Chemistry IGCSE - Atoms, elements and compounds continued
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Structure of metallic bonding
electrostatic attraction between the positive ions in a giant metallic lattice and a ‘sea’ of delocalised ions
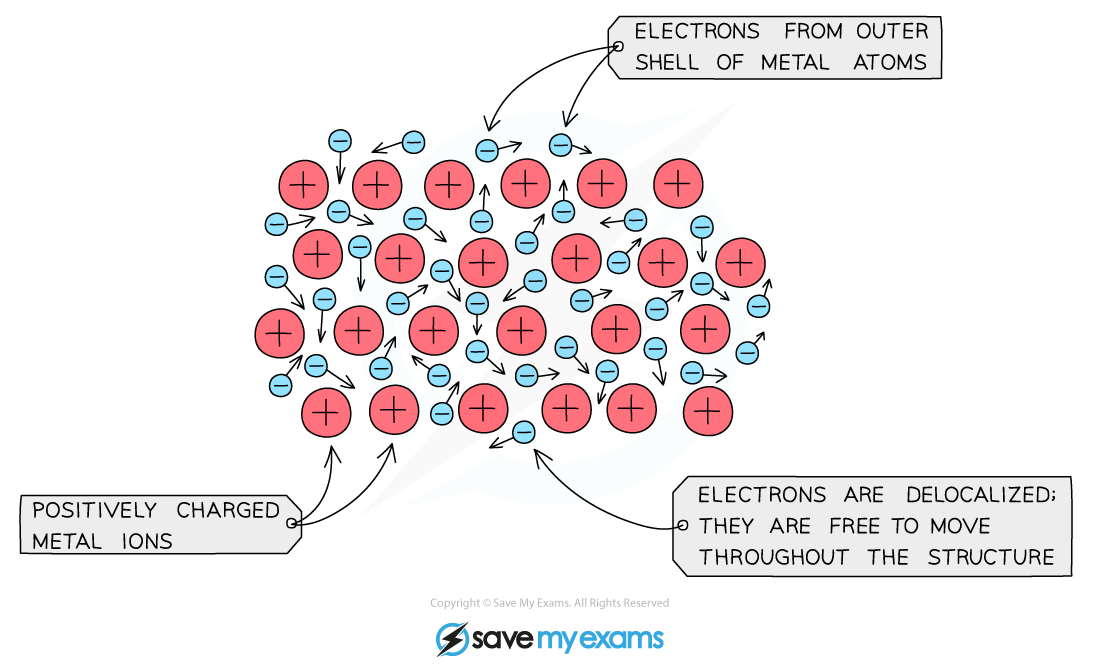
Explain in terms of structure and bonding that metals have good electrical conductivity
delocalised electrons can flow through the structure when a current is apllied
Explain in terms of structure and bonding that metals are malleable
layers of ion can slide over each other
Periodic table
an arrangement of elements in periods and groups and in order of increasing proton number/atomic number
Describe the change from metallic to non-metallic character across a period
Increase in nuclear charge and decrease in atomic size → tendency to gain electrons increases → non - metallic character increases
Explain similarities in the chemical properties of elements in the same group in terms of their electronic configuration
same number of valence electrons → similar chemical properties
