Algebra II Function Families
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
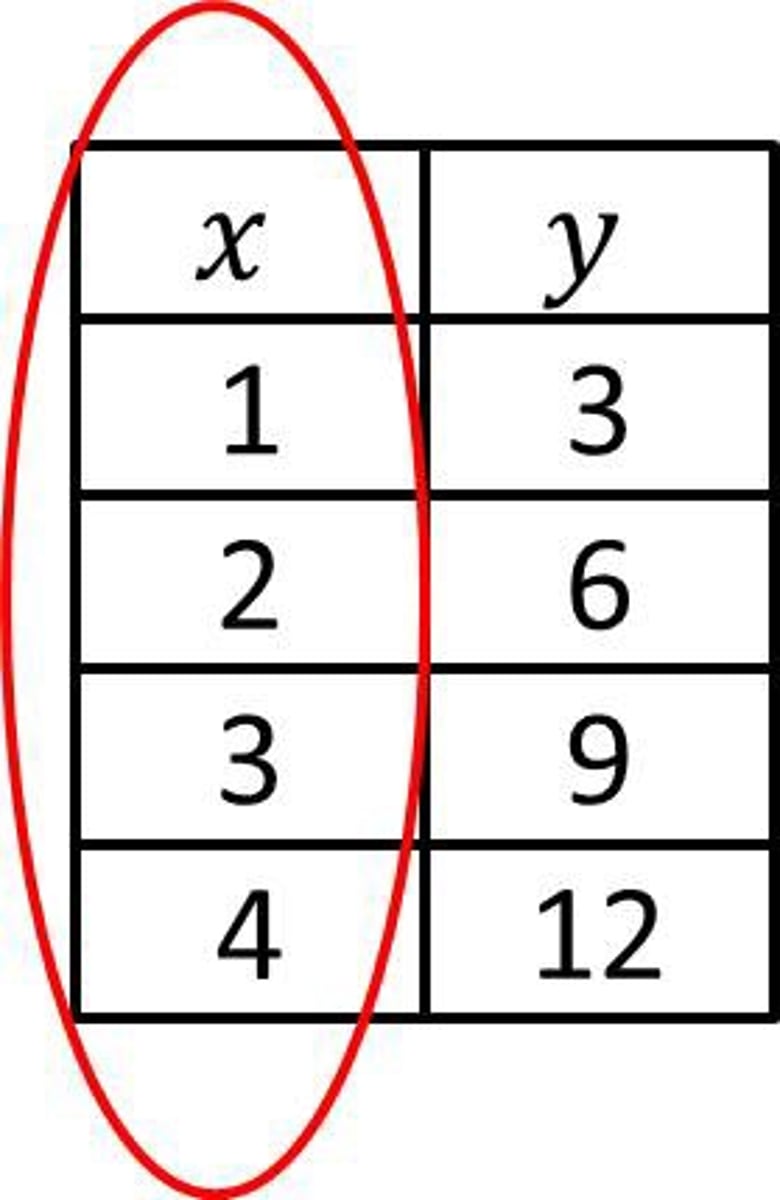
Domain
All of the input or x values in a function
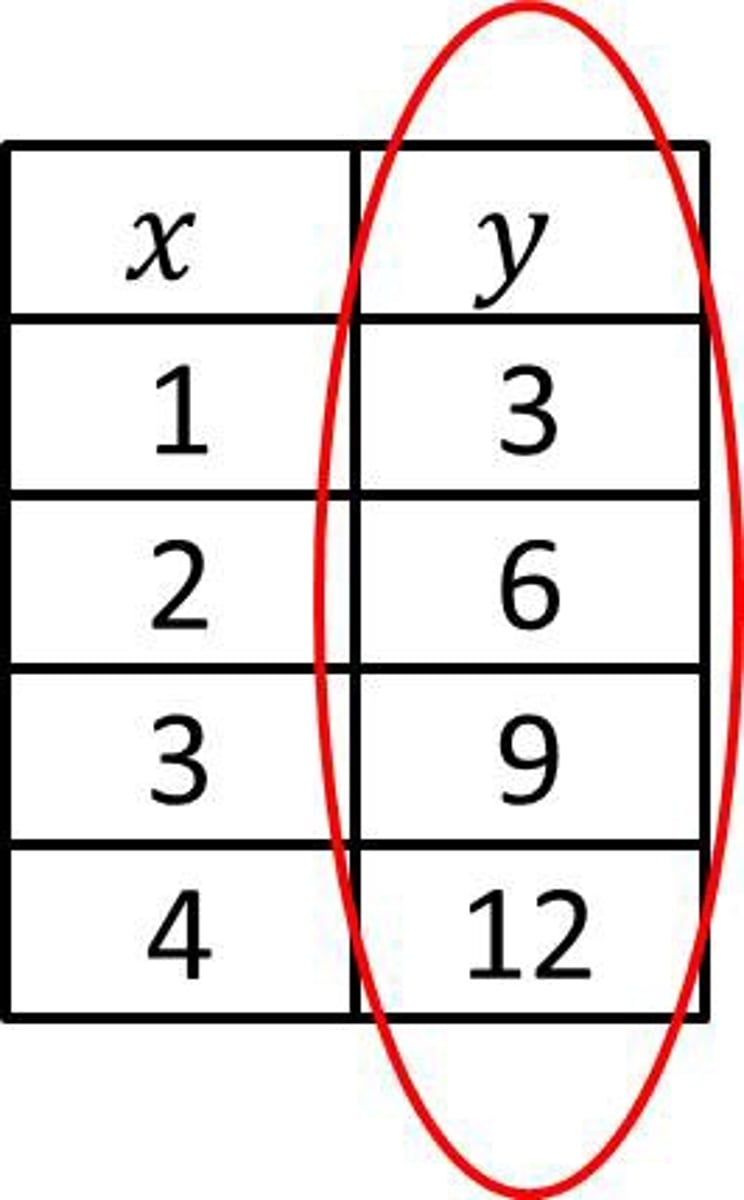
Range
All of the output or y values in a function
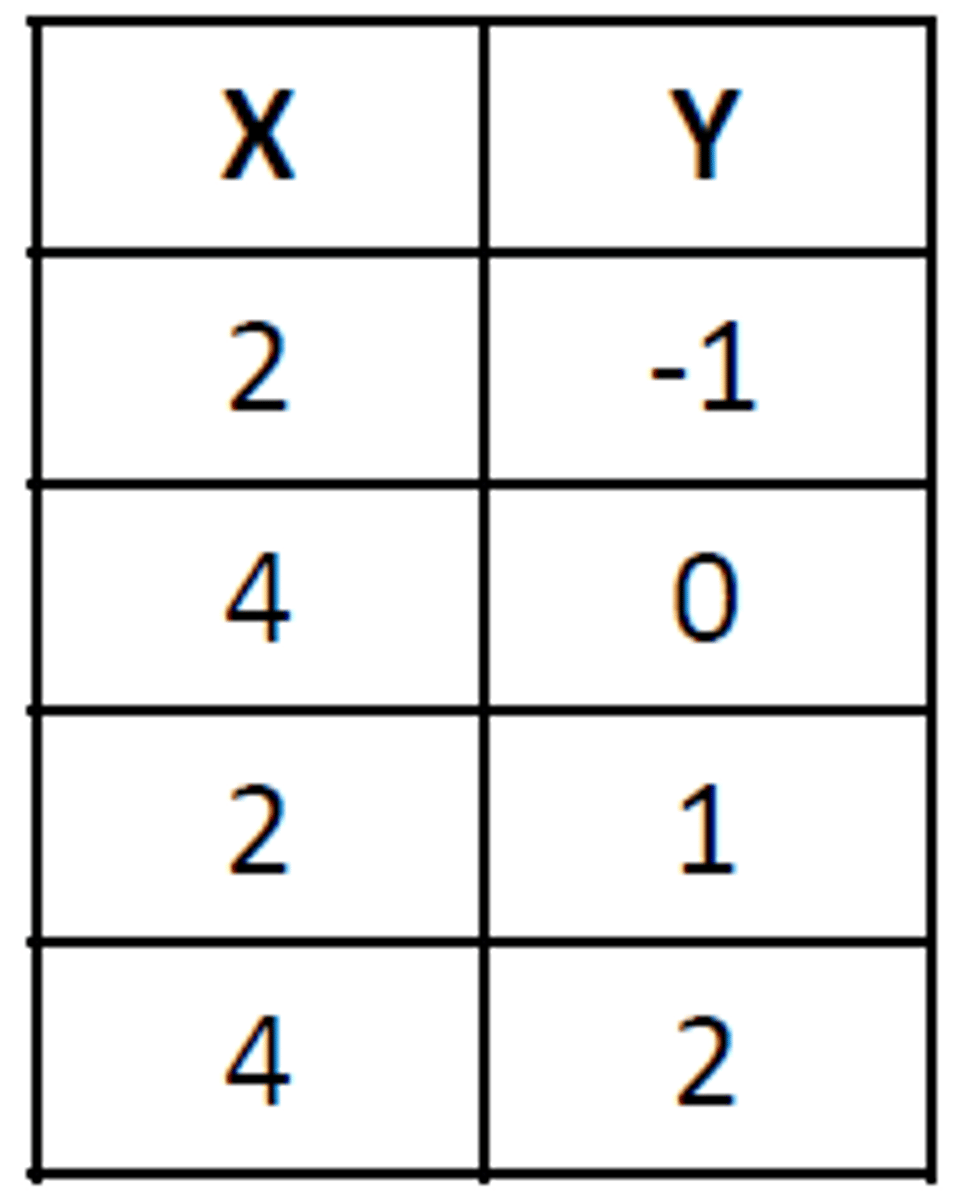
function
1. A relationship from one set (called the domain) to another set (called the range) that assigns to each element of the domain exactly one element of the range. 2. The action or actions that an item is designed to perform.
