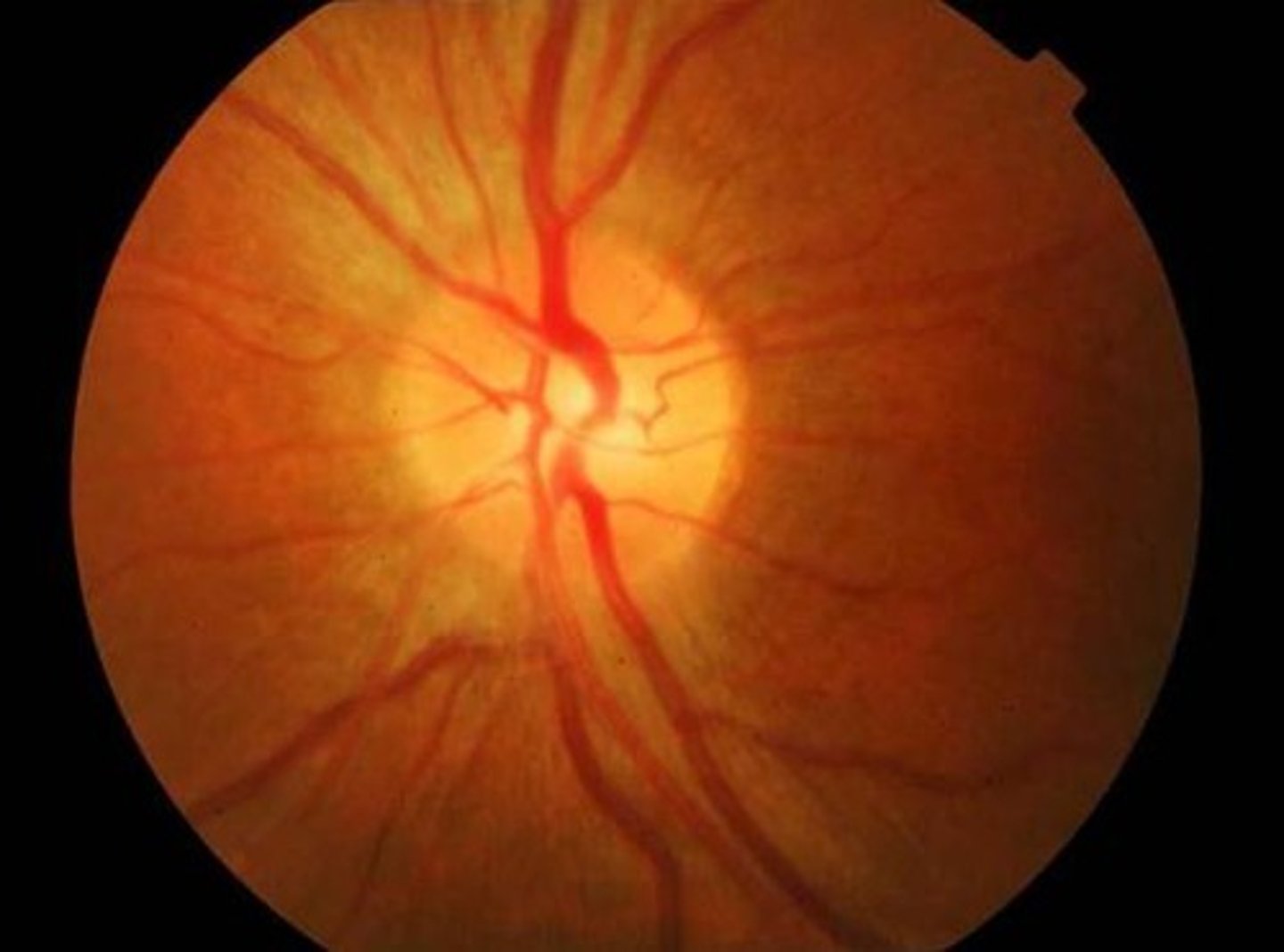
Pt is a 70 yo female presenting with scalp & jaw pain when she chews. Fundascopic exam reveals a pale optic disc. You suspect inflammation of the external carotid artery at the superficial temporal artery, so what should you do next?
a. immediately start the pt on a prednisone burst to avoid vision loss
b. immediately start the pt on IV acetazolamide followed by PO pilocarpine or timolol
c. get a temporal bx
d. get a CT scan of the head
c. get a temporal bx
THEN immediately start the pt on a prednisone burst to avoid vision loss
Pt is presenting bilateral progressive loss of vision over the past 6 months. They have a hx of DM and dx studies reveal increased ICP of 23 nml. What is the likely dx?
a. primary open-angle glaucoma
b. acute closed-angle glaucoma
a. primary open-angle glaucoma
can result in blindness
Tx:
- diet modification
- stop smoking
- Timolol (to decrease IOP)
what is a NORMAL ICP?
10-22
Pt is presenting with the sudden onset of severe right eye pain, redness, and blurred vision. They also admit to N/V, HA, and halos around lights. PE reveals a steamy cornea, a fixed mid-dilated pupil, and shallow anterior chamber. What is the dx?
a. primary open-angle glaucoma
b. acute closed-angle glaucoma
b. acute closed-angle glaucoma
What is the tx of primary open-angle glaucoma?
a. abx
b. steroids
c. diet modification, quit smoking, decrease caffeine intake
d. IV acetazolamide followed by PO pilocarpine or timolol
c. diet modification, quit smoking, decrease caffeine intake
What is the tx of acute closed-angle glaucoma?