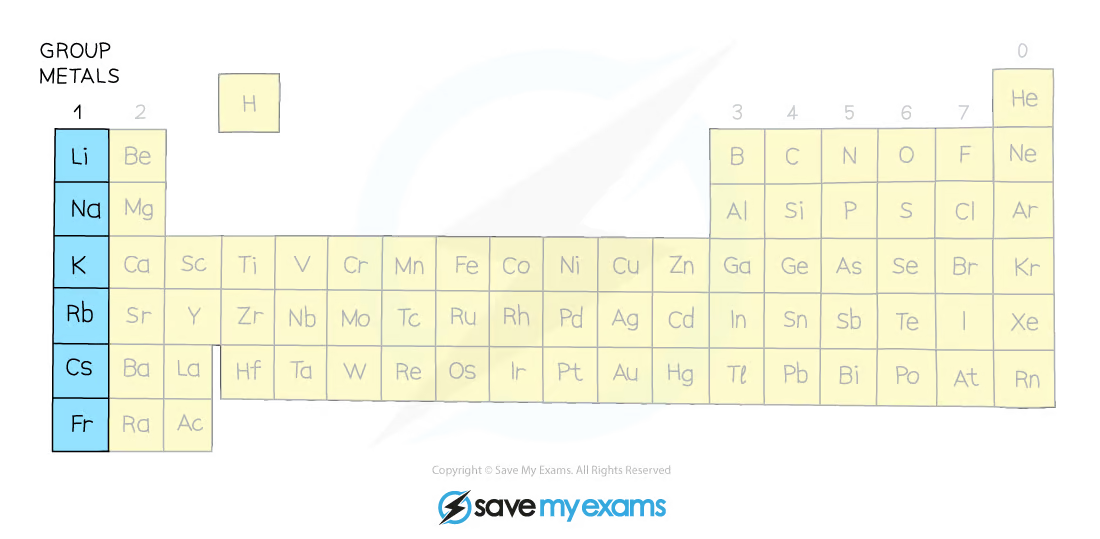
Alkali metals
In group 1
Alkali metals’ decreasing melting and boiling point
delocalised electrons are further away from the nucleus → metallic bonds weaker
Alkali metals’ increasing density
mass increases when you move down the group
Alkali metals’ increasing reactivity with water
Outer electrons further away from the nucleus as you go down the group → valence electrons more easily lost/less tightly held together by positive nucleus
Similarities of group 1
- reactive metals
- soft
- low BP + MP
- reacts fast to air, will tarnish easily, losing shininess
- reacts with water to produce alkaline solutions of metal hydroxide and hydrogen gas
- increase reactivity
- mainly white compounds which dissolve in water
Lithium reaction with water
produce hydrogen gas
Sodium reaction with water
melts into a sphere that moves around the surface → effervescing (fizzing)
Potassiums reaction to water
metal melts into sphere → moves quickly on surface → lilac flame
Equation for reaction with oxygen