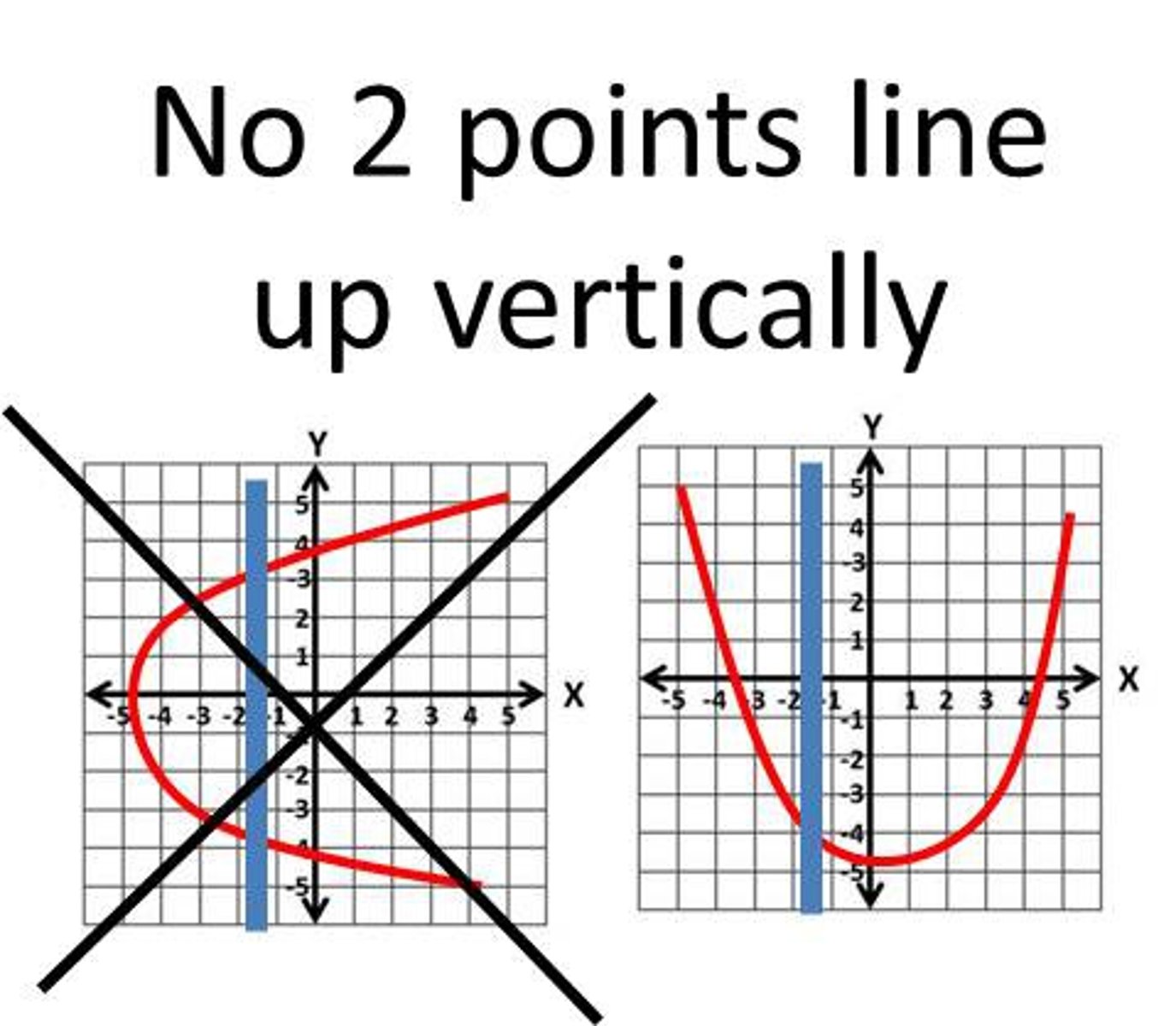
vertical line test
A test used to determine whether a relation is a function by checking if a vertical line touches 2 or more points on the graph of a relation
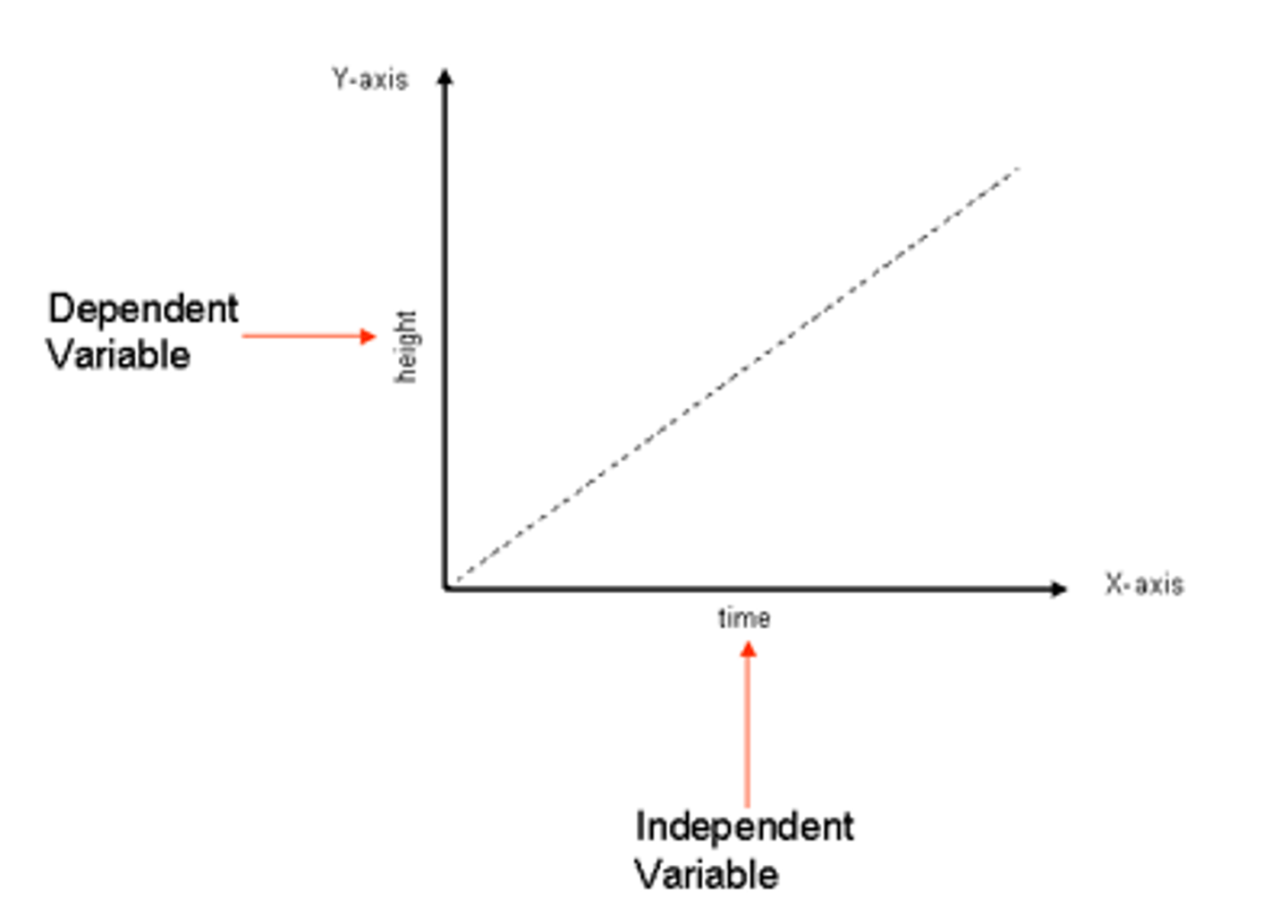
independent variable
a variable (often denoted by x ) whose variation does not depend on that of another.
dependent variable
a variable (often denoted by y ) whose value depends on that of another.
continuous
A graph without breaks or jumps

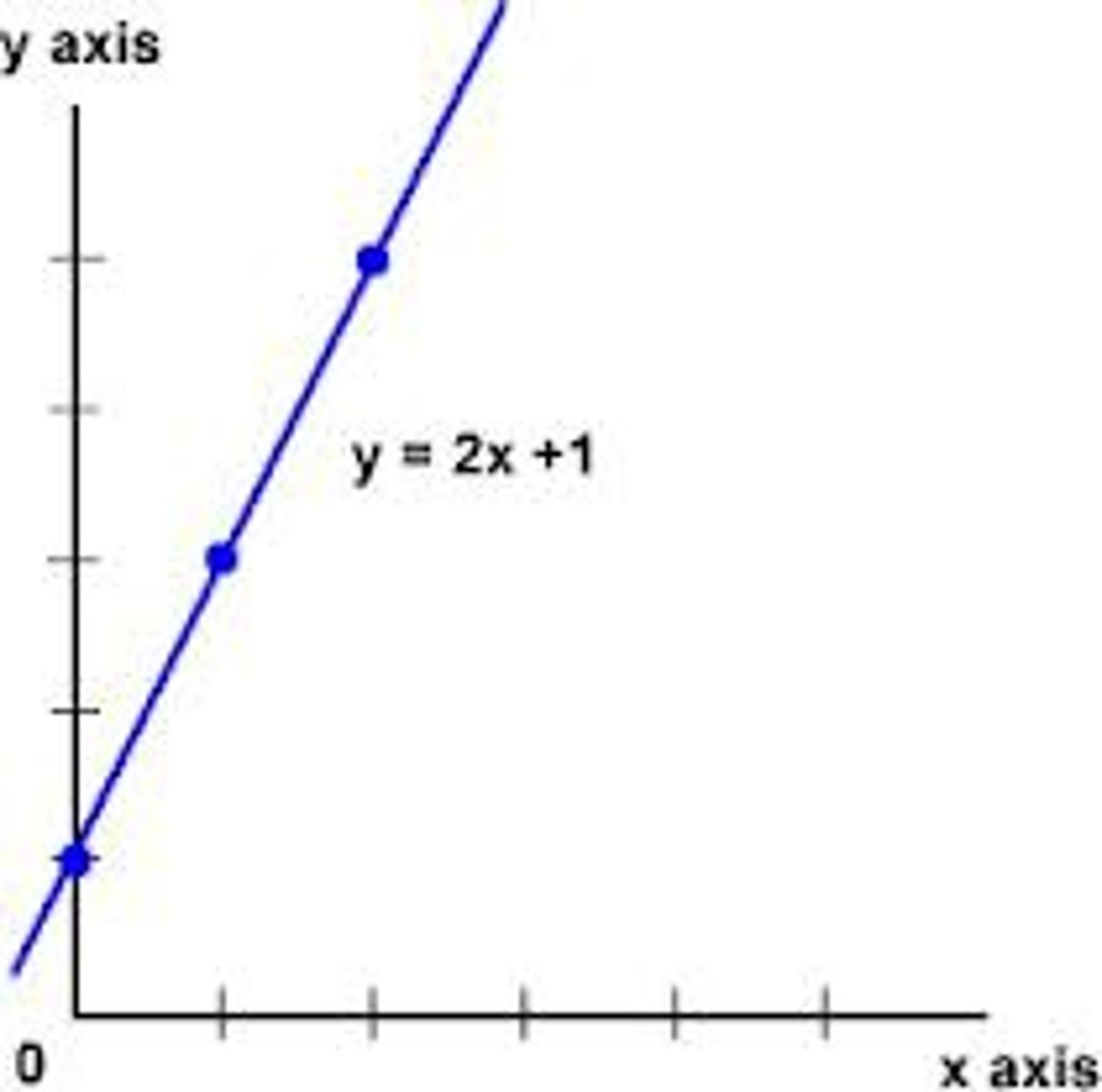
linear function
straight line, a function that grows in equal differences. The first rate of change is always the same.
