14 Surface Water and Floods
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Drainage basin
the total area drained by a stream and its tributaries
Divide
ridge or high ground that divides one drainage basin from another
Continental Divide
separates the streams that flow into the Pacific from those that flow into the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico
Dendritic
drainage pattern resembling the branches of a tree
Radial pattern
streams diverge outward like the spokes of a wheel, such as on conical mountains
Rectangular pattern
tributaries have frequent right-angle bends
Trellis pattern
streams forming alongside parallel ridges & valleys
Discharge
volume of water passing a particular point in a stream over time
cutbank
zone of erosion (more erosion than deposits)
Point bar
dominent deposition (low velocity, more deposits than erosion)
Channel Shape
Shape of stream bed
Roughness
bedrock material (changeable)
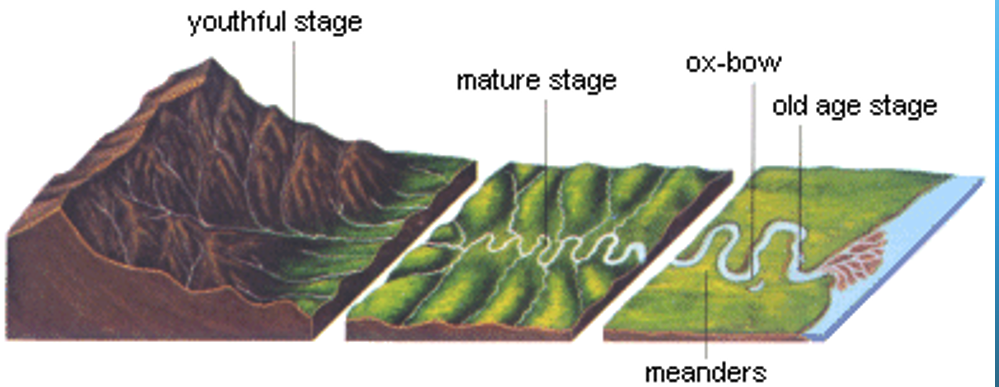
Juvenile (young) river
High velocity, steep, U shaped sides, can erode any sediment, can cary large sediments, tend to cut/erode vertically more than laterally, can form braids.
Braided Streams
High velocity river carrying enough sediment to randomly deposit mounds of sediment. Can form through storm surges
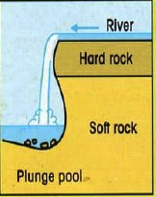
Waterfall formation step 1
falling water and rock particles or boulders loosen and wear away the softer rock
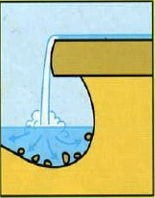
Waterfall formation step 2
the hard rock above is undercut as erosion of the soft rock continues
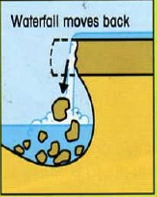
Waterfall formation step 3
the hard rock collapses into the plunge pool to be broken up and washed away by the river. The position of the falls moves back.
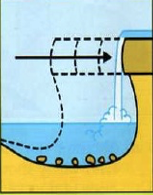
Waterfall formation step 4
erosion continues, and the waterfall slowly eats its way, upstream, leaving a gorge behind
Mature (middle aged) rivers
Moderate gradient, can erode some sediments, wider than juvenile, erosion roughly equals deposition, flood plain beginning.
Old age rivers
Slow moving, shallow gradient, only erodes small/dissolved sediments, wide floodplains, wider than deep, deposition is higher than erosion.
Levees
mounds of sediment deposited from flooding. (looks like a berm).
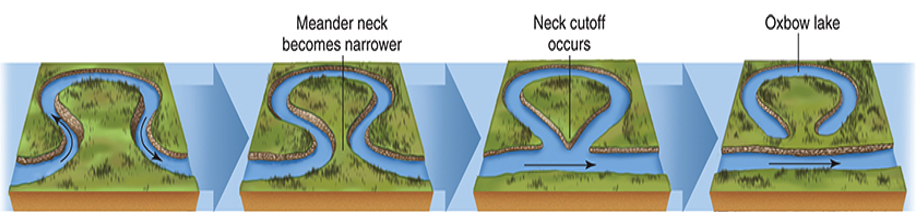
Oxbow (or horseshoe) lake
Used to be a tight bend in river, but eroded away.
River timeline
Delta
body of sediment deposited at the mouth of a river when flow velocity decreases
Grand canyon formation process
Tectonic uplift of the Colorado Plateau caused the river to act young again and carve the canyon
Two factors of flooding
clay rich soils, water table close to the surface
Urban flooding
Hardtop surfaces inhibit infiltration and increase rapid runoff
Artificial levees
designed to increase capacity of river channel and works well until stream overtops levees, leading to extremely rapid flooding and erosion
Flooding solutions
Dams, Artificial levees, wise land-use planning
Delta
Old age river system, carries small particles
Alluvial Fan
Juvenile river system, carries large particles