ACCT 302 Flashcards
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
Revenue Budget (1)
Budgeted Sales in Units x Selling Price per Unit = Total Revenues/Budgeted Sales
Production Budget (2)
Budgeted unit sales + target ending fg inventory = total required units - beginning fg inventory = units of finished goods to be produced
Direct Material Usage Budget in Quantity and Dollars (3A)
Required Production x Materials per unit = Production needs (Q) * Cost per pound = Production Needs ($)
Direct Material Purchases Budget (3B)
To be Used in Production + Target Ending Inventory = Total Requirements
Total Requirements - Beginning Inventory = Purchases to be Made
Cost Budget
Purchases to be Made (Q) * Cost per unit of material
Direct Manufacturing Labor Costs Budget (4)
Units to be Produced × Direct Labor Hours per Unit = Total DL Hours
Total Direct Labor Hours × Hourly Wage Rate = Total DL Cost
Manufacturing Overhead Costs Budget (5)
Fixed Costs - Variable Costs = Total machine setup overhead costs
Budgeted unit costs of ending FG inventory (6A)
(DM Cost per Unit + DL Cost per Unit + MOH Cost per Unit)=Budgeted Unit Cost
Budgeted Unit Cost × Ending Inventory Units = Total Ending FG Inventory
Ending FG Inventory Budget (6B)
Desired Ending FG Inventory (Q) * Unit Product Cost = Ending FG Inventory ($)
COGS Budget (7)
(Beg FG Inventory+DM Used+DL+MOH)−Ending FG Inventory
Nonmanufacturing Costs Budget
Budgeted Sales × Variable S&A Rate
Variable Expense + Fixed S&A Expense = Total S&A Expense
A budget is the quantitative expression of a
proposed plan of action by management for a specified period
A budget is an aid to coordinating what needs to be done to
implement that plan
A budget generally includes the plan’s both financial and nonfinancial aspects and serves
as a road map for the company to follow in an upcoming period.
Budgets are an integral part of management control systems. Budgets do the following:
1. Promote coordination and communication among subunits within the company
2. Provide a framework for judging performance and facilitating learning
3. Motivate managers and other employees
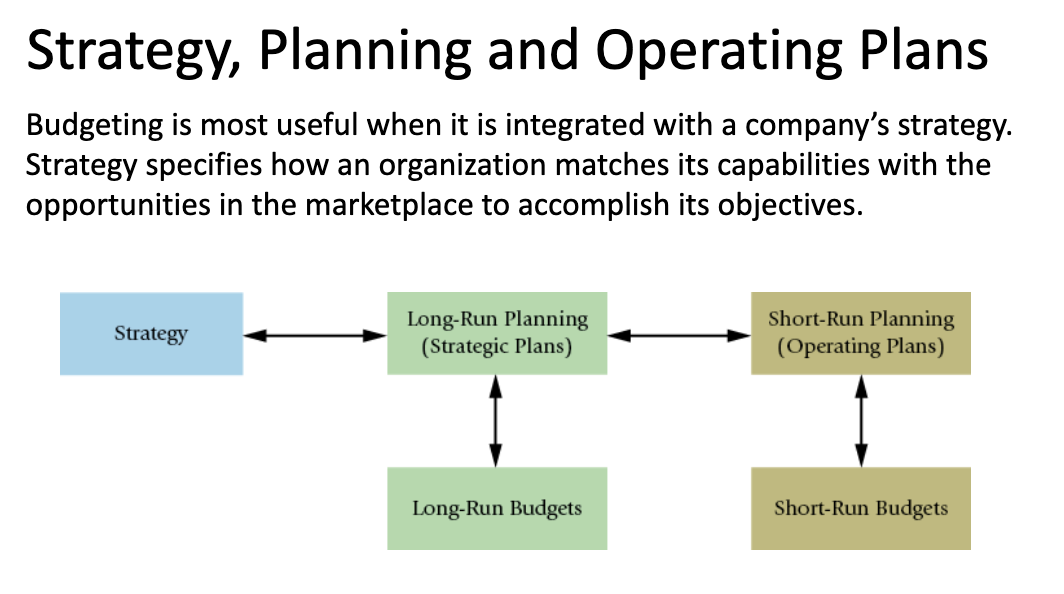
Strategy specifies how an organization
matches its capabilities with the opportunities in the marketplace to accomplish its objectives.
