BSNL 114 LECTURE 16 - ETSUYA
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
brain
develops a neural tube with several vesicular structures that gives rise to several regions
telencephalon
has cerebrum and lateral ventricles
diencephalon
has thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus and 3rd ventricle
mesencephalon
or mid brain and its aqueduct
Metencephalon
has pons, cerebrellum, and upper part of the 4th ventricle
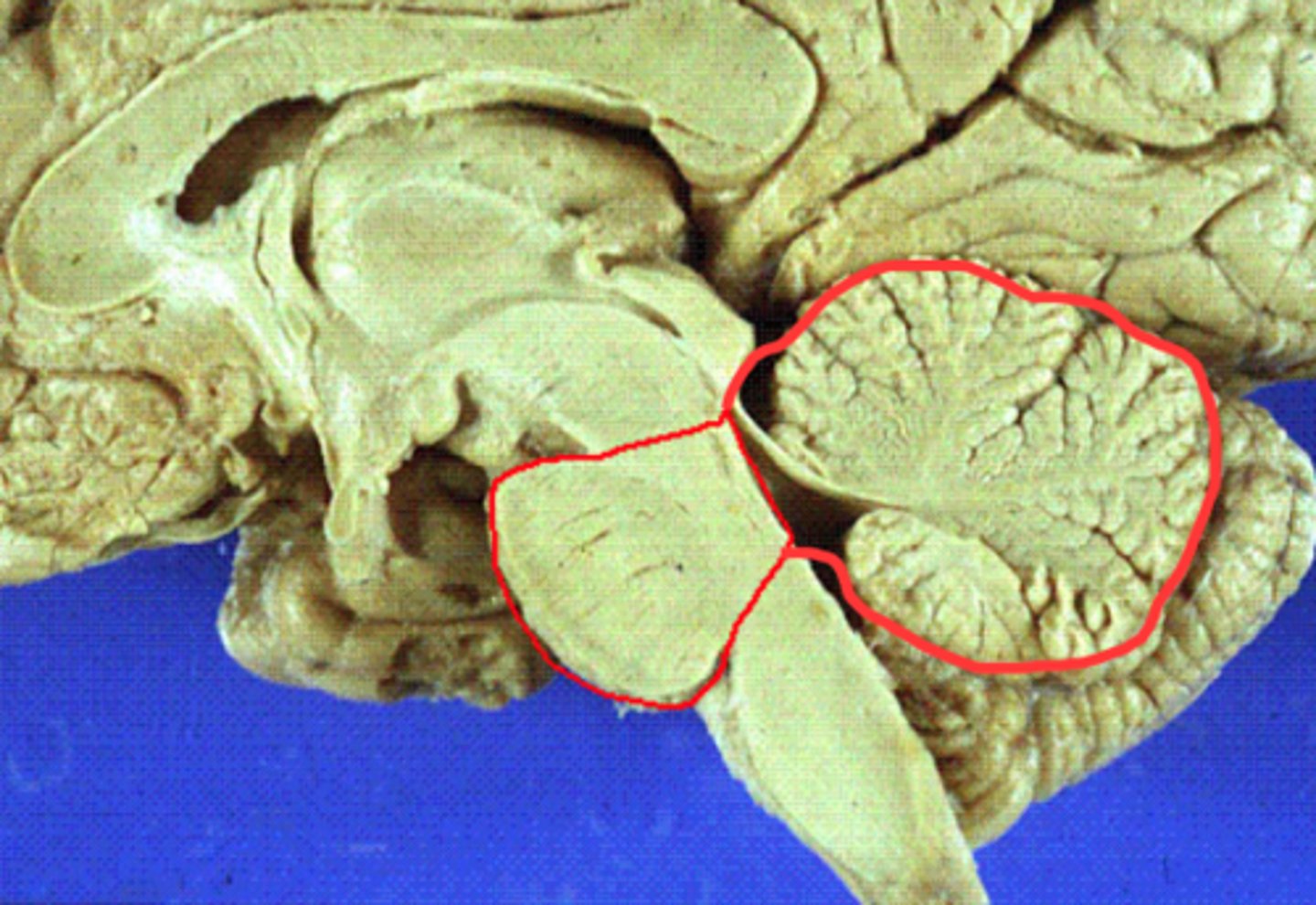
Myelencephalon
has medulla oblongata and lower 4th ventricle
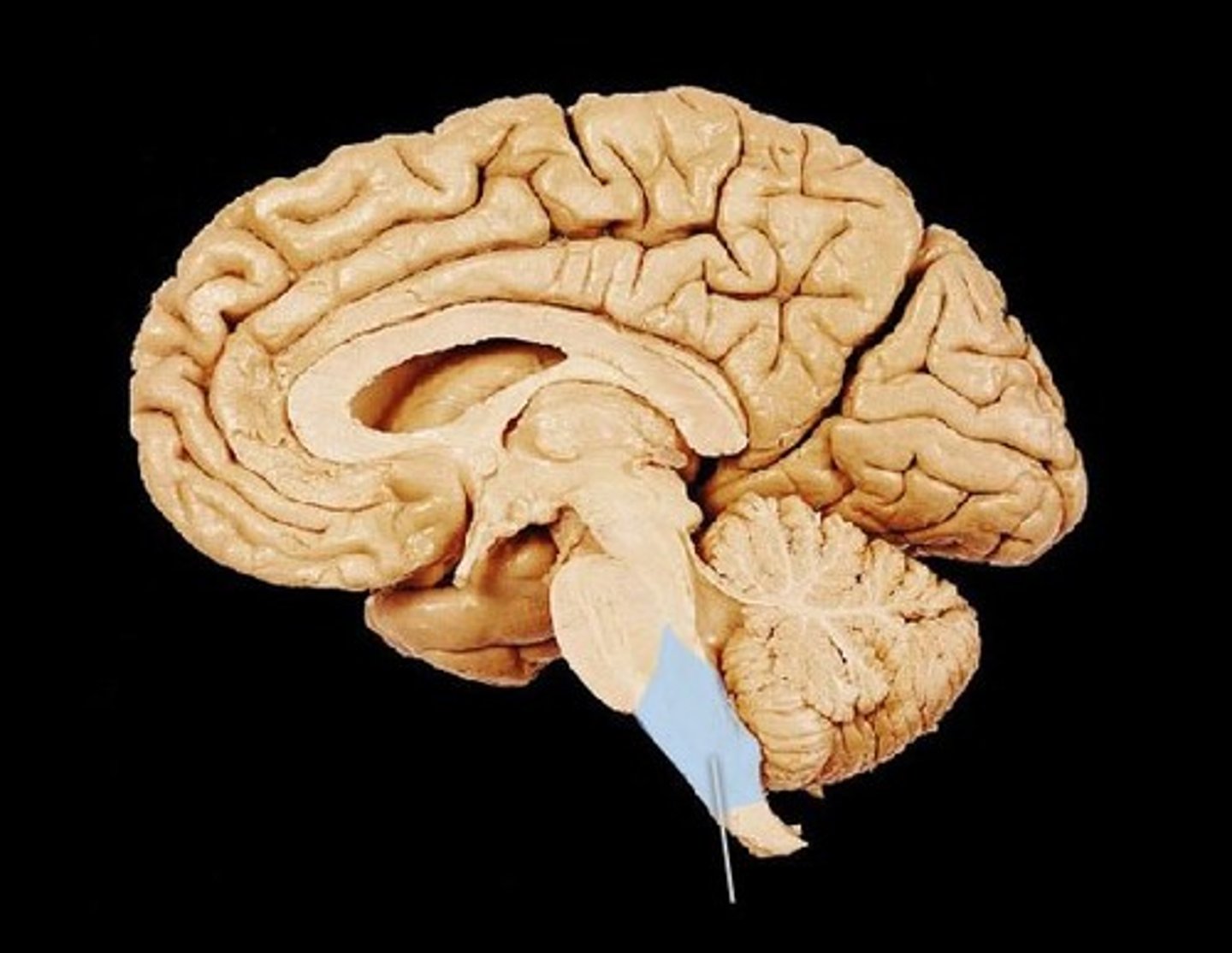
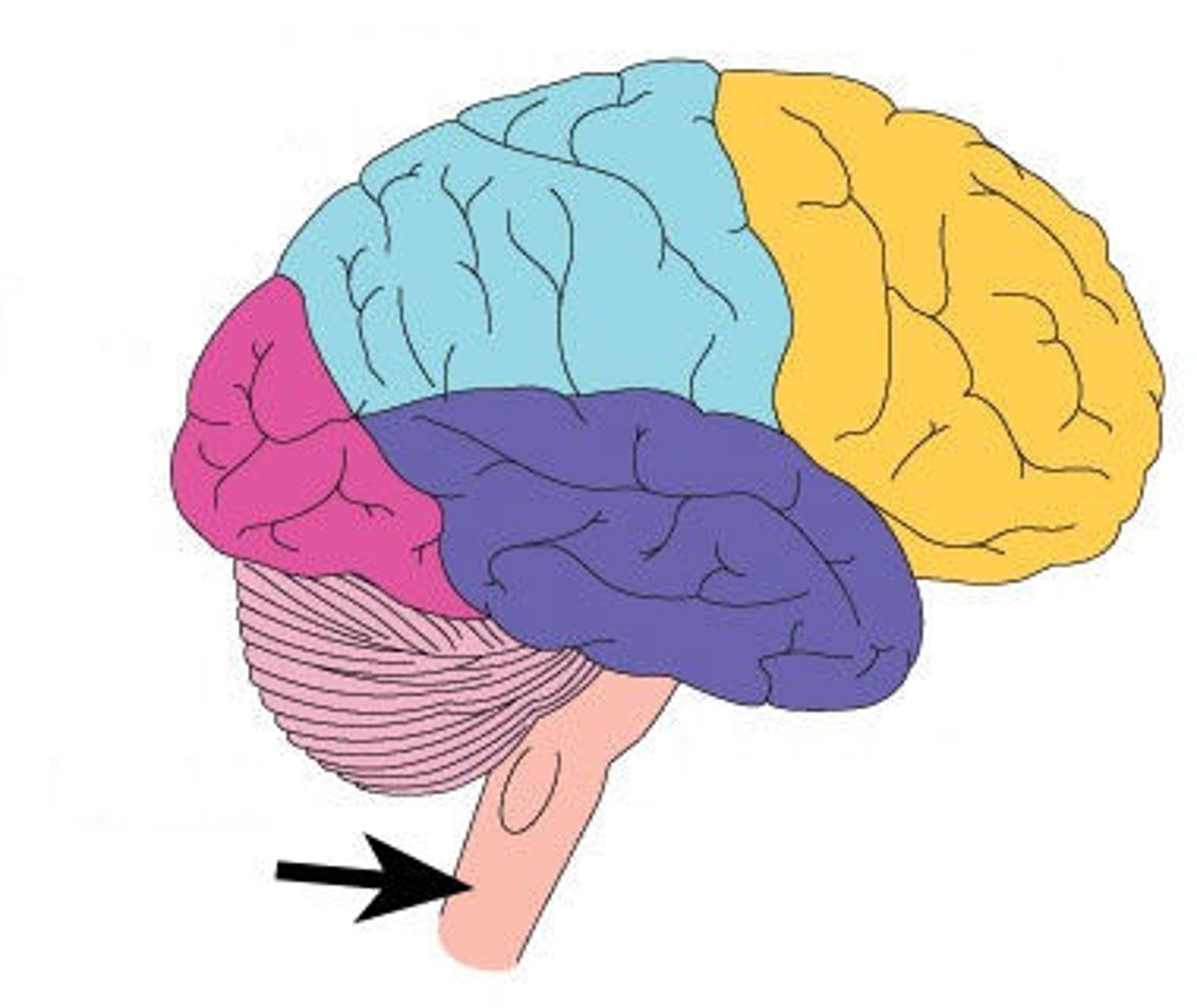
brain stem
continuous with the spinal cord and consists of the medulla oblongata, pons, and midbrain
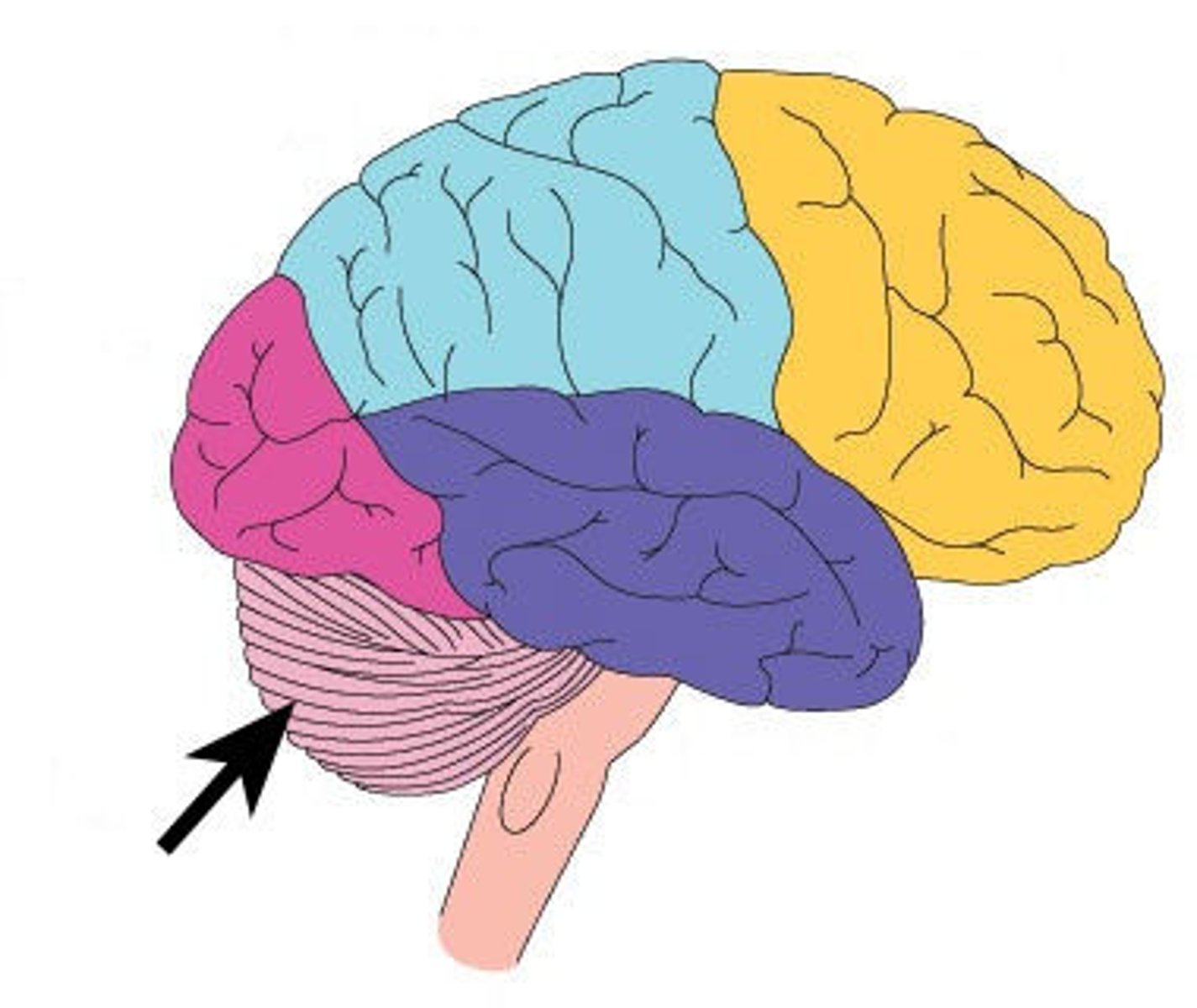
Cerebellum
posterior part of the brain that coordinates muscle movements and maintains balance
Cerebrum (telencephalon)
supported on diencephalon and brain stem
2 important anatomical structures that protect the brain
cranium & meninges
cranium
bony part of brain
meninges
fibrous tissue
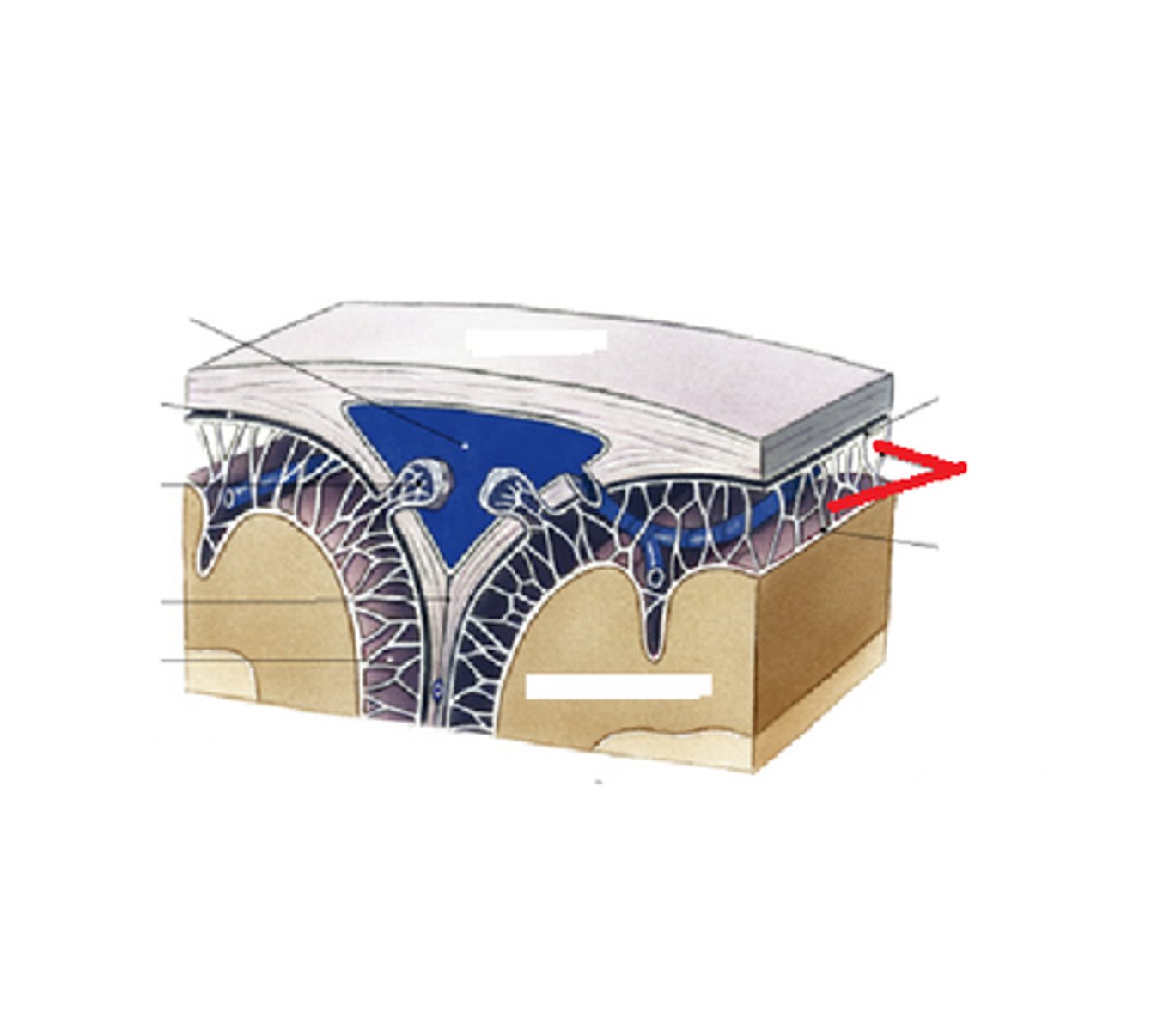
3 layers make up the meninges
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
dura mater
outer periosteal layer & inner meninges layer
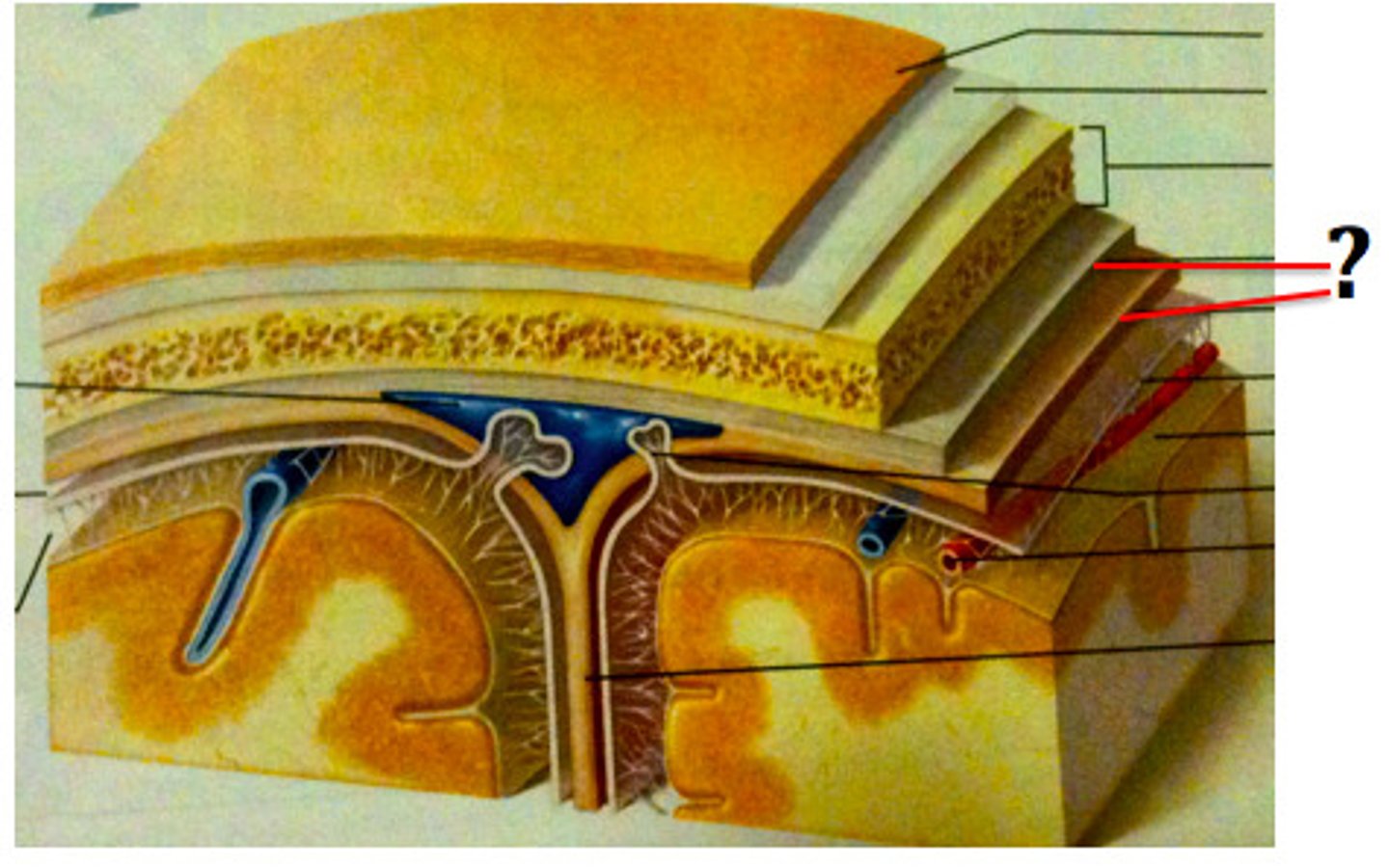
periosteal and meningeal
