C1.1 Enzymes and metabolism
1/18
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Enzymes
Organic catalysts, speed up cell reactions which maintain life functions
Metabolism
All the chemical reactions occurring in one organism, can be independent or interact
Each reaction controlled by an enzyme
Anabolic reactions
Build complex organic molecules (condensation reactions)
Require energy
E.g photosynthesis, protein synthesis, glycogen formation
Catabolic reactions
Break down complex molecules into monomers
Release energy
E.g digestion, oxidation of substrates in respiration
Types of energy
Kinetic
Chemical
Thermal (measured in kcals)
Electric current
Mechanical
Sound
Potential
Radioactivity
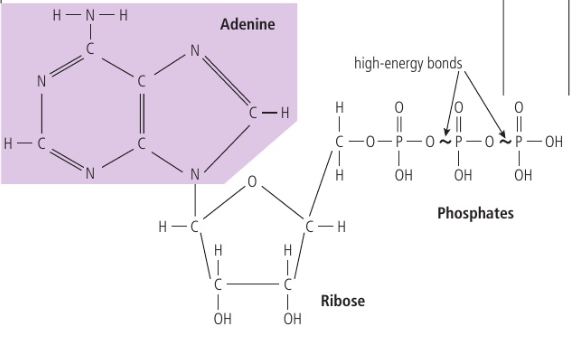
ATP
Energy current of the cell
Protein enzymes
Long chains of amino acids bent into 3D globular shape
Active site
Composed of a few amino acids, matching the substrate
Interaction between amino acids give it necessary properties to carry out catalysis
If shape is changed, enzyme is denatured and no longer works
Induced fit model
Developed from lock-key model
Many enzymes undergo changes in shape when combined with substrates, causing stress on chemical bonds of substrate which become destabilised and increase reaction rate
Activation energy
Energy necessary to destabilise bonds of reactant so reaction can proceed
Substrate needs certain of amount of kinetic energy when entering active site to provide it
Ways to increase reaction rate
Increase energy of reacting molecules and rate of collisions, usually by adding heat
Lower activation energy to break bonds more easily, usually with enzymes (cannot force a reaction, only makes it more likely)
Reversible reactions
Some require different enzymes to catalyse the reverse reaction
Substrate-active site collisions
In order to react, this needs to happen so need energy for it
Often the substrate or enzyme is anchored to a membrane to make it more efficient
Mechanism of enzyme action
Surface of substrate makes contact with enzyme’s action site
Change shape to provide fit
Temporary complex called the enzyme-substrate complex forms
Activation energy is lowered, substrate altered by rearrangement of existing atoms
Transformed substrate is released
Unchanged enzyme is then free to repeat

Factors affecting enzyme-catalysed reactions
Temperature
pH
Substrate concentration
Effect of temperature
Increases molecular motion, and thus reaction rate
But enzymes have an upper limit- too high will denature the enzyme
Denaturation can be temporary (intra-molecular bonds will reestablish) but if it’s too high, it is permanent
Effect of pH
Amino acids in enzymes have areas with pos./neg. charge, the substrate must match the charged amino acids
If solution is acidic, H+ conc rises and bonds with negative charges- prevent matching
If solution is too basic, OH- conc rises and bonds with positive charges- prevent matching
Enzymes have different optimums, generally neutral is best but there are exceptions (pepsin active in acidic stomach)
Effect of substrate concentration
Collision theory→ increase here means there are molecules to react and collide, increasing reaction rate
But there is a limit as enzymes have max rate at which they work and only one active site- if they are all occupied then increasing substrate concentration won’t do anything
Measuring enzyme-catalysed reactions
Measure rate at which substrate is used or product is produced