P1 & P2 Triple Content
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
moment of force
the turning effect of the force about a pivot that an object can rotate around
lever
increases distance from the pivot to allow for less effort for same amount of load
it rotates around the pivot
equilibrium
when something is balanced
The principle of moments
If an object is balanced, the total clockwise moment is equal to the total anti-clockwise moment.
forces are perpendicular to the distance from the pivot
F1d1 = F2d2
pivot diagram
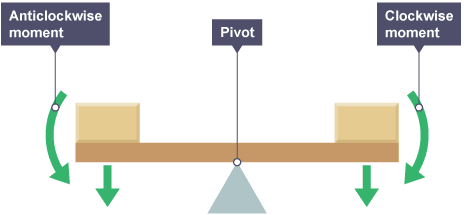
Moment equation
Moment(Nm) = Force(N) x Distance perpendicular from the pivot(m)
work done but measured in Nm & distance perpendicular from pivot
mechanical advantage
a measure of how many times force is multiplied to fulfil a task
mechanical advantage equation
load(what is lifted) / effort(force exerted)
gears
consists of wheels with toothed edges that rotate on an axle/shaft that acts as the pivot
properties of the gear
the teeth of one gear fits into another’s, meaning they can turn each other
the teeth all move in the same direction HOWEVER, one gear moves clockwise, the other anti-clockwise.
diagram of gear’s operation
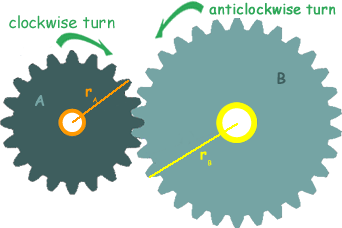
Force applied to gear is NOT moment
different gear sizes changes the distance from the pivot, as a larger gear has a force that acts further
larger = larger force. smaller = smaller force
gear ratio
tells you the number of times drive gear must turn to turn the driven once
gear ratio equation
driven gear’s number of teeth / drive gear’s number of teeth
pressure
the concentration of a force or force per unit area
pressure equation
pressure(Nm or Pa) = Force(N) x area(m2)
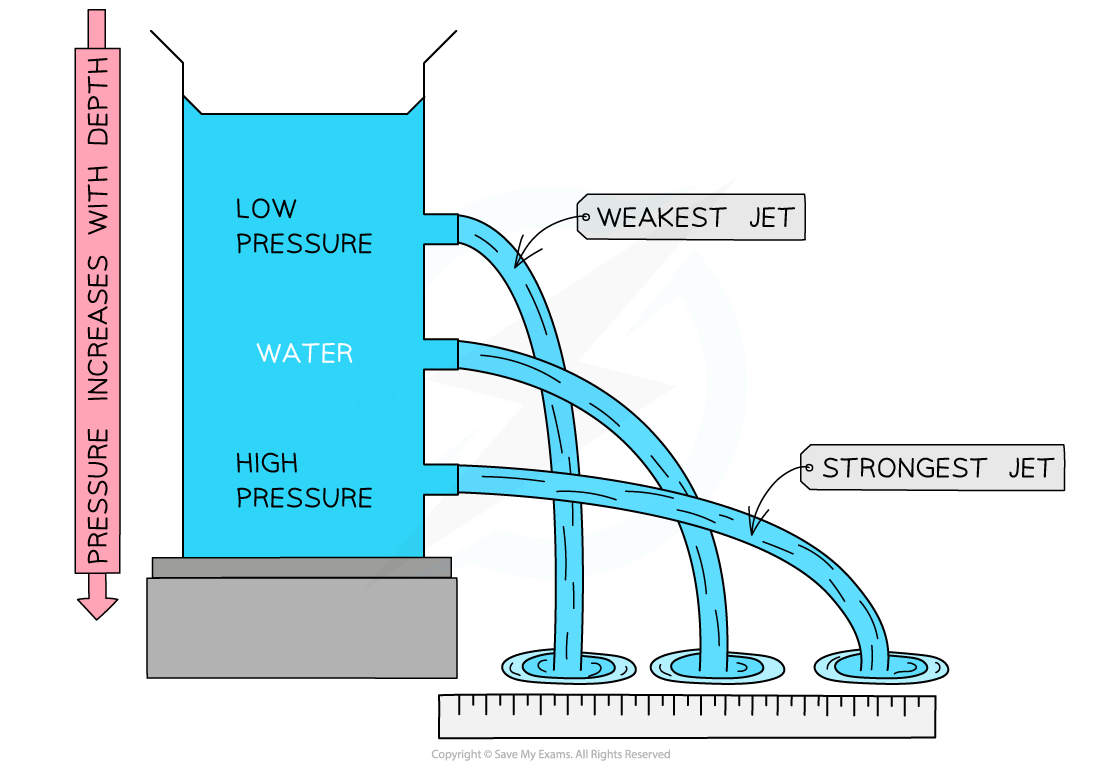
pressure in liquid
pressure is exerted evenly across the whole surface in all directions
force is only exerted perpendicularly to each surface
(only when submerged at a specific depth)
hydraulics