two layers of dura mater

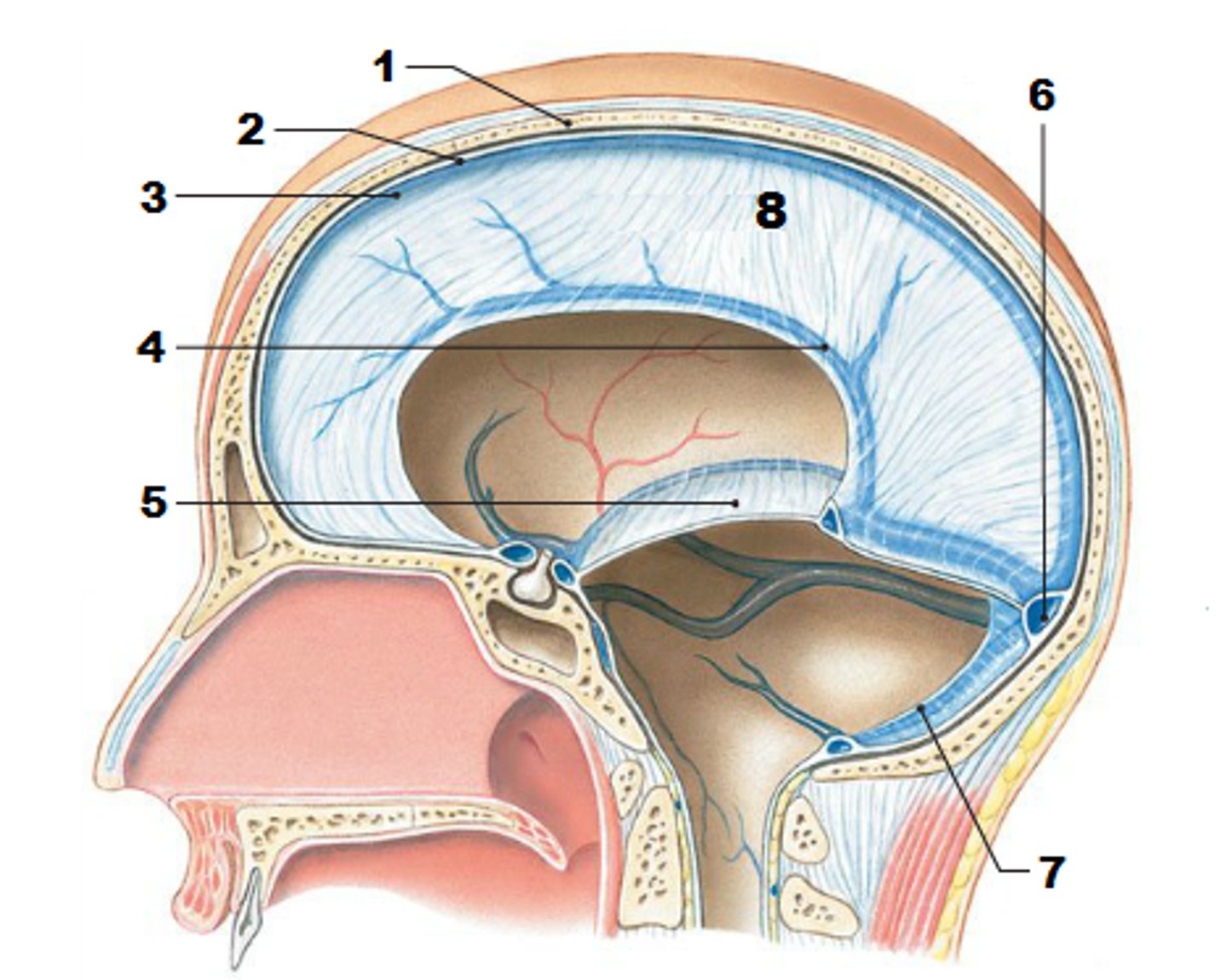
falx celebri
large, sickle-shaped, separates the cerebral hemispheres
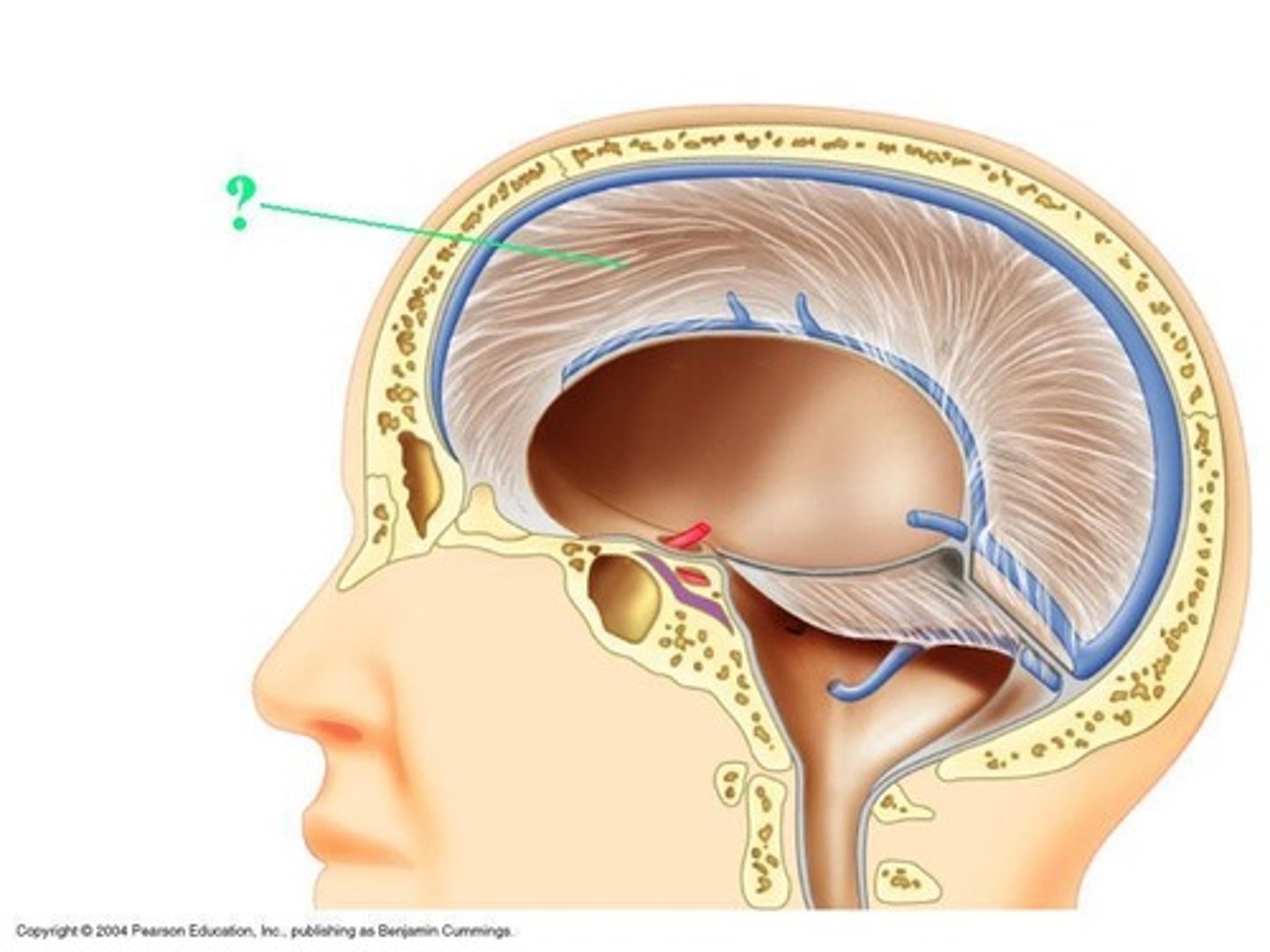
tentorium cerebelli
2nd largest, crescent-shaped, separates cerebrum (occipital lobes) from cerebellum (arrow #5)
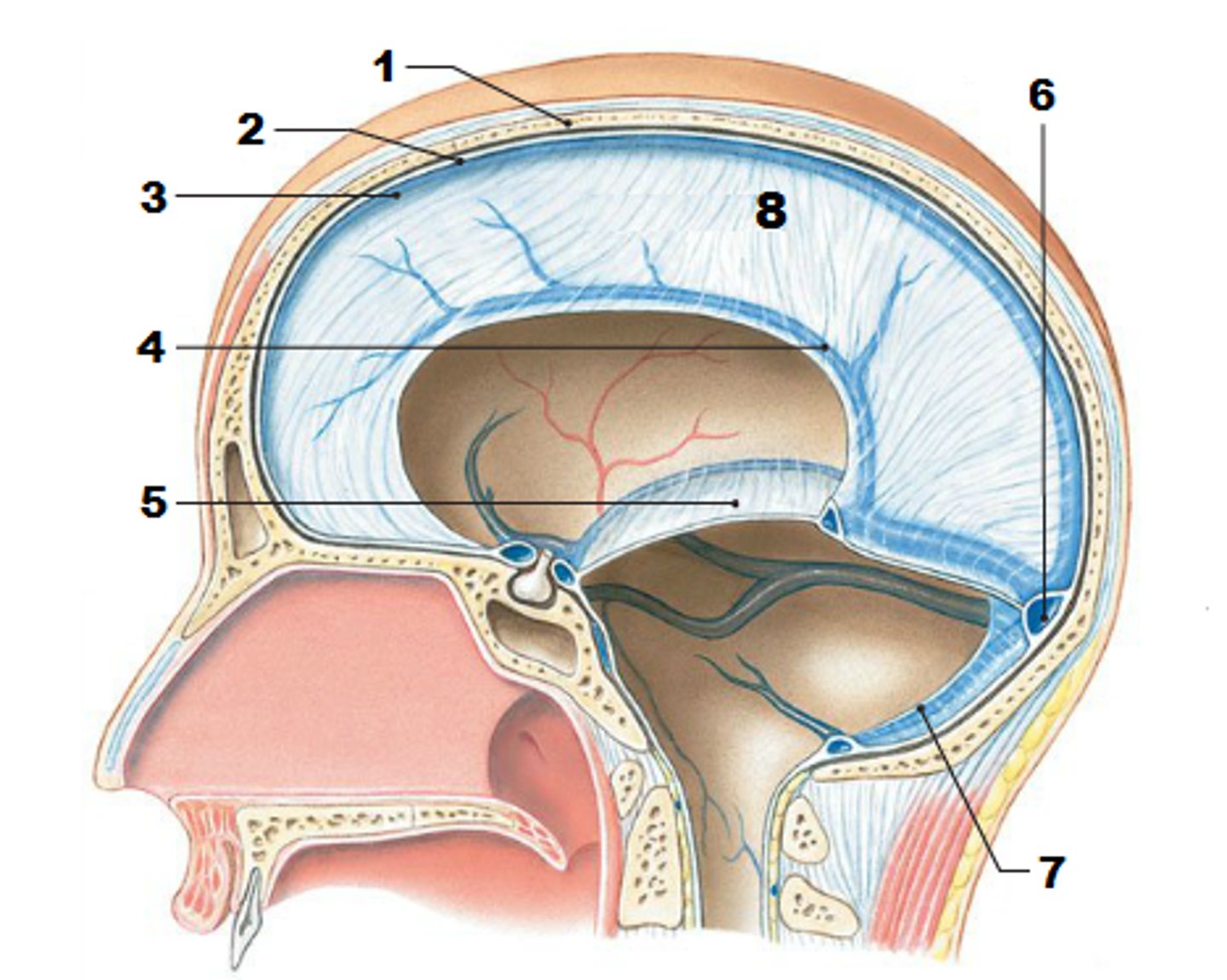
falx cerebelli
seperates the two hemispheres of the cerebellum. it lies inferior to the tentorium cerebelli, separating cerebellar hemispheres (arrow #7)
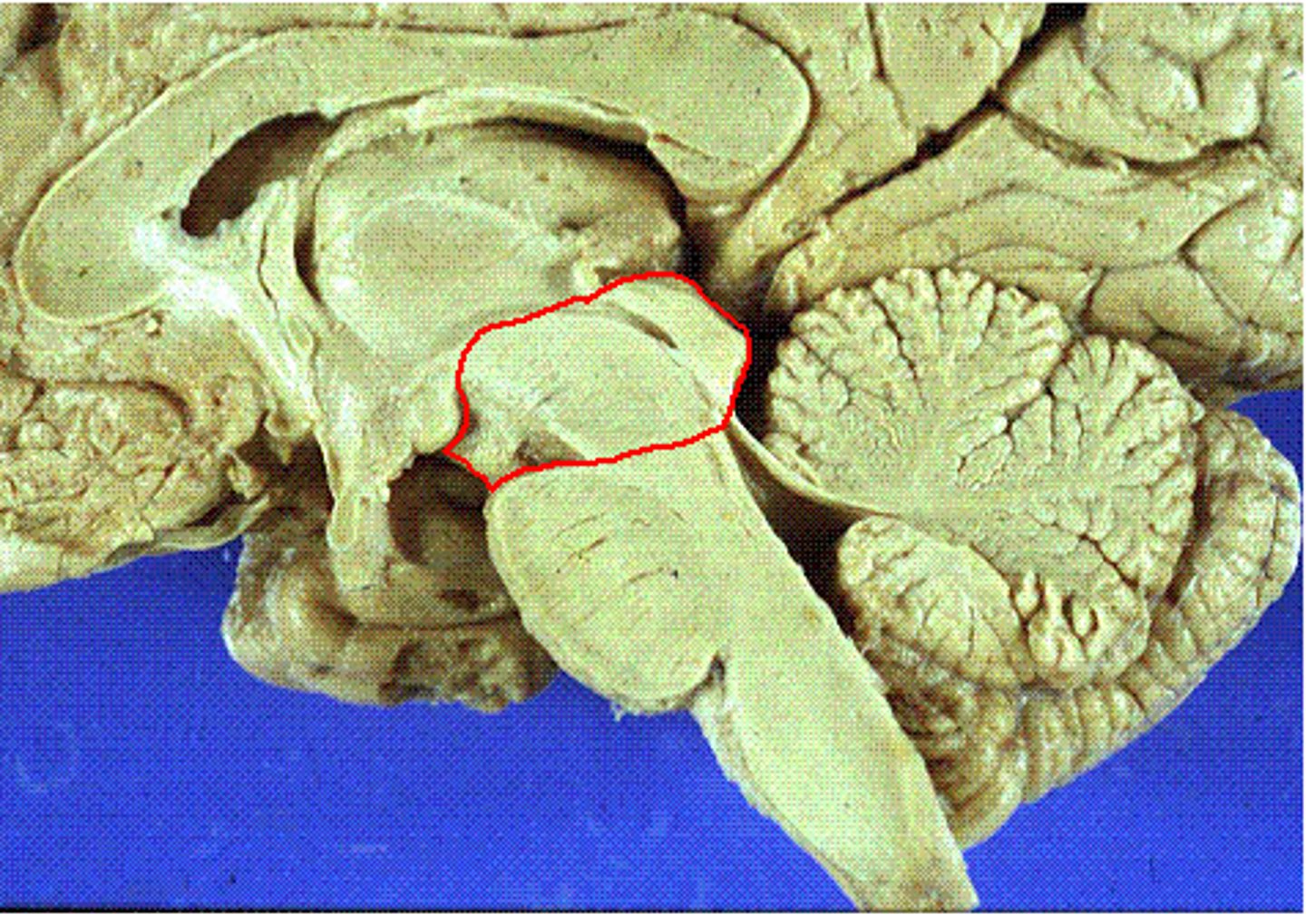
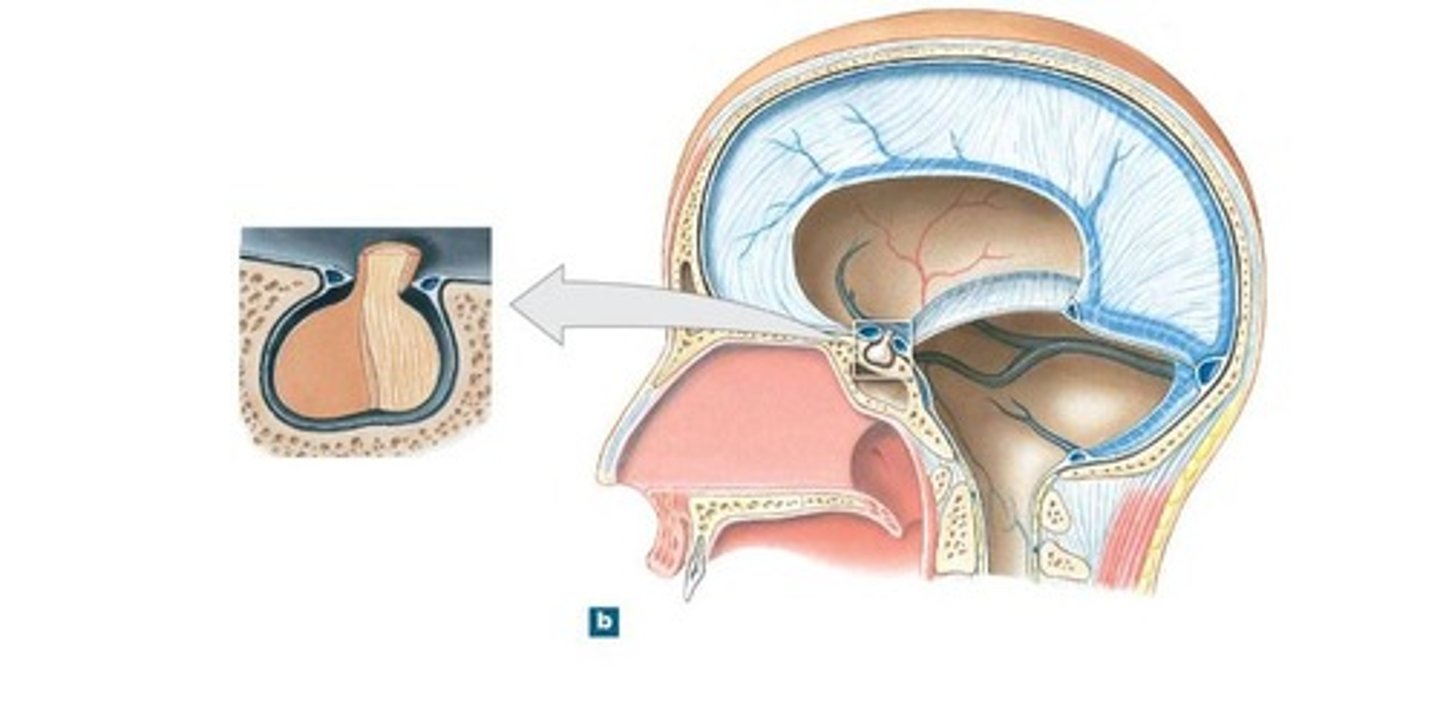
diaphragm sellae
smallest infolding covering pituitary gland & sella turcica
arachnoid
middle layer of meninges; weblike appearance that attaches it to deepest layer
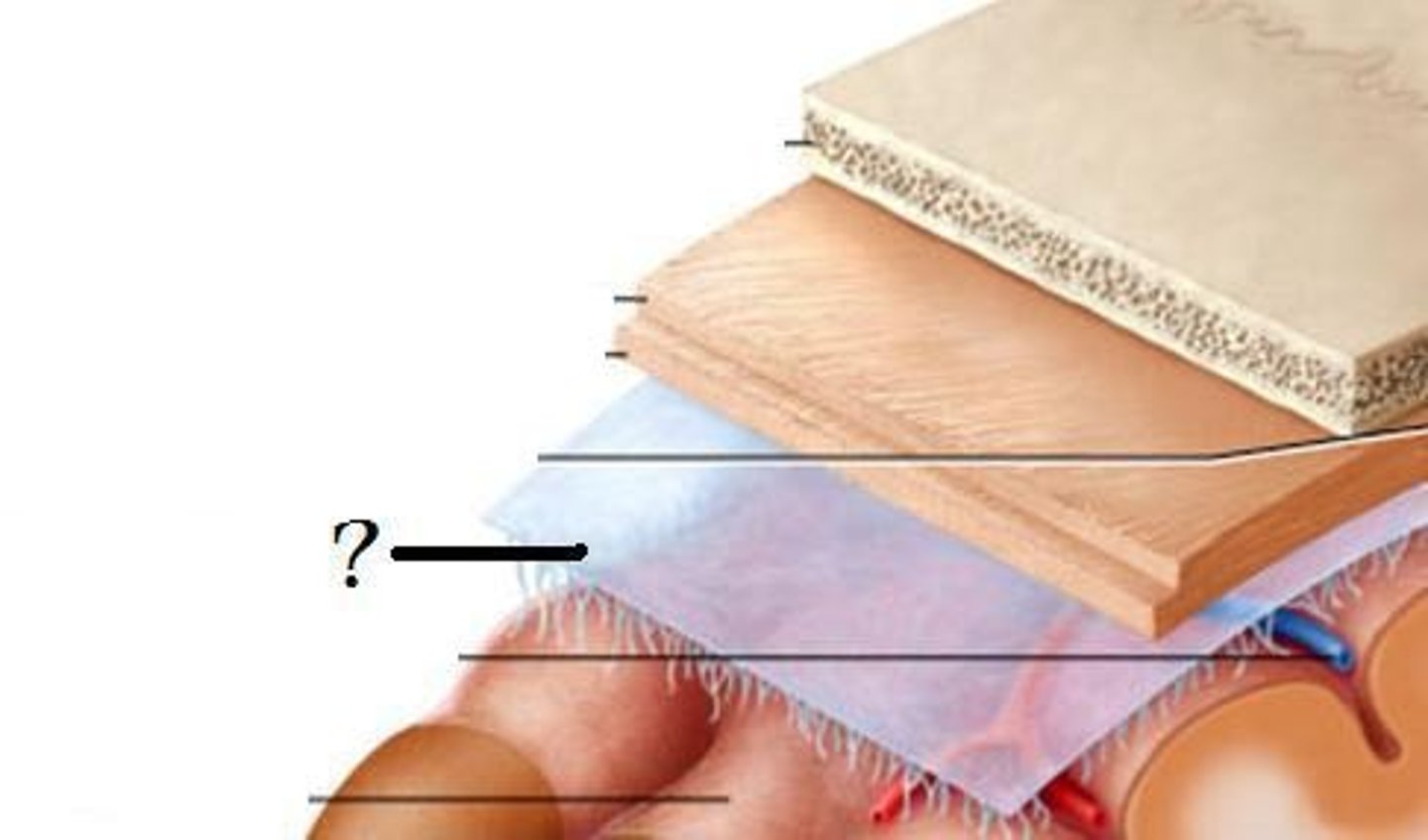
arachnoid trabeculae
filaments between the arachnoid and pia mater within the subarachnoid space
superior sagittal sinus
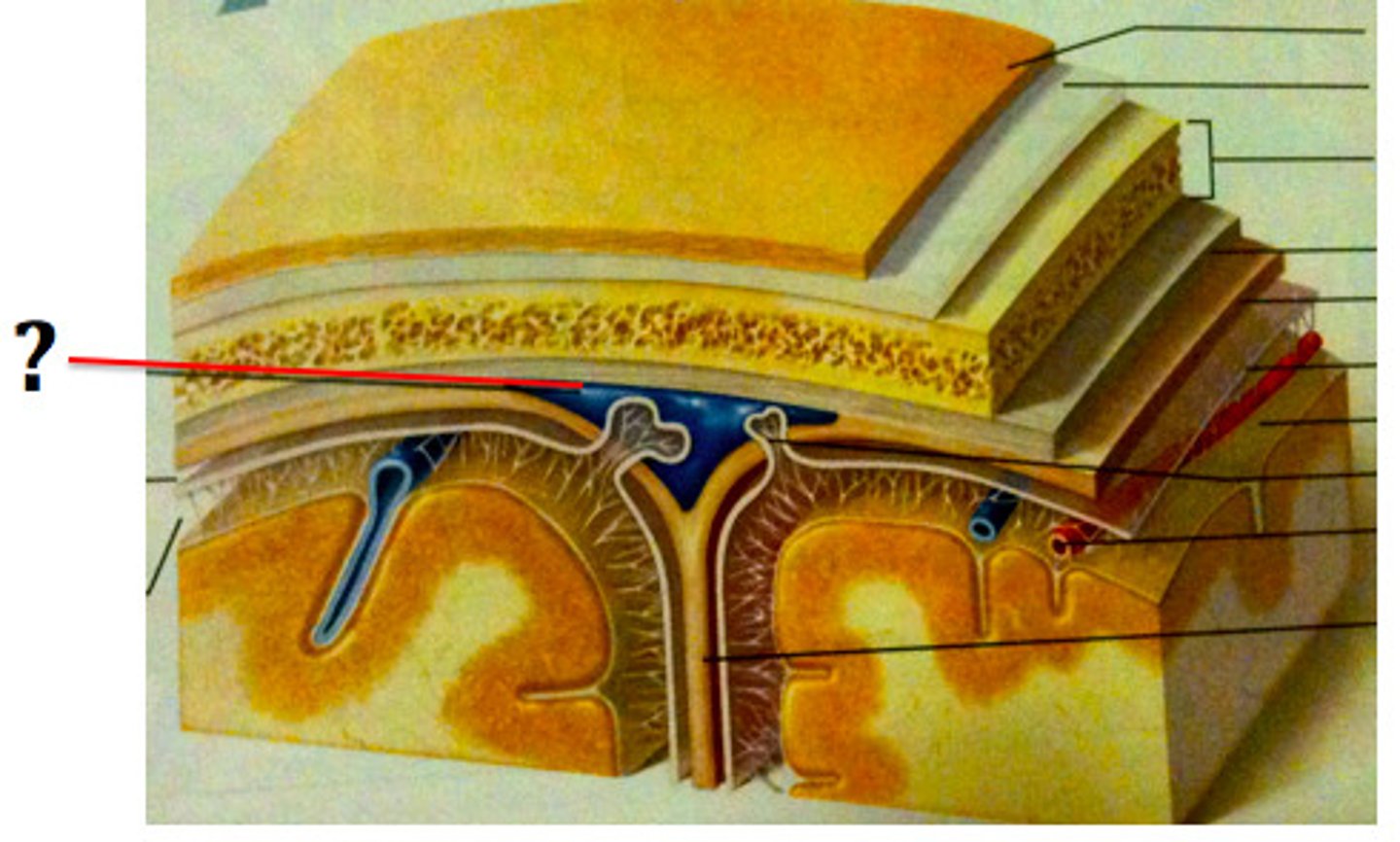
subdural space
space between dura mater and arachnoid mater
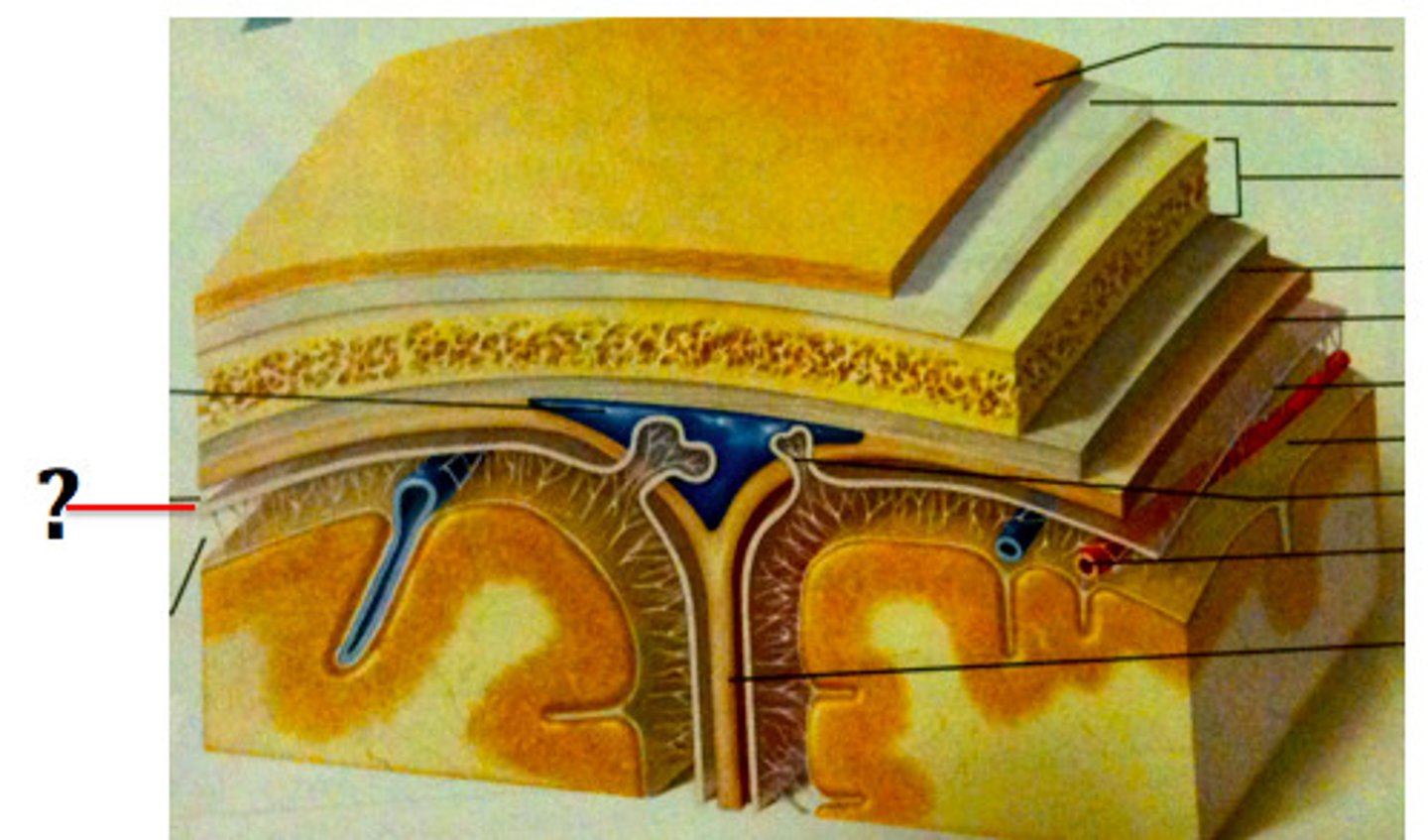

subarachnoid space
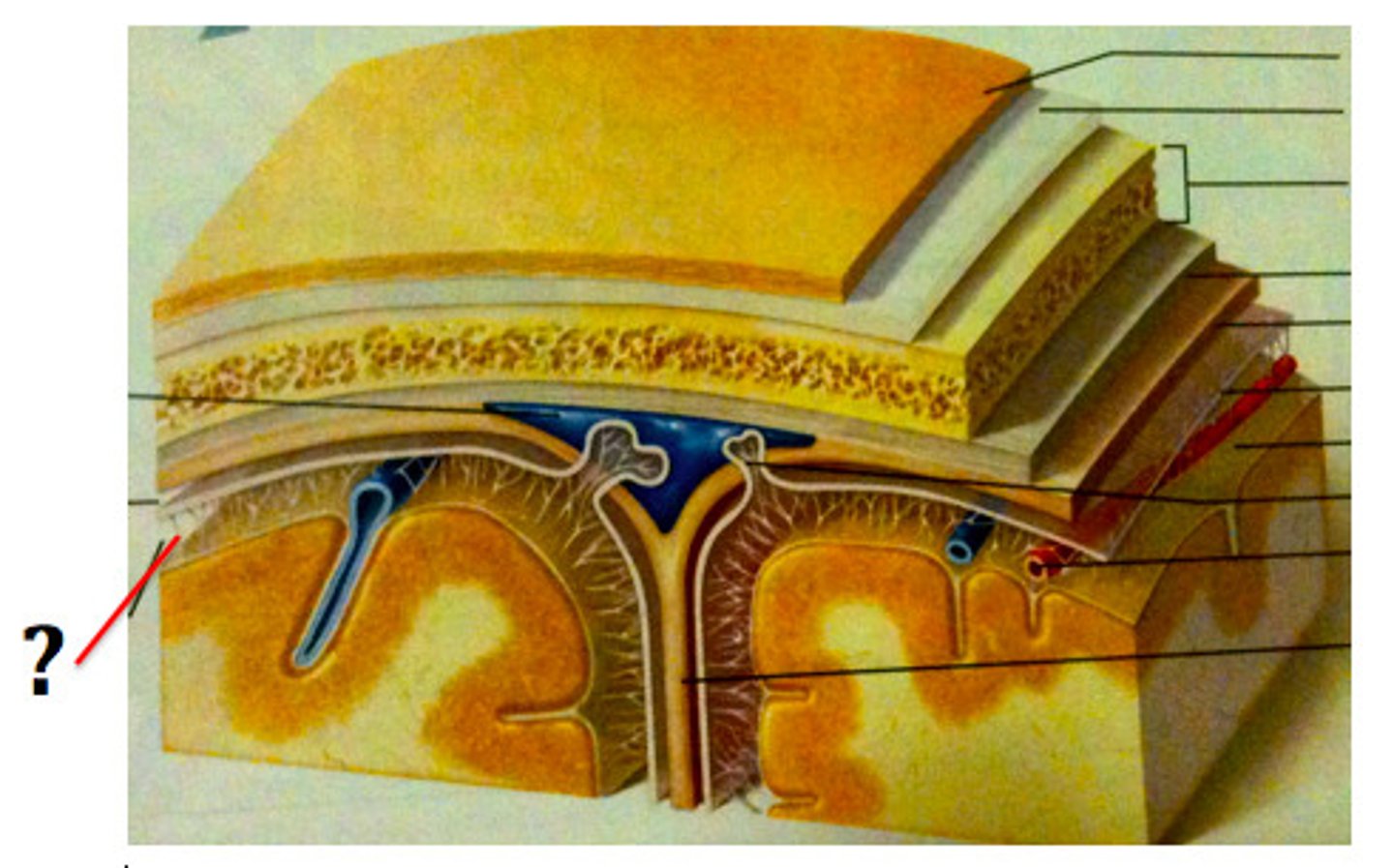
skin of scalp
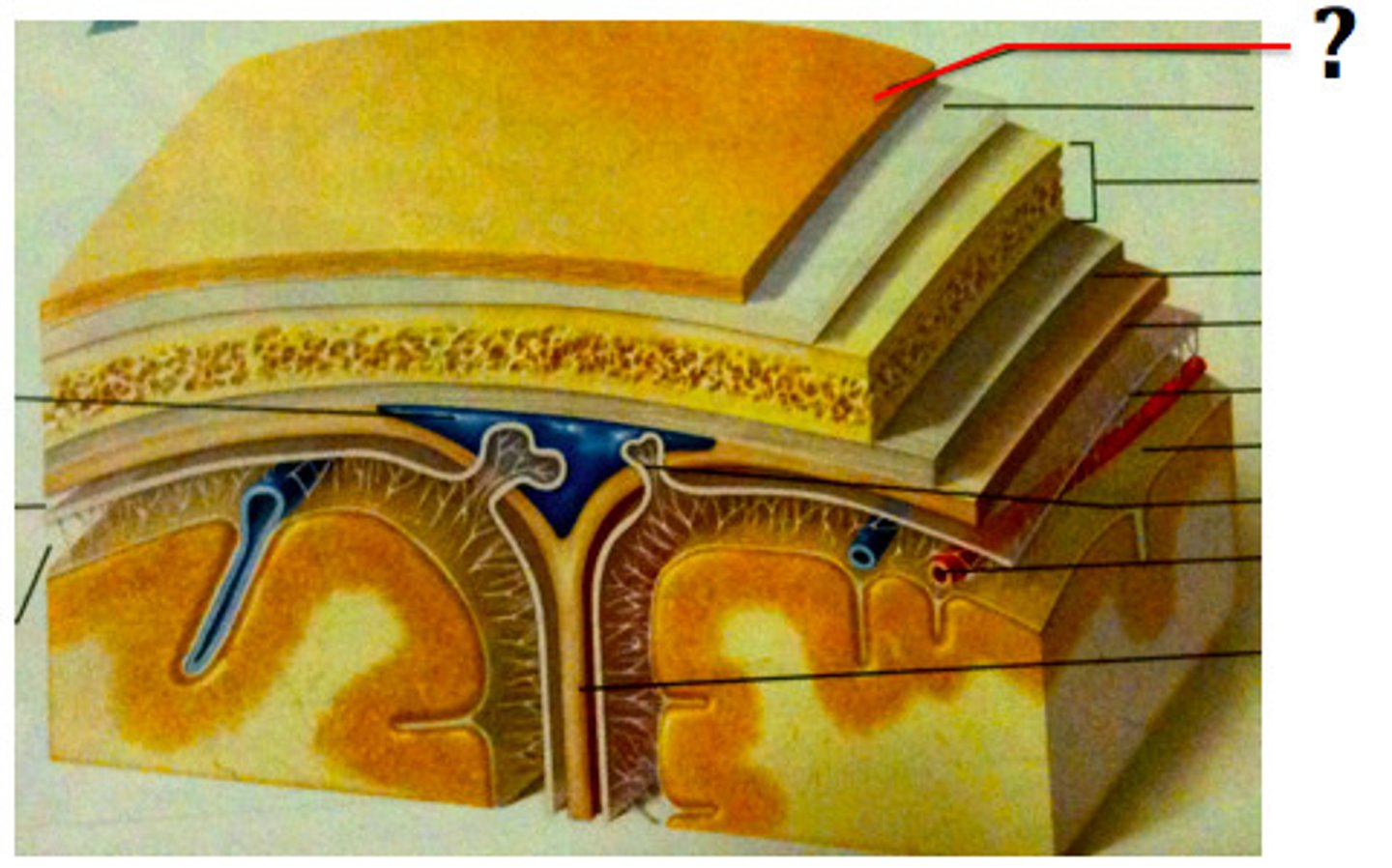
arachnoid mater
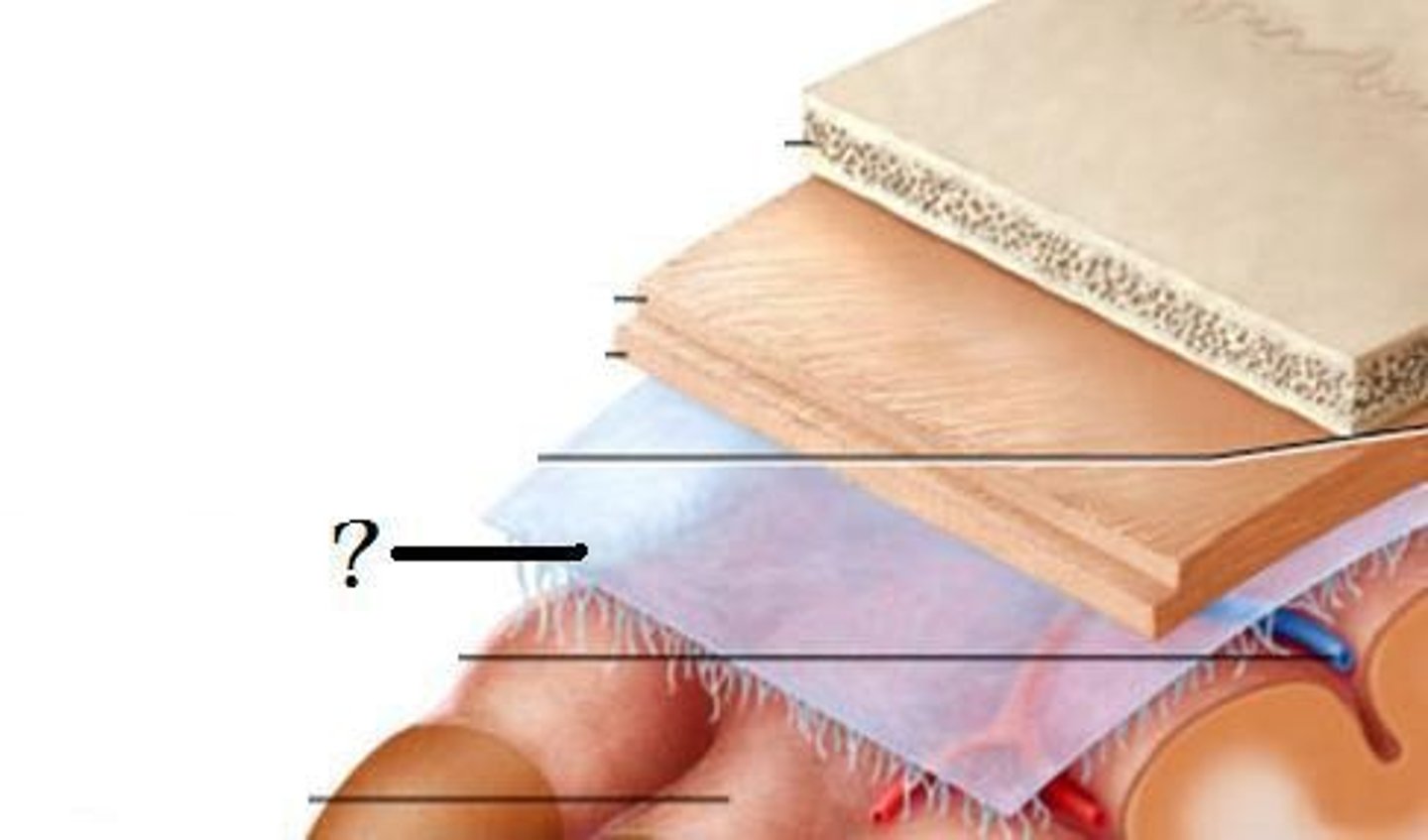
pia mater
the delicate innermost membrane enveloping the brain and spinal cord.