quadratic function
y=x^2, a u-shaped or n-shaped graph. The second rate of change is always the same.
exponential function
y=ab^x, an L shaped graph, the rate of change is found through multiplying the y-values.
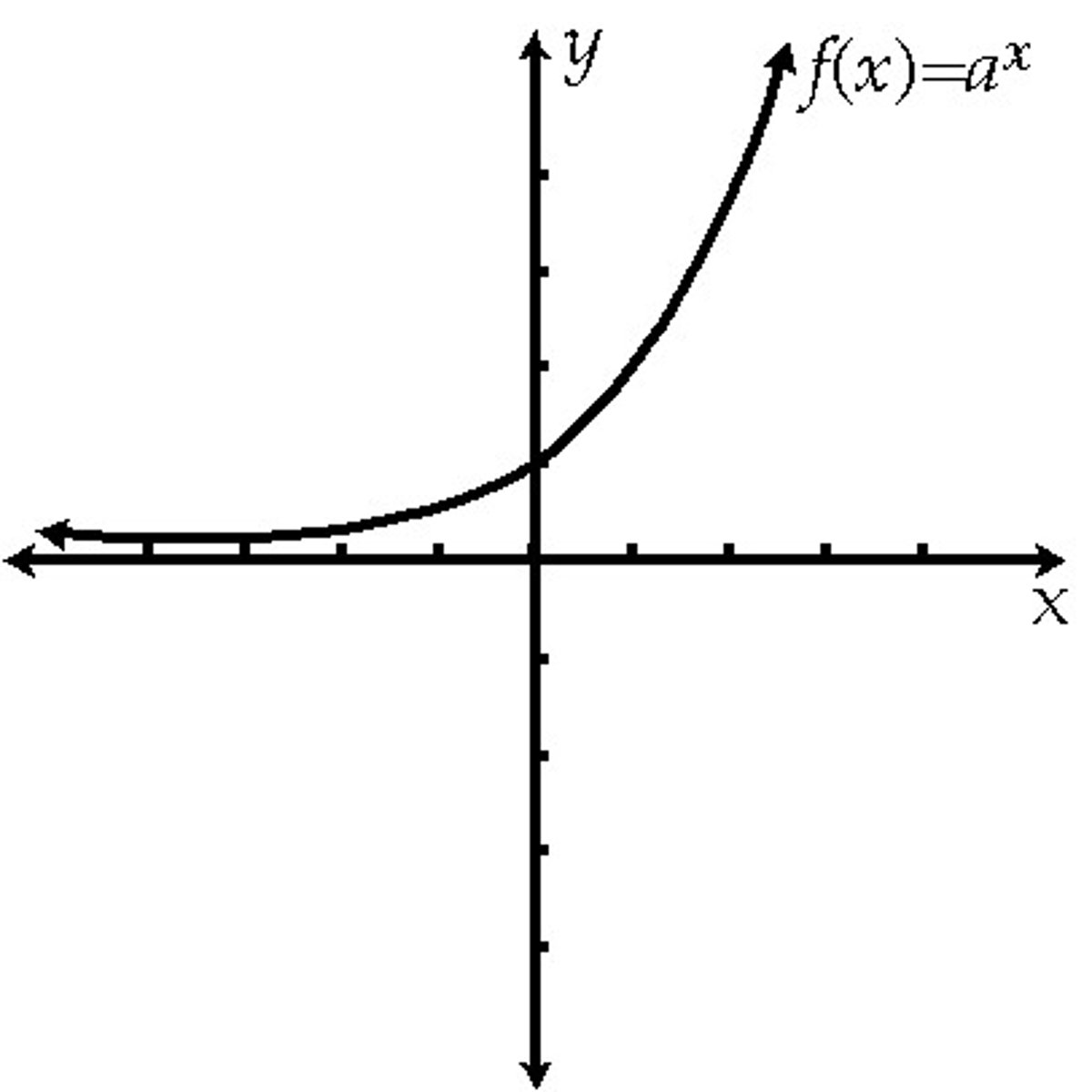
increasing
The graph of a function goes up on a portion of its domain when viewed from left to right

decreasing
The graph of a function goes down on a portion of its domain when viewed from left to right.