a. abx
b. steroids
c. diet modification, quit smoking, decrease caffeine intake
d. IV acetazolamide followed by PO pilocarpine or timolol
d. IV acetazolamide followed by PO pilocarpine or timolol
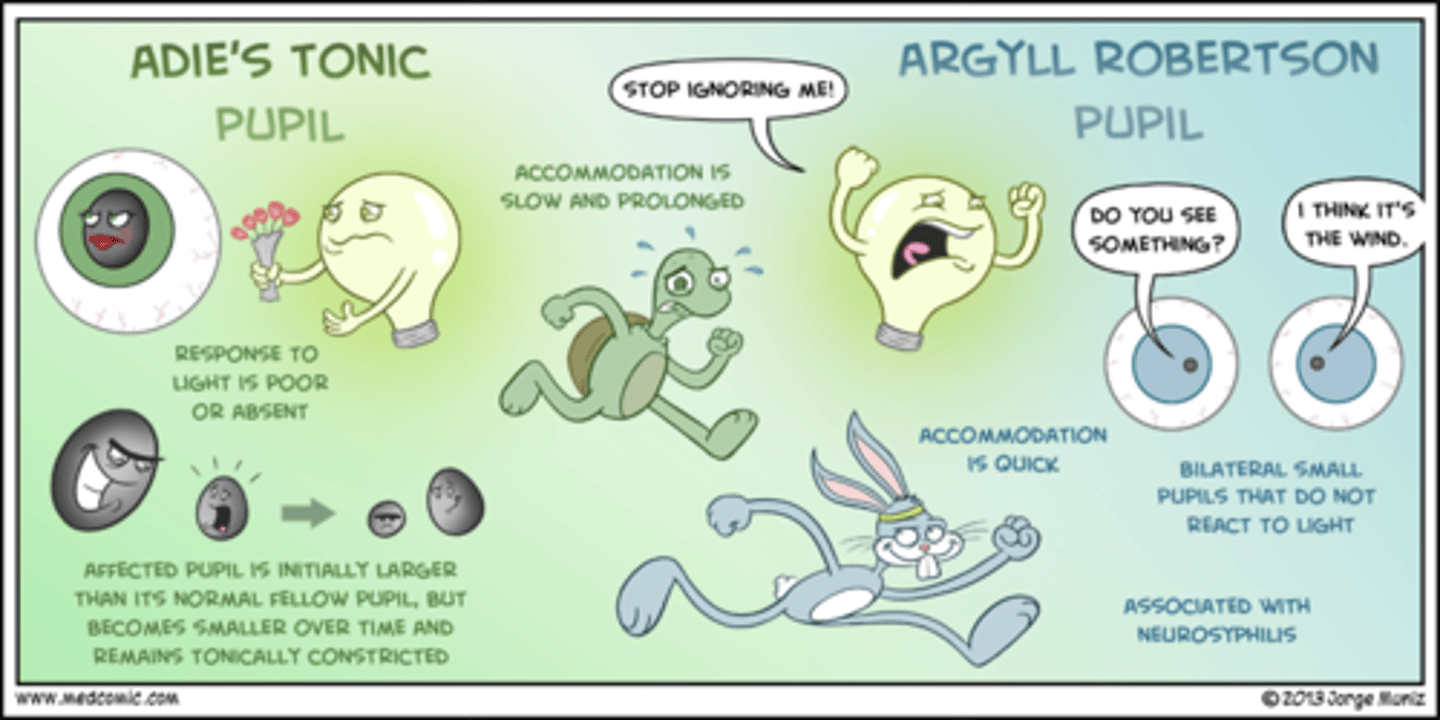
(Adie's/Marcus Gunn) pupil is an afferent pupillary defect where the pupil dilates instead of constricts when the penlight shines in it and is associated with disease of the retina or optic nerve
(Adie's/Marcus Gunn) pupil is a tonic pupil with parasympathetic denervation that constricts poorly to light, but reacts better to accommodation
Marcus Gunn
Adie's
Pt is presenting with bilaterally small pupils. They constrict on accommodation but do NOT constrict with bright light. Which of the following is associated with neurosyphilis?
a. Adie's pupil
b. Marcus Gunn pupil
c. Argyll Robertson pupil
d. Horner's syndrome
c. Argyll Robertson pupil
Pt is presenting with unilateral ptosis, myosis, & anhydrosis ("PAM"). PE reveals delayed eyelid elevation. What is the next step in confirming a dx for this pt?
a. cocaine drop test
b. CT scan
c. MRI
d. fluorescein stain
a. cocaine drop test
this is Horner's syndrome
1 hr after instillation, a NORMAL pupil will dilate more than a HORNER'S pupil... so the degree of anisocoria is increased(an affected pupil will NOT dilate)
aniscoria of > 0.8 mm after cocaine administration = (+) result
if there is ptosis on the eyelid on the same side as the SMALL pupil, the pt has (CN III palsy/Horner's syndrome)
if there is ptosis on the eyelid on the same side as the LARGE pupil, the pt has (CN III palsy/Horner's syndrome)
Horner's syndrome
CN III palsy
what is the most common cause of conductive hearing loss?
cerumen impaction
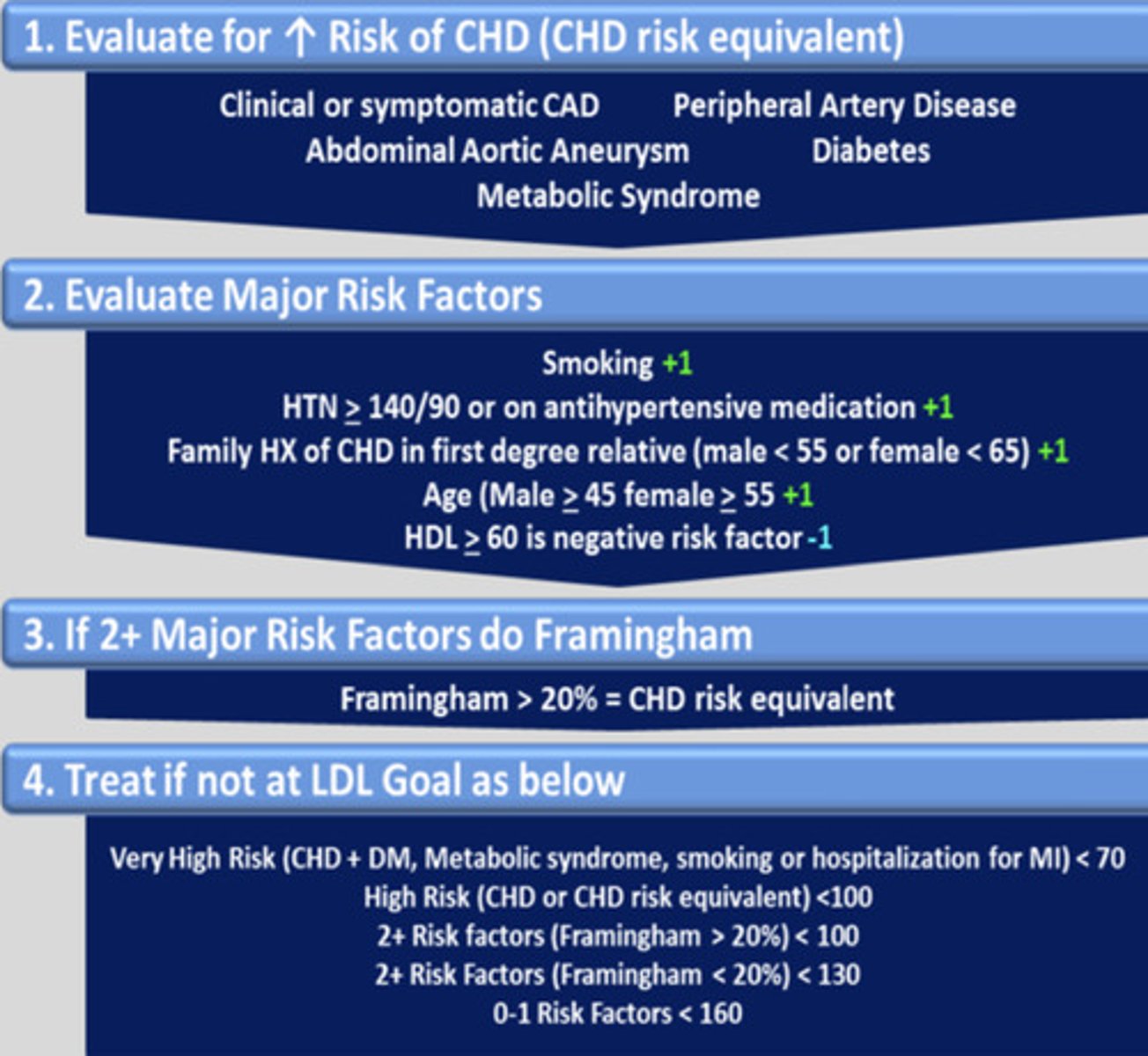
screening for hyperlipidemia
USPSTF: screen ALL pts > 21 yo
ACC/AHA: screen ALL pts with CV disease and DM
AAP/NCEP: screen ALL kids at 9-11 yo AND at 17-21 yo
what do we use Framingham Guidelines for?
a. staging of colorectal cancer
b. classification of ASCVD
c. to determine the LDL goals of pts
d. to dx a pt with hyperlipidemia
c. to determine the LDL goals of pts
after starting a pt on a statin for their high cholesterol, when should we monitor them after starting it?
how often should we check levels & monitor the pt?
4-12 weeks
3-12 months
which of the following hyperlipidemia meds works by decreasing LDL & TGs, but can cause myopathy, rhabdomyolysis, & increased liver enzymes (which is why it would NOT be given to pts with liver disease)?