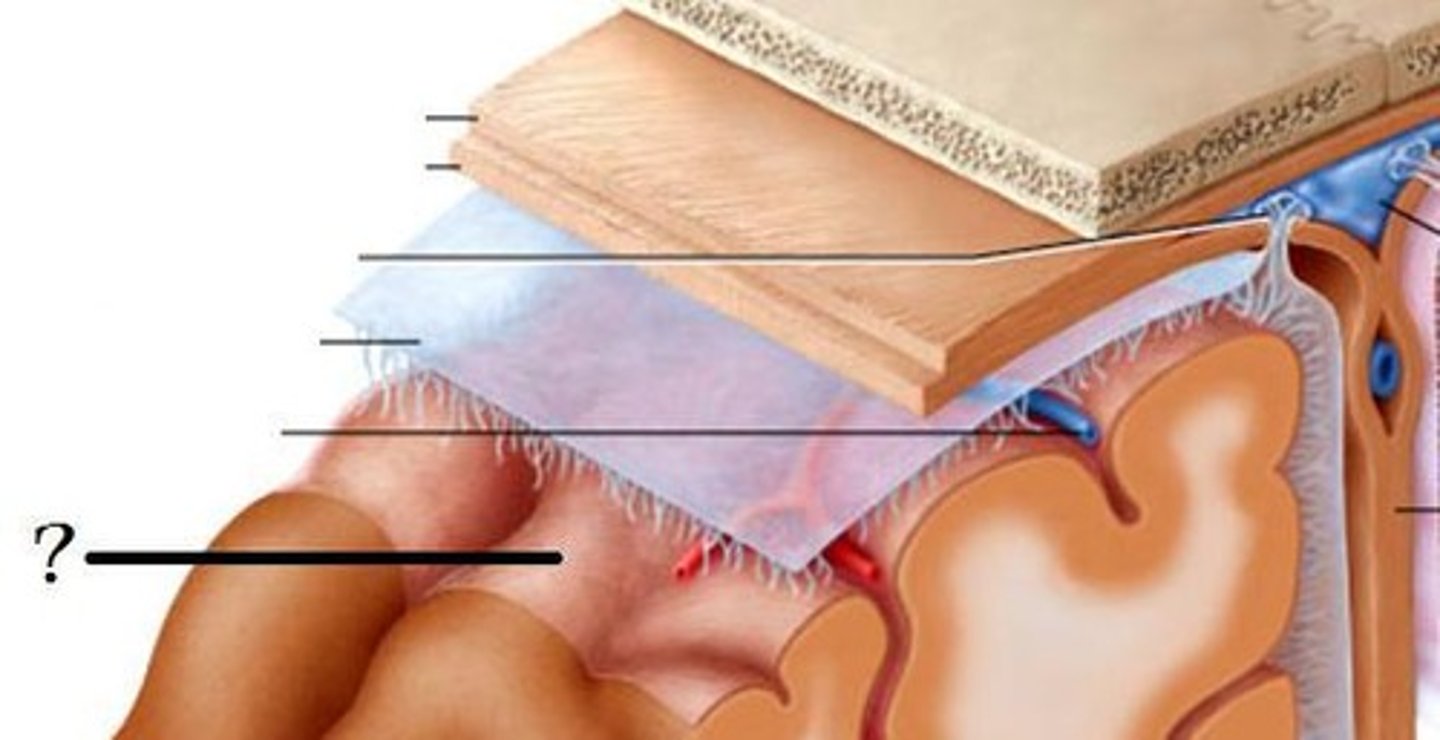
leptomeninges
The pia mater and arachnoid together
blood-brain barrier
complex system that separates the circulating blood from ECF of the brain. It is essential to prevent harmful substances from reaching the brain
Cerebral Spinal Fluid (CSF)
clear, colourless fluid that circulates within the brain and spinal cord, serving several important functions in the CNS
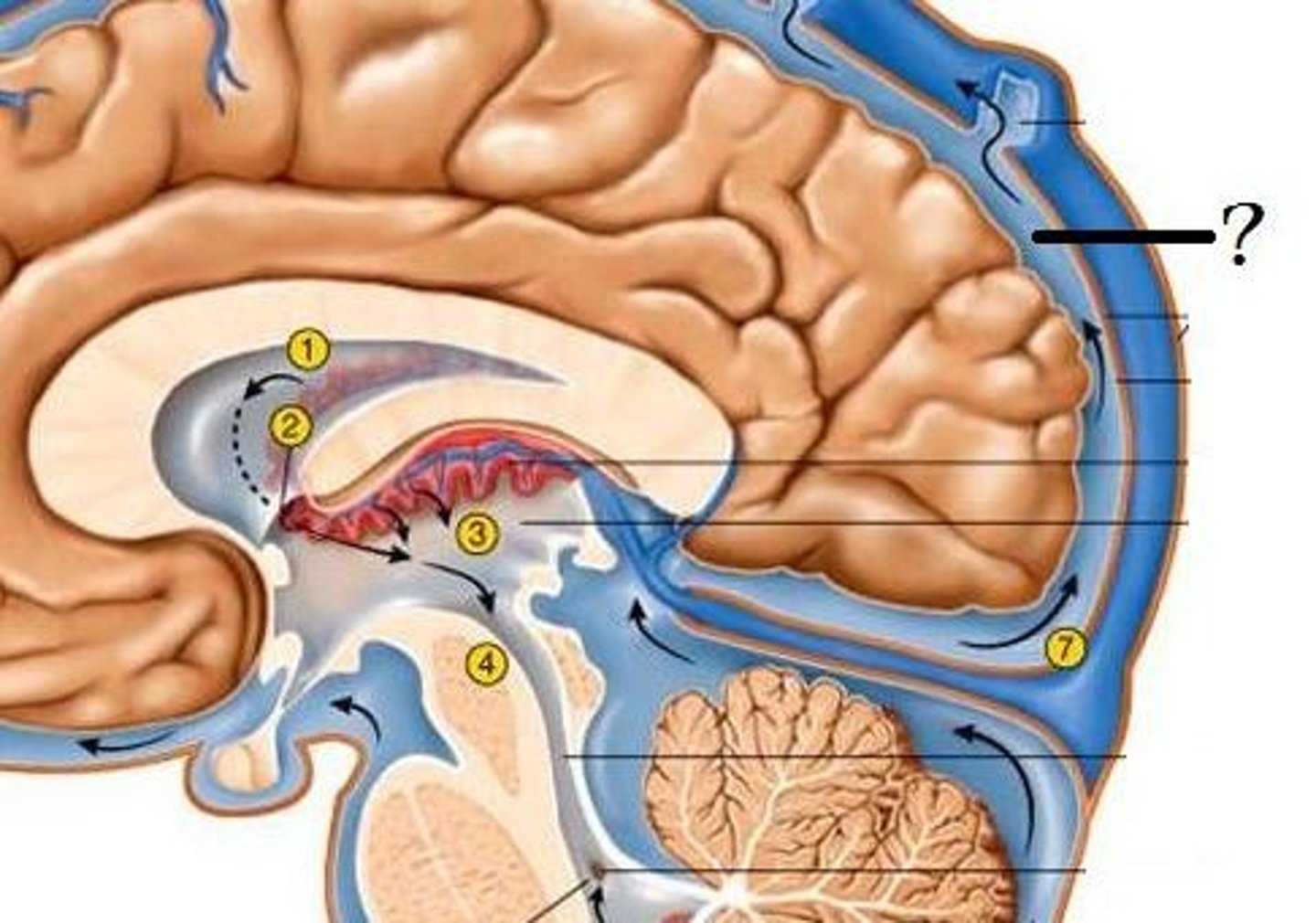
Circulation of CSF
CSF from the lateral ventricles → interventricular foramina → third ventricle → cerebral aqueduct → fourth ventricle → subarachnoid space or central canal.
mechanical protection of CSF
functions as shock-absorbing medium protecting brain and spina cord
chemical protection in CSF
provides optimal ionic composition for neural signalling
circulation in CSF
helps in exchange of nutrients and waste products between the blood and adjacent nervous tissue
temperature regulation in CSF
helps in maintaining a stable temperature
brain stem
between spinal cord and diencephalon
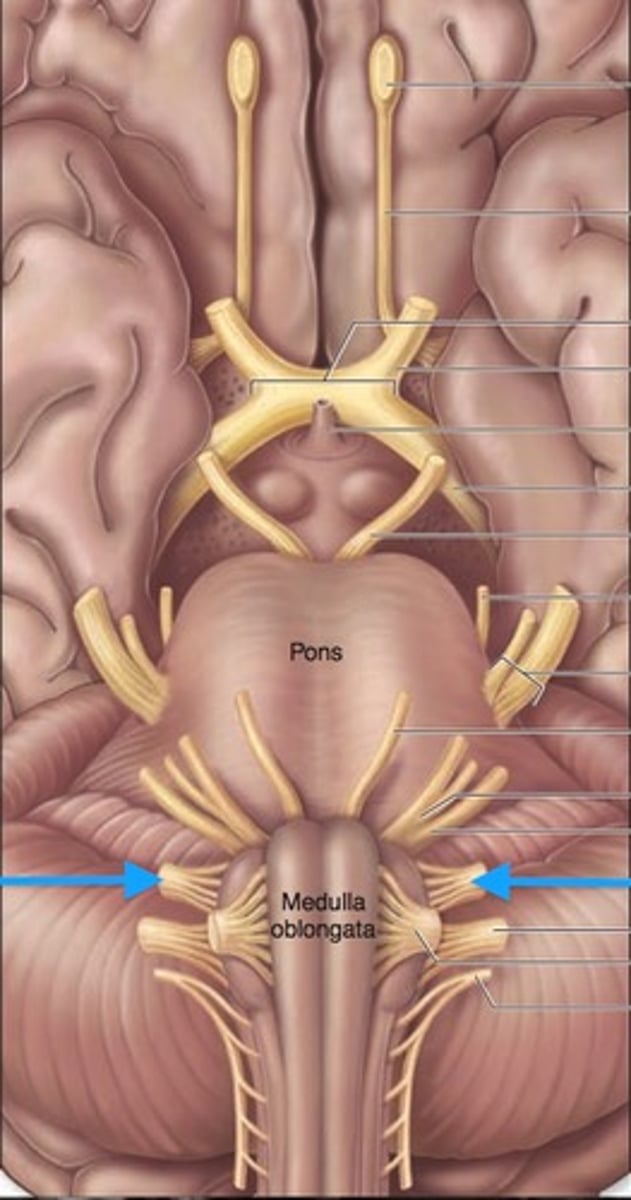
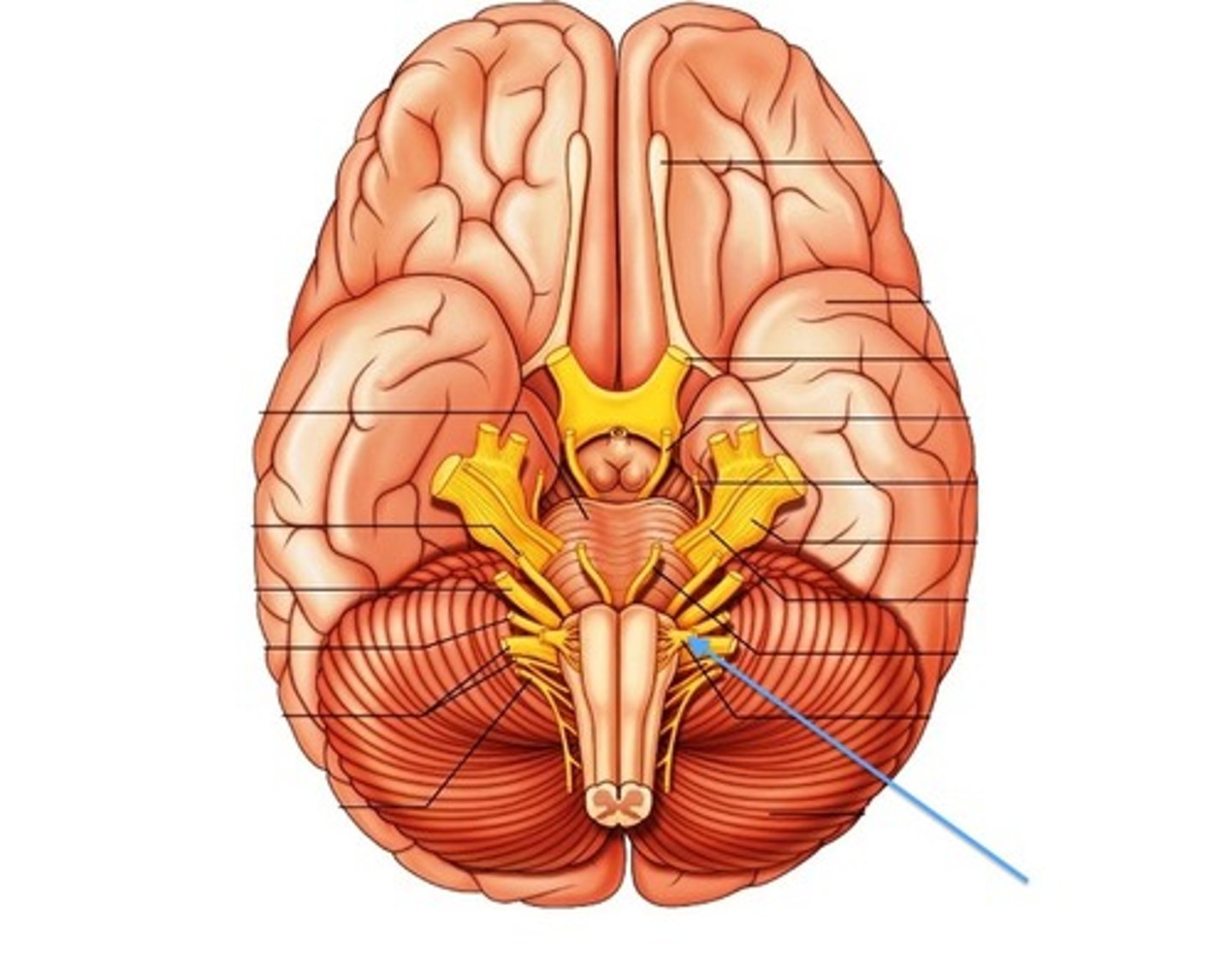
medulla oblongata
most inferior part of the brain stem; regulates breathing, heart rate, & blood pressure
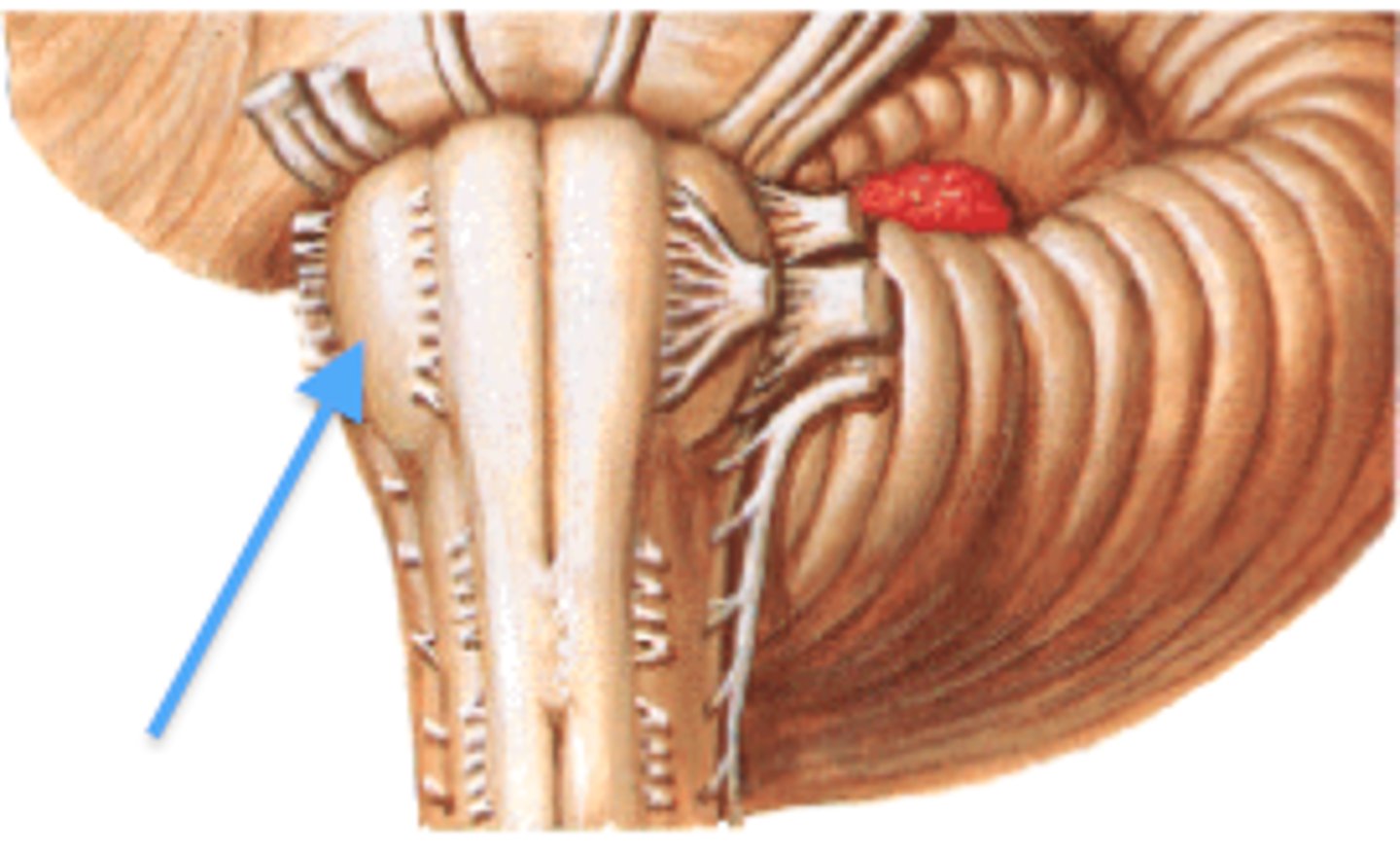
the 'olives'