Before the start of a fiscal year,
managers at all levels take into account past performance, market feedback, and anticipated future changes to initiate plans for the next period.
Senior managers give subordinate managers a frame of reference,
a set of specific financial or nonfinancial expectations, against which they will compare actual results.
Managers and management accountants investigate
any deviations from the plan
The most frequently used budget period is
1 year
Businesses may also use a rolling budget. This budget is always available for a specified future period, by continually adding a
month, quarter, or year to the period just ended.
Operating Budget
building blocks leading to the creation of the Budgeted Income Statement
Financial Budget
building blocks based on the Operating Budget that lead to the creation of the Budgeted Balance Sheet and the Budgeted Statement of Cash Flows
What is part of the operating budget?
Revenue Budget
Ending Inventory Budget
Production Budget
Direct Material Costs Budget
Direct Manufacturing Labor Costs Budget
Manufacturing Overhead Costs Budget
COGS Budget
Period Costs
Budgeted Income Statement
What is part of the Financial Budget
Capital Expenditures Budget
Cash Budget
Budgeted Balance Sheet
Budgeted Statement of Cash Flows
Master Budget
Expresses management’s operating and financial plans for a set period (usually a fiscal year), and it includes a set of budgeted financial statements. It is a big plan that helps a company know how much money they will need and how much they will earn.
The Budgeted Income Statement
Revenue Budget - COGS Budget = Gross Margin - Nonmanufacturing Costs Budget = Operating income
Cash Collection
Revenue Budget
Collection from customers during the period
Accounts receivables by the end of the period
Cash payment (disbursement)
Material purchase budget
Payment to suppliers during the period
Accounts payables by the end of the period
Responsibility Center
a part, segment, or subunit of an organization whose manager is accountable for a specified set of activities
Responsibility Accounting
a system that measures the plans, budgets, actions and actual results of each Responsibility Center
profit center
accountable for revenues and costs
investment center
accountable for investments, revenues, and costs
Budgets offer feedback in the form of variances:
actual results deviate from budgeted targets
Variances provide managers with
early warning of problems
a basis for performance evaluation
a basis for strategy evaluation
Controllability
the degree of influence that a manager has over costs, revenues, or related items for which he is being held responsible
Responsibility accounting focuses on
information sharing, not in laying blame on a particular manager
Budgetary slack
the practice of underestimating budgeted revenues or overestimating budgeted costs to make budgeted targets easier to achieve
Stretch targets
challenging but achievable levels of expected performance, intended to create a little discomfort.
Kaizen budgeting
explicitly incorporates continuous improvement anticipated during the budget period in the budget numbers.
Which of the following is true of master budgets?
A. They include only financial aspects of a plan and exclude nonfinancial aspects.
B. Includes both financial and nonfinancial aspects of management’s plans.
C. They aid in quantifying the expectations of all stakeholders.
D. They must be administered rigidly after they are committed to.
Includes both financial and nonfinancial aspects of management’s plans.
Which of the following is a reason why top managers want lower-level managers to participate in the budgeting process?
A. To reduce the time and cost expended in the budgeting process.
B. To ensure that they do not introduce any budgetary slack.
C. To ensure that the budgets are administered rigidly given the changing market conditions.
D. To benefit from their experience with the day-to-day aspects of running the business.
To benefit from their experience with the day-to-day aspects of running the business.
Which of the following is a component of operating budgets?