a machine that uses liquid to transmit a force
as pressure in a liquid is the same everywhere, force from one piston lifts the other as pressure remains balanced(and increases)
hydraulic pressure equation representation
P1 = P2
F1/A1 = F2/A2 (equation for pressure)
F2 = F1 x (A2/A1) (mechanical advantage)
atmospheric pressure
the force exerted on a surface by the weight of the air column above it, caused by the collisions of air molecules
pressure decreases higher up as there’s less molecules, meaning less weight.
atmospheric pressure equation
Weight = density x gravity x volume(h*w*l)
atmospheric pressure equation units
volume = m3
density = kg/m3
gravity= N/kg
liquid pressure
when an object is immersed in a liquid, it is exerted evenly across the whole surface of the object in all directions
liquid pressure factors
pressure at a point increases with height of column(weight) above it
more density means higher weight= higher pressure
liquid pressure equation
pressure = height x density x gravitational field strength
liquid pressure equation units
pressure = N/m2 / Pa
height = meters
gravity = N/kg3
density = kg/m3
upthrust
caused by difference in pressure between top and bottom of the object
submerged object experiences greater pressure on bottom surface than top surface
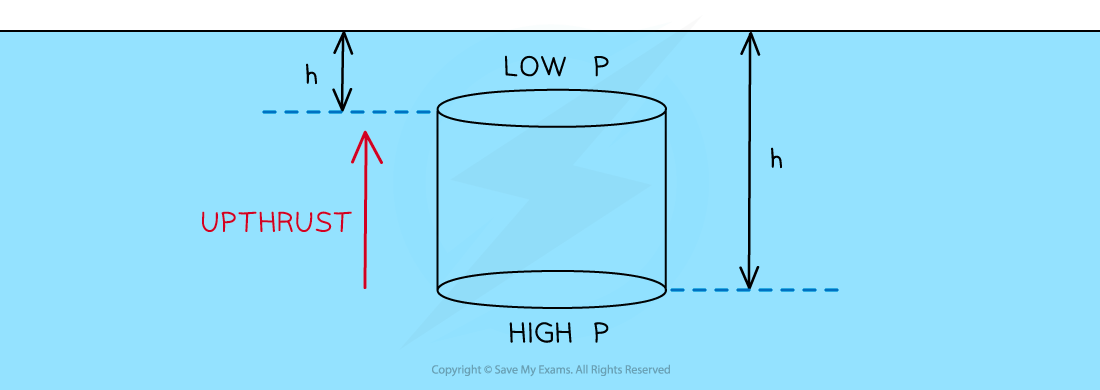
requirements of upthrust
if one force is larger than the other, the object will sink
if the object is less dense than the fluid density, it’ll float as it will never displace enough fluid to hold its weight
Boyle’s law
as volume decreases, particles collide more frequently and pressure increases
gas pressure is inversely proportional to volume, this is Boyle’s law
Boyle’s law equation(volume pressure relationship)
pressure1 * volume1 / temperature1
= after change
pressure2 * volume2 / temperature2
Rearranging Boyle’s Law
as the equation is constant, removing whichever element is fixed
rearrange the equation and solve with values available