oval-shaped structures located on the anterior surface of the medulla, lateral to the pyramids
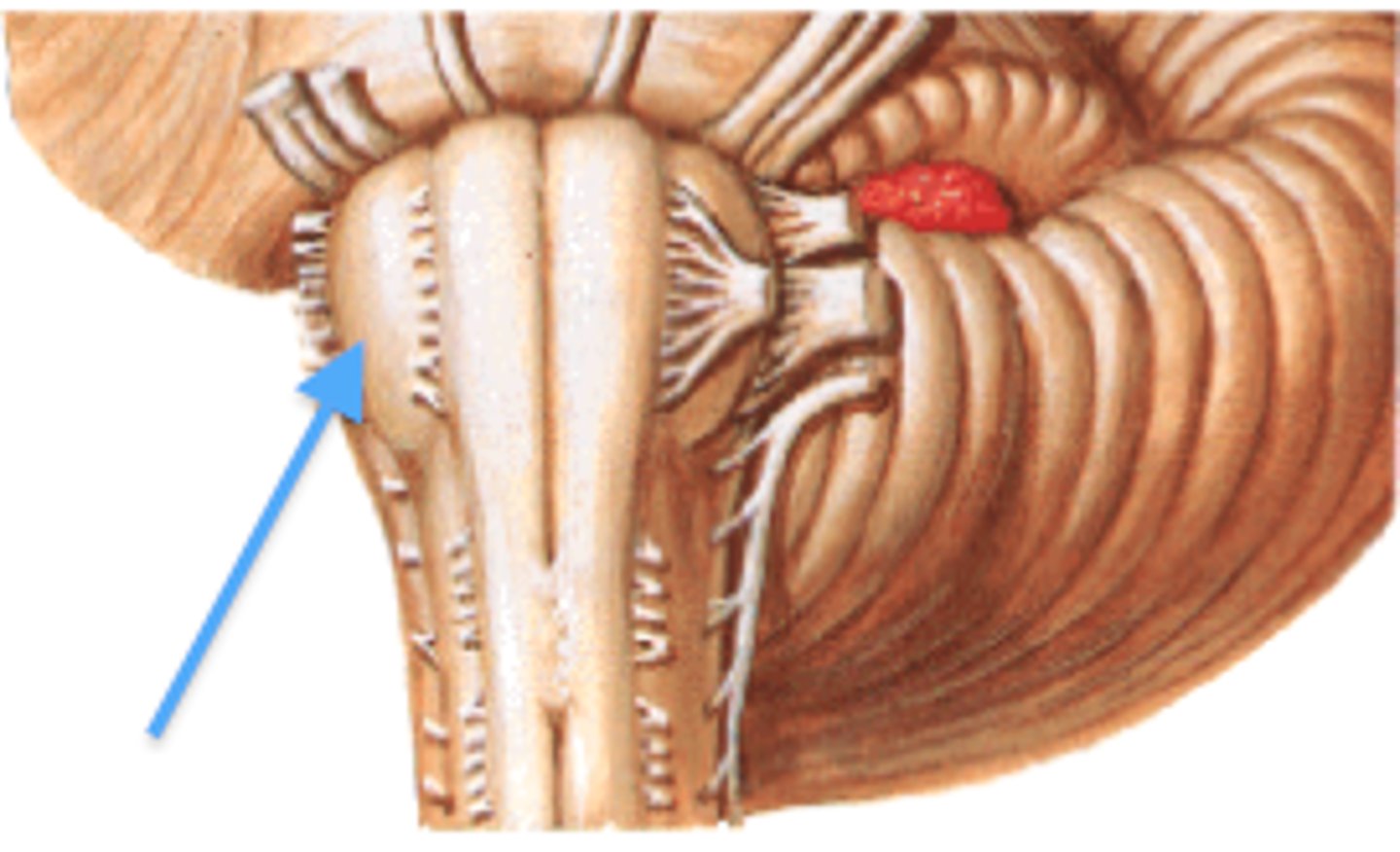
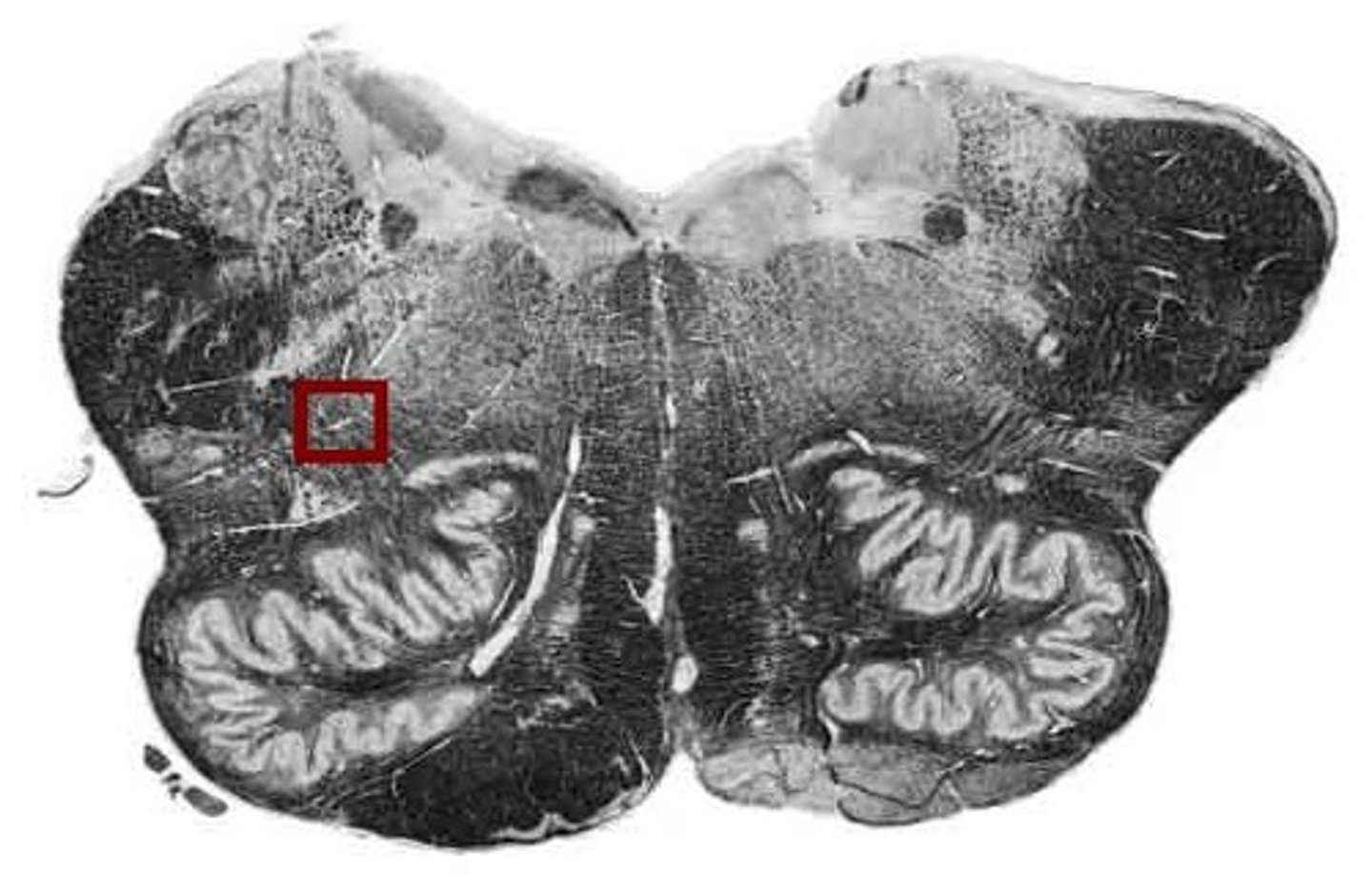
nucleus ambiguus
involved in swallowing (deglutition) & vocalization
dorsal/ventral respiratory group
regulates breathing
solitary nucleus
receives and processes sensory information from cardiovascular, respiratory, and gastrointestinal systems
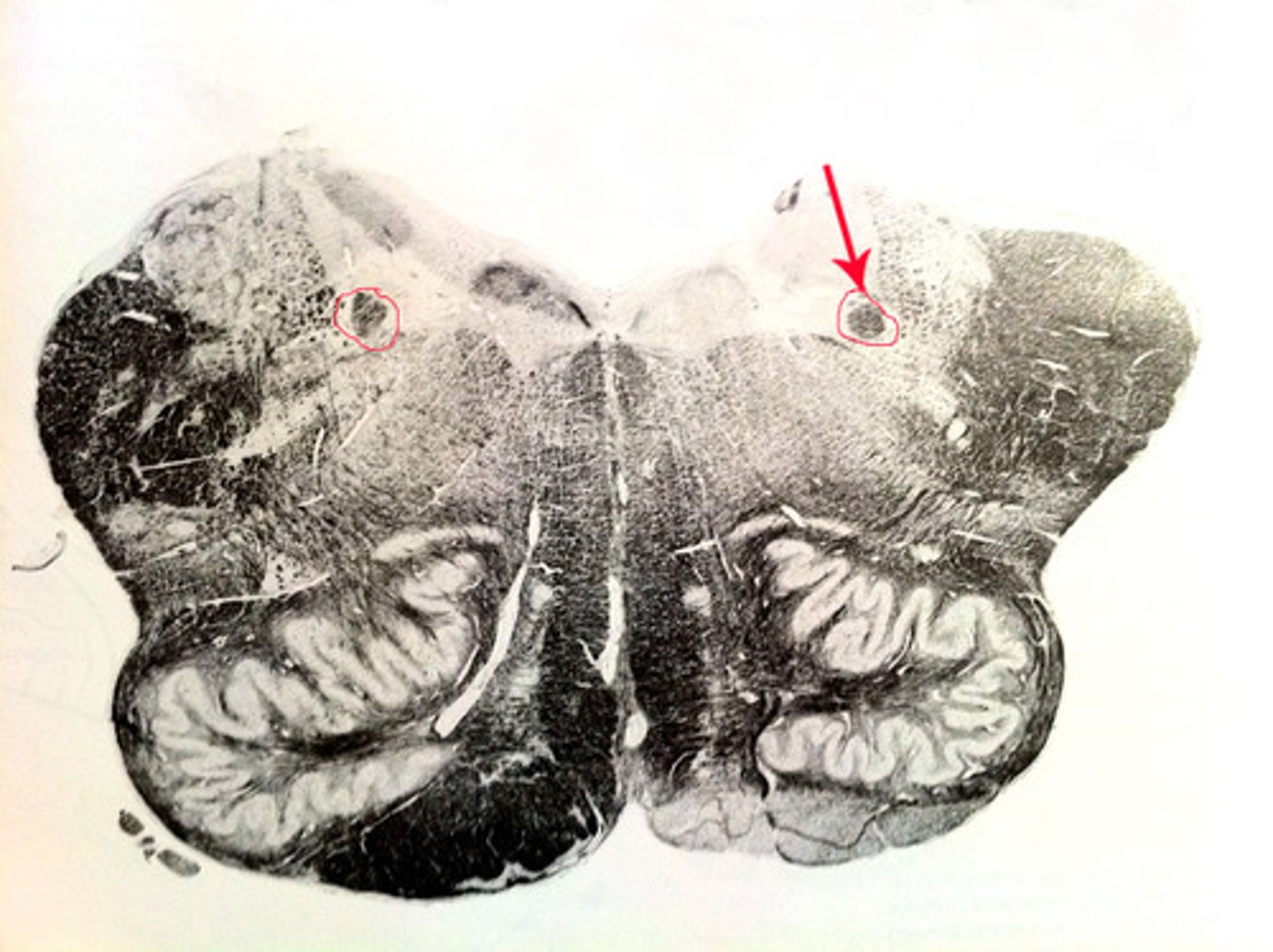
hypoglossal nucleus
controls movement of tongue and speech
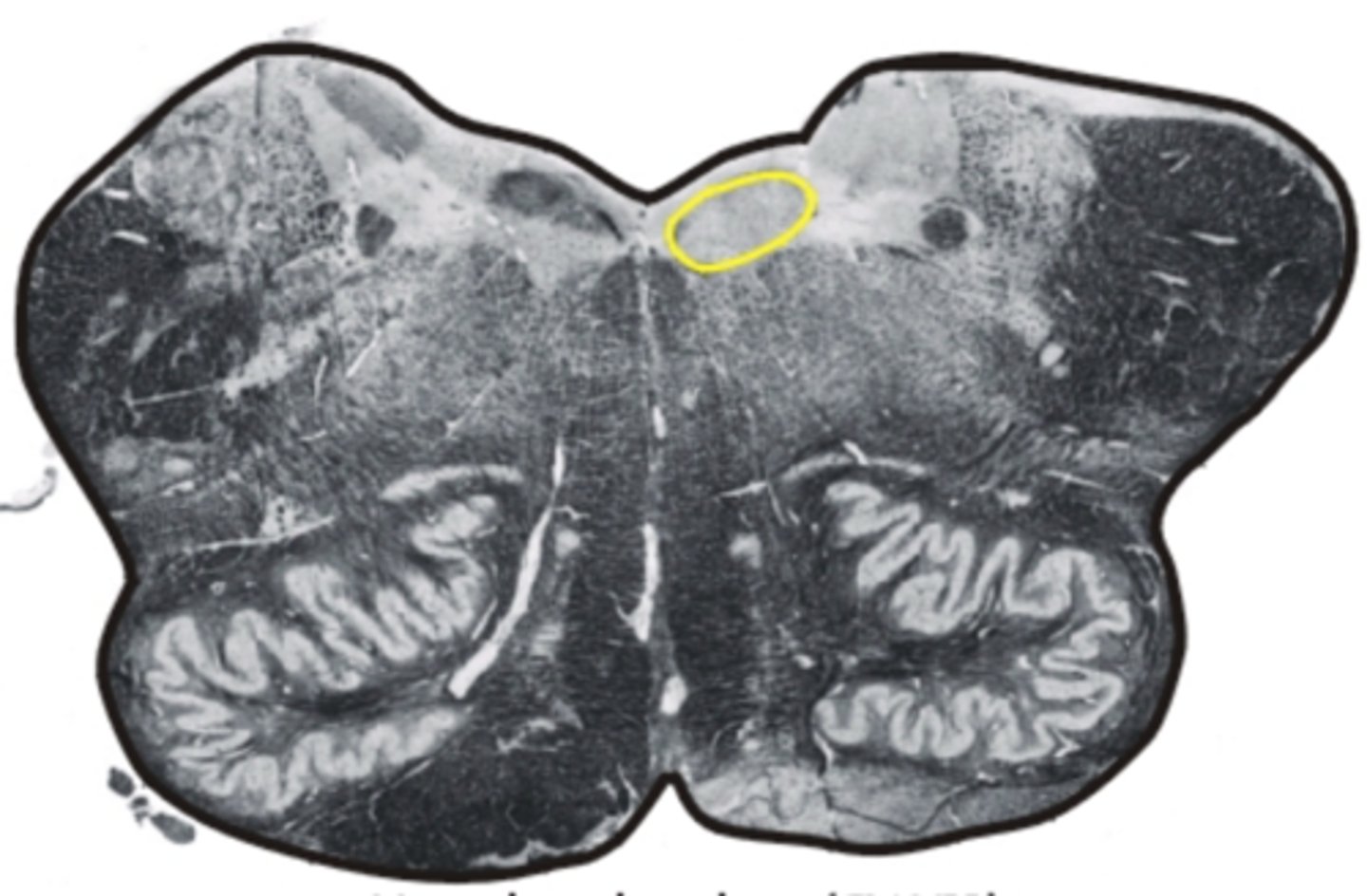
inferior olivary nucleus
associated with motor coordination & fine-tuning of movements
vestibulocochlear nerve
receives sensory input & sends motor output to cochlea of the inner ear for hearing
glossopharyngeal nerve
relays sensory & motor impulses related to taste, swallowing & deglutition
vagus nerves
processes input/output of pharynx, larynx & thoracic/abdominal viscera
accessory nerves
controls swallowing via vagus nerves
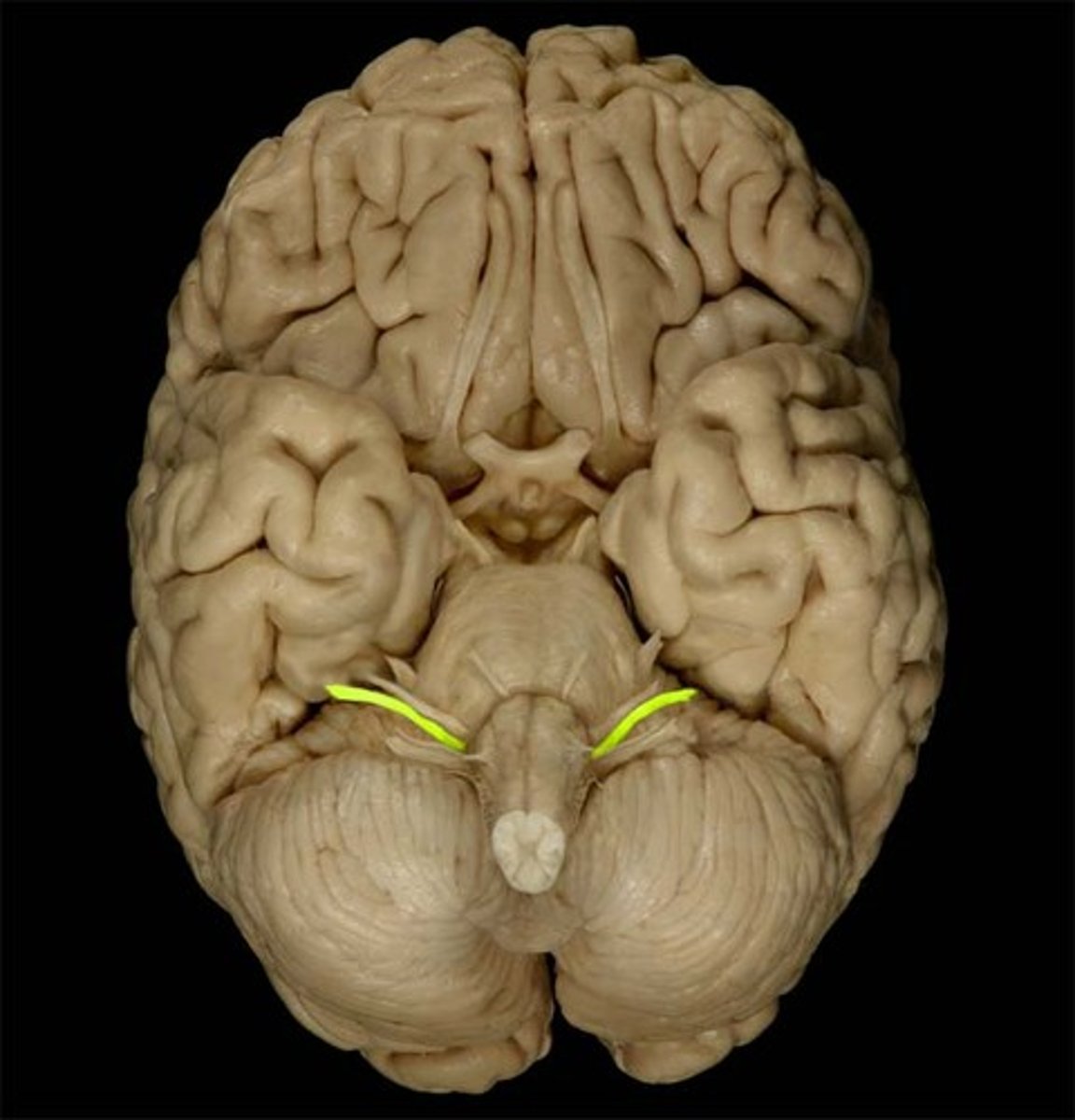
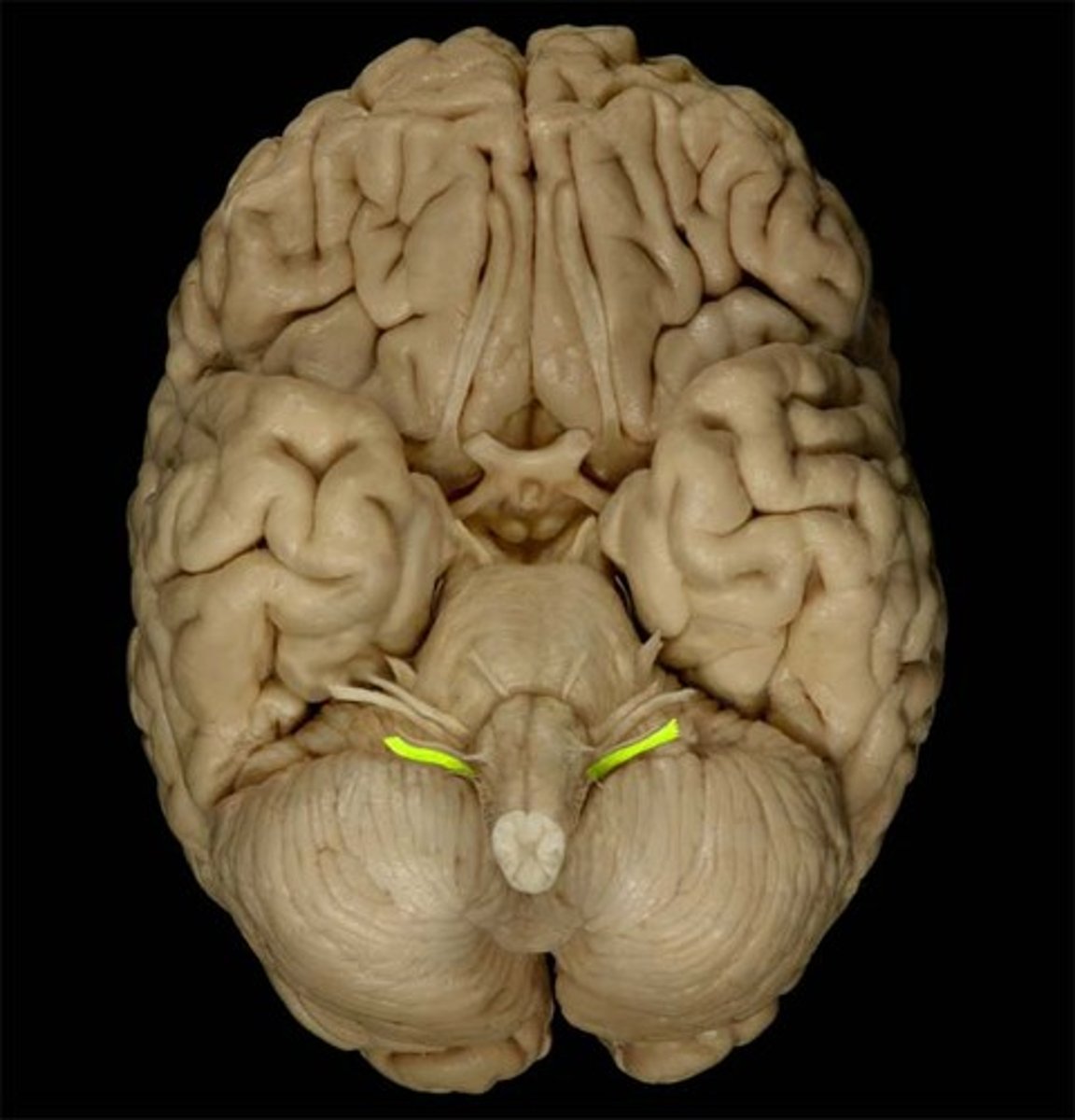
hypoglossal nerves
controls tongue movement; speech
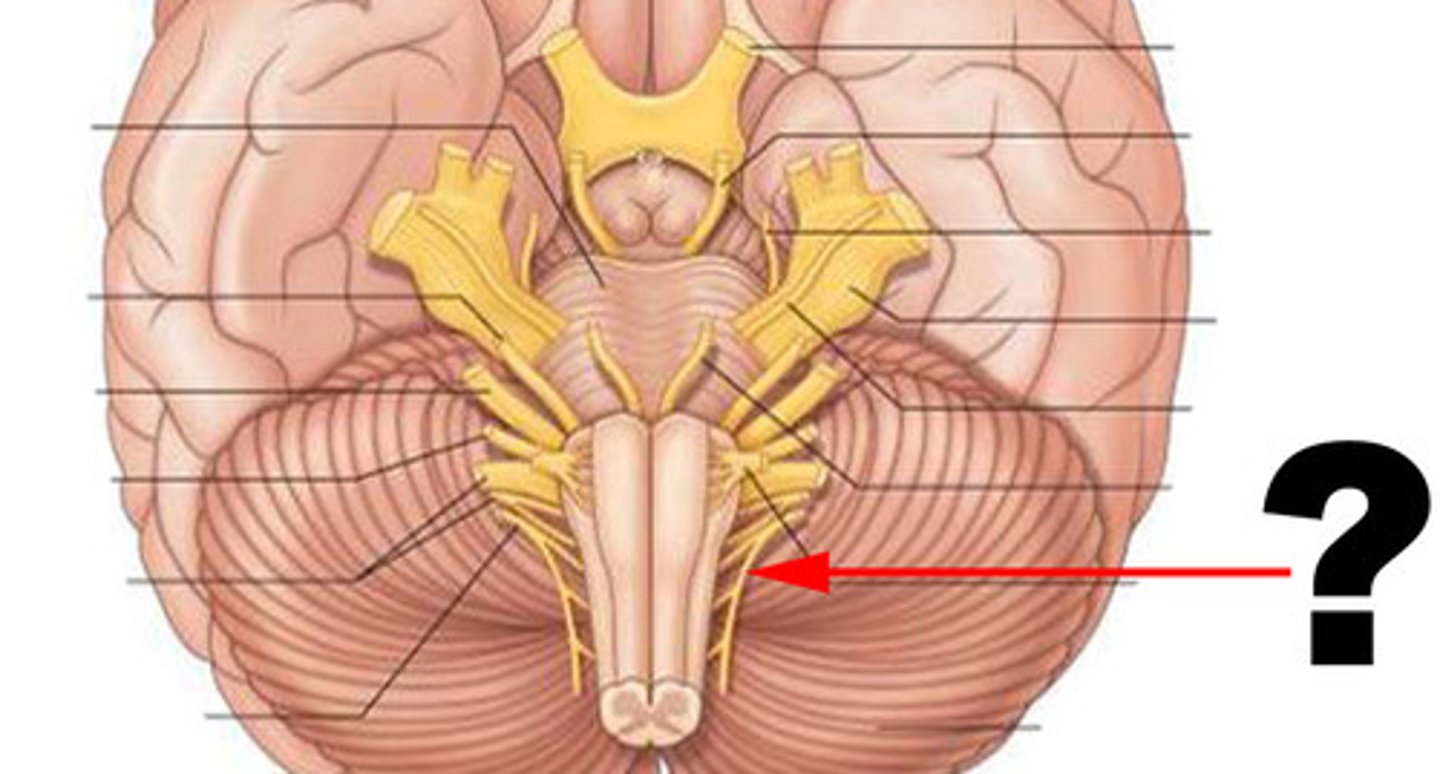
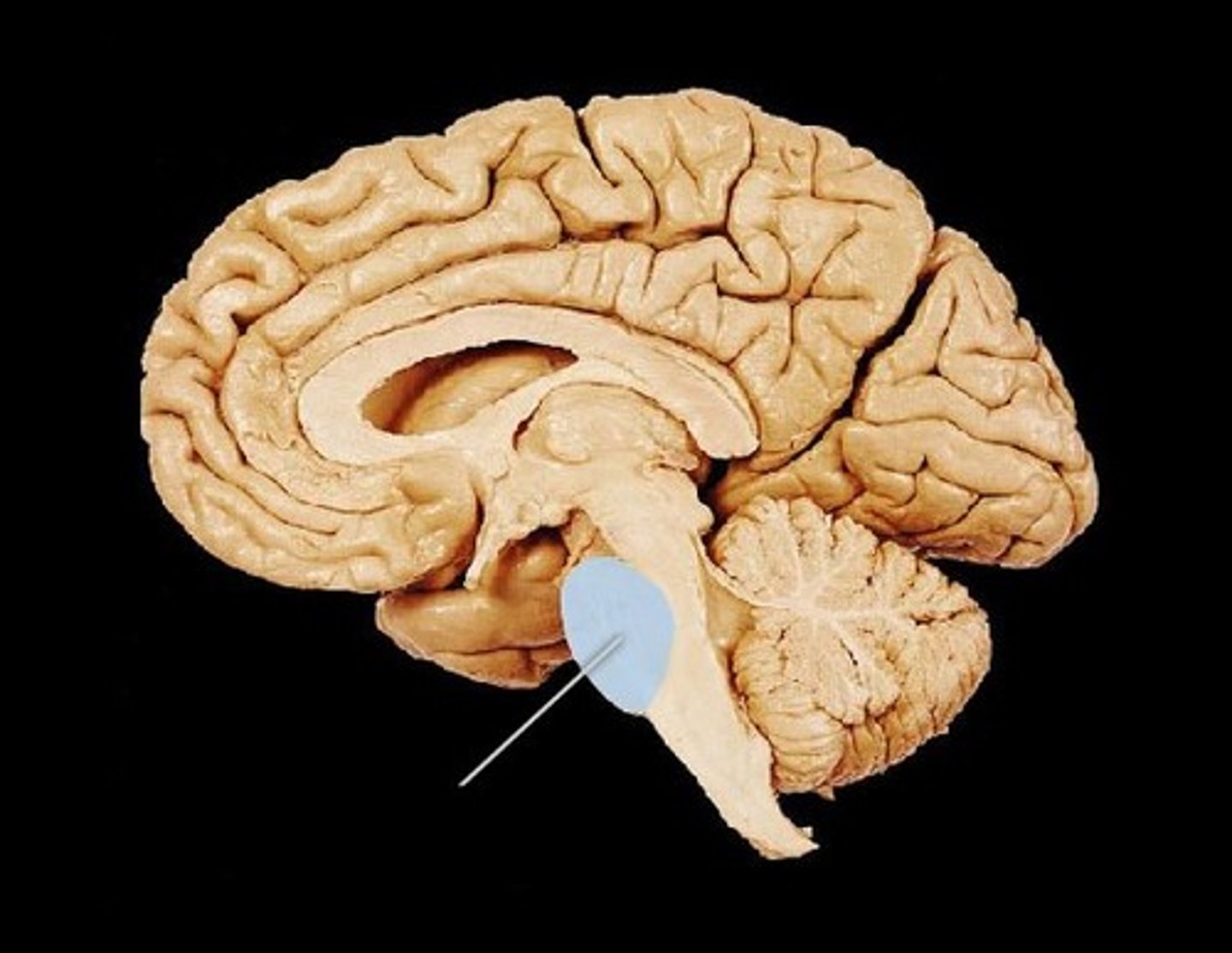
pons
center structure of the brain stem, located between the midbrain and the medulla oblongata