rate of change
A ratio that compares the amount of change in a dependent variable to the amount of change in an independent variable.
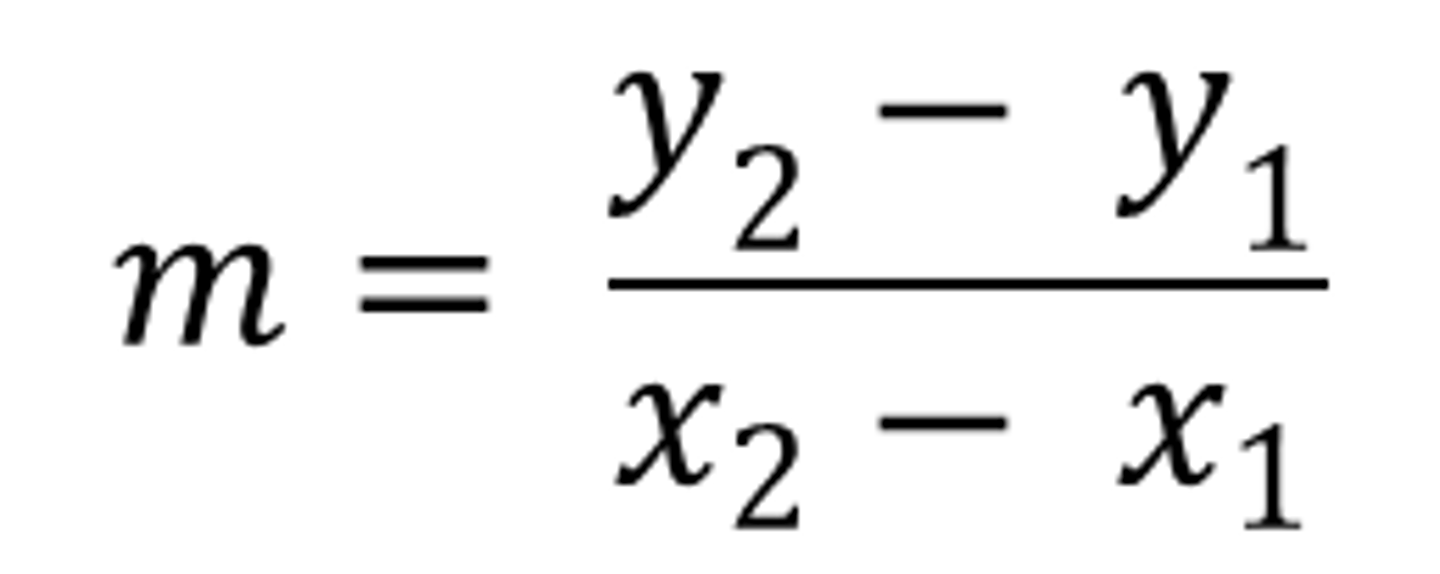
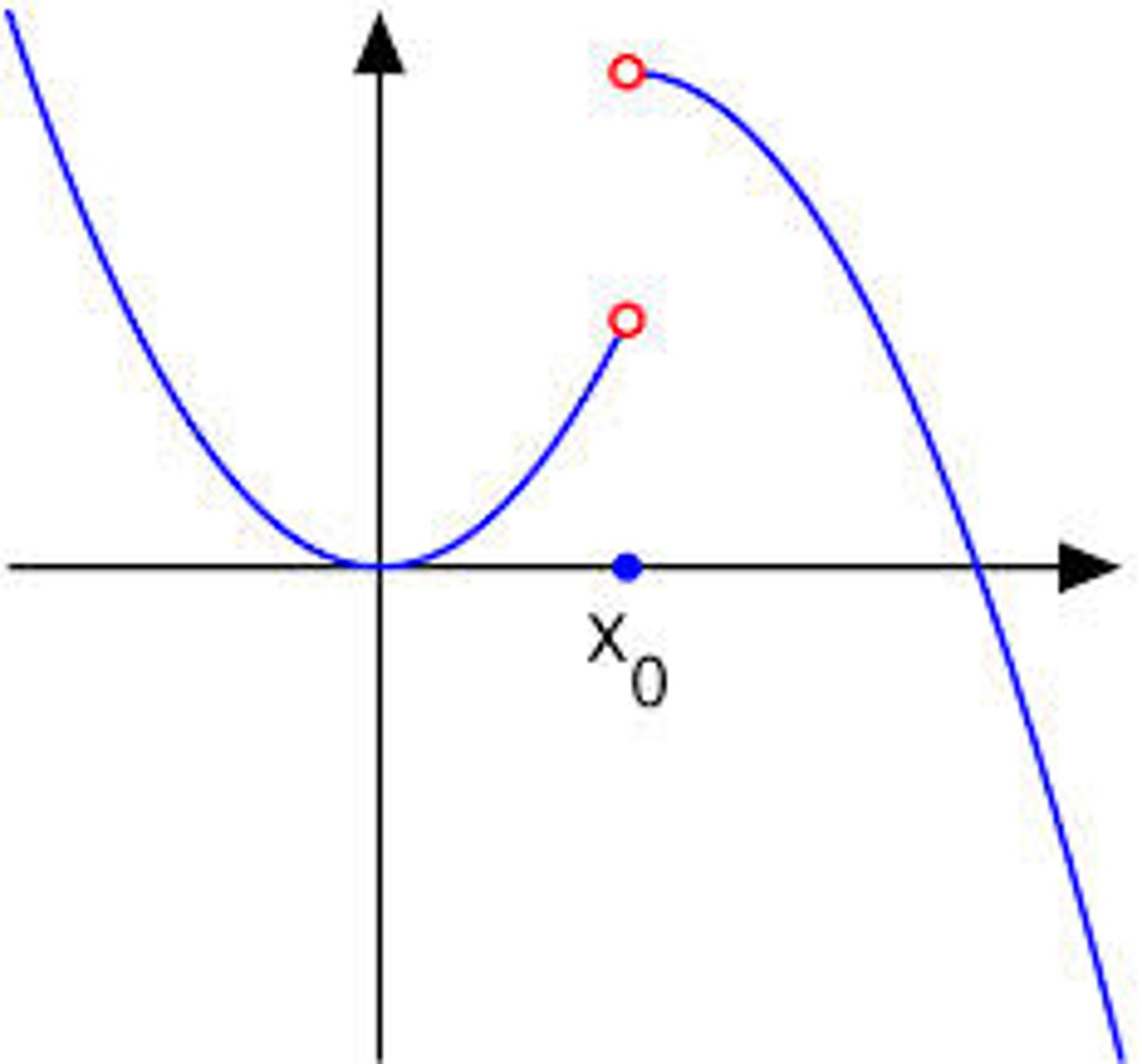
Discontinuous
A graph that is broken by a jump, hole or vertical asymptote. (you have to pick up your pencil to complete the drawing)
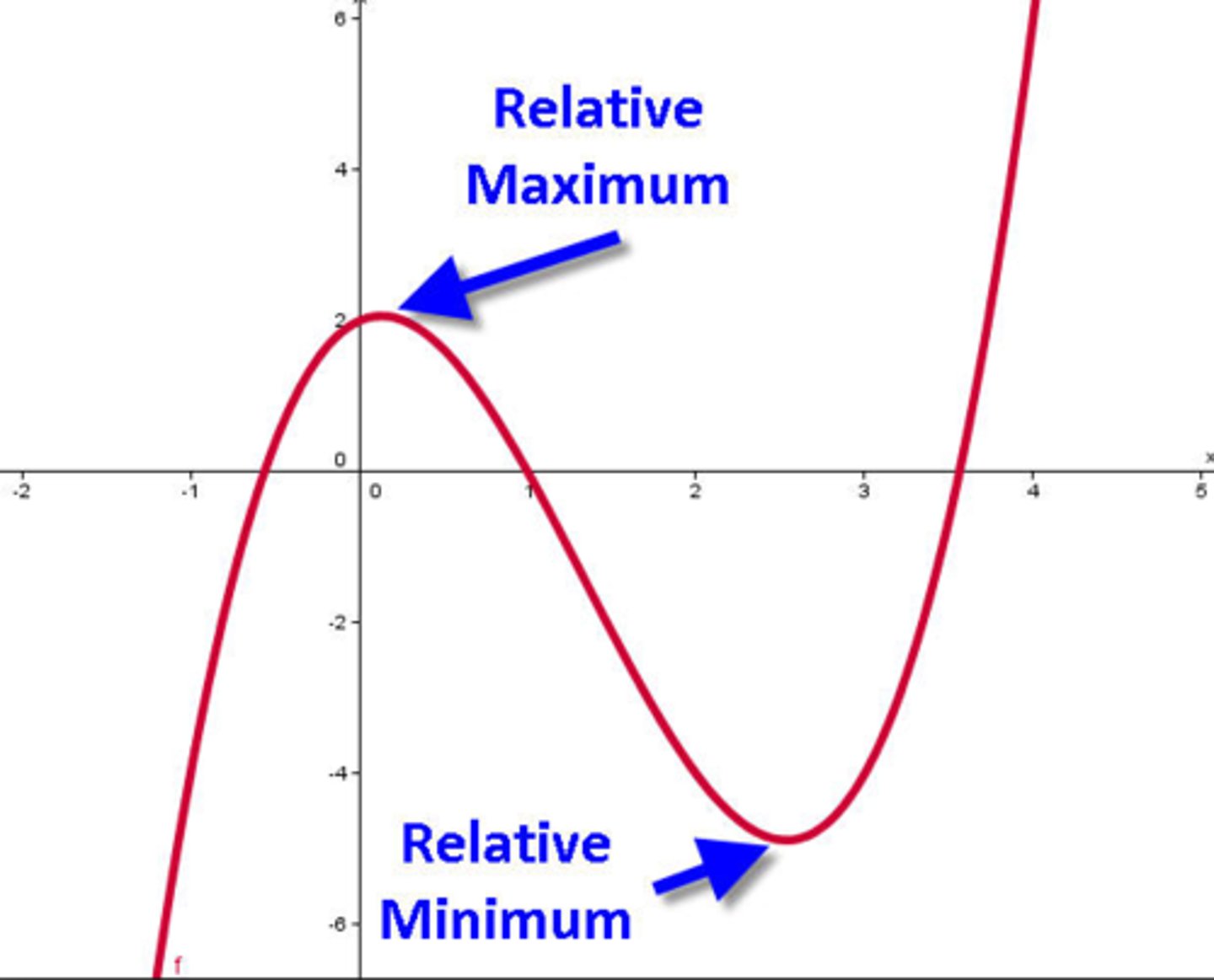
Relative Maximum
The highest point on the graph in an interval. (the peak of a mountain)
