HA exam 3- hair skin and nails NO LESIONS
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
pallor
paleness
anemia
deficiency of rbcs
shock
decreased perfusion, vasoconstriction
albinism
no pigment in the skin, hair, and eyes
vitiligo
white patches on the skin; caused by the destruction of melanocytes
cyanosis
bluish discoloration of the skin resulting from poor circulation or inadequate oxygenation of the blood
central cyanosis
chronic heart and lung disease causes arterial desaturation
peripheral cyanosis
exposure to cold, anxiety
erythema
redness in skin
hyperemia
increased blood in engorged arterioles (ex- inflammation, fever, alcohol intake, bruising)
polycthemia
too many rbcs in blood
venous stasis
decreased blood flow from area, engorged venules
jaundice
yellowing of the skin
carotenemia
yellowing of the skin; from excess beta-carotene in body
uremia
renal failure causes retained urochrome pigments in the blood
addisons disease
cortisol deficiency stimulates increased melanin production
Pressure Injuries: Stage 1
non-blanching erythema; if you press on it lightly, it does not turn white
Pressure Injuries: Stage 2
partial-thickness skin loss (blister)
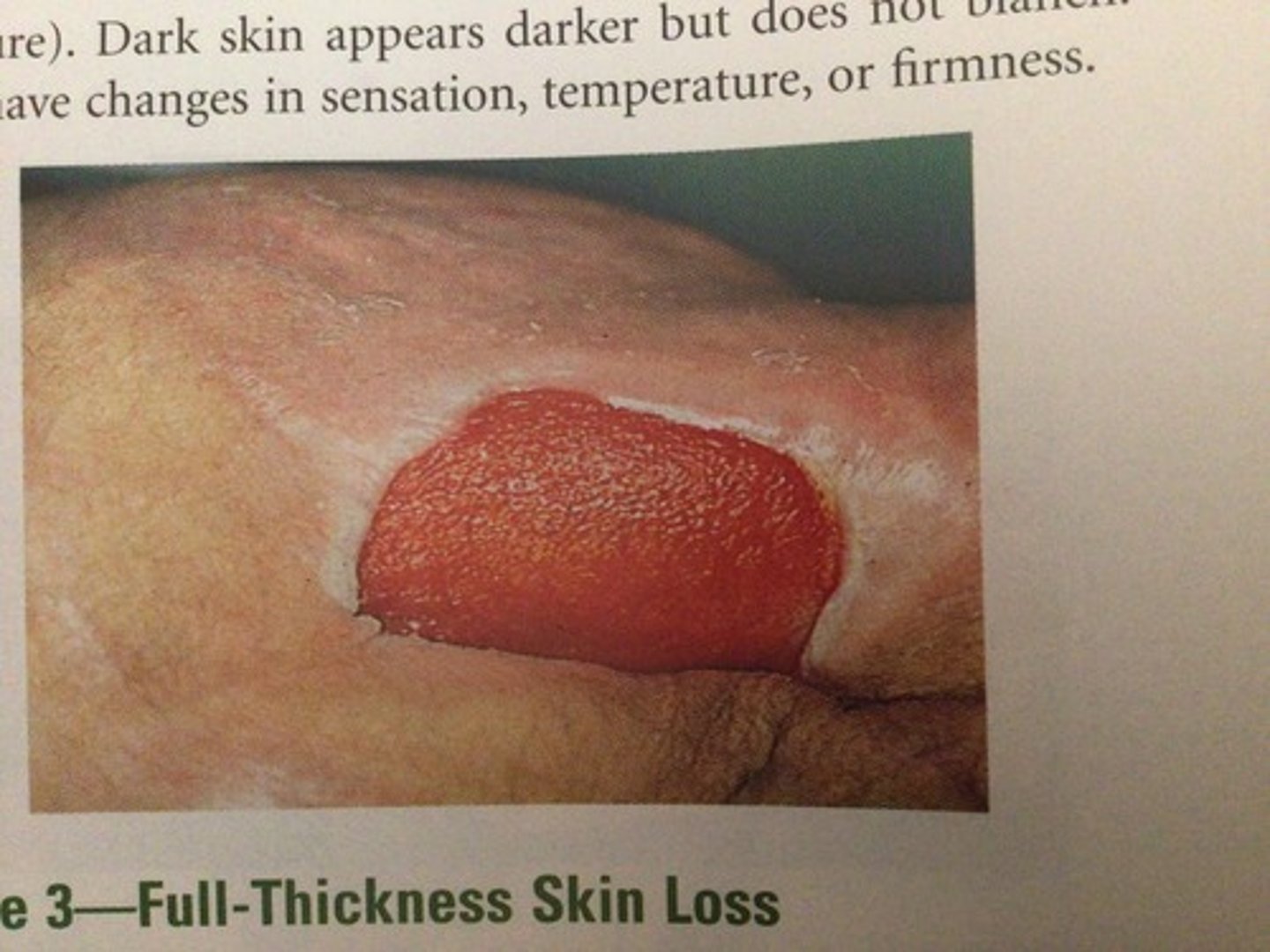
Pressure Injuries: Stage 3
full-thickness skin loss (open wound)
Pressure Injuries: Stage 4
full-thickness skin or tissue loss (see muscle or bone)
1
Pressure Injuries: Stage
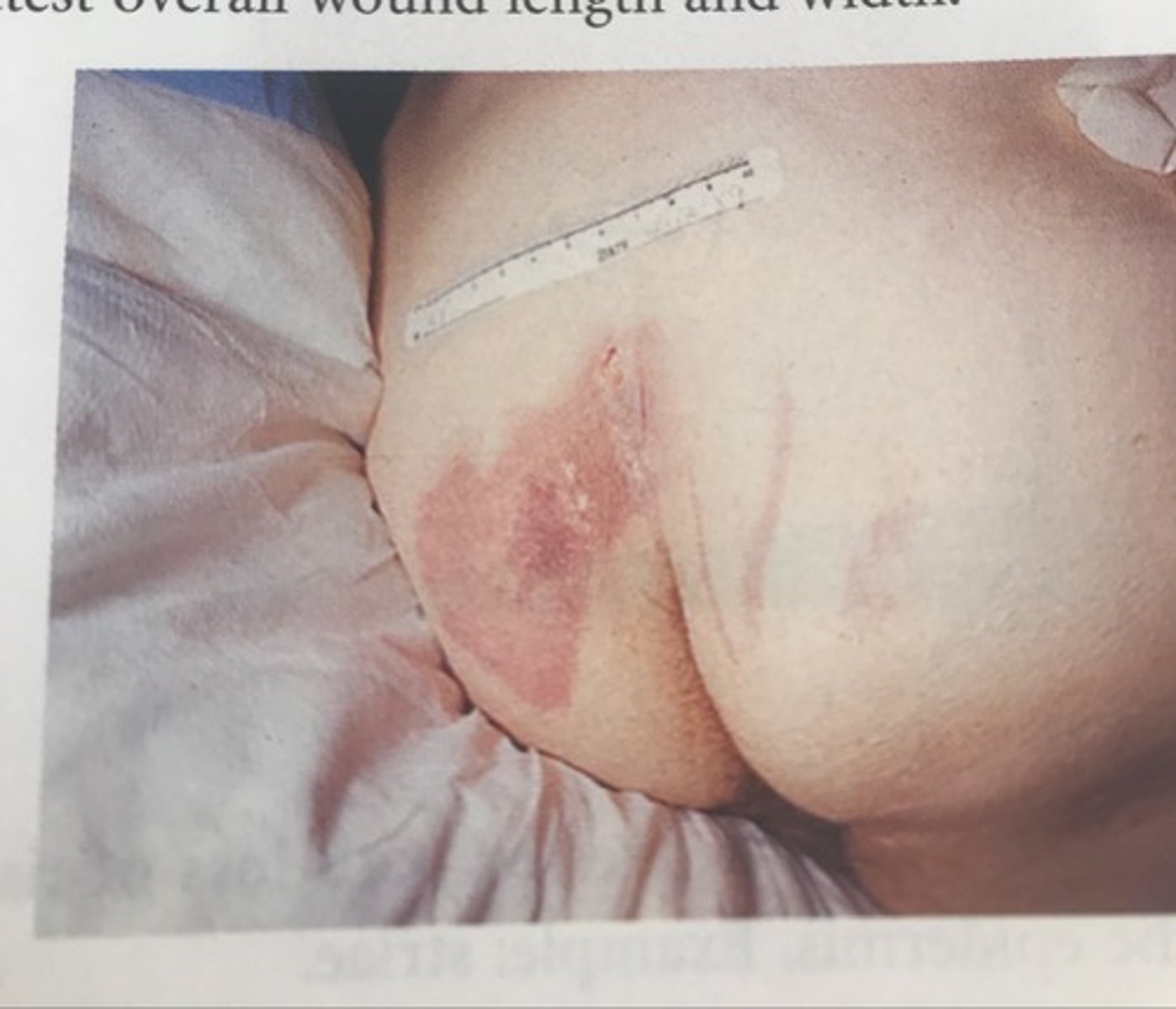
2
Pressure Injuries: Stage
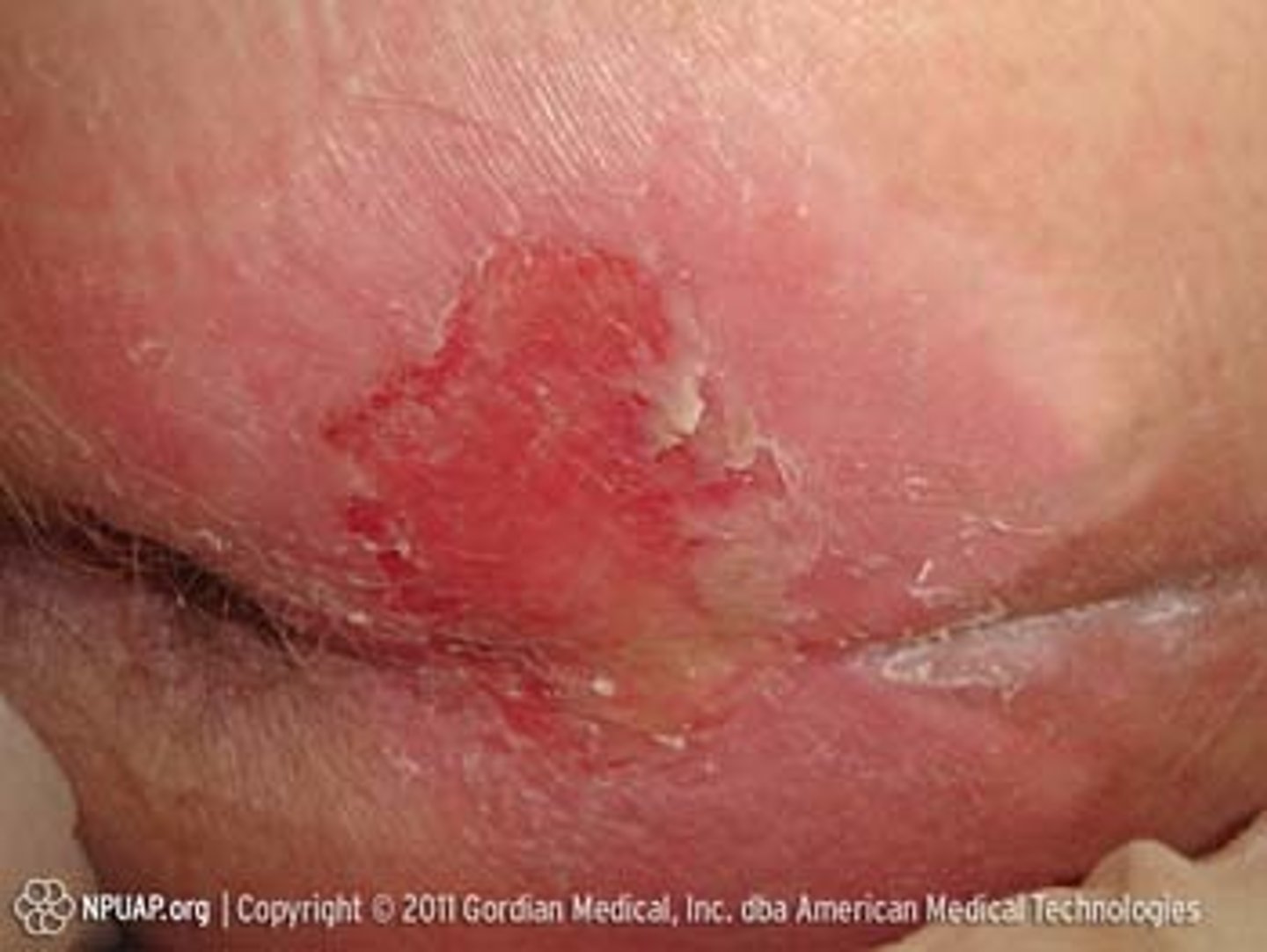
3
Pressure Injuries: Stage
4
Pressure Injuries: Stage
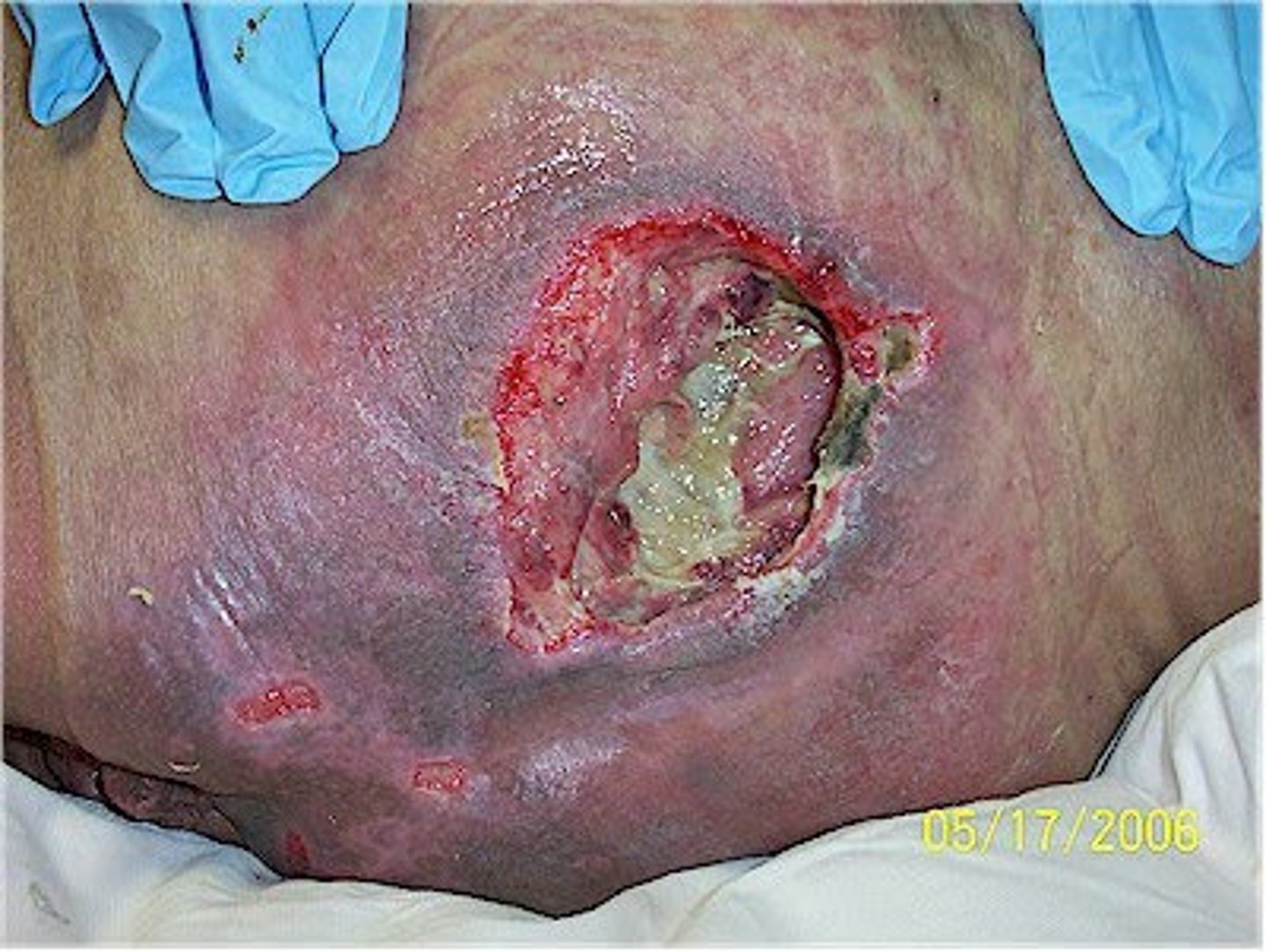
ecchymosis
bruising
skin elasticity
turgor
bruise
contousion
psoriasis