pontine nuclei
serves as relay striations between cerebral cortex & cerebellum in regards to motor coordination
trigeminal nerves
regulates sensory input from head & face, governs chewing
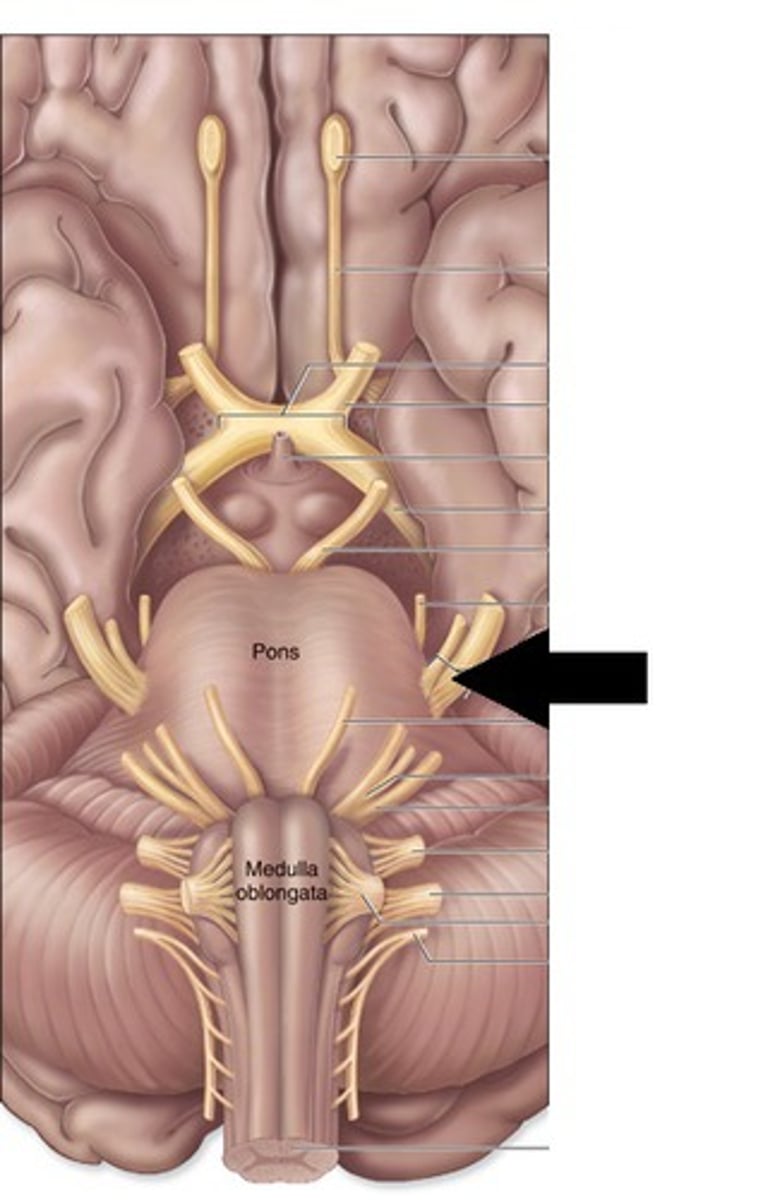
abducens nerves
controls eyeball movement, particularly abduction (outward gaze)
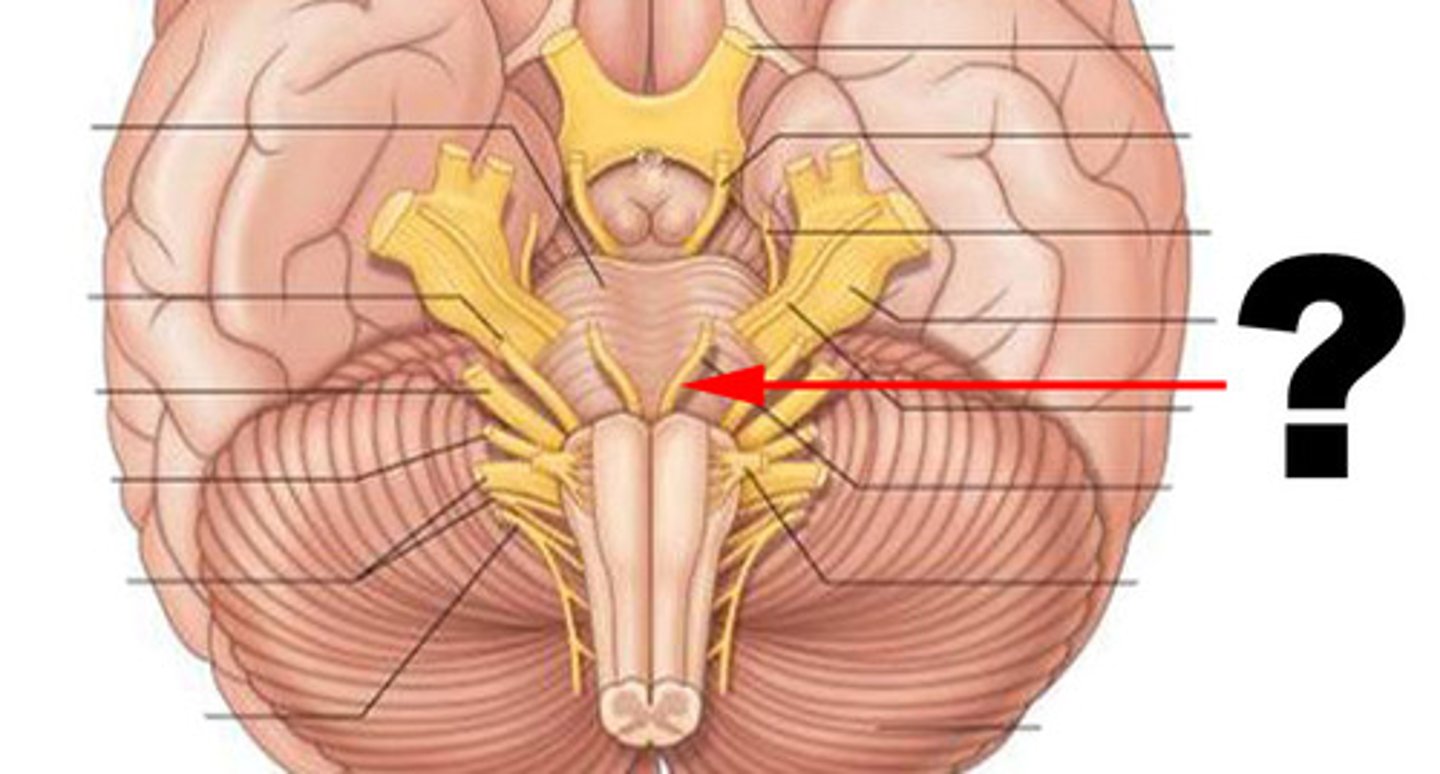
facial nerves
regulates facial movements, saliva, tears
vestibulocochlear nerves
the vestibular and cochlear nuclei in the pons are involved in balancing and hearing
midbrain
or mesencephalon extends from pons to diencephalon. the pons is the center structure of the brain stem, located between the midbrain and the medulla oblongata
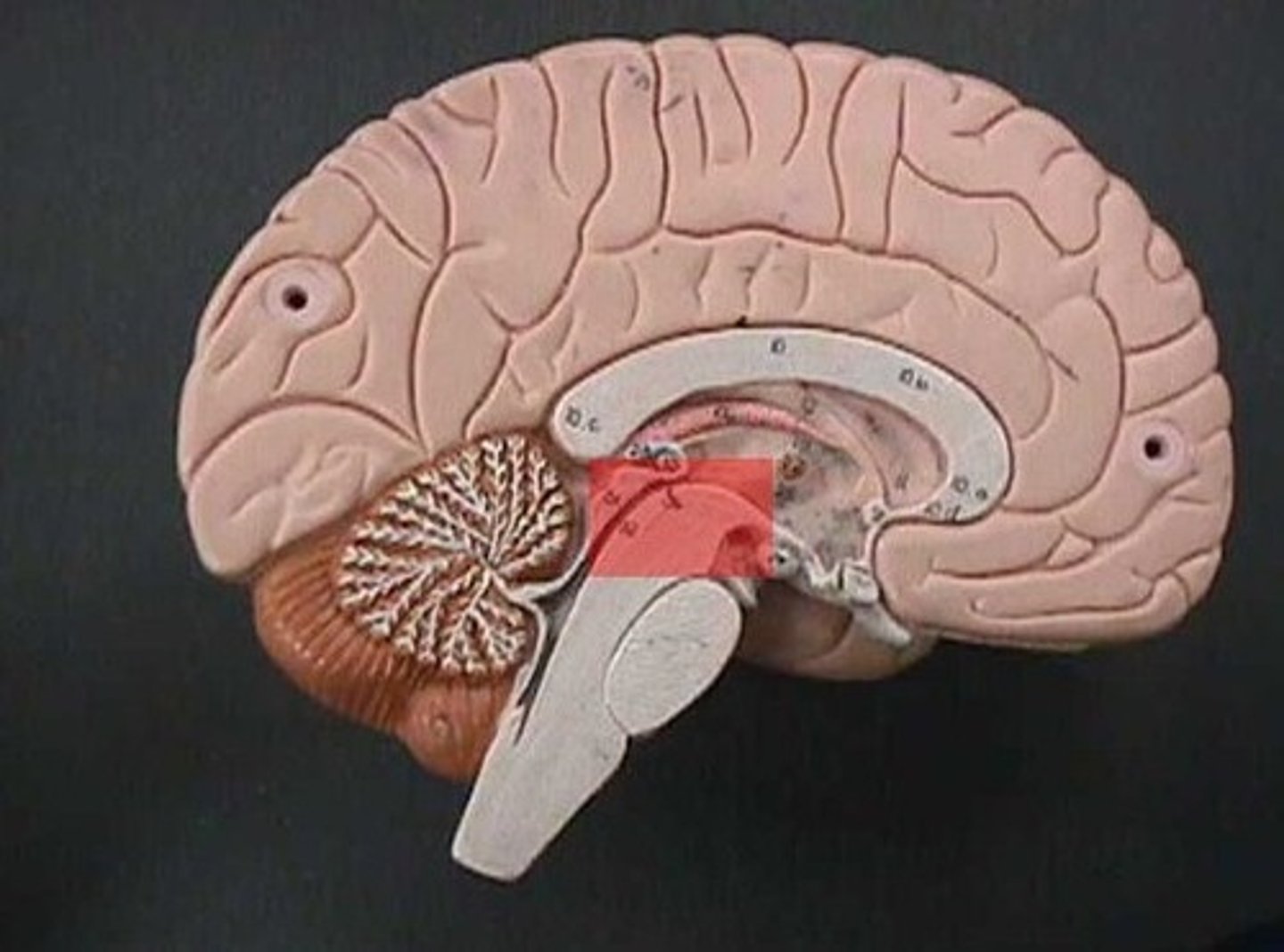
tectum of midbrain
superior and inferior colliculi
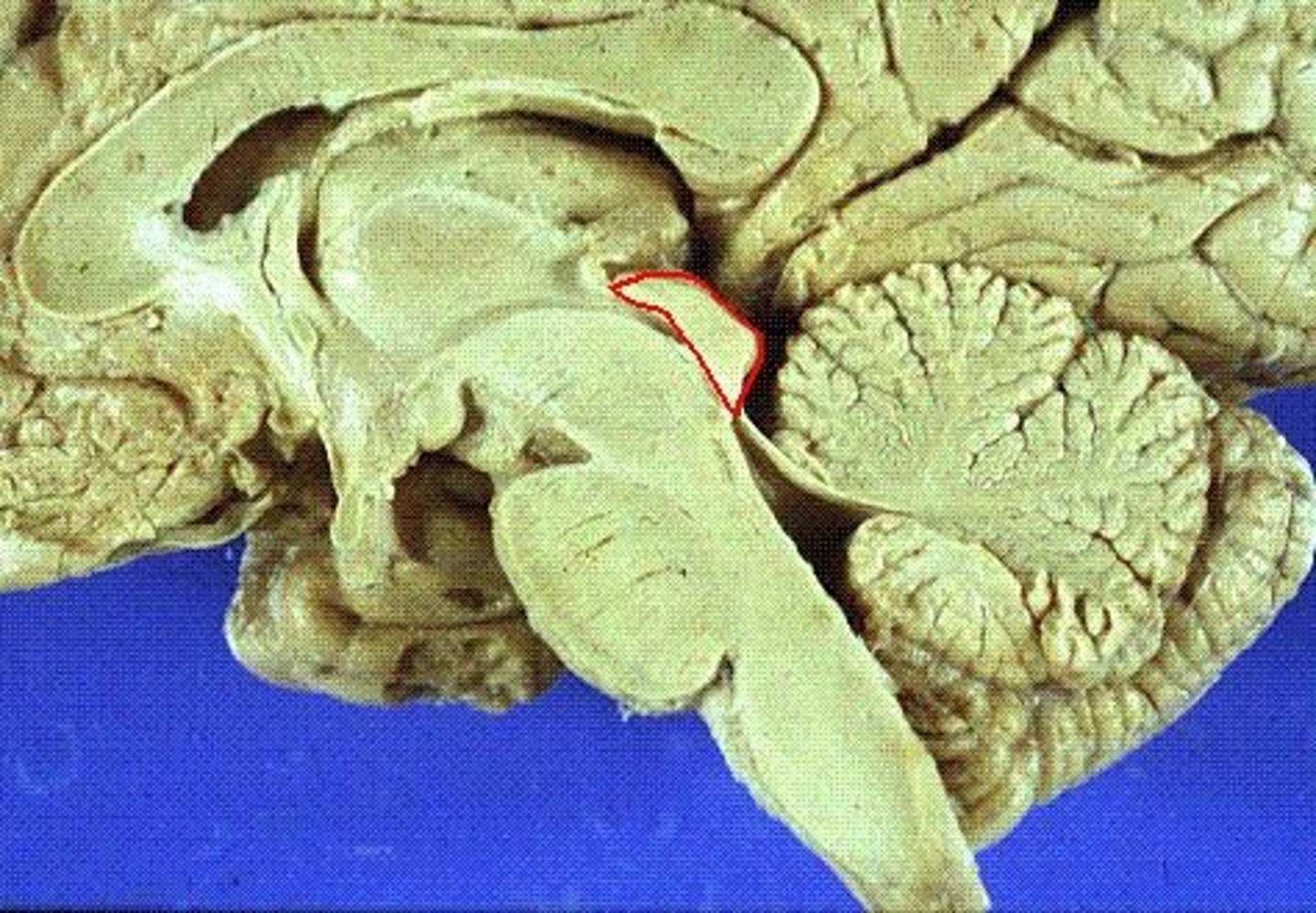
tegmentum of midbrain
involved in movement and arousal

cranial nerves
12 pairs of nerves that carry messages to and from the brain
oculomotor nucleus in the midbrain
controls eye movements & pupillary constriction
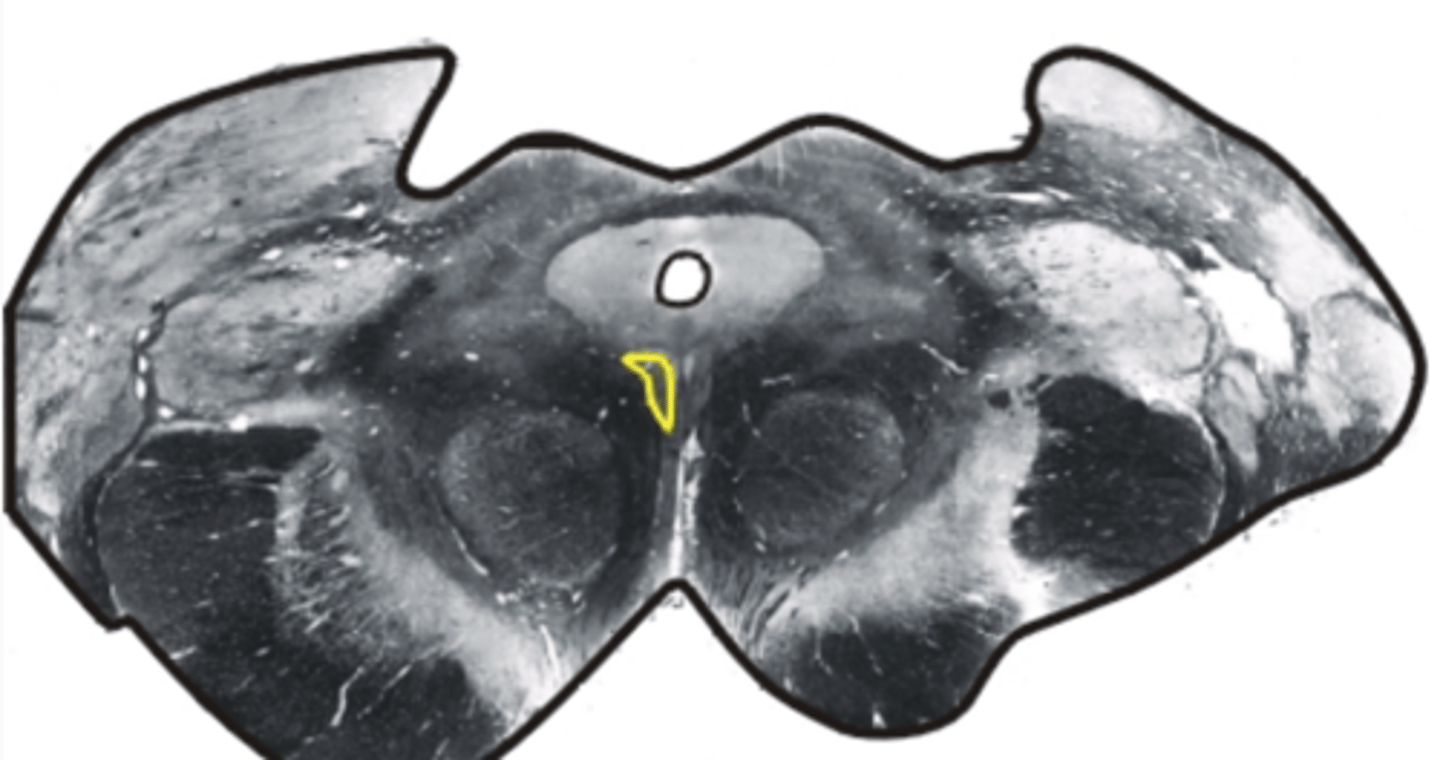
trochlear nucleus
controls superior oblique eye muscles
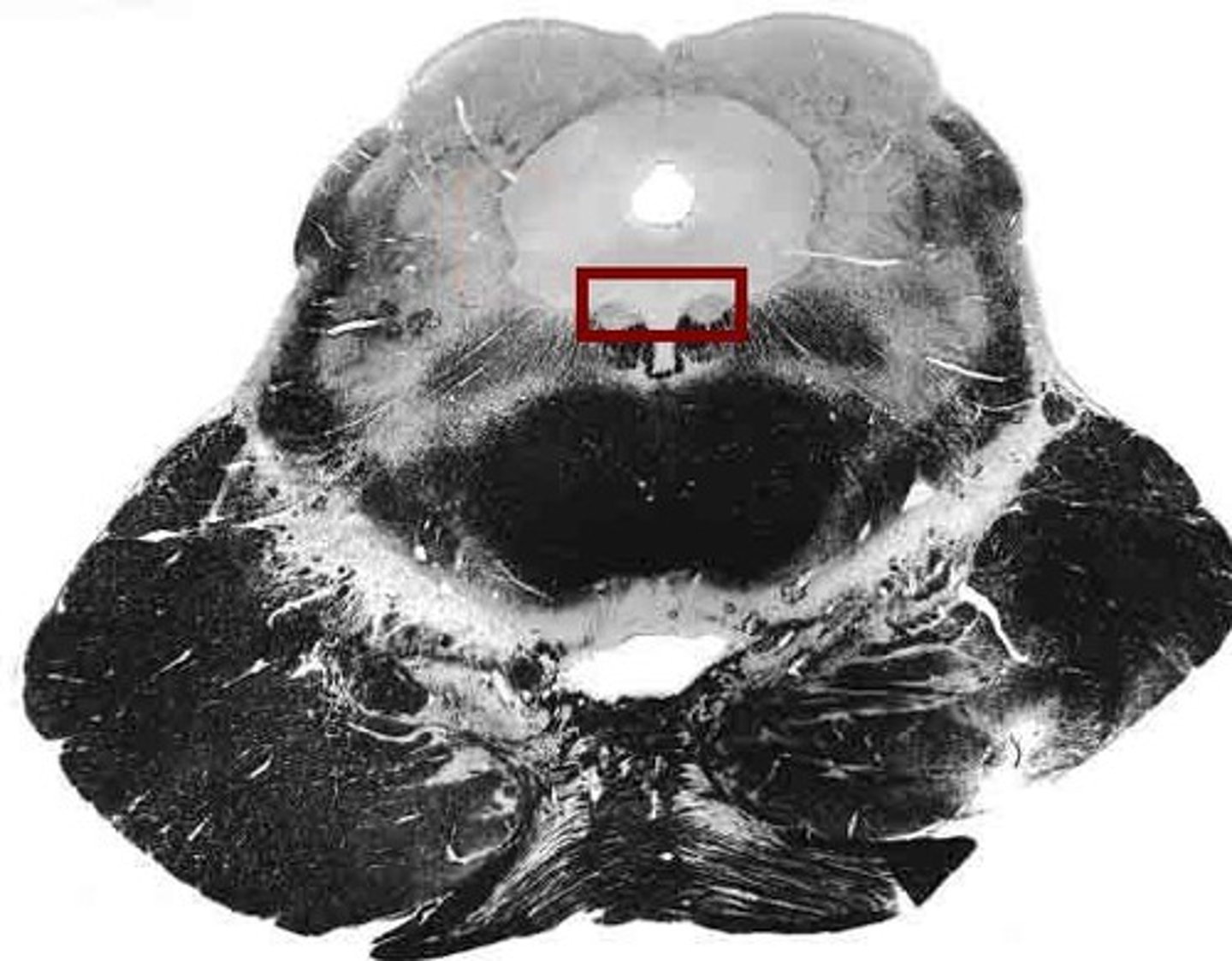
Edinger-Westphal nucleus
part of oculomotor complex controlling ciliary muscle for accommodation of the lens & pupil constriction