a. atorvastatin
b. gemifibrozil
c. questran
d. hydrochlorothiazide
a. atorvastatin
atorvastatin & rosuvastatin are 1st LINE for hyperlipidemia
**NO GRAPEFRUIT**
which of the following is a major pt education point when prescribing statins for a pt with hyperlipidemia?
a. do not take if you have severe renal disease
b. do not eat grapefruit while taking this med
c. this med will likely cause GI distress
d. drink alot of water and take ASA before taking med to reduce flushing
b. do not eat grapefruit while taking this med
which of the following is a major pt education point when prescribing fibrates for a pt with hyperlipidemia (Gemifibrozil and Tricor)?
a. do not take if you have severe renal disease
b. do not eat grapefruit while taking this med
c. this med will likely cause GI distress
d. drink alot of water and take ASA before taking med to reduce flushing
a. do not take if you have severe renal disease
severe renal & liver disease are CONTRAINDICATED with these meds
S/E:
- dyspepsia
- gallstones
- myopathy
which of the following is a major pt education point when prescribing bile acid sequestrates for a pt with hyperlipidemia (Questran and Welchol)?
a. do not take if you have severe renal disease
b. do not eat grapefruit while taking this med
c. this med will likely cause GI distress
d. drink alot of water and take ASA before taking med to reduce flushing
c. this med will likely cause GI distress
this med also decreases the absorption of other drugs and does NOT work well to decrease LDL
MOA: blocks cholesterol absorption at the intestinal brush border
which of the following is NOT an adverse effect of ezetimibe (hyperlipidemia med)?
a. angioedema
b. pancreatitis
c. hepatitis
d. gallstones
d. gallstones
this is an adverse effect of fibrates (Gemifibrozil and Tricor)
which of the following is a major pt education point when prescribing niacin for a pt with hyperlipidemia?
a. do not take if you have severe renal disease
b. do not eat grapefruit while taking this med
c. this med will likely cause GI distress
d. drink alot of water and take ASA before taking med to reduce flushing
d. drink alot of water and take ASA before taking med to reduce flushing
S/E:
- **FLUSHING**
- hyperglycemia
- upper GI distress
- hepatotoxicity
contraindications:
- severe gout
- liver disease
- peptic ulcers
which of the following is NOT considered a 1st line tx of A Fib when treating LONG term?