Element | Equation |
Original | alkali metal + oxygen → alkali metal oxide |
Lithium | 2Li(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2LiOH + H2(g) |
Sodium | 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g) |
Potassium | 2K(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2KOH + H2(g) |
Halogens
in group 7 → diatomic non - metals
Halogens’ increasing density
more electron shells when you move down → increase atomic mass and size
Halogens’ decreasing reactivity
atomic mass increases → increase in electron shells → atoms are larger → valence shell further away from nucleus → reduce ability to attract electrons
Halogens trends
- reactivity → decreases
- density → increases
- colour → gets darker
- BP + MP → increase → larger atoms, strong IMF between molecules
Appearance of chlorine at r.t.p (room temperature and pressure)
chlorine → a pale yellow-green gas
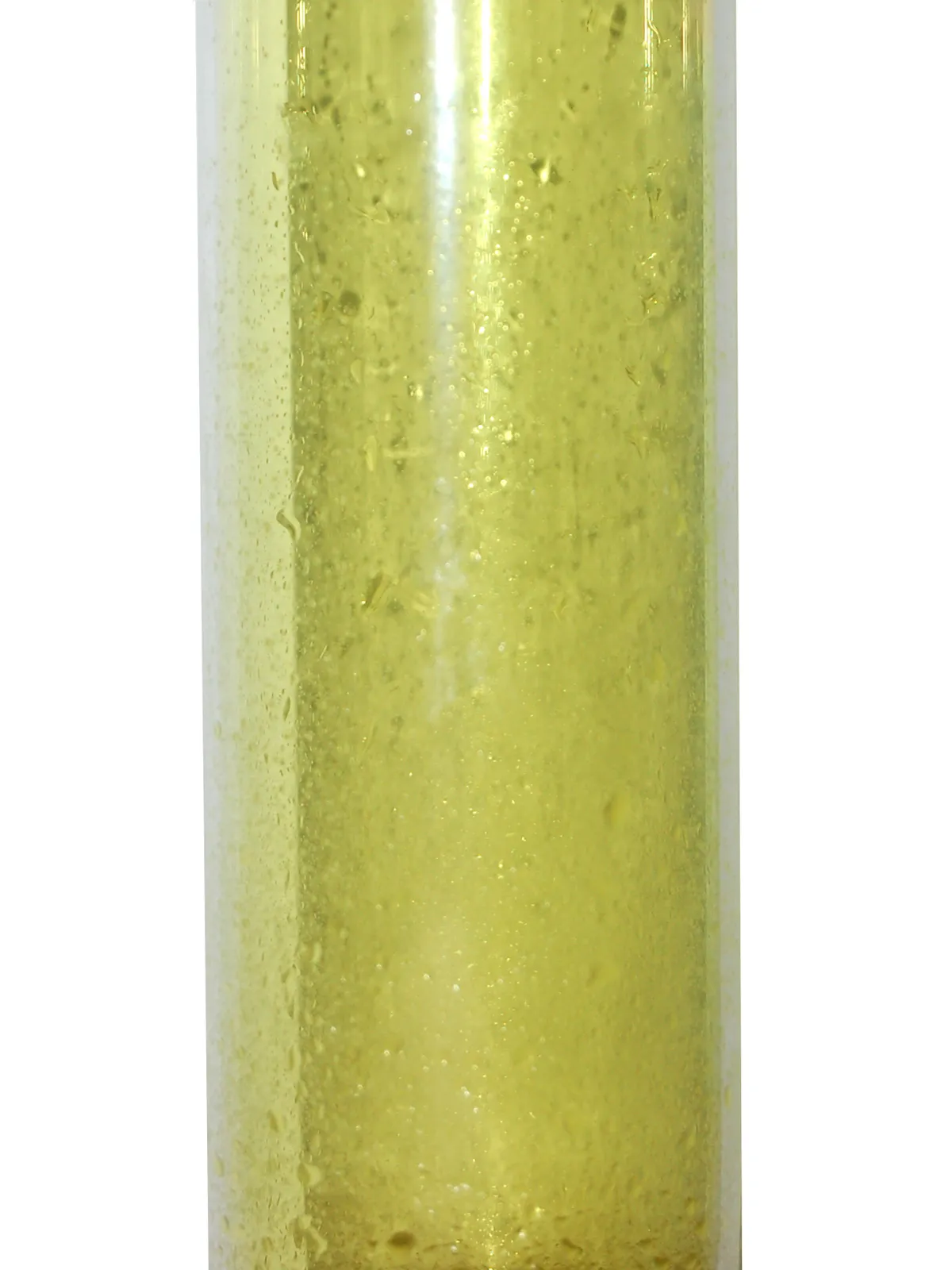

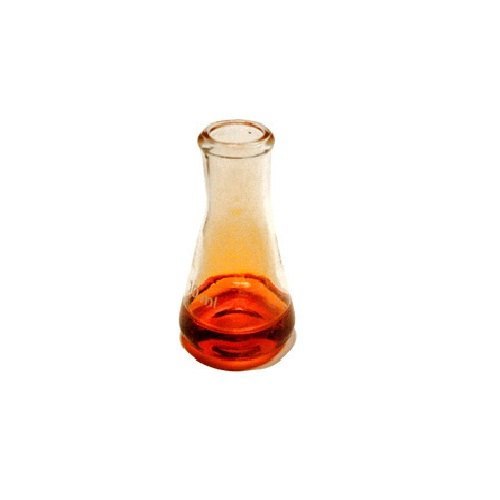
Appearance of bromine at r.t.p (room temperature and pressure)