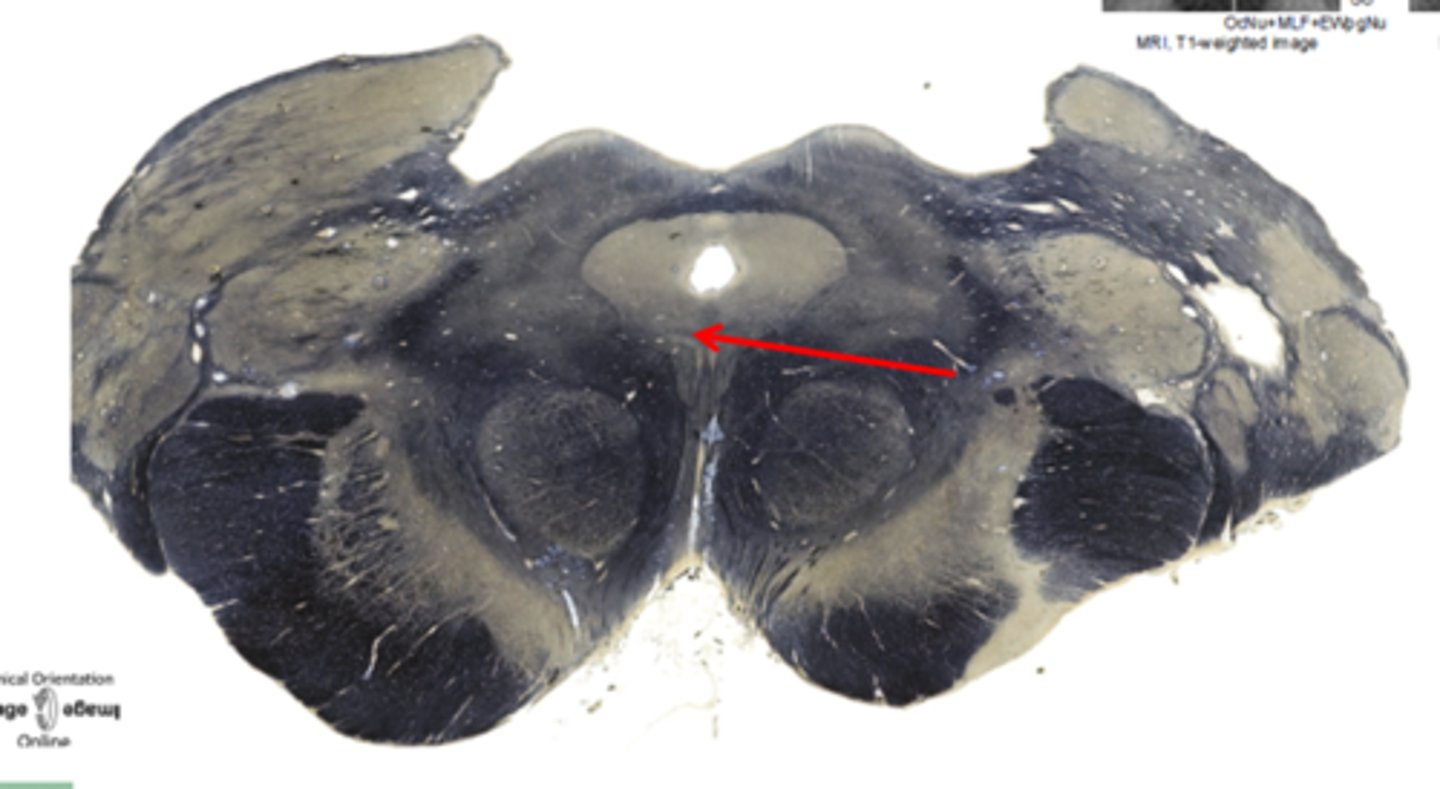
cerebral peduncles
located on the ventral surface of midbrain. has corticospinal tract (voluntary movements) & corticobulbar tracts (motor control of face & head)
reticular formation (RF)
complex network of nuclei & pathways located in the brainstem, extending from the medulla through the pons & midbrain. it plays a crucial role in various physiological functions & maintaining overall brain arousal
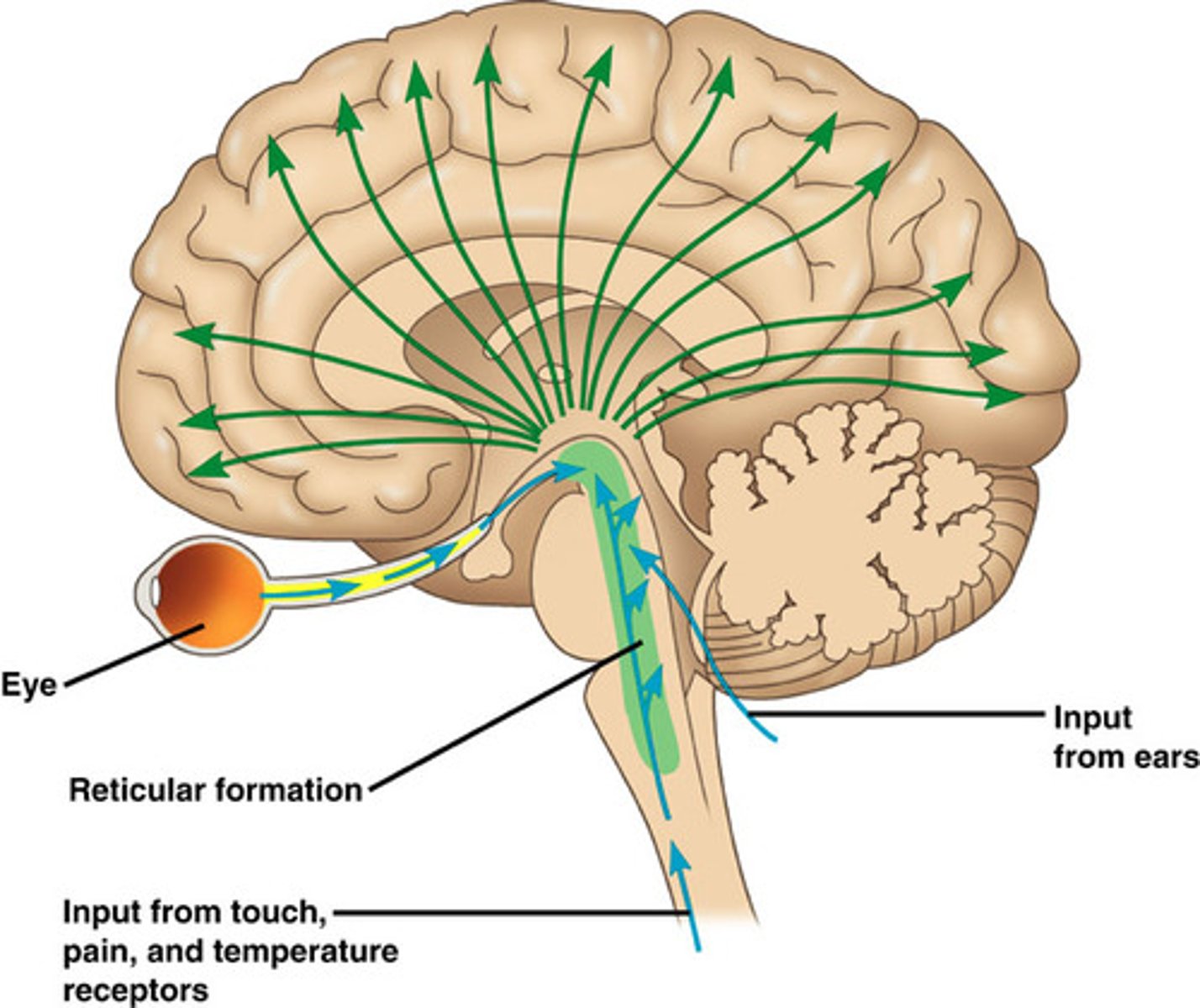
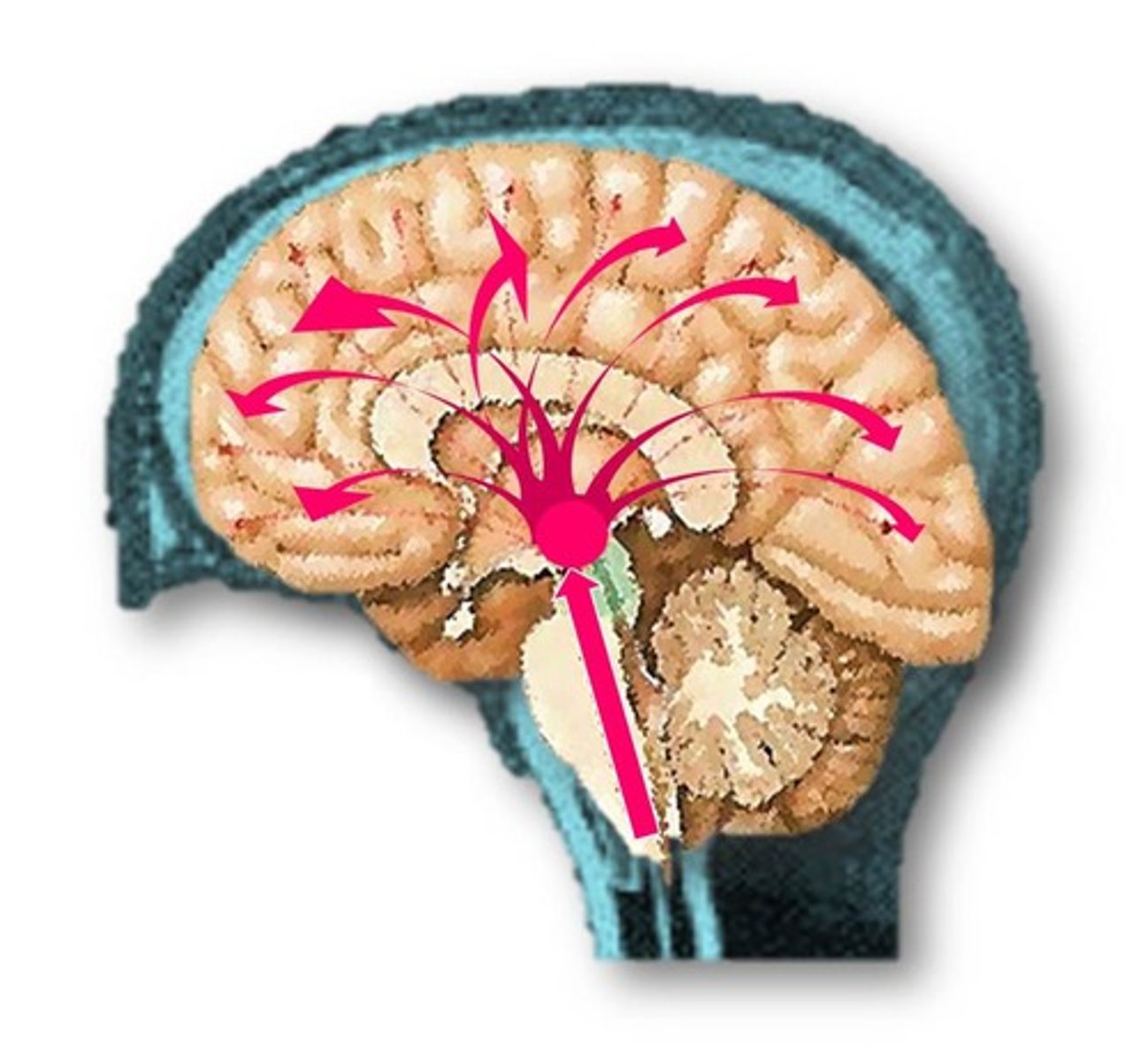
Reticular Activating System (RAS)
transmits sensory axons to the cerebral cortex directly and through the thalamus
Ralph nuclei
regulates mood, sleep, and pain perception
locus coeruleus
involved in attention, arousal, and stress responses
Pontine reticular formation
regulates REM sleep and arousal
medullary reticular formation
controls autonomic functions
Cerebrum
ability to read, write, speak; complex analysis etc.
cerebral sulci
the grooves between the cerebral gyri on the surface of the cerebrum
interlobar sulci of cerebrum
grooves that separate the various lobes of the cerebrum
cerebral fissures
grooves that separate parts of the brain
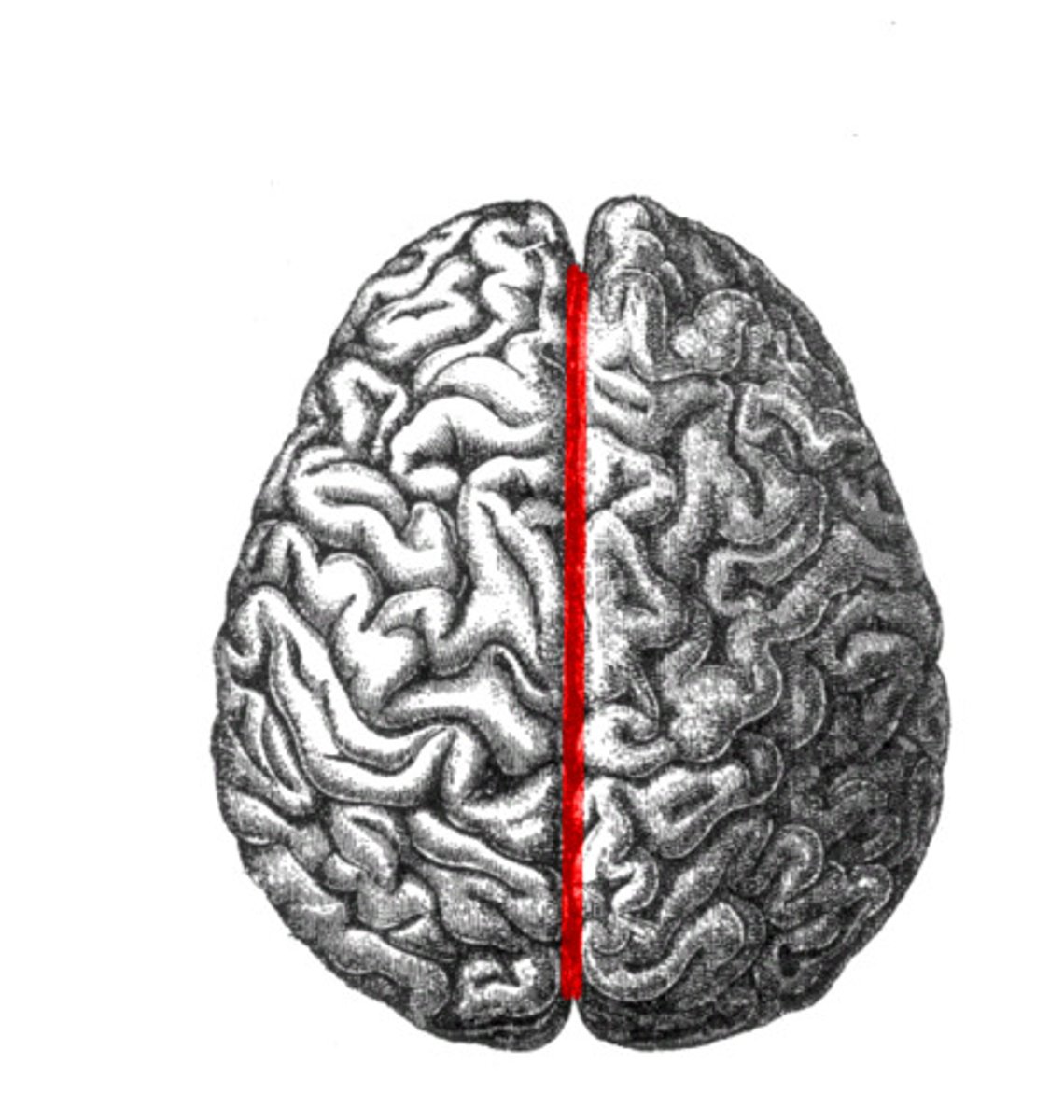
longitudinal cerebral fissure
separates cerebrum into right & left cerebral hemispheres