a. warfarin
b. eliquis
c. pradaxa
d. xarelto
a. warfarin
1st line = non-vitamin K PO antagonists
T/F: we can use LMWH or heparin as bridge therapy when starting a pt on warfarin
TRUE
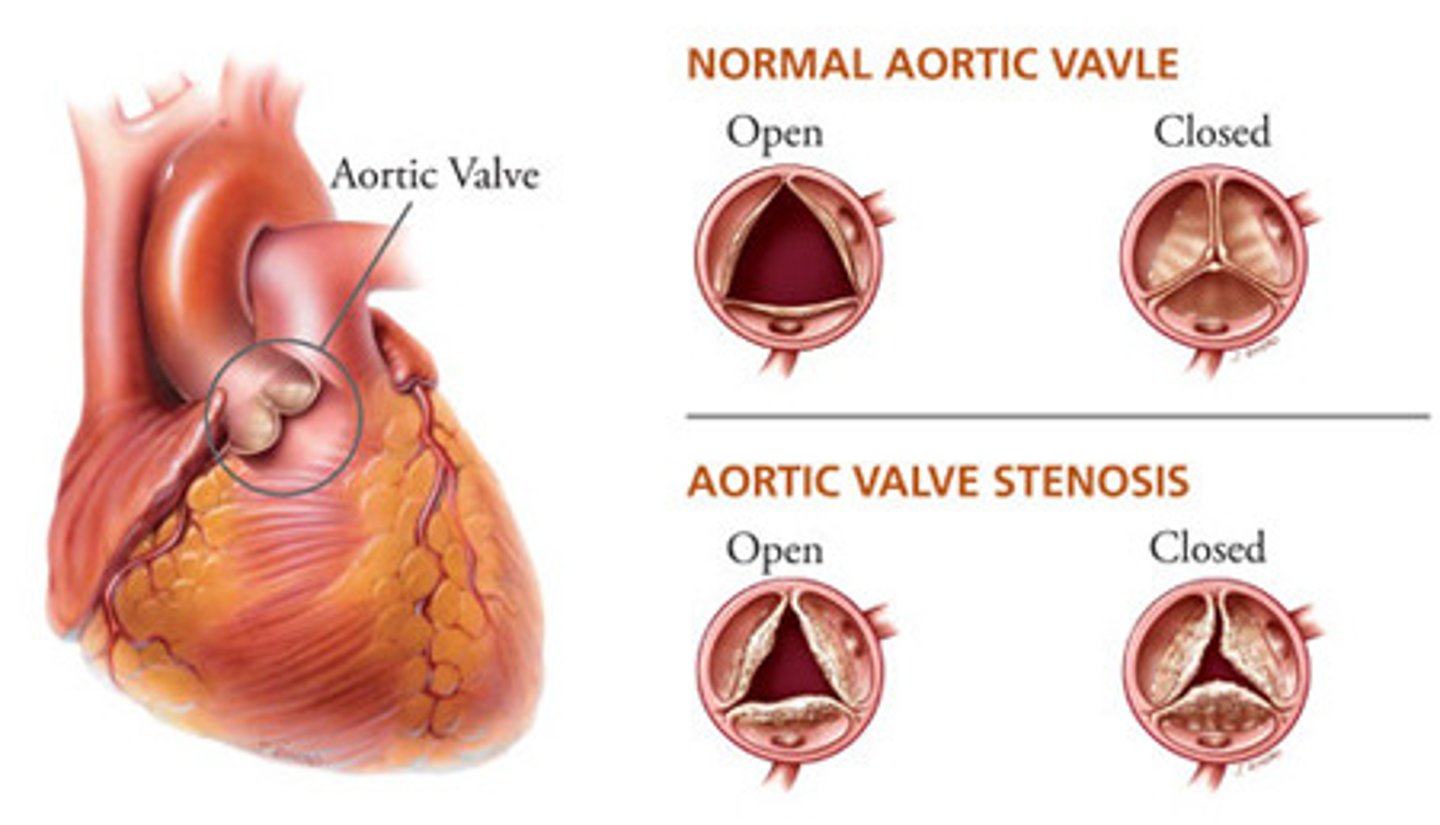
which of the following is NOT part of the triad classifying aortic stenosis?
a. exertional dyspnea
b. orthopnea
c. syncope
d. angina
b. orthopnea
Pt is presenting with chest pain, syncope, and exertional SOB. PE reveals an S2 paradoxical split & pulsus parvus et tardus. You hear a crescendo-decrescendo systolic ejection murmur at the right 2nd ICS that radiates to the carotid. What is the dx?
a. aortic stenosis
b. aortic regurgitation
c. coarctation of the aorta
d. mitral regurgitation
a. aortic stenosis
this murmur is aka "diamond crescendo" murmur
Dx: TEE
Tx: valve replacement
Pt is presenting with a decrescendo blowing diastolic murmur that increases when they lean forward. PE reveals pulsus alternans & bisferens pulses. They also have a precordial impulse and displaced PMI. Which of the following describes the murmur that this can develop into?
a. opening snap with a low pitched diastolic rumble at the apex in the left lateral decubitus position
b. an apical low pitched diastolic rumble at the apex
c. crescendo-decrescendo after a mid-systolic click at the apex
d. blowing pansystolic at the LLSB
b. an apical low pitched diastolic rumble at the apex
this is an Austin Flint murmur
Pt is presenting with aortic regurgitation
aortic regurgitation PE signs:
a wide pulse pressure with forceful arterial pulse upswing and rapid fall
a. water hammer pulse
b. Traube's pulse
c. Corrigan's pulse
d. Quincke's sign
a. water hammer pulse
aortic regurgitation PE signs:
pistol-shot bruit over the femoral pulse
a. water hammer pulse
b. Traube's pulse
c. Corrigan's pulse
d. Quincke's sign
b. Traube's pulse
aortic regurgitation PE signs:
an unusually large carotid pulsation
a. water hammer pulse
b. Traube's pulse
c. Corrigan's pulse
d. Quincke's sign
c. Corrigan's pulse
aortic regurgitation PE signs:
pulsating blanching & reddening of the fingernails with light pressure
a. water hammer pulse
b. Traube's pulse
c. Corrigan's pulse
d. Quincke's sign
d. Quincke's sign
aortic regurgitation PE signs:
head bobbing that is caused by carotid pulsations
a. DeMusset's sign
b. Quincke's sign
c. Muller's sign
d. Duroziez's sign
a. DeMusset's sign
aortic regurgitation PE signs:
pulsatile bobbing of the uvula
a. DeMusset's sign
b. Quincke's sign
c. Muller's sign
d. Duroziez's sign
c. Muller's sign
aortic regurgitation PE signs:
to and fro murmur over the femoral artery that is best heard with mild pressure to the artery
a. DeMusset's sign
b. Quincke's sign
c. Muller's sign
d. Duroziez's sign
d. Duroziez's sign
T/F: a CXR of a pt with aortic regurgitation will be non-specific
FALSE
it will show and enlarged heart and pulmonary edema
what is the MCC of congenital aortic stenosis?