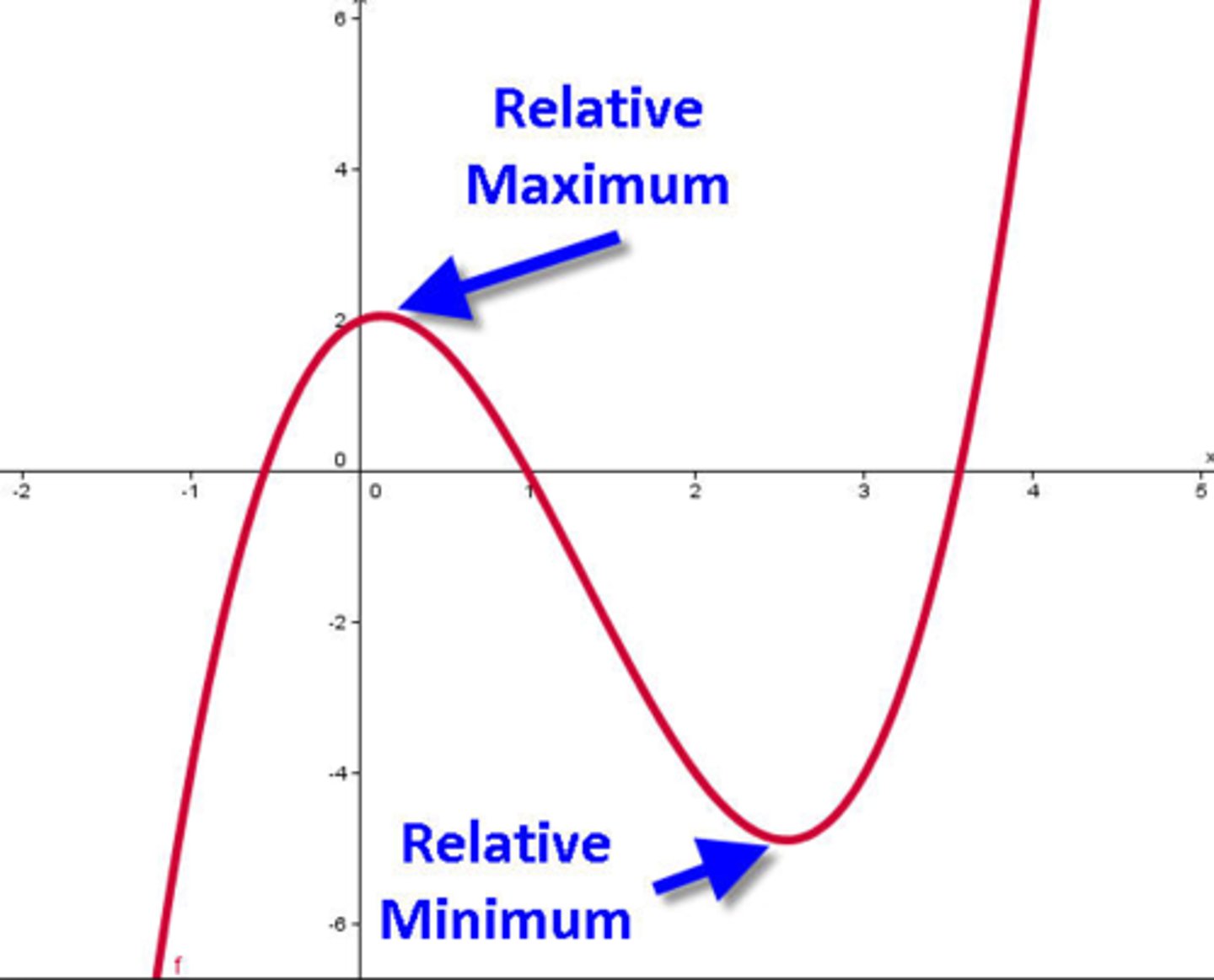
Relative Minimum
The lowest point on the graph in an interval (the valley of a mountain)
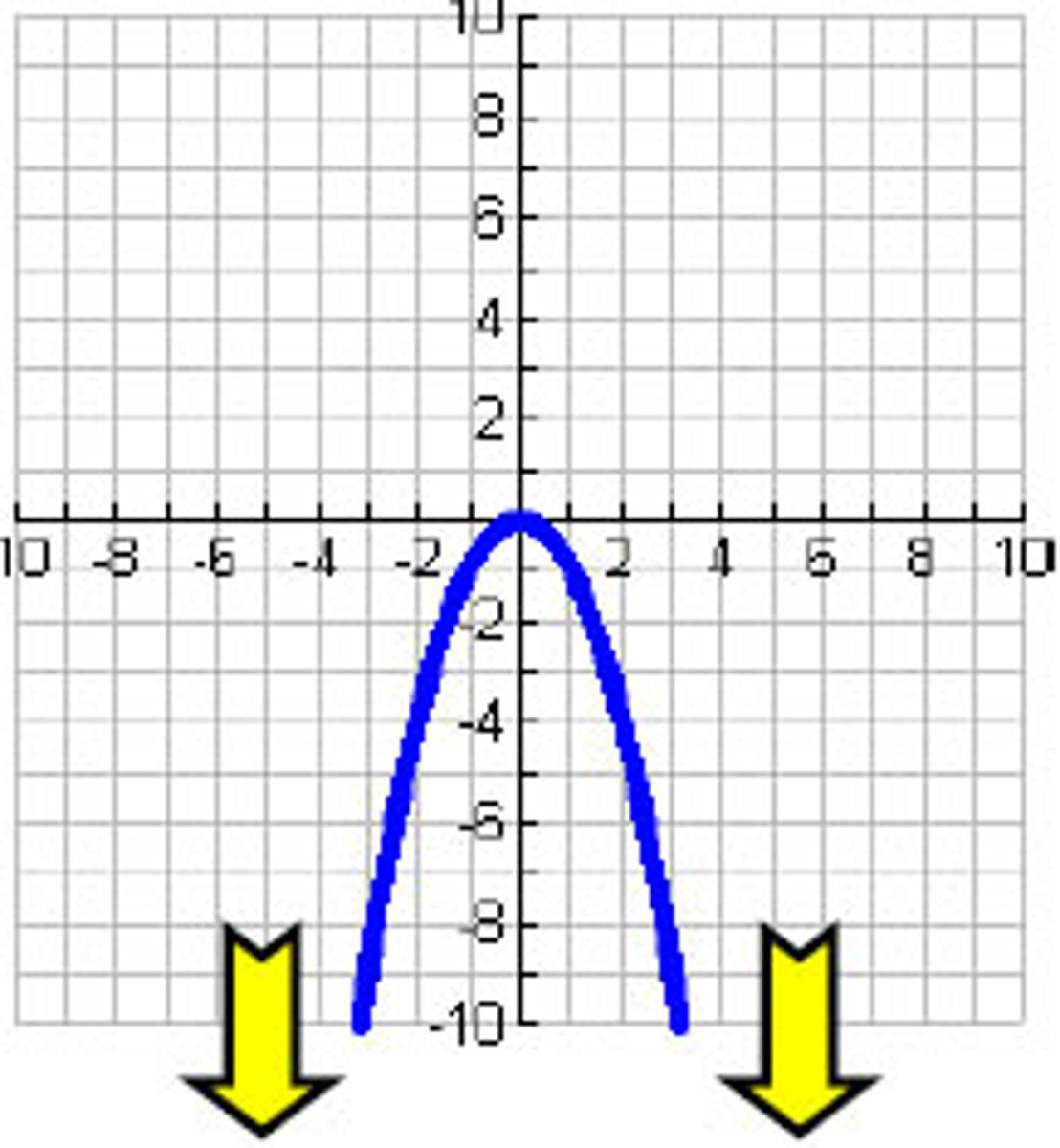
End behavior
The y-value of a graph when the x-value approaches negative infinity or positive infinity
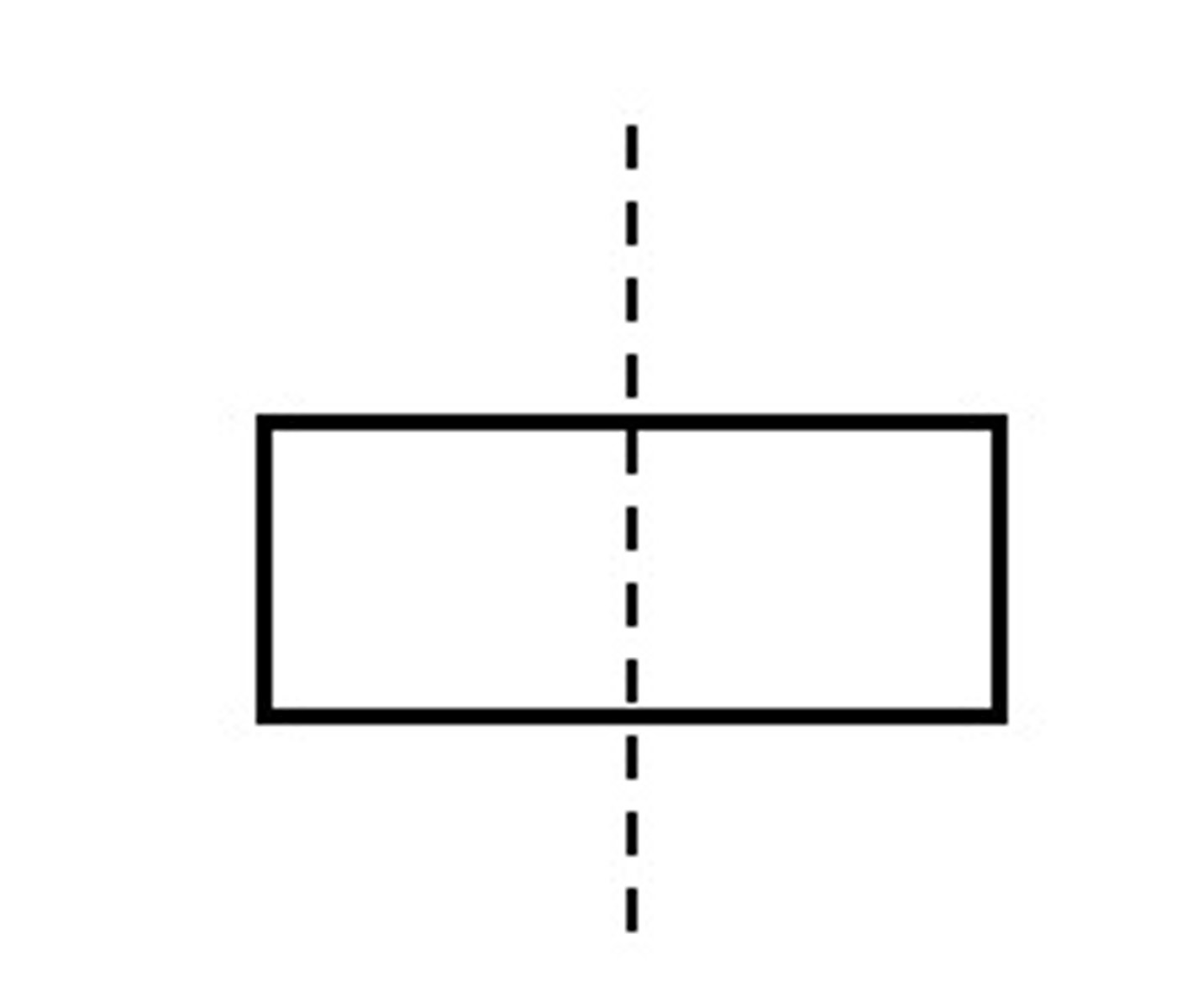
vertical line symmetry
An imaginary line that can be drawn vertically through a graph, which will cut the graph into two perfect halves.