chronic, recurrent dermatosis marked by itchy, scaly, red plaques covered by silvery gray scales
hiruitism
excessive hair growth
view index finger at angle of nail base
when examining nails,
160 degrees
180 degrees or more = clubbing
nails should be (degrees)
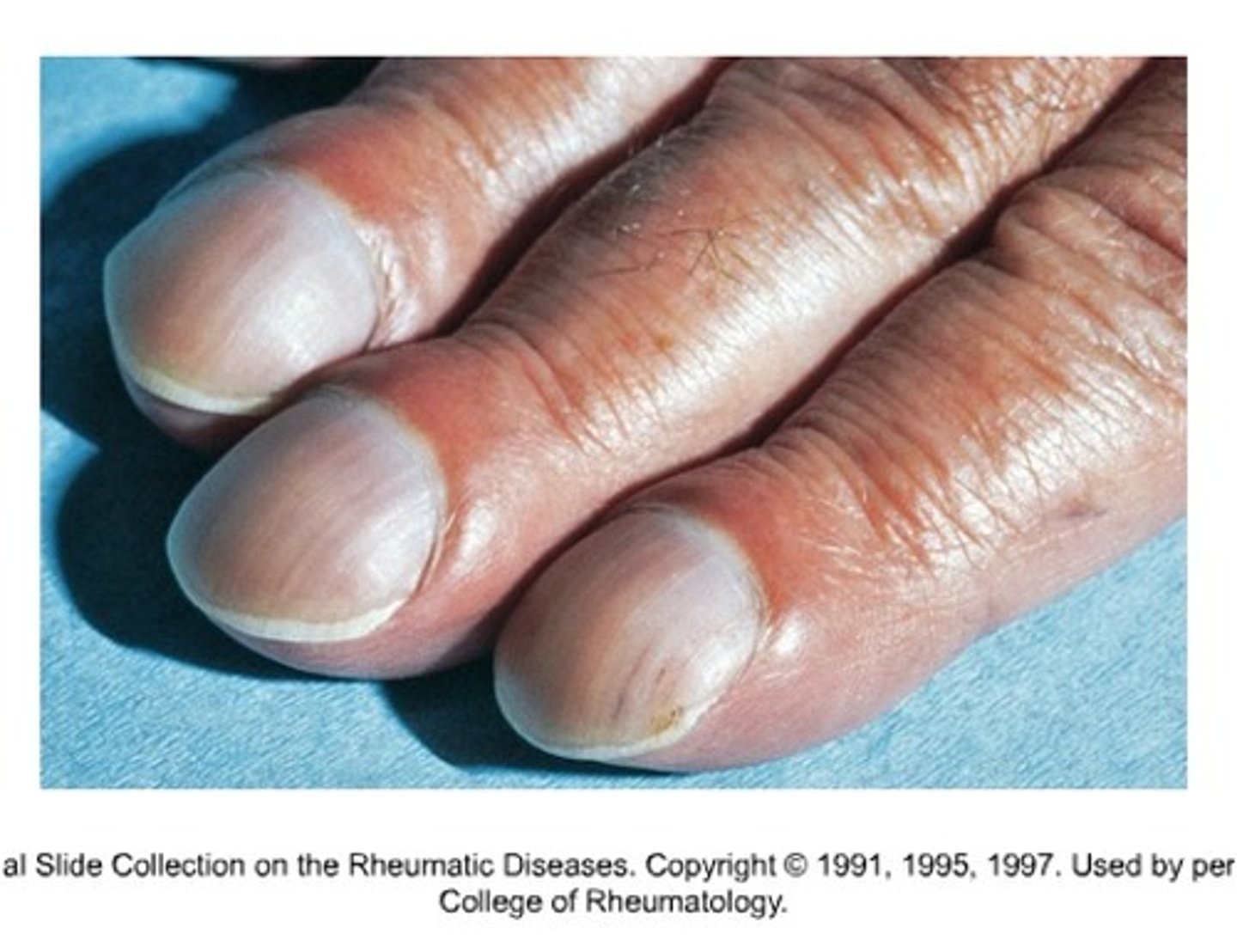
less than 2 seconds
capillary refill should be
thickened areas of epidermis
Keratoses
xerosis
dry skin
Solar lentigines
liver spots
mobility and turgor, hair growth, nail growth, and brittle nails
in aging adult, decreased
UV radiation
The most important risk factor for skin cancer
whites
increased risk for skin cancer in
melanoma
Increased risk for ______ w/increased number of sunburns
elasticity (skinfolds and sags), sweat and sebaceous glands decrease in # and function (dry), skin breakdown (due to slower cell replacement/delayed wound healing)
in the aging adult, loss of/decreased
functioning melanocytes decrease
cause of gray hair in the aging adult
discoloration due to increasing capillary fragility
senile purpura happens in the aging adult. this is
Pruritus
severe itching
Anasarca
full body edema
injury working its way out
deep tissue injury