a. IV drug use
b. a biscuspid aortic valve
c. a tricuspid aortic valve
d. Berry aneurysm
b. a biscuspid aortic valve
the valve is supposed to have 3 CUSPS
Pt is presenting with an acyanotic congenital heart disorder that is a result of the fibrotic narrowing of the aortic lumen, leading to increased BP in the aorta and great vessels. PE reveals a crescendo-decrescendo systolic murmur at the left upper back, a strong carotid pulse, and weak lower extremity pulses. Which of the following is associated with the dx?
a. (+) ASO titer
b. a patent formen ovale that causes strokes in young pts
c. "rib notching" + "figure 3" on a CXR
d. Traube's pulse
c. "rib notching" + "figure 3" on a CXR
this is coarctation of the aorta
other S/S:
**different BP's in the UE & LE**
- CHF symptoms
- HTN
- Turner syndrome (webbed neck + short stature)
Pt is a 21 yo female presenting with epistaxis, cold extremities, and claudication. Which of the following is associated with different blood pressures in the upper & lower extremities and Berry aneurysms?
a. aortic stenosis
b. aortic regurgitation
c. coarctation of the aorta
d. mitral regurgitation
c. coarctation of the aorta
Pt is presenting with ascites and peripheral edema. PE reveals JVP, S3, hepatic enlargement, and a parasternal lift. You note a murmur that increases with inspiration & decreases with valsalva at the 4th ICS. What does this murmur likely sound like?
a. opening snap with a low pitched diastolic rumble at the apex in the left lateral decubitus position
b. an apical low pitched diastolic rumble at the apex
c. crescendo-decrescendo after a mid-systolic click at the apex
d. blowing pansystolic at the LLSB
d. blowing pansystolic at the LLSB
this is tricuspid regurgitation
Pt is a tall, thin female presenting with palpitations. She has a murmur that is a crescendo-decrescendo after a mid-systolic click at the apex. It increases with valsalva & decreases with squatting. Which of the following should she be treated with?
a. nifedipine
b. beta blockers
c. valve surgery
d. warfarin
b. beta blockers
this is mitral valve prolapse... leaflets prolapse into left atrium during systole
what is the tx for an asx pt presenting with aortic regurgitation?
a. nifedipine
b. beta blockers
c. valve surgery
d. warfarin
a. nifedipine
this is a CCB to help decrease afterload of the heart
if SX = pt will need surgery
which of the following describes the murmur of mitral stenosis?
a. opening snap with a low pitched diastolic rumble at the apex in the left lateral decubitus position
b. an apical low pitched diastolic rumble at the apex
c. crescendo-decrescendo after a mid-systolic click at the apex
d. blowing pansystolic at the LLSB
a. opening snap with a low pitched diastolic rumble at the apex in the left lateral decubitus position
this murmur will increase with squatting and decrease with valsalva
S/S:
- palpitations
- dyspnea
- heart failure
- bisferens pulse
- ortner syndrome
tetralogy of fallot
HINT: "PROV"
Pulmonic stenosis
RVH
Overriding aorta
VSD - this is what causes the shunting to occur, so the pressure in the RV is higher than the LV
what is the MC heart valve affected by rheumatic fever?
a. aortic valve
b. pulmonic valve
c. mitral valve
d. tricuspid valve
c. mitral valve
THIS CAN LEAD TO **MITRAL STENOSIS**
ALL of the other valves are affected too though!
T/F: endocarditis is caused by GAHBS
FALSE
rheumatic fever is caused by GAHBS!
which of the following is NOT part of the "triple abx" tx being treated for endocarditis with a prosthetic valve?
a. vancomycin
b. PCN G
c. gentamicin
d. rifampin
b. PCN G
this is the primary 1st line tx tho if the pt has a native valve
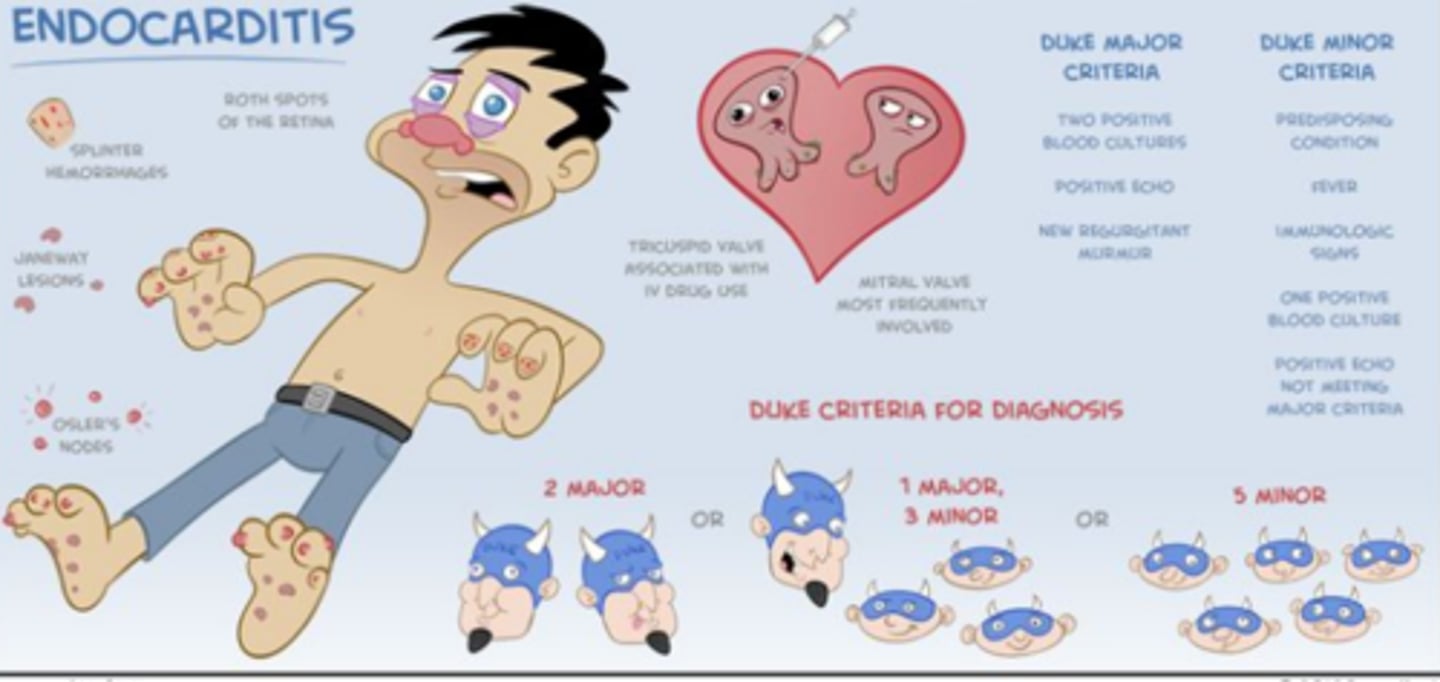
DUKE CRITERIA
for dx of infective endocarditis
MAJOR:
- 2 (+) blood cultures
- evidence of vegetation, abscess, or dehiscence of prosthetic valve on ECHO
MINOR:
- 1 (+) blood culture
- predisposing condition
- fever
- immunologic s/s (Osler's nodes, Roth spots, glomerulonephritis)
(acute/subacute) bacterial endocarditis develops gradually over weeks to months and typically affects a heart that is already damaged
(acute/subacute) bacterial endocarditis develops rapidly and causes significant valve damage in pts with normal hearts OR a heart that is already damaged from IVDA, prosthetic valves, or sepsis
the MCC of (acute/subacute) bacterial endocarditis is staph aureus with the tricuspid valve typically being affected in IVDA
the MCC of (acute/subacute) bacterial endocarditis in NON-IVDA is strep viridans
subacute
acute
acute
subacute
which of the following occurs when pathogen travel by blood and enmesh in fibrin & platelets to create vegetations that settle on the valves of the heart, preventing the complete closure and resulting in a murmur?