bromine → a red-brown liquid

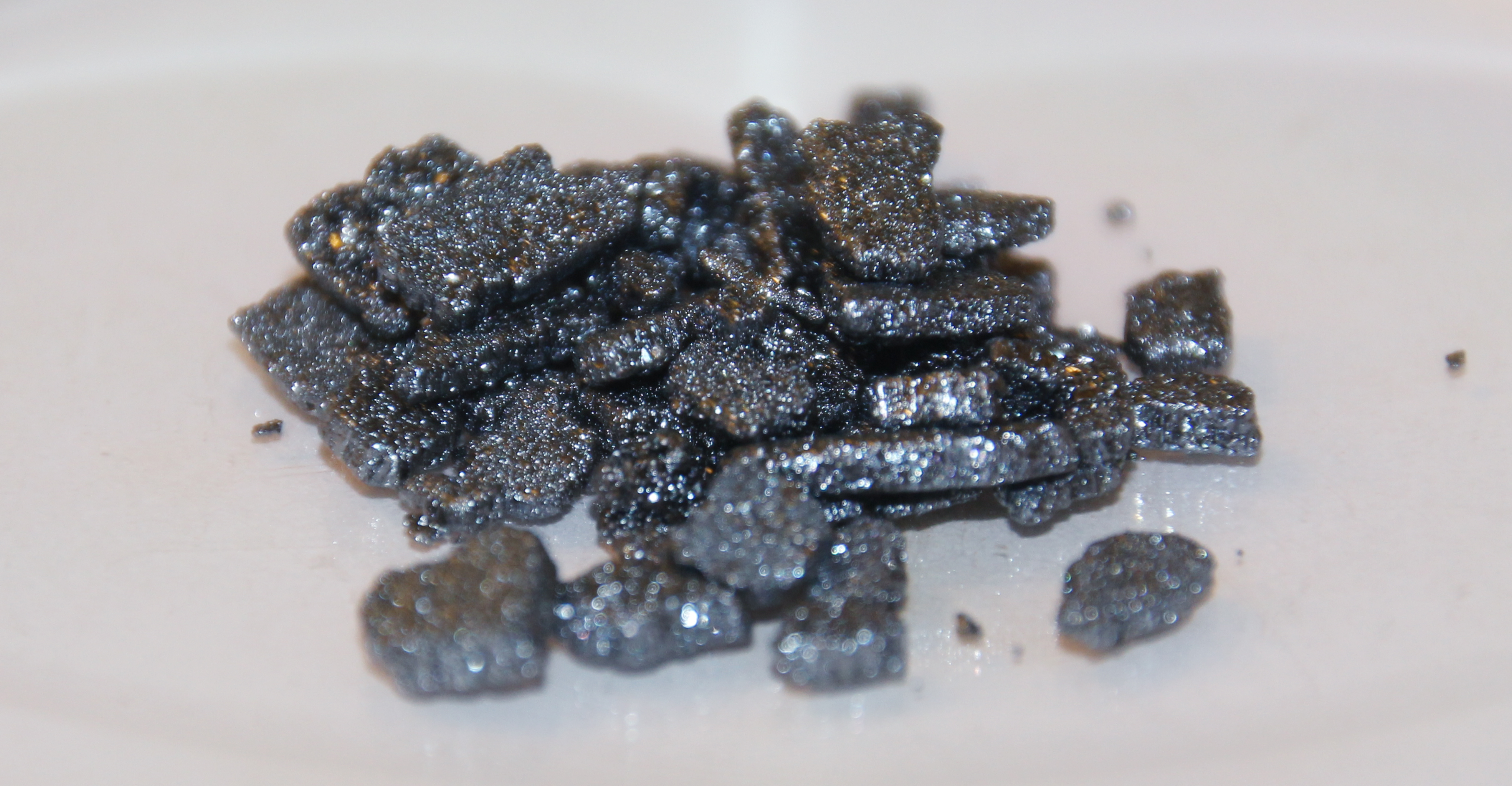
Appearance of iodine at r.t.p (room temperature and pressure)
iodine → a grey-black solid

Halide
Ion of respective halogen combined with a metal ion
Describe and explain the displacement reactions of halogens with other halide ions
A more reactive halogen will displace a less reactive halide from its compound in solution
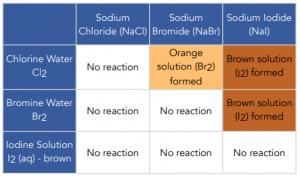
Equation of displacement
Element | Equation |
Chlorine displacing potassium Bromide | Cl2(aq)+2KBr(aq)→2KCl(aq)+Br2(l) |
Chlorine displacing potassium iodide | Cl2(aq)+2KI(aq)→2KCl(aq)+I2(s) |
Bromine displacing potassium iodide | Br2(aq)+2KI(aq)→2KBr(aq)+I2(s) |
Transition metals
- high densities → large atomic masses and closely packed atomic structures
- high melting points → delocalised electrons → stronger IMF between molecules
- low reactivity
- form coloured compounds
- often act as catalysts in elements and in compounds
Noble gases
group 8 → unreactive, monatomic gas → have complete valence shells → stable