A. Production budget
B. Budgeted statement of cash flows
C. Capital expenditures budget
D. Budgeted balance sheet
Production Budget
In which order are the following developed? First to last:
A = Production budget
B = Direct materials costs budget
C = Budgeted income statement
D = Revenues budget
A. ABDC
B. DABC
C. DCAB
D. CABD
DABC
Expected Cash Collections
Current Sales Collected: Current Sales × % collected this month
Past Credit Collections: Last Month’s Sales × % collected this month
Total Expected Collections: Add both amounts together
Variance
difference between an actual and an expected (budgeted) amount
Favorable Variance (F)
has the effect , when considered in isolation, of increasing operating income relative to the budget amount
Unfavorable Variance (U)
has the effect , when considered in isolation, of decreasing operating income relative to the budget amount
Management by Exception
the practice of focusing attention on areas not operating as expected (budgeted)
Static (Master) Budget
is based on the output planned at the start of the budget period
Static-Budget Variance (Level 0 variances)
the difference between the actual result and the corresponding static budget amount
Levels 1, 2, and 3 analyses examine the
Level 0 variance, breaking it down into progressively more detailed levels of analysis.
Flexible Budgets calculates
budgeted revenues and budgeted costs based on the actual output in the budget period
Flexible budgets are prepared at
the end of the period, after managers know the actual output
Hypothetical budget
prepared at the start of the budget period if the company had correctly forecast the actual output for the period
Flexible budgets show revenue and costs that should have been
incurred at the actual level of activity, enabling “apples to apples” comparisons.
Sales Volume Variances
Compares static and flexible budgets.
Only difference between static and flexible budget is
The level of activity. Static uses our planned (expected) activity. Flexible uses actual level of activity.
Deficiencies of the Static Budget:
Static budgets are prepared for a single, planned level of activity. Performance evaluation is difficult when actual activity differs from the planned level of activity. Comparing static and actual costs are like comparing apples and oranges. The relevant question is: How much of the cost variances are due to higher activity, and how much are due to control costs?
Some possible reasons we might incur an unfavorable Sales-Volume
Variance include:
1. Failure to execute the sales plan
2. Weaker than anticipated demand
3. Aggressive competitors taking market share
4. Unanticipated market preference away from the product
5. Quality problems
Flexible-Budget Variance
Comparing actual budget to the flexible-budget.
Standard Costing
Targets or standards are established for direct material and direct labor. The standard costs are recorded in the accounting system. Actual price and usage amounts are compared to the standard and variances are recorded.
Flexible budget revenue vs Actual revenue
The difference is selling price variance
Flexible budget costs vs actual costs
The differences are cost variances.
Price Variance
The difference between an actual input price and a budgeted input price multiplied by the actual input quantity.
How to calculate Price Variance
Actual Quantity of input x (Actual price of input- Budgeted price of input).
Efficiency Variance
Difference between the actual input of quantity and budgeted input quantity for actual output multiplied by the budgeted price.
How to calculate efficiency variance labor and material cost analysis?
Budgeted Price of input x (Actual Quantity of Input Used - Standard Quantity Allowed for actual output)
Responsibility for Materials Variances
The standard price is used to compute the efficiency variance so that the production manager is not held responsible for the purchasing manager’s performance
The efficiency variance is computed only on
the quantity (AQ) used
The price variance is computed on
the entire quantity (AQ) purchased.
Production managers are usually held accountable for labor variances because they can influence the:
Mix of skill level assigned to work tasks.
Level of employee motivation.
Quality of production supervision.
Quality of training provided to employees
Which of the following is correct regarding the drivers of operating and financial budgets?
The sales budget will drive the cost of goods sold budget
The revenues budget identifies
The expected level of sales for the company
Which of the following statements incorporates the principles of a rolling budget?
Managers should roll forward their budget each time a period is complete
The three main advantages of a budget are:
Promote coordination and communication among subunits within the company.
Provide a framework for judging performance and facilitating learning
Motivate managers and other employees.
The direct materials USAGE budget is based on
The units to be produced during a period
DM Used
Beg DM + Purchases - Ending DM
Total Manufacturing Cost Incurred
DM used + DL + MOH Allocated
COGM
Beg WIP + Total Manufacturing Cost - Ending WIP
COGS
Beg FG + COGM - Ending FG
Which of the following must be produced before a budgeted income statement can be created?