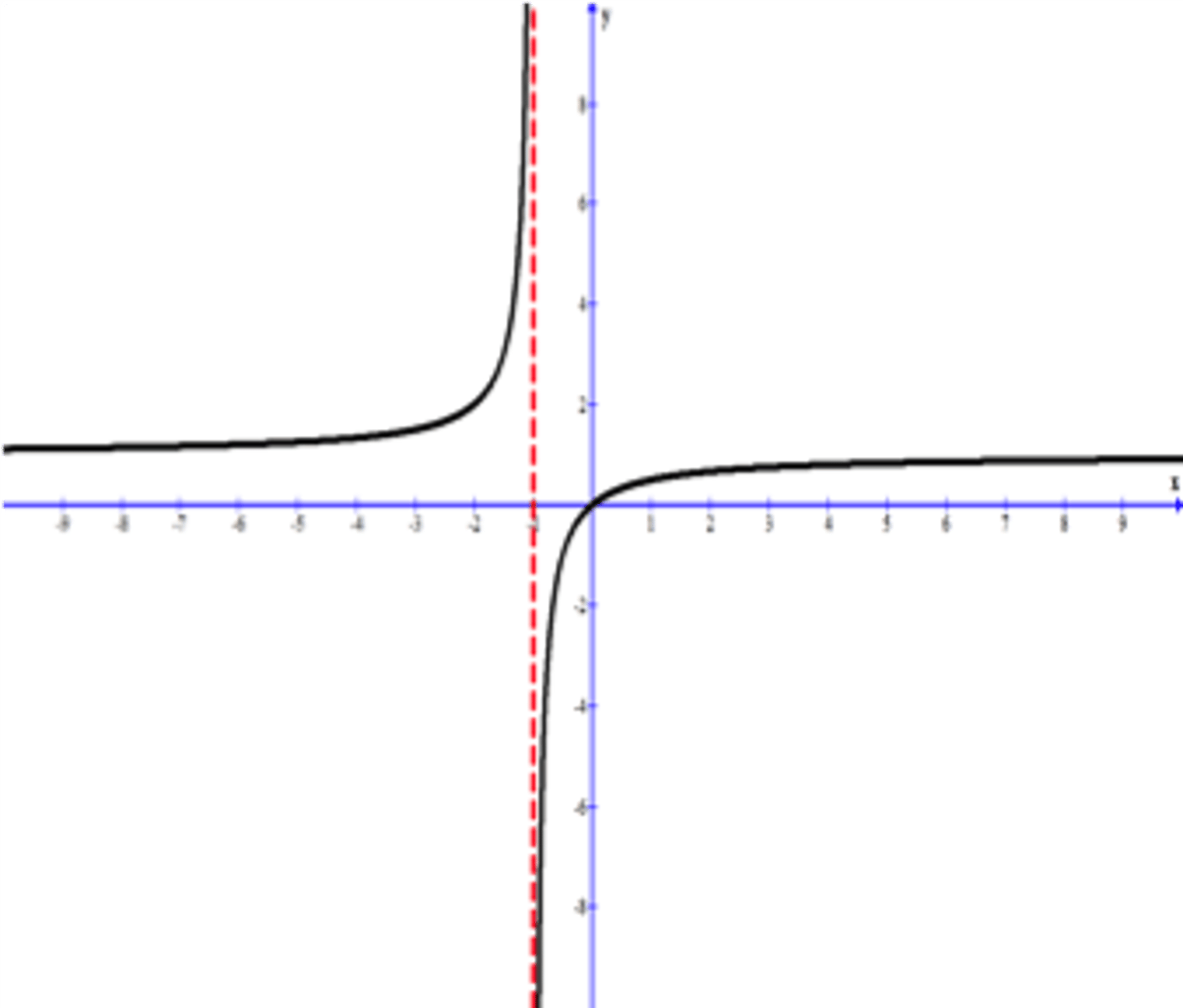
Vertical Asymptote
a vertical line that a graph approaches but never crosses
Horizontal Asympote
A line that describes the end behavior of a function. As x-values approach infinity or negative infinity, the y-values will approach a constant number.
Even Function
The graph of the function is reflective over the y-axis. f(x)=f(-x)
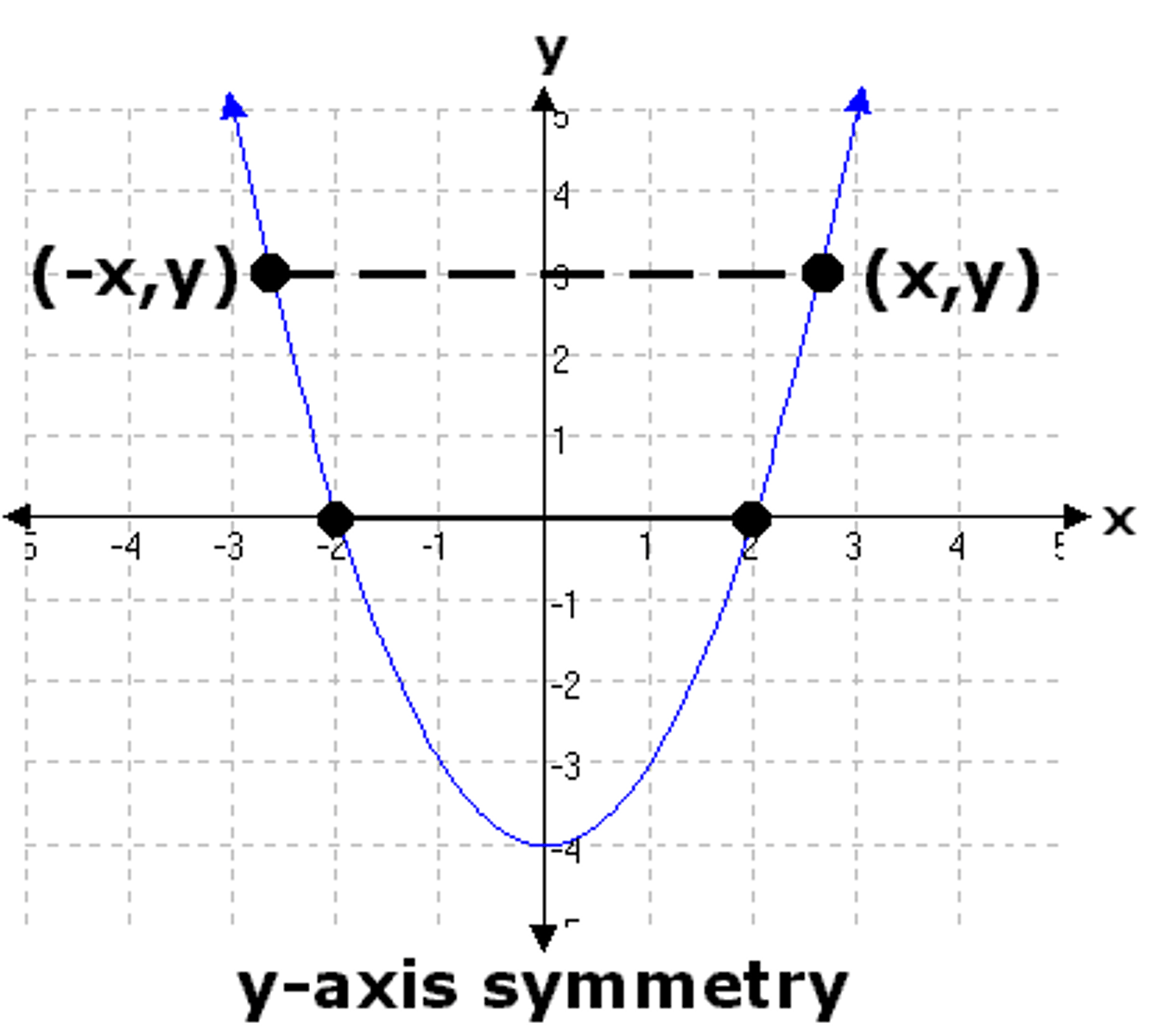
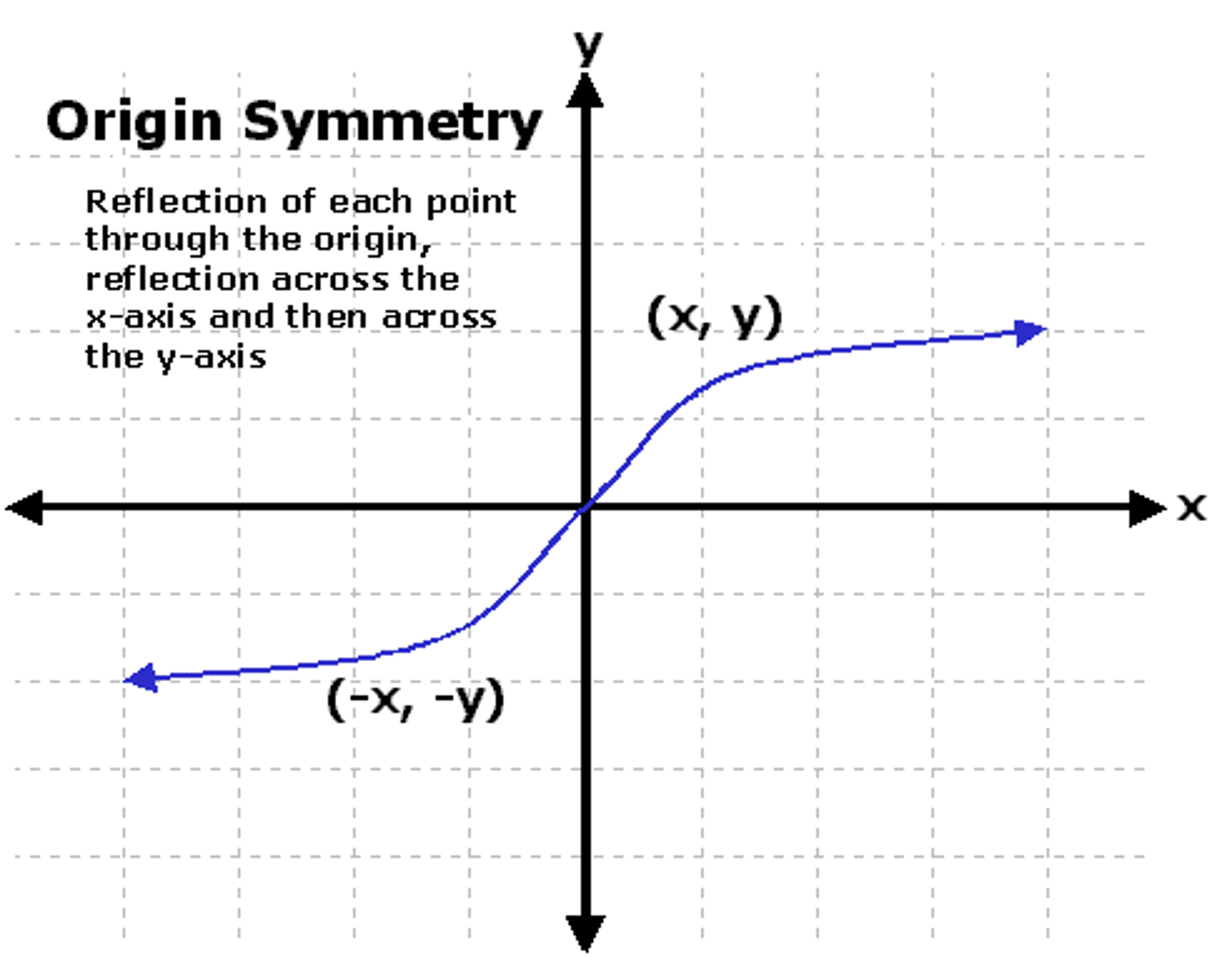
Odd Function
The graph of the function is reflective over the origin. f(-x)=-f(x)
Average Rate of Change