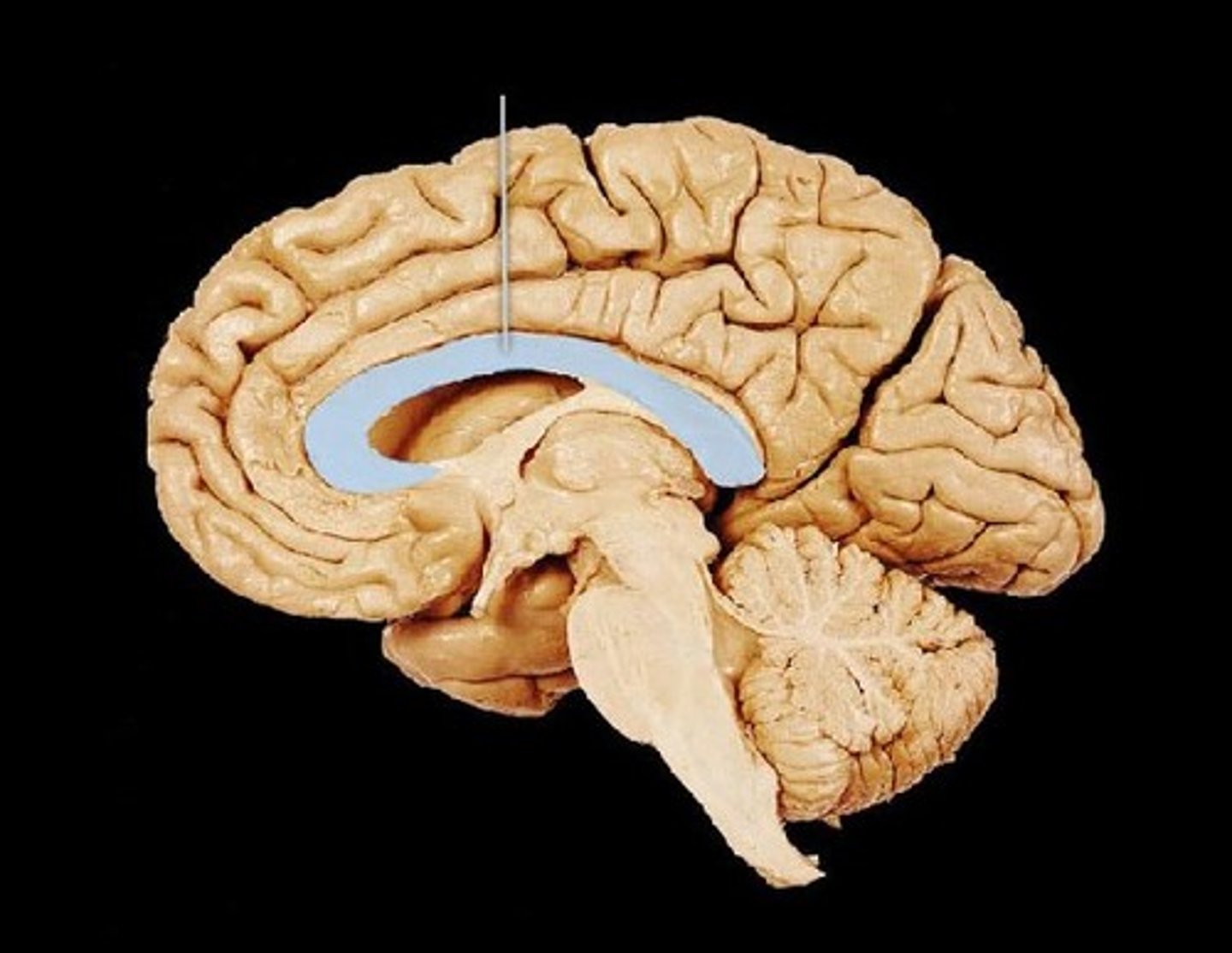
corpus callosum
broad band of white matter containing axons that extend between the cerebral hemispheres
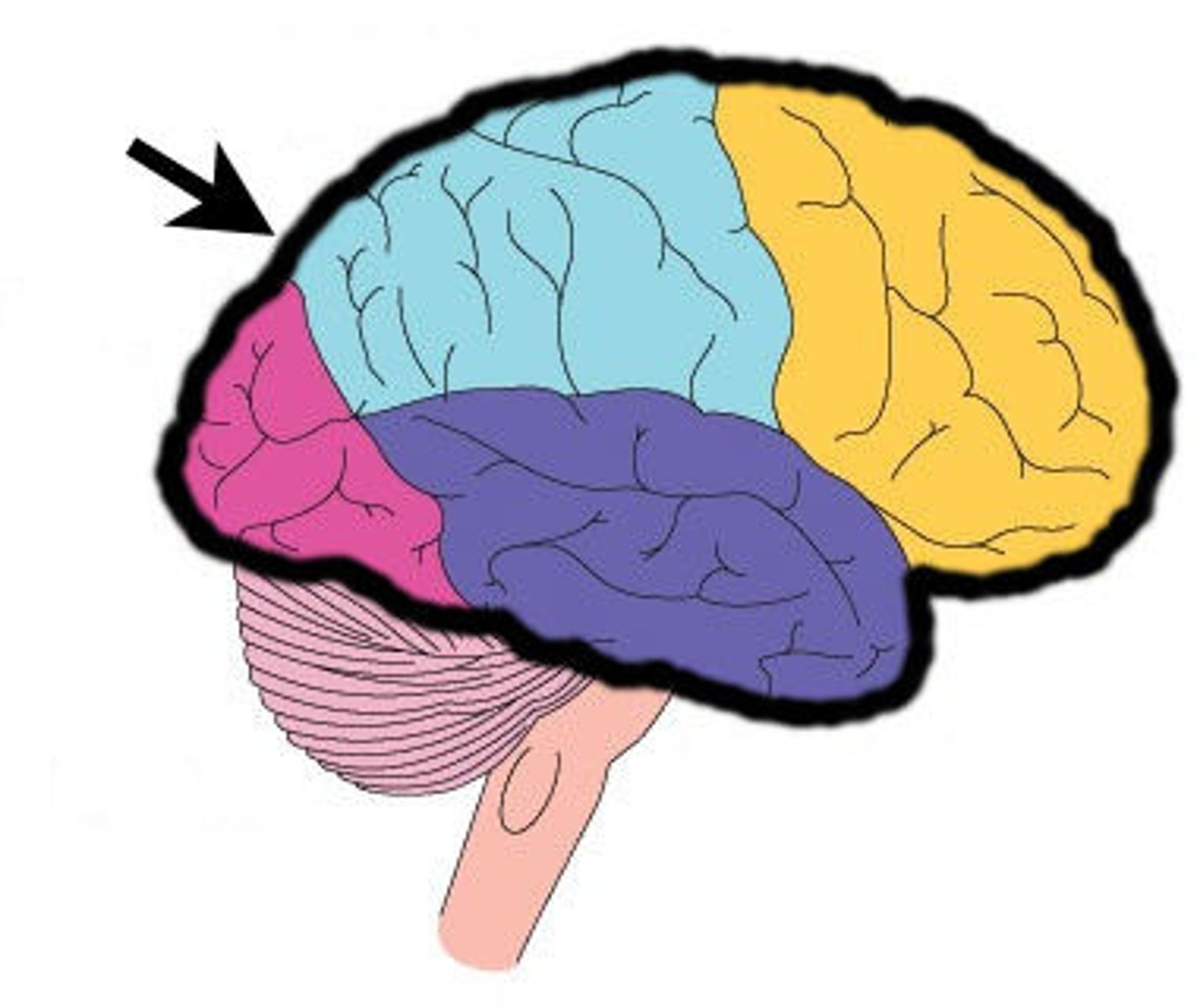
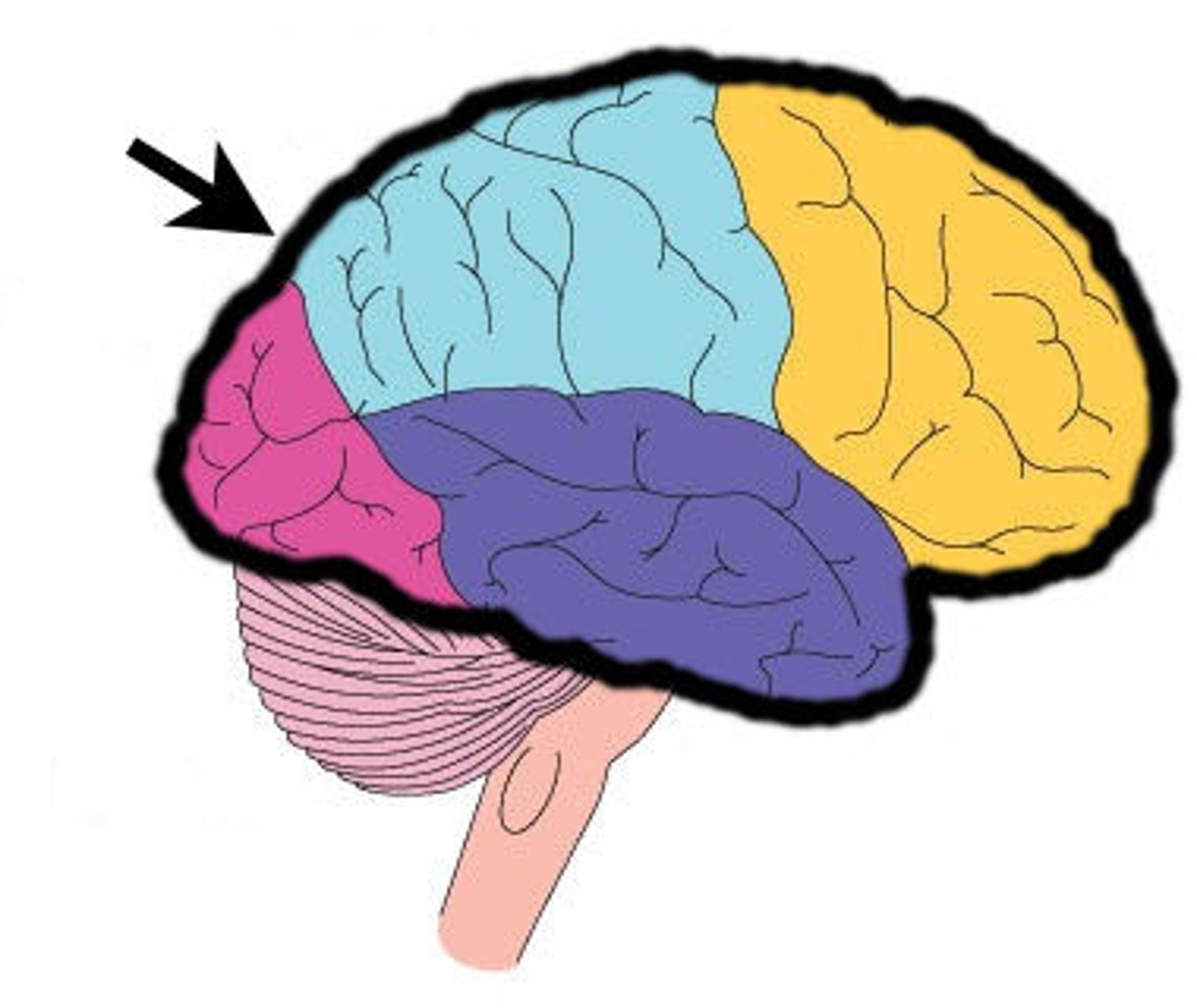
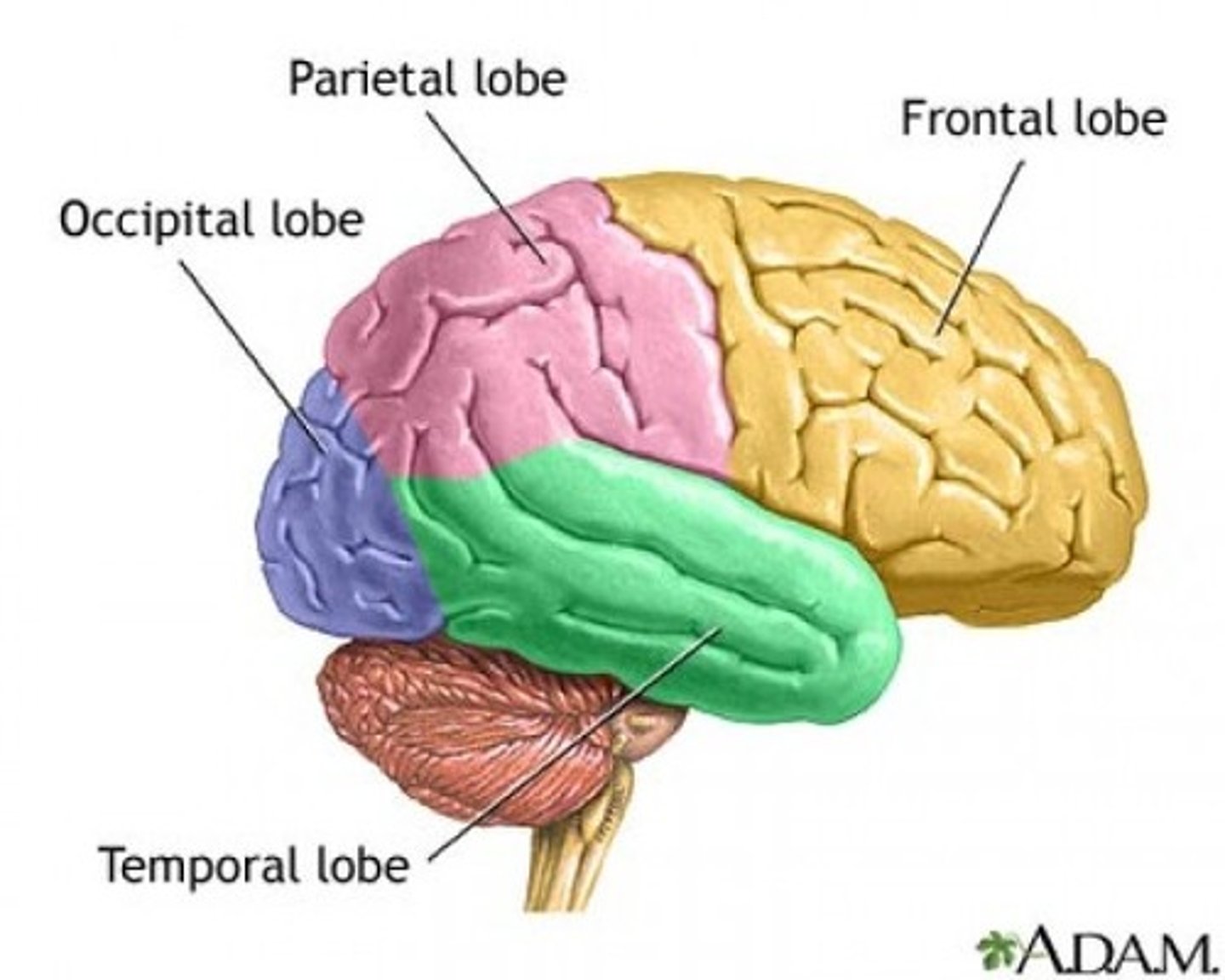
Lobes of the cerebrum
frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital
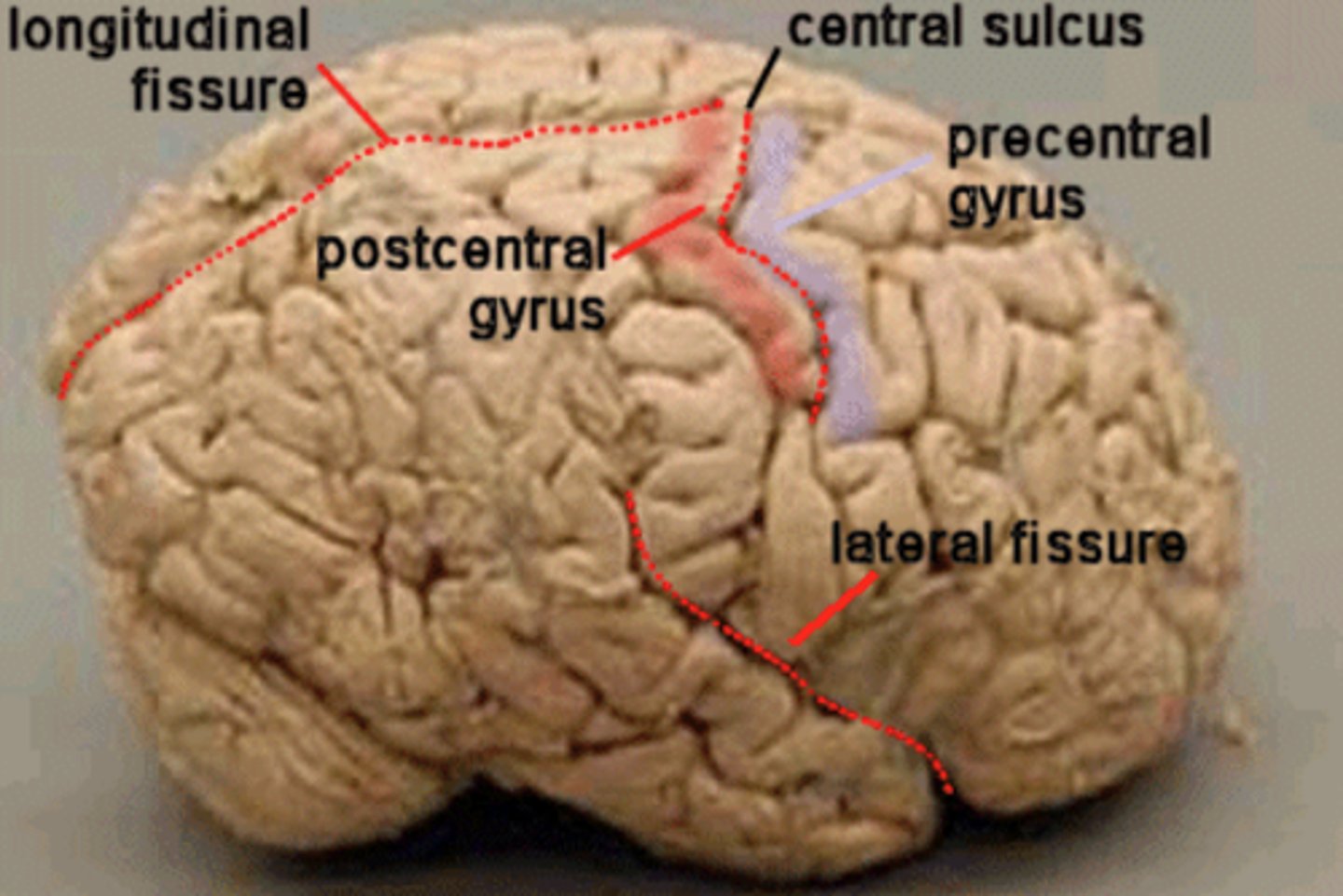
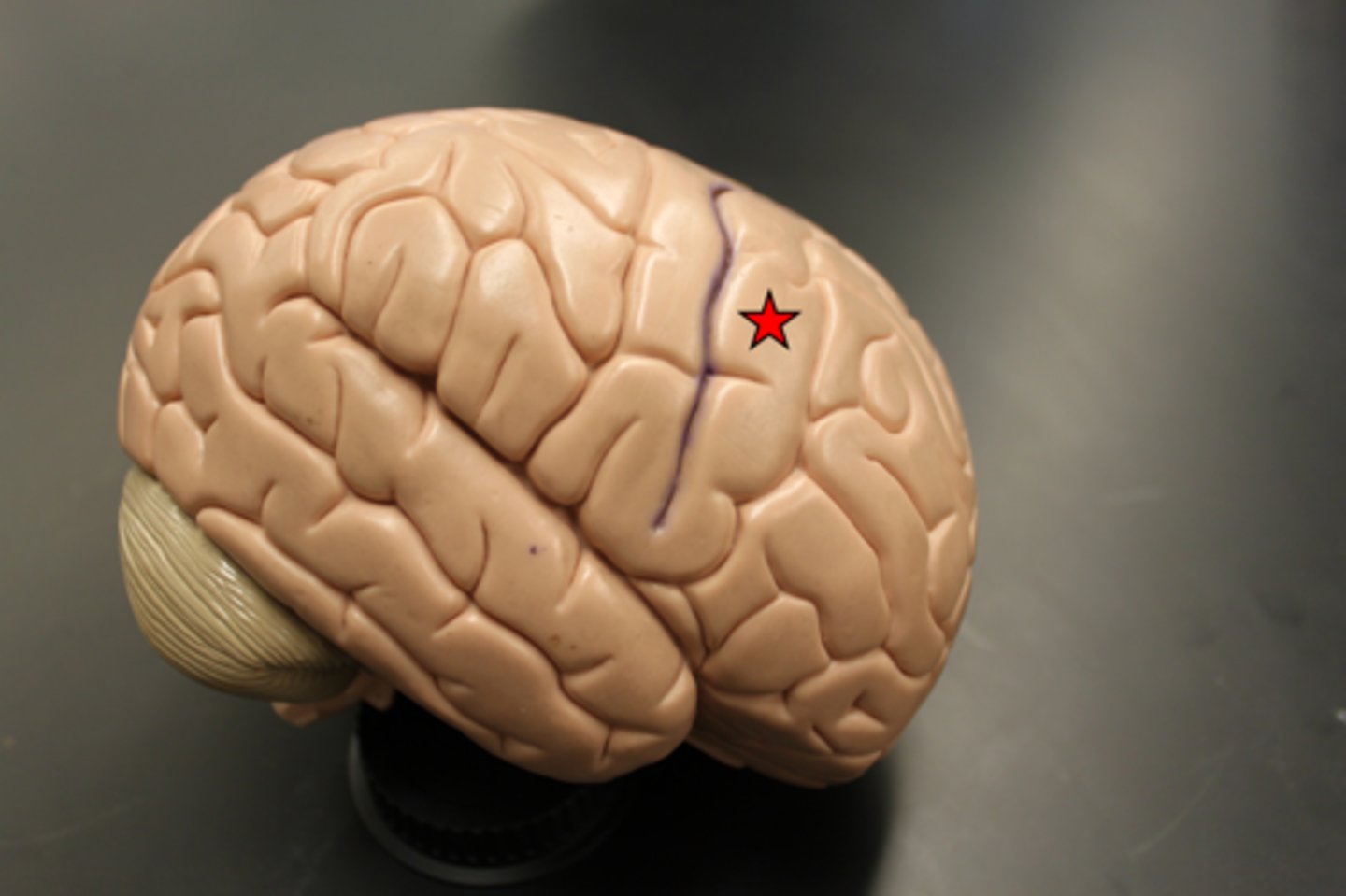
Precentral cerebral gyrus
primary motor cortex of the cerebrum is situated anterior to the central sulcus
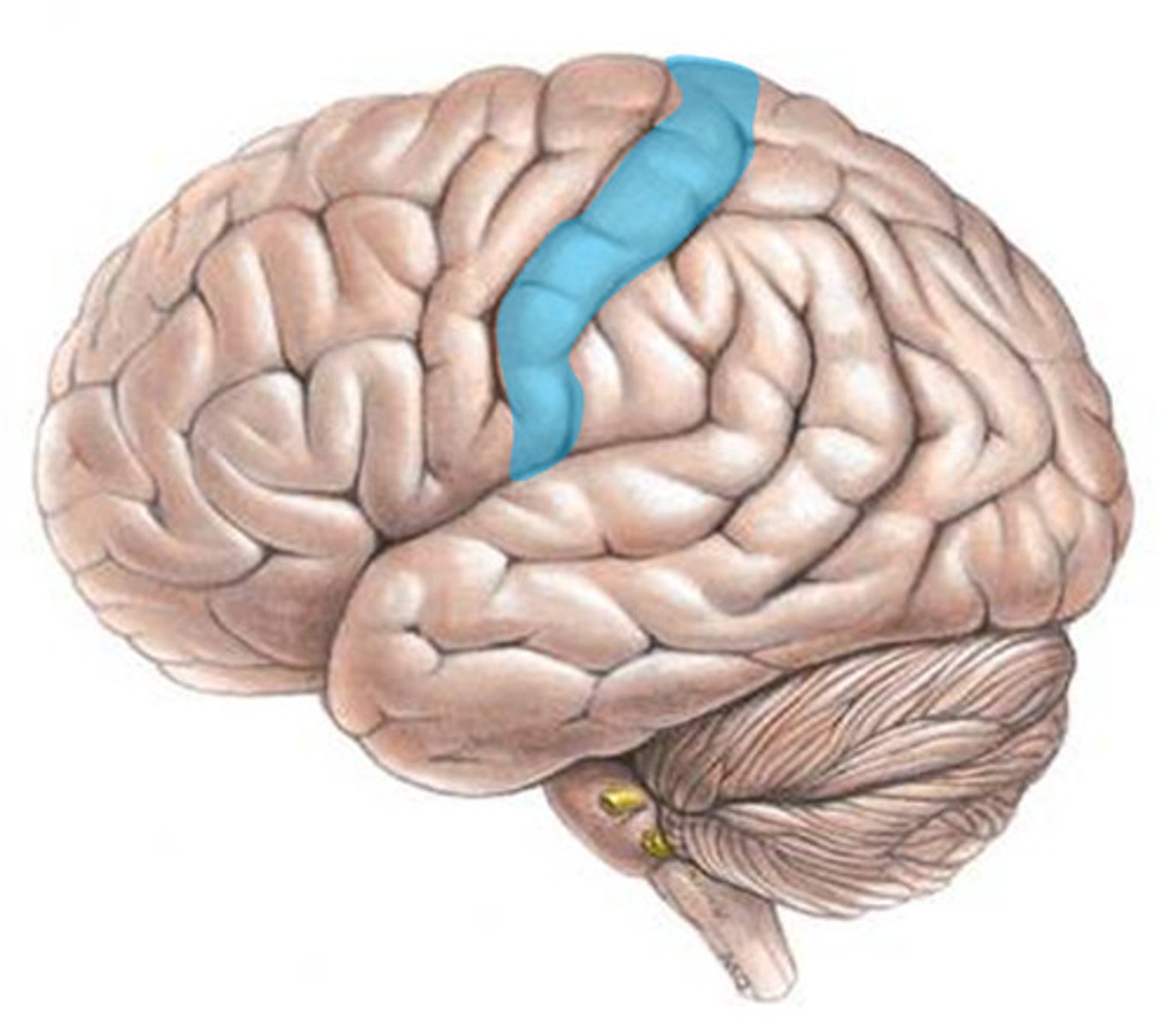
postcentral gyrus
the strip of parietal cortex, just behind the central sulcus, that receives somatosensory information from the entire body
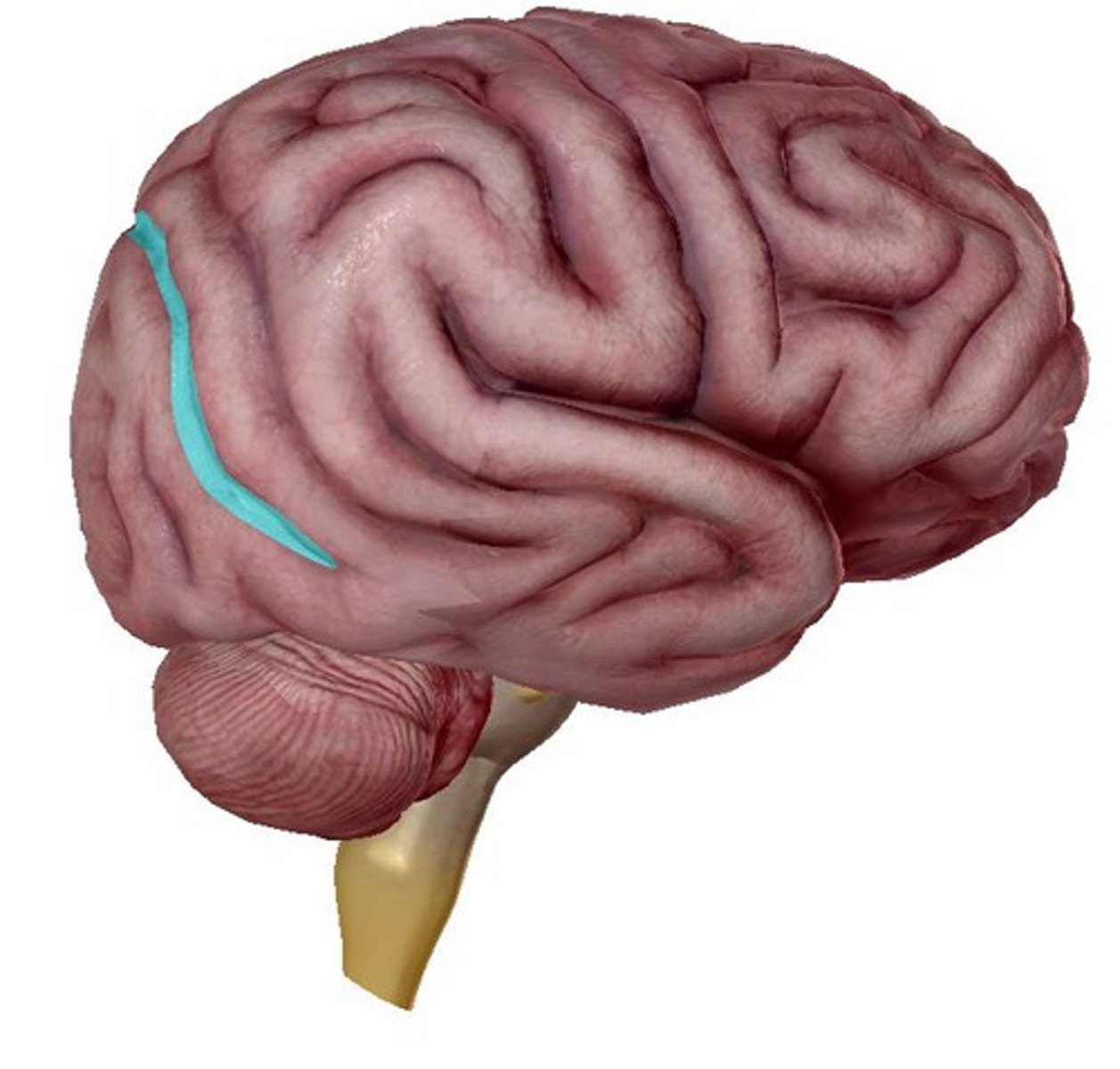
lateral cerebral sulcus
separates the frontal lobe from the temporal lobe
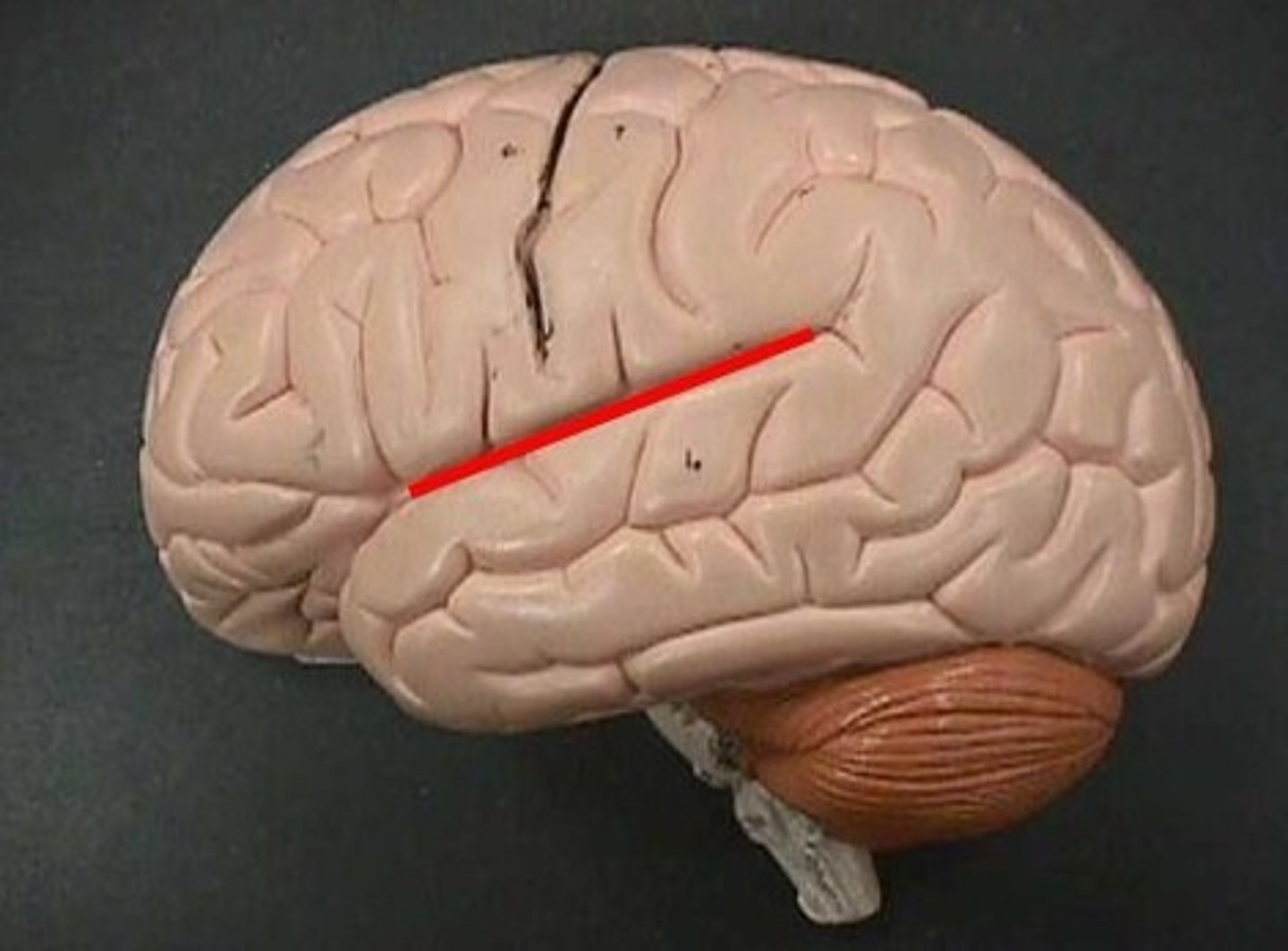
parieto-occipital sulcus
separates parietal and occipital lobes
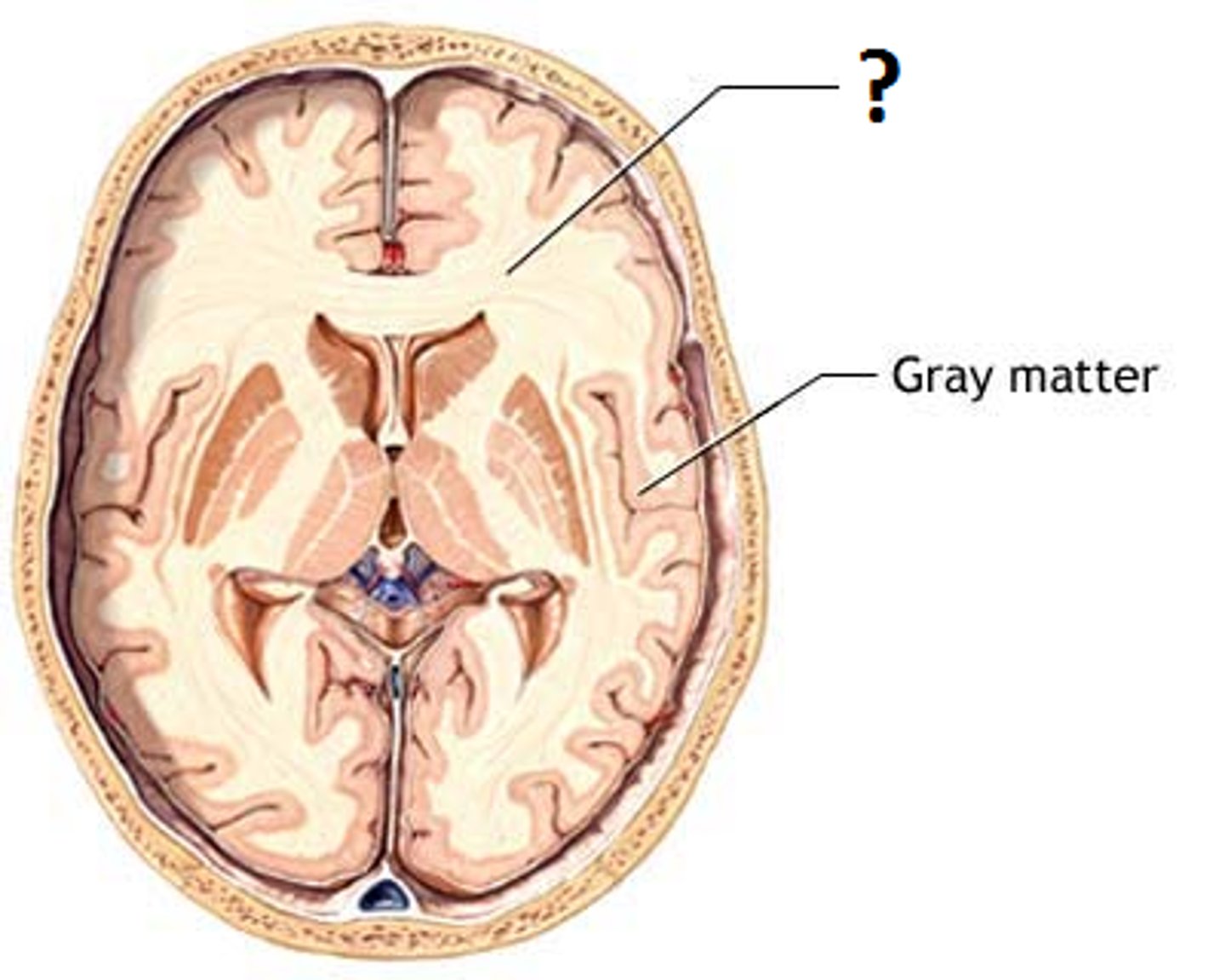
white matter
myelinated axons
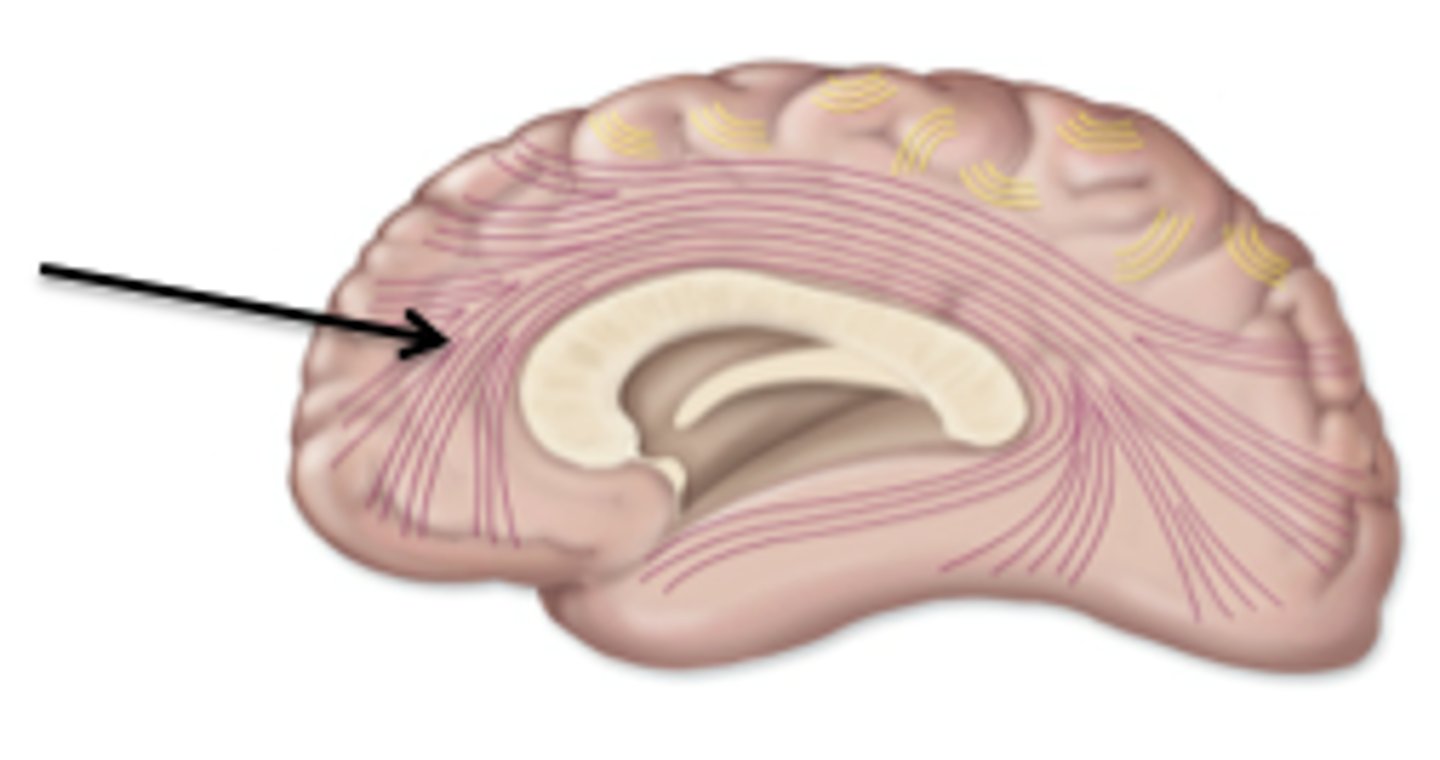
Association tracts of white matter
conducts nerve impulses between cerebral gryri in the same hemisphere
commissural tracts of white matter
conducts nerve impulses one cerebral gyri to corresponding gyri in the other cerebral hemisphere.