a. acute rheumatic fever
b. infective endocarditis
c. pericarditis
d. peripheral arterial disease
b. infective endocarditis
S/S of endocarditis:
(Osler nodes/Janeway lesions/Roth spots) are located on the palms
(Osler nodes/Janeway lesions/Roth spots) are located on the fingers & toes
(Osler nodes/Janeway lesions/Roth spots) are located on the retina
Janeway lesions
Osler nodes
Roth spots
which of the following is NOT a complication of endocarditis?
a. valve dysfunction
b. abscess formation
c. peripheral embolization
d. mitral stenosis
d. mitral stenosis
this is a complication of rheumatic fever
T/F: pts with infective endocarditis that have their native valves are treated with anticoagulation
FALSE
anticoagulation is contraindicated in these pts due to the risk of intracerebral hemorrhaging
Pt is presenting with chest pain that improves when they lean forward and worsens when they lay flat. It radiates to their back, shoulder, and neck. They also admit to a fever and dyspnea. PE reveals a pericardial "friction rub" present at the diaphragm over the left sternal border that is increased with expiration. An EKG shows diffuse ST elevation, T wave inversion, & PR depression. What is the major complication of this dx?
a. mitral stenosis
b. rheumatic fever
c. HTN
d. Dressler's syndrome
d. Dressler's syndrome
this is pericarditis... Dressler's syndrome is when pericarditis occurs shortly after an MI or cardiac surgery (the heart becomes irritated and inflamed)
Tx:
- if recurrent = **COLCHICINE**
- NSAIDs
- pericardial window
what is Beck's triad?
characteristics of cardiac tamponade
1. JVD
2. hypotension
3. muffled heart sounds
other S/S:
- Kussmaul's sign: increased venous distension & pressure during inspiration
- pulsus paradoxus: > 12 mmHg decrease in SBO with inspiration
T/F: Kussmaul's sign and pulsus paradoxus are associated with constrictive pericarditis
FALSE
there is NOT pulsus paradoxus present
which of the following is associated with a calcification ring present on CXR?
a. myocarditis
b. pericardial effusion
c. cardiac tamponade
d. constrictive pericarditis
d. constrictive pericarditis
caused by scarring and loss of normal elasticity, leading to fibrotic thickening & calcifications that adhere to the heart