Slope of secant line between two points, use to estimate instantaneous rate of change at a point.. (choose any two points on the graph and find the slope)
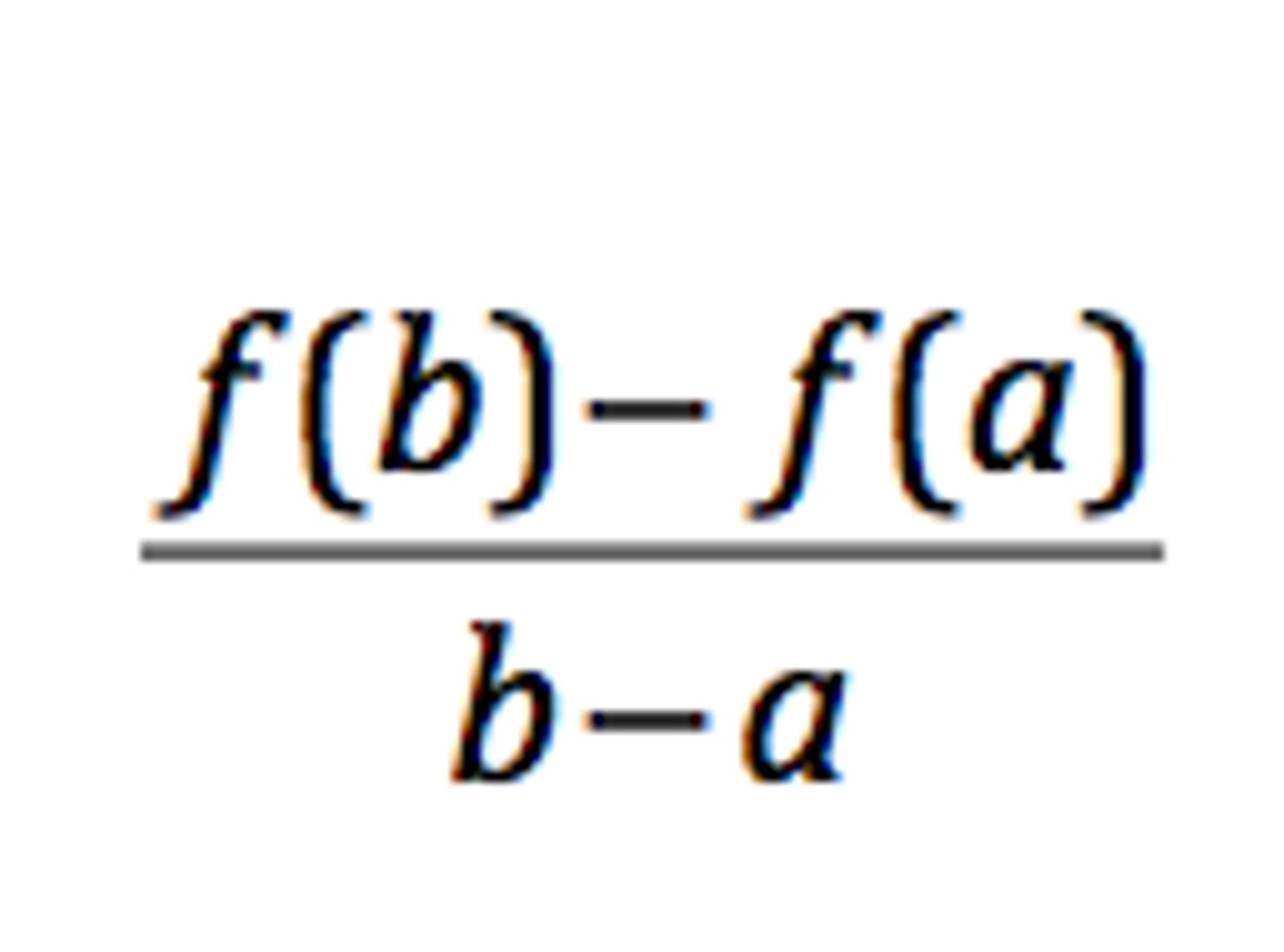
Period
The distance a graph will repeat itself. (a heart beat on a monitor has a periodic rhythm)
Midline
the midway point between a periodic function's maximum and minimum
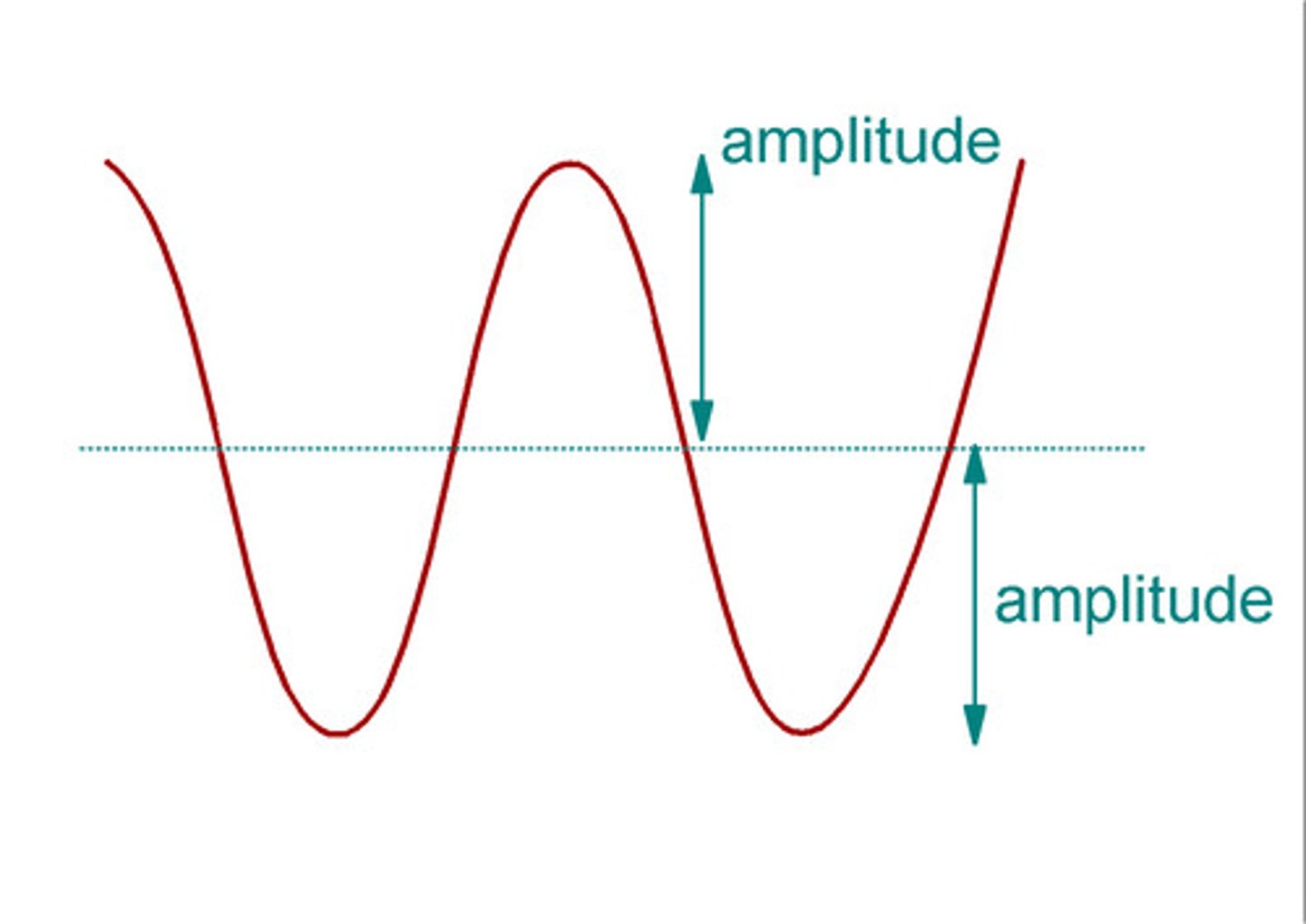
Amplitude
the height of a peak from the midline
Transformation