projection tracts
conduct nerve impulses from cerebrum to lower parts of the CNS or from lower pars of the CNS to the cerebrum
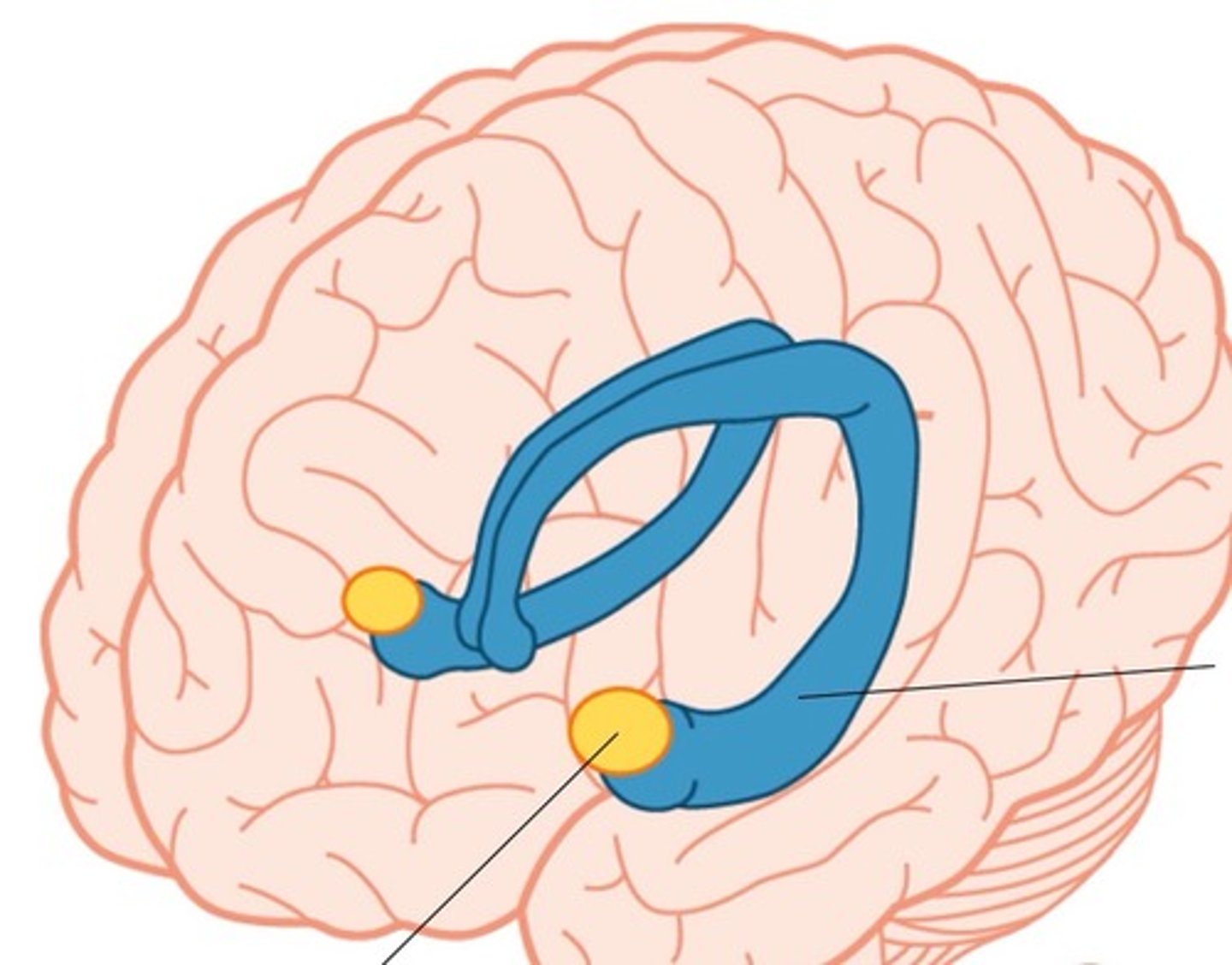
limbic system
a rung of structures that encircles the upper part of the brainstem & corpus callosum inside of the cerebrum & floor of diencephalon
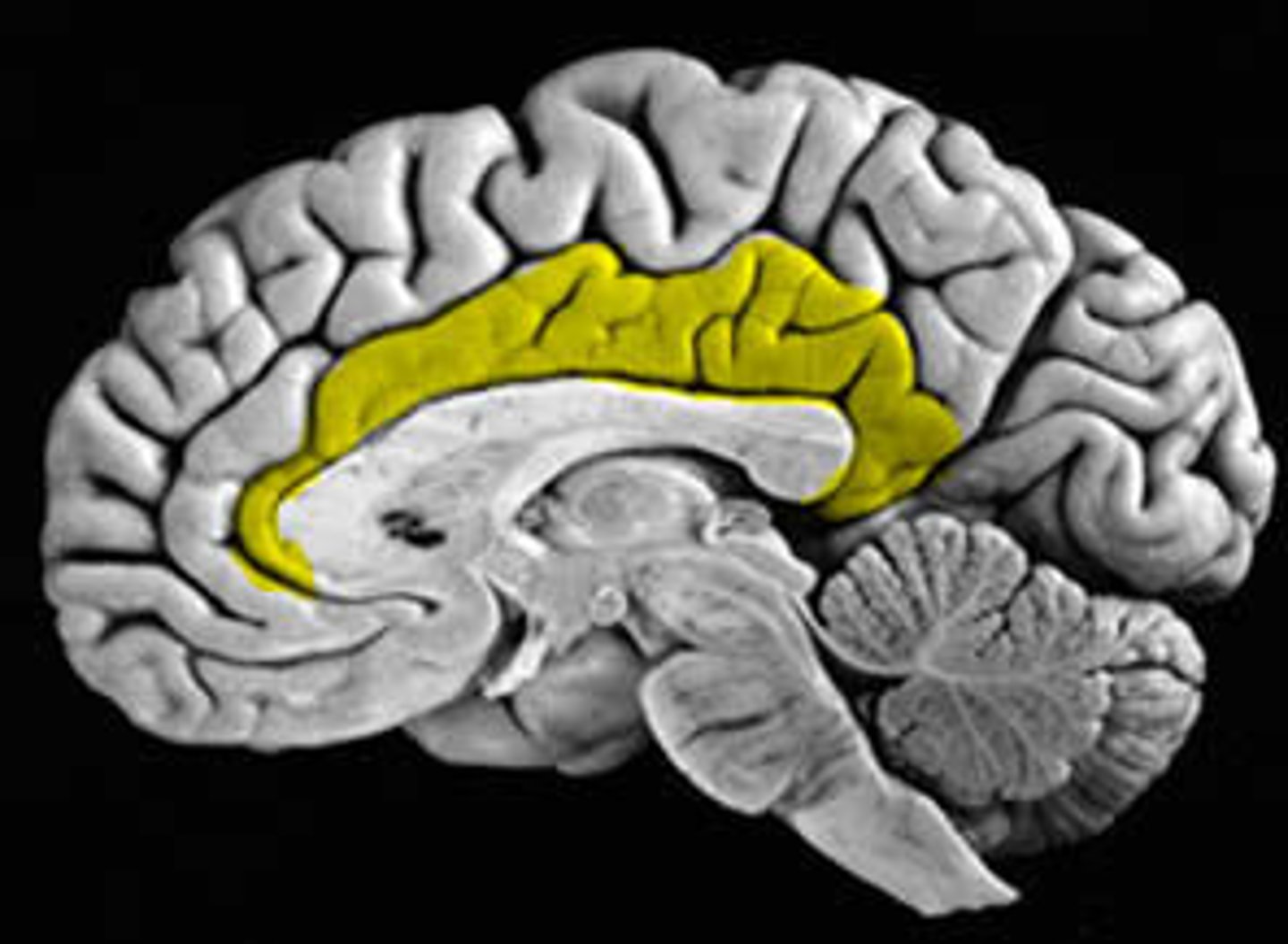
limbic lobes
a rim of cerebral cortex on medial surface of each hemisphere. includes cingulate gyrus & parahippocampal gyrus
dentate gyrus
lies between the hippocampus and parahippocampal gyrus
amygdala
lies close to caudate nucleus - responsible for emotions
septal nuclei
located inferior ro corpus callosum
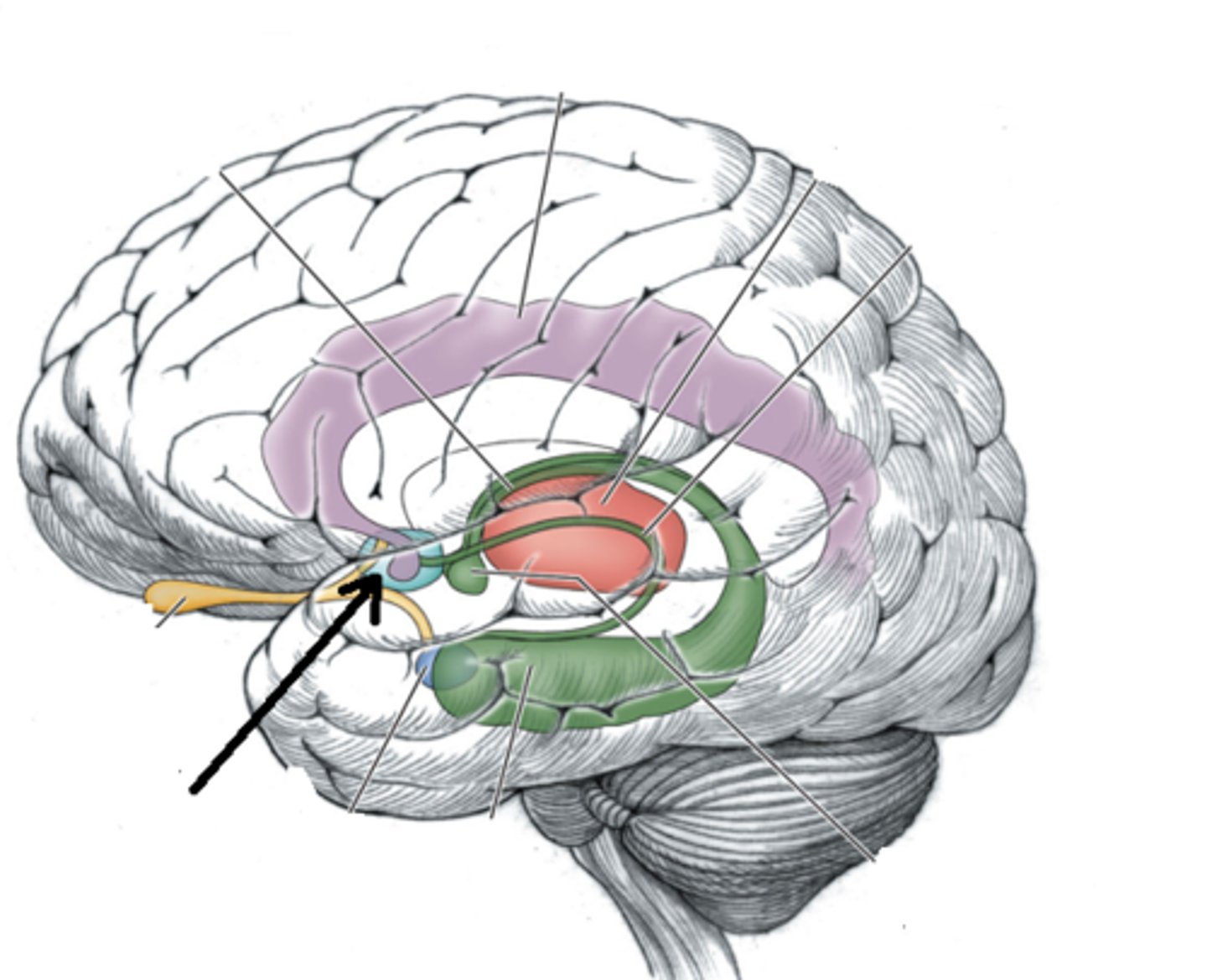
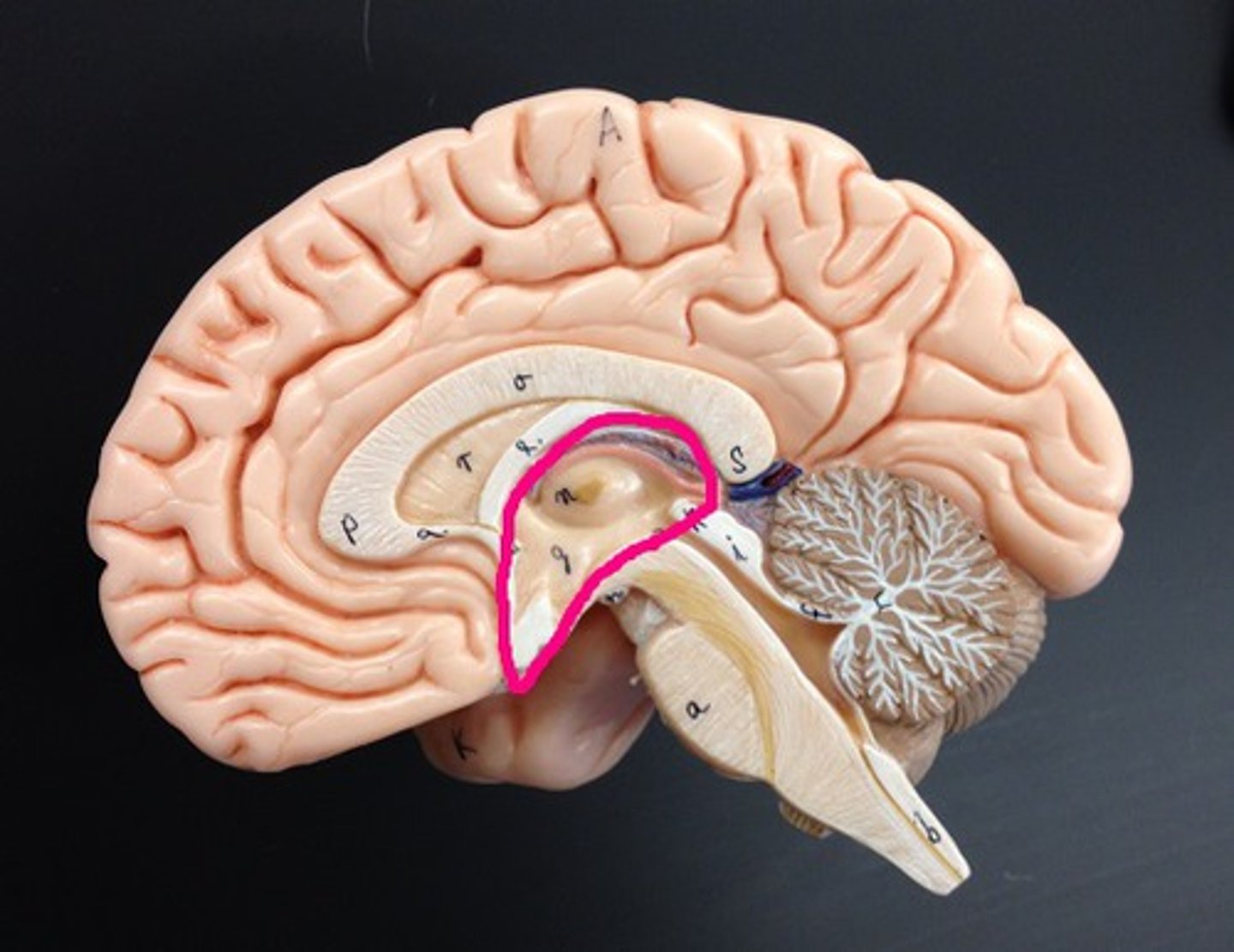
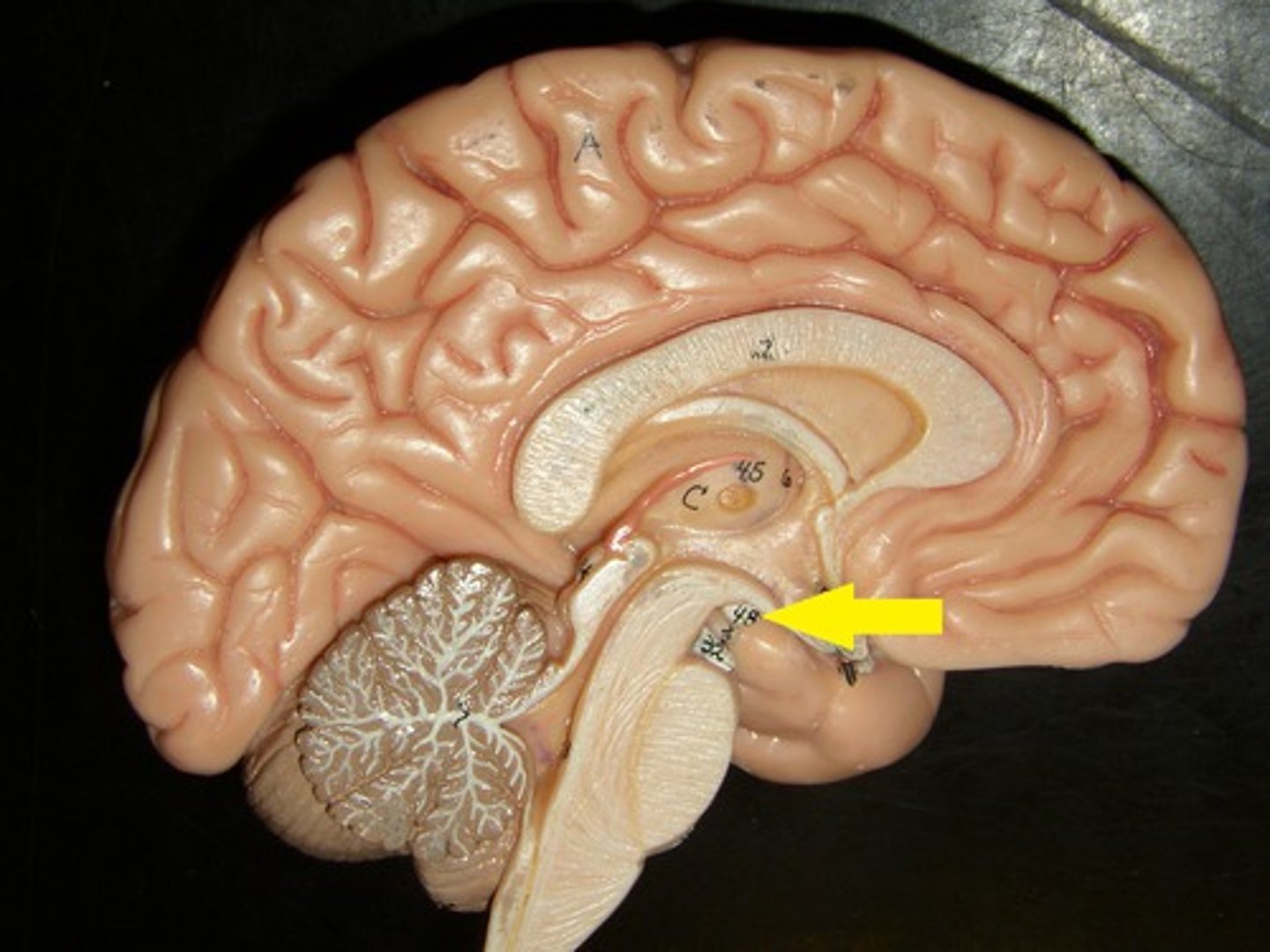
mammillary bodies
lies close to the midline near cerebral peduncles. associated with recollective memory
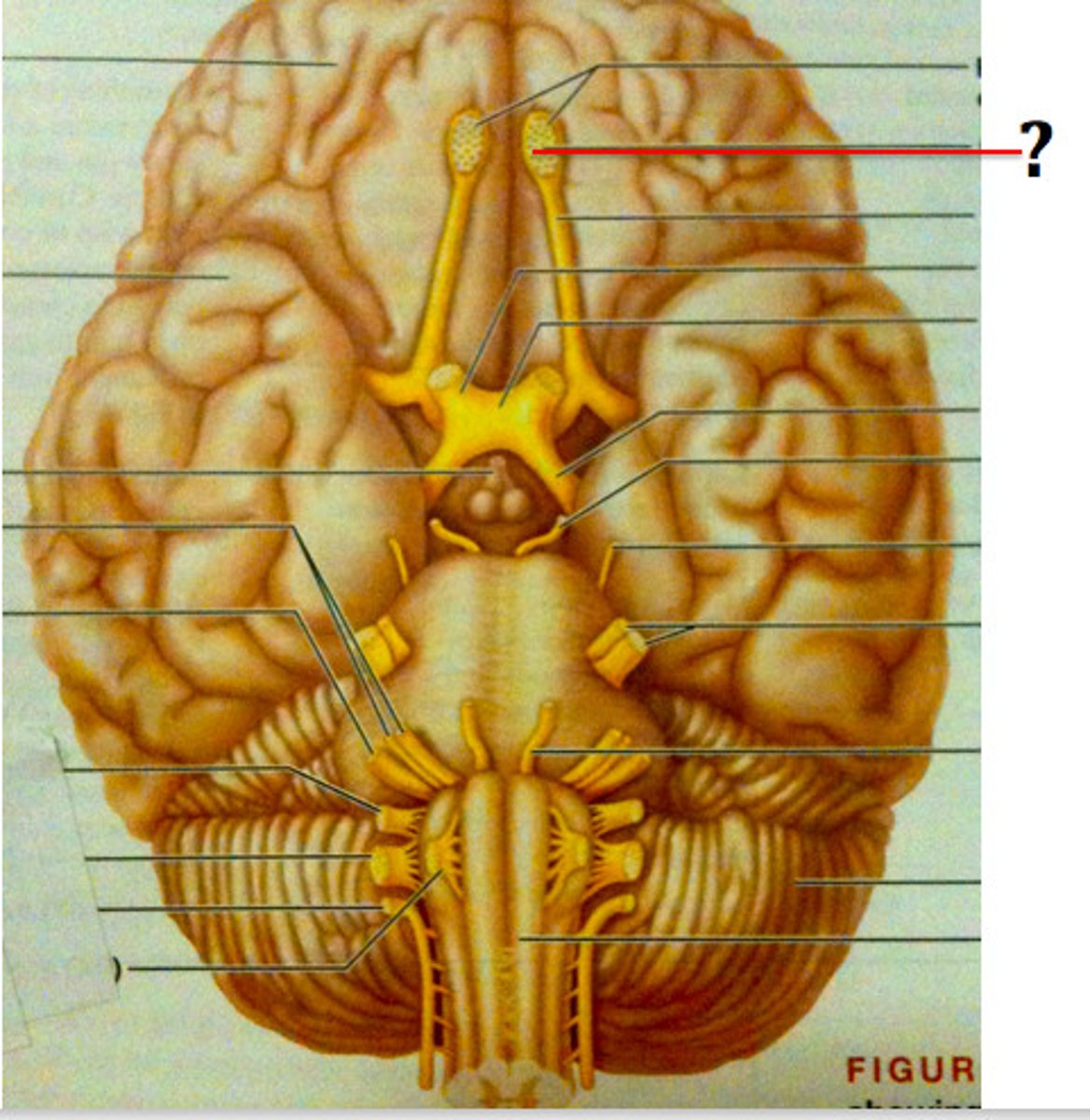
olfactory bulbs
rests on the cribriform plate. related to smell (olfaction)
cerebral cortex
specific types of sensory, motor, & integrative signals are processed in certain regions of the cerebral cortex.
