Chapter 4: Alkanes and Stereochemistry
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
alkanes
family of hydrocarbons, single bonded C-H
isomers
compounds that have the same # and kinds of atoms but differ in atomic arrangement
constitutional isomers
isomers that have their atoms connected in a different order
different carbon skeletons, functional groups or position of functional groups
primary carbon
bonded to one other carbon
secondary carbon
bonded to 2 other carbons
tertiary carbon
bonded to 3 other carbons
quaternary carbon
bonded to 4 other carbons
alkane properties
paraffins: little affinity for other substances
reacts w/oxygen, halogens and few more
reactions w/oxygen occur during combustion
stereochemistry
3D aspects of molecules —> 3D structure determines properties and biological behavior of molecules
conformations
3D shape of molecule (rotation around single bonds are frozen)
sawhorse representation
views carbon-carbon bond from angle
shows all C-H bonds
newman projects
views carbon-carbon bond directly end-on
represents 2 carbons by a circle
staggers and eclipsed
staggered
lowest energy, most stable
all 6 C-H bonds are as far away as possible
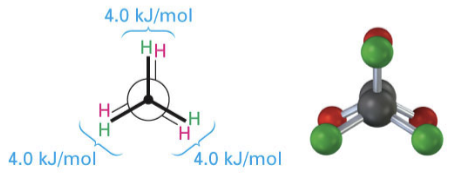
eclipsed
highest energy, least stable
6 C-H bonds are as close together as possible
greatest steric and torsional strain
anti-conformation
lowest energy conformation, 2 largest substituents are 180 degrees apart
multiple carbons
type of staggered confirmation
gauche conformation
2 methyl (CH3) groups lie 60 degrees apart
higher energy than anti-conformation
steric strain
type of staggered confirmation
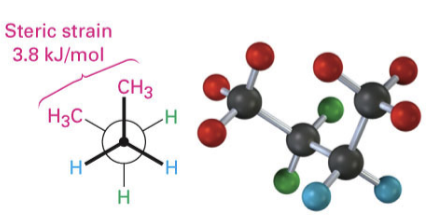
steric strain
repulsive interaction in molecule when 2 groups are closer together than their atomic radii allow (between non bonded atoms in close proximity)
anti-conformation vs gauche conformations
cis-trans isomerism
cycloalkanes have top and bottom face = isomerism
stereoisomers
compounds with atoms connected in the same order, but differ in 3D orientation
cis or trans
constitutional isomers
atoms are connected in a different order
ring strain + stability of cycloalkanes
cyclic molecules can assume nonplanar conformations to minimize angle + torsional strain by ring-puckering
larger rings have more possible conformations
larger than 3 atoms
measure strain measuring heat of combustion energy
angle strain
expansion or compression of bond angles away from most stable
torsional strain
eclipsing of bonds on neighboring atoms
staggered vs eclipsed conformations
cyclopropane conformation
planar, 3-membered ring
C-C-C bond angles of 60 degrees
sp3 bonds are bent + weakened
all C-H bonds are eclipsed
cyclobutane
less angle strain but more torsional strain (larger number of ring hydrogens)
bend increases angle strain but decreases torsional strain
not quite eclipsed
cyclopentane
no angle strain but high torsional strain (planar)
non-planar reduces torsional strain
cyclohexane chair conformation
ring is free of angle and torsional strain
alternating atoms in common plane w/tetrahedral angles
chair conformation
bonds are staggered
cyclohexane boat conformation
less stable than boat due to steric and torsional strain
4 eclipsed H-pairs on C 2, 3, 5 and 6 that produce torsional strain
bonds are staggered + eclipsed
axial
point straight up or down
equatorial
point outwards
more stable
flipping from chair to boat conformation
hydrogens change from equatorial to axial
1,2 cis
a,e or e,a
1,2 trans
a,a or e, e
1,4 cis
same as 1,2 cis
1,3 cis
opposite of 1,2 cis (a,a or e, e)