The movement of a graph from the parent function to a new position on the coordinate plane - translation, reflection, rotation, or dilation
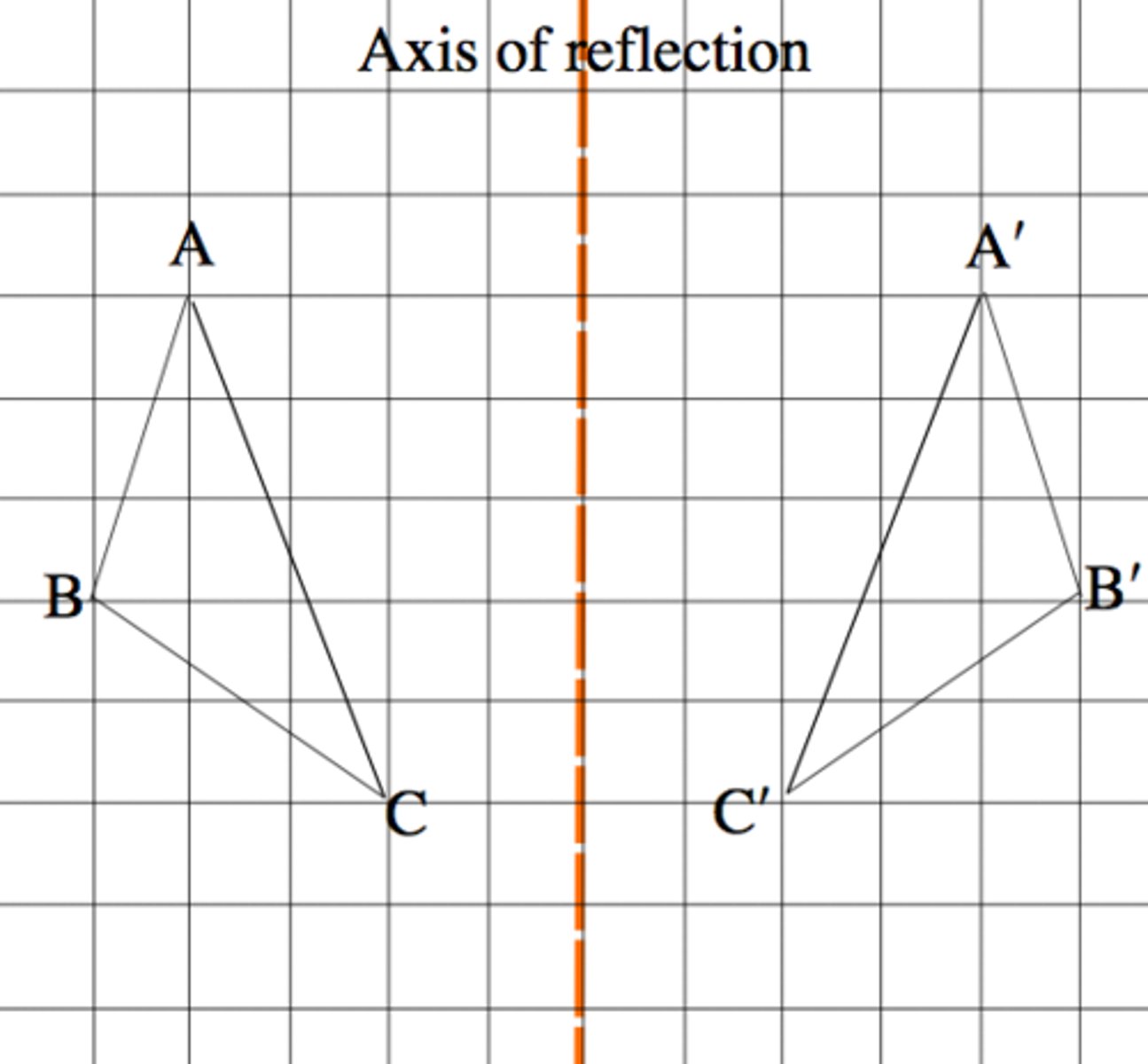
Polynomial
A monomial or the sum of monomials; The graph typically has more than one relative maximum or minimum
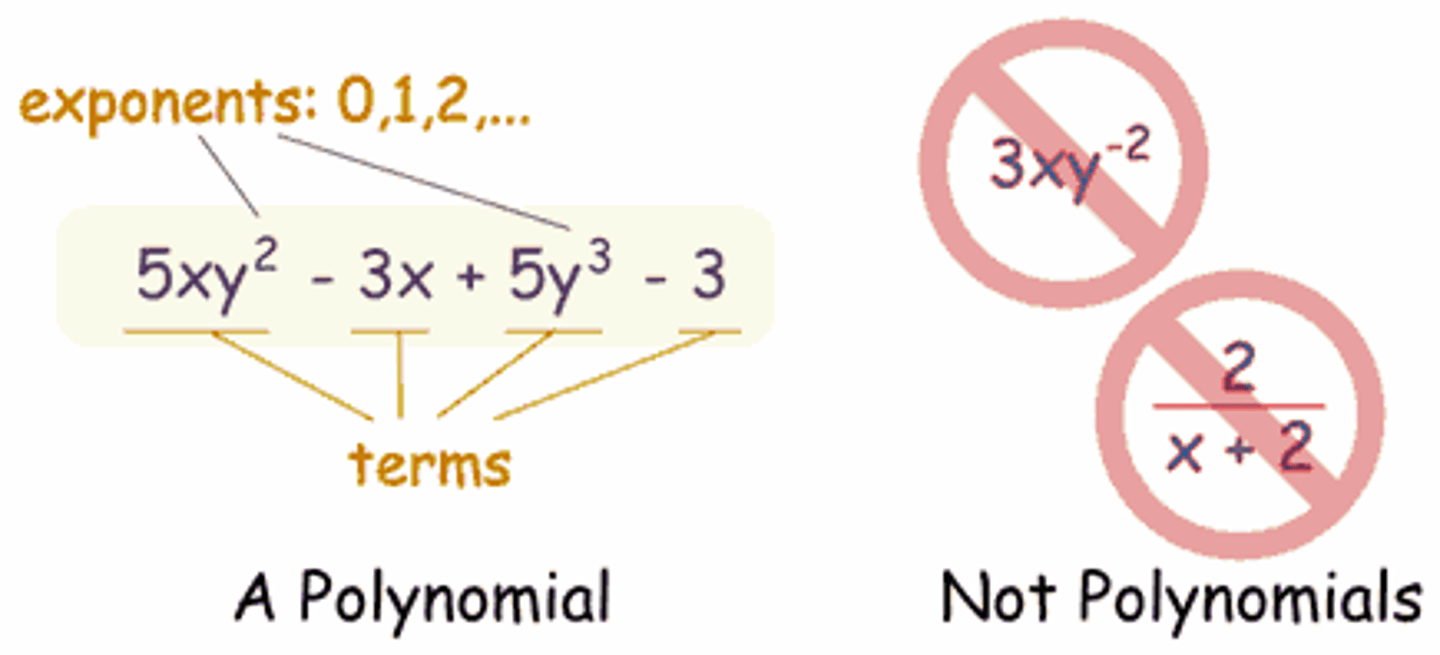
periodic function
a function whose graph has a repeating pattern
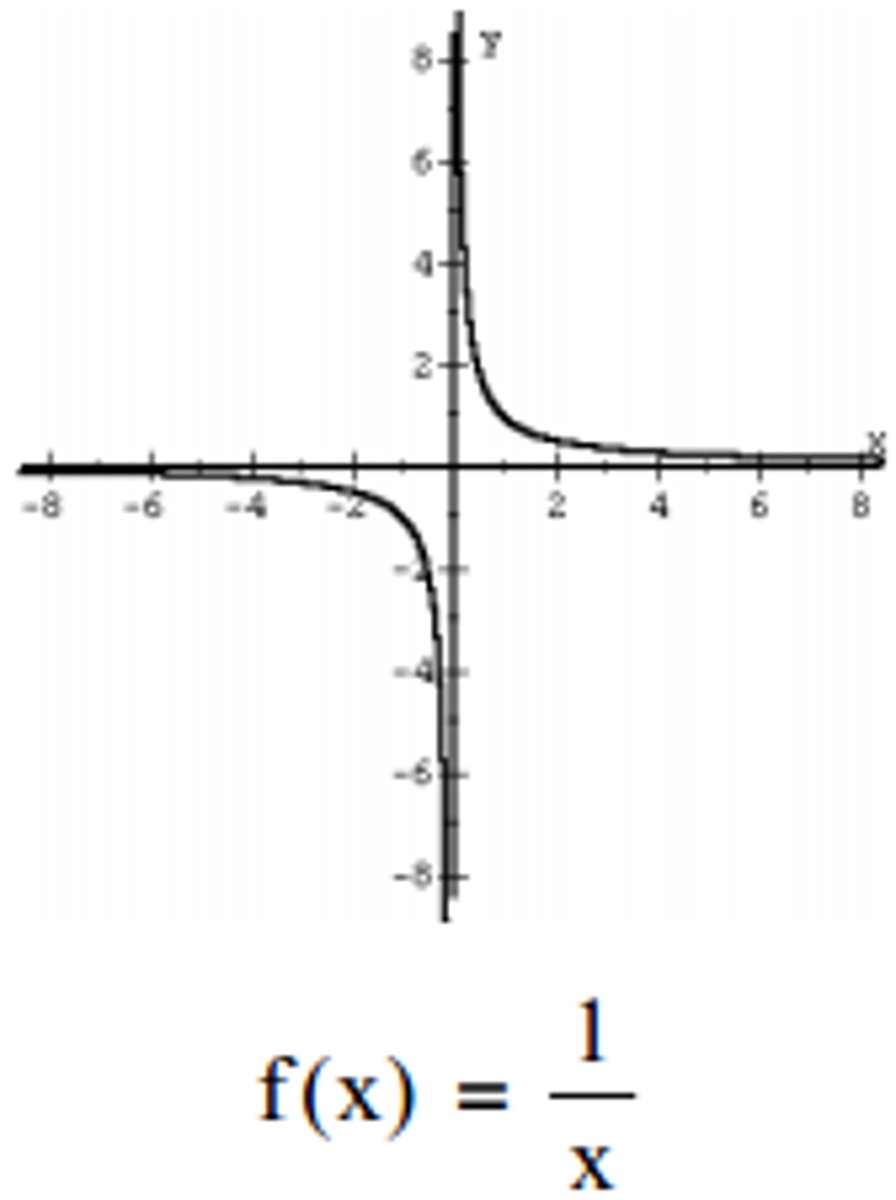
rational function
a function whose rule can be written as a rational expression. (Rational is synonyms with fraction - a function whose equation is written as a fraction)