Sales budget, production budget, direct labor budget and finished goods budget
Which of the following statements incorporates the principles of rolling budgeting?
Managers should roll forward their budget each time a period is complete.
Which of the following information is needed to prepare a flexible budget?
Actual units sold
An unfavorable flexible-budget variance for variable costs may be the result of
using more input quantities than were budgeted
An unfavorable labor price variance indicates which of the following?
A. The company spent more on variable overhead items than budgeted.
B. The company used more labor hours than budgeted.
C. The company spent more on labor per hour than budgeted.
D. The company used less labor hours than budgeted
The company spent more on labor per hour than budgeted.
Effective planning of variable overhead costs means that managers must
A. increase the expenditures in the variable overhead budgets
B. focus on activities that add value for the customer and eliminate nonvalue-added activities
C. increase the linearity between total costs and volume of production
D. identify the product advertising requirements and factor those into the variable overhead budget
focus on activities that add value for the customer and eliminate nonvalue-added activities
Compared to variable overhead costs planning, fixed overhead cost planning has an additional strategic issue beyond undertaking only essential activities and efficient operations. That additional requirement is best described as:
A. focusing on the highest possible quality
B. increasing the linearity between total costs and volume of production
C. choosing the appropriate level of capacity that will benefit the company in the long-run
D. identifying essential value-adding activities
choosing the appropriate level of capacity that will benefit the company in the long-run
When variable overhead spending variance is unfavorable, it can be safely assumed that
A. actual rate per unit of cost-allocation base is higher than budgeted rate
B. actual quantity of cost-allocation base used is higher than budgeted quantity
C. actual rate per unit of cost-allocation base is lower than budgeted rate
D. actual quantity of cost-allocation base used is lower than budgeted quantity
actual rate per unit of cost-allocation base is higher than budgeted rate
When machine-hours are used as an overhead cost-allocation base and annual leasing costs for equipment unexpectedly increase, the most likely result would be to report a(n)
A. unfavorable variable overhead spending variance
B. favorable variable overhead efficiency variance
C. unfavorable fixed overhead flexible-budget variance
D. favorable production-volume variance
C. unfavorable fixed overhead flexible-budget variance
An unfavorable fixed overhead spending variance indicates that ________.
A. there was more excess capacity than planned
B. the price of fixed overhead items cost more than budgeted
C. the fixed overhead cost-allocation base was not used efficiently
D. the denominator level was more than planned
the price of fixed overhead items cost more than budgeted
Which of the following costs is inventoried when using variable costing?
A. Rent on factory building
B. Electricity consumed in manufacturing process
C. Sales commission paid on each sale
D. Advertising costs incurred for the product
Electricity consumed in manufacturing process
In general, if inventory DECREASES during an accounting period,
A. variable costing will report less operating income than absorption costing
B. absorption costing will report less operating income than variable costing
C. variable costing and absorption costing will report the same operating income
D. both variable costing and absorption costing will show losses
absorption costing will report less operating income than variable costing
Under absorption costing, if a manager’s bonus is tied to operating income, then increasing inventory levels compared to last year would result in
A. greater operating income and therefore increasing the manager's bonus
B. less operating income and therefore decreasing the manager's bonus
C. not affecting the manager’s bonus
D. being unable to determine the manager's bonus using only the above information
greater operating income and therefore increasing the manager's bonus
What is the key difference between a static budget and a flexible budget?
A static budget is based on the level of output at the beginning of the period; a flexible budget is based on the actual output level in the budget period.
Operating Income
Revenue - VC = CM
CM - FC
Actual Results
Actual Q * Actual Cost
Flexible Budget
AQ * Standard Cost
Static Budget
Standard Q * Standard Cost
For planning and control purposes, fixed overhead costs are
a lump sum amount that is not controlled on a per-unit basis.