this is a thickened pericardium WITHOUT effusion present!
T/F: HTN is the major cause of CHF and LVH
TRUE
it is also a major risk factor for atherosclerosis!
(primary/secondary) HTN is aka "essential HTN" and does NOT have an identifiable or reversible cause
(primary/secondary) HTN has a known identifiable or reversible cause that is secondary to another cause
primary
secondary
cardiac enzyme panel
- CBC
- CMP = glucose, albumin, protein, Na+, Ca+, K+, HCO3, Cl-, BUN, creatinine, alk phos, ALT, SGPT, AST, SGOT, bilirubin
- Mg+ level
- digoxin level
- thyroid panel
- troponin I
- drug tox screening
cardiac enzyme labs: CBC, CMP, PT/INR, PTT, Mg+, serial cardiac enzymes
cardiac enzymes:
(CK/LDH/troponin) is detectable in 24 hrs and peaks at 3 days
(CK/LDH/troponin) is detectable in 6-12 hrs and peaks at 24 hrs
(CK/LDH/troponin) is the best for detecting an MI
LDH
CK
troponin
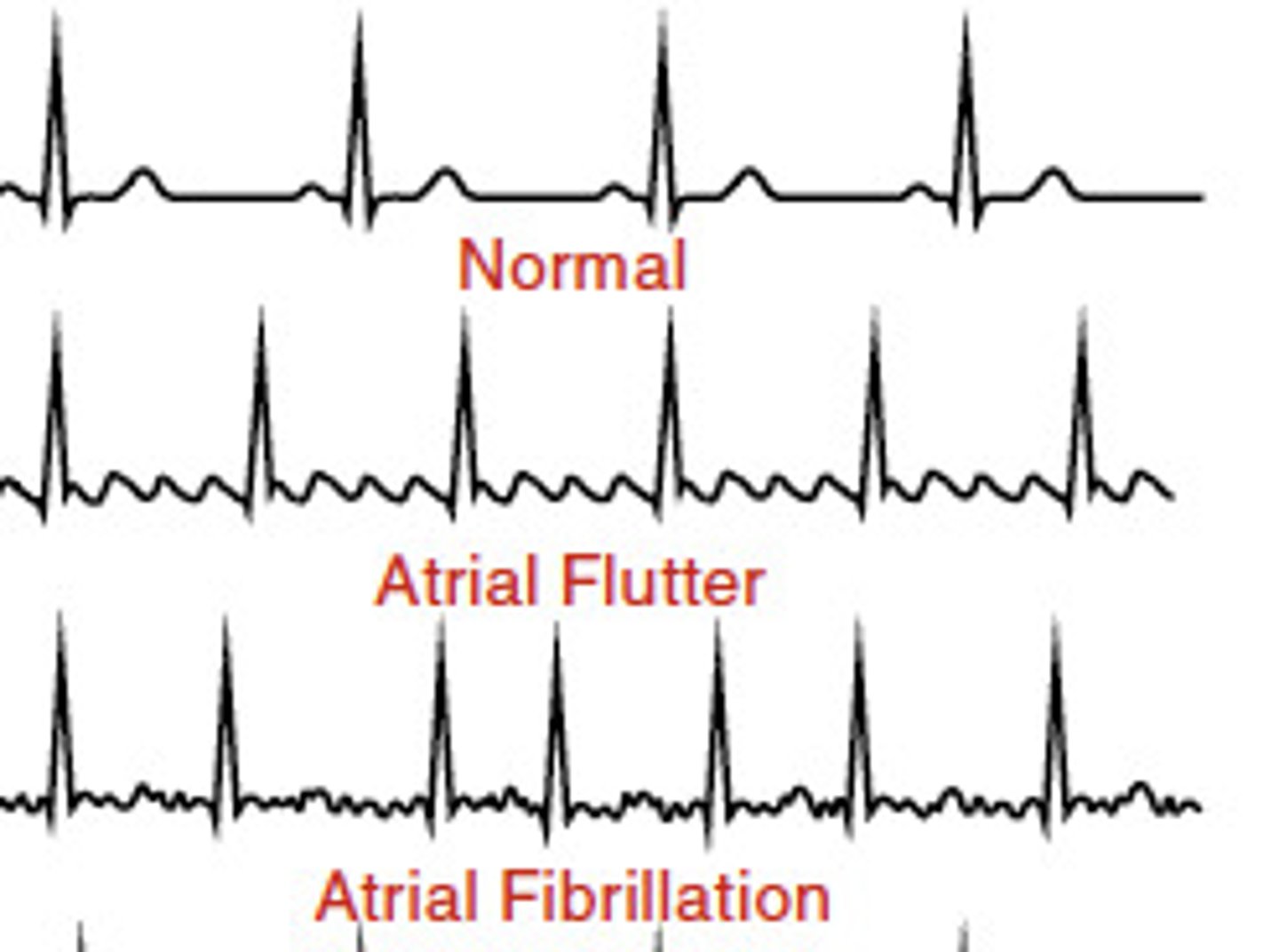
which of the following EKGs will present as "irregularly irregular" without a discernible P waves and a ventricular rate pf > 100 bpm?
a. a flutter
b. a fib
c. v fib
d. v tach
b. a fib
this is a common paroxysmal supraventricular arrhythmia (PSVT)
warfarin activates that (intrinsic/extrinsic) pathway
can we give this to pts with active bleeding or if they are a high fall risk?
what is the goal INR of a pt on warfarin?
intrinsic
NO!
goal INR = 2-3
this is a PO blood thinner that takes a few days to become therapeutic! so we can use bridge therapy with heparin or LMWH
(troponin/myoglobin) is the first cardiac enzyme to spike, but (troponin/myoglobin) is the most specific cardiac enzyme
myoglobin
troponin
which of the following will show electrical alternans on an EKG?
a. myocarditis
b. pericardial effusion
c. cardiac tamponade
d. constrictive pericarditis
c. cardiac tamponade
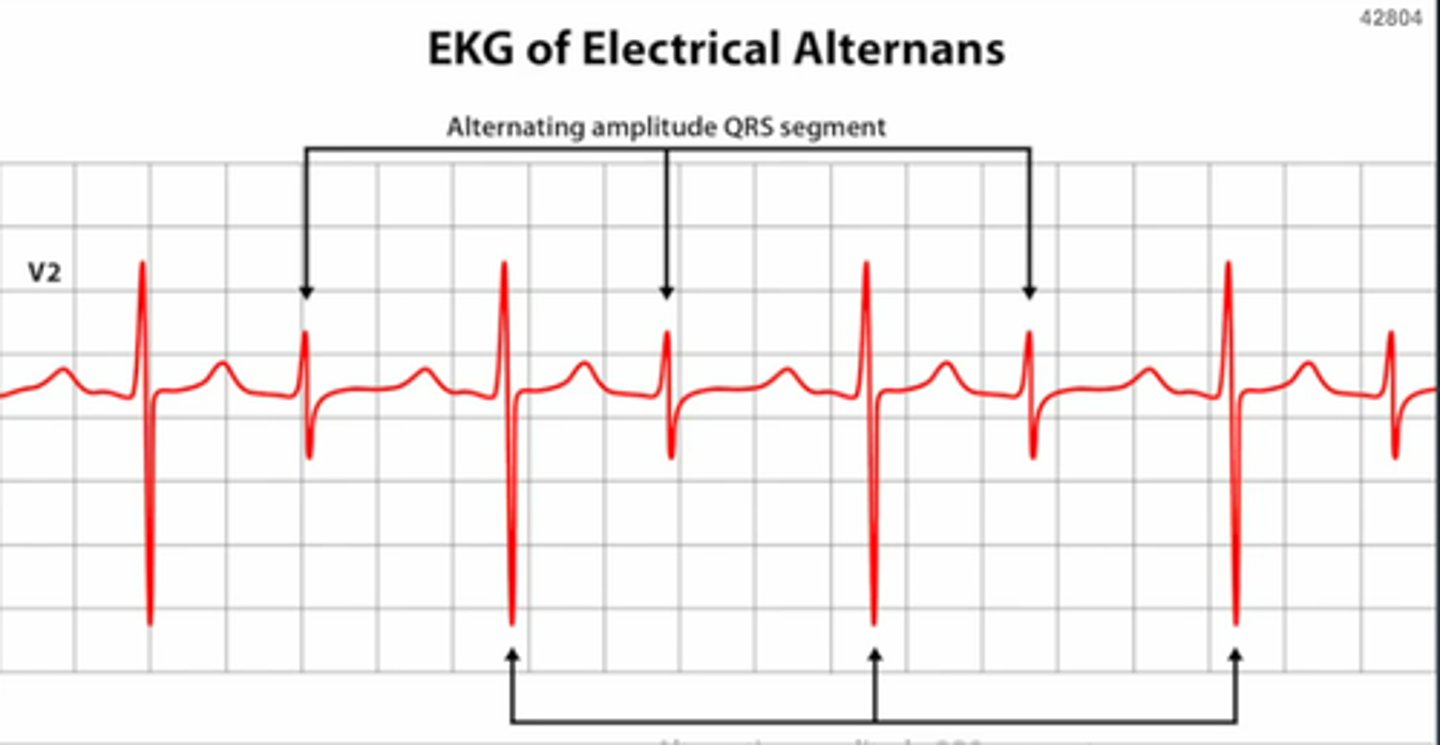
T/F: any pt with a valvular heart disease and a fib should be put on warfarin
TRUE
peripheral (arterial/venous) disease is more common and leads to atherosclerosis
peripheral (arterial/venous) disease is caused by incompetent valves, resulting in venous stasis and ulceration from edema & inflammation
what are the 6 P's? are they are associated with arterial or venous disease?
arterial
venous
6 P's of PAD: these are all caused by critical limb ischemia
pulselessness
pallor
pain
paresthesia
poikothermia
paralysis
Pt us presenting with leg claudication and painful ulcers on their lateral malleolus with a "punched out" appearance. PE reveals lower extremity hair loss, cold temp, and weak pulses. The pt is currently taking 81 mg aspirin every day. What is the next course of tx for this pt?
a. add clopidogrel
b. add cilostazol
c. incorporate lifestyle changes after stopping meds
d send to cath lab
b. add cilostazol
this pt has peripheral arterial disease (PAD)
T/F: PAD has decrease prevalence with age
FALSE
there is increased prevalence with age... PAD CORRELATES TO CV MORTALITY!
developmental risk factors:
- smoking
- DM
- old age
- chronic kidney disease
- HTN
- hyper-coagulable state
what is the GOLD standard for dx of peripheral arterial disease?
a. angiography
b. doppler ultrasound
c. TEE
d. DEXA scan
a. angiography
which of the following tx of PAD causes laxity of the RBC membrane, allowing them to squeeze through stenosed arteries without rupturing?
a. clopidogrel
b. aspirin
c. pentocifylline
d. pravasatin
c. pentocifylline
T/F: thromboangitis obliterans causes chronic venous disease
FALSE
it causes chronic arterial insufficiency... it is intense inflammation followed by arterial & venous occlusion, resulting in the fibrous encasement of the entire neurovascular bundle
what is the main cause of thromboangitis obliterans (aka "Buerger's disease") mainly seen in young pts?
a. DM
b. smoking
c. Raynaud's
d. MVP
b. smoking
which of the following is aka "intermittent claudication" that occurs with activity goes away with 1-2 min of rest?
a. chronic venous disease
b. atherosclerotic obliterans
c. arteriovenous fistula
d. thromboangitis obliterans ("Buerger's disease")
b. atherosclerotic obliterans
Tx:
- stop smoking and lose weight
- optimize DM therapy
- manage lipids
- foot care
Pt is a 23 yo male presenting with "cold sensitivity" that occurs with a triphasic color scheme of white, red, then blue (similar to Raynaud's). They initially had tender phlebitis and admit to smoking a lot. PE reveals decreased foot & radial pulses. What is the dx that is a non-atheromatous disease?
a. chronic venous disease
b. atherosclerotic obliterans
c. arteriovenous fistula
d. thromboangitis obliterans ("Buerger's disease")
d. thromboangitis obliterans ("Buerger's disease")
this is a type of chronic arterial insufficiency
this is intense inflammation followed by arterial & venous occlusion, resulting in the fibrous encasement of the entire neurovascular bundle
T/F: Raynaud's is commonly present among older males
FALSE
it is common among YOUNG FEMALES... make sure to check for underlying illness!
**triphasic color response = white, blue, red
Tx:
**CCB** to relax & open small blood vessels
**alpha blockers** to counteract vasoconstrictors
**vasodilators**
which of the following is NOT one of the 3 types of arterial vasospastic disease?
a. cold sensitivity (Raynaud's type)
b. livedo reticularis
c. AV fistula
d. acrocyanosis
c. AV fistula
cold sensitivity (Raynaud's) - mostly seen in young women
livedo reticularis - "fishnet" mottling that is accentuated by the cold in all parts of the extremities (possibly trunk)
acrocyanosis - this is the MC... persistent, diffuse cyanosis of the fingers, toes, hands, & feet
peripheral arterial disease results in ulcers on the (medial/lateral) malleolus and there (will/will not) be edema present
an ABI of less than ____ is indicative of PAD
peripheral vascular disease results in ulcers on the (medial/lateral) malleolus and there (will/will not) be edema present
lateral
will not
< 0.9
medial
will
what is the MC disorder of the venous system?
a. venous insufficiency
b. chronic arterial insufficiency
c. DVT
d. PVD
a. venous insufficiency
this manifests as varicose veins --> swollen ankles --> aching legs --> skin changes --> venous ulcers --> burning/itching skin --> EDEMA
this is from over-dilation of the venous vessels in the legs
causes of varicose veins: pregnancy, menopause, aging, prolonged standing, leg injury, abdominal strain
Tx:
- NSAIDs
- sclerotherapy
- compression stockings
- surgery or laser
what is it called when right sided HF leads to left sided HF?
HFrEF involves (systolic/diastolic) dysfunction
HFpEF involves (systolic/diastolic) dysfunction
the cut off the determine the level of dysfunction of the heart is _____%
cor pulmonale
systolic - impaired contractility & increased afterload
diastolic - impaired filling & relaxation
55%
> 55% = diastolic issue
< 55% = systolic issue
Pt is presenting with leg swelling and progressive SOB. They admit to having to sleep on 2 pillows every night so that they can breathe. PE reveals rales, loud P2, and S3 gallop. What is the dx?
a. left sided heart failure
b. right sided heart failure
a. left sided heart failure
Pt is presenting with peripheral pitting edema and RUQ discomfort. PE reveals JVD and hepatomegaly. What is the dx?
a. left sided heart failure
b. right sided heart failure
b. right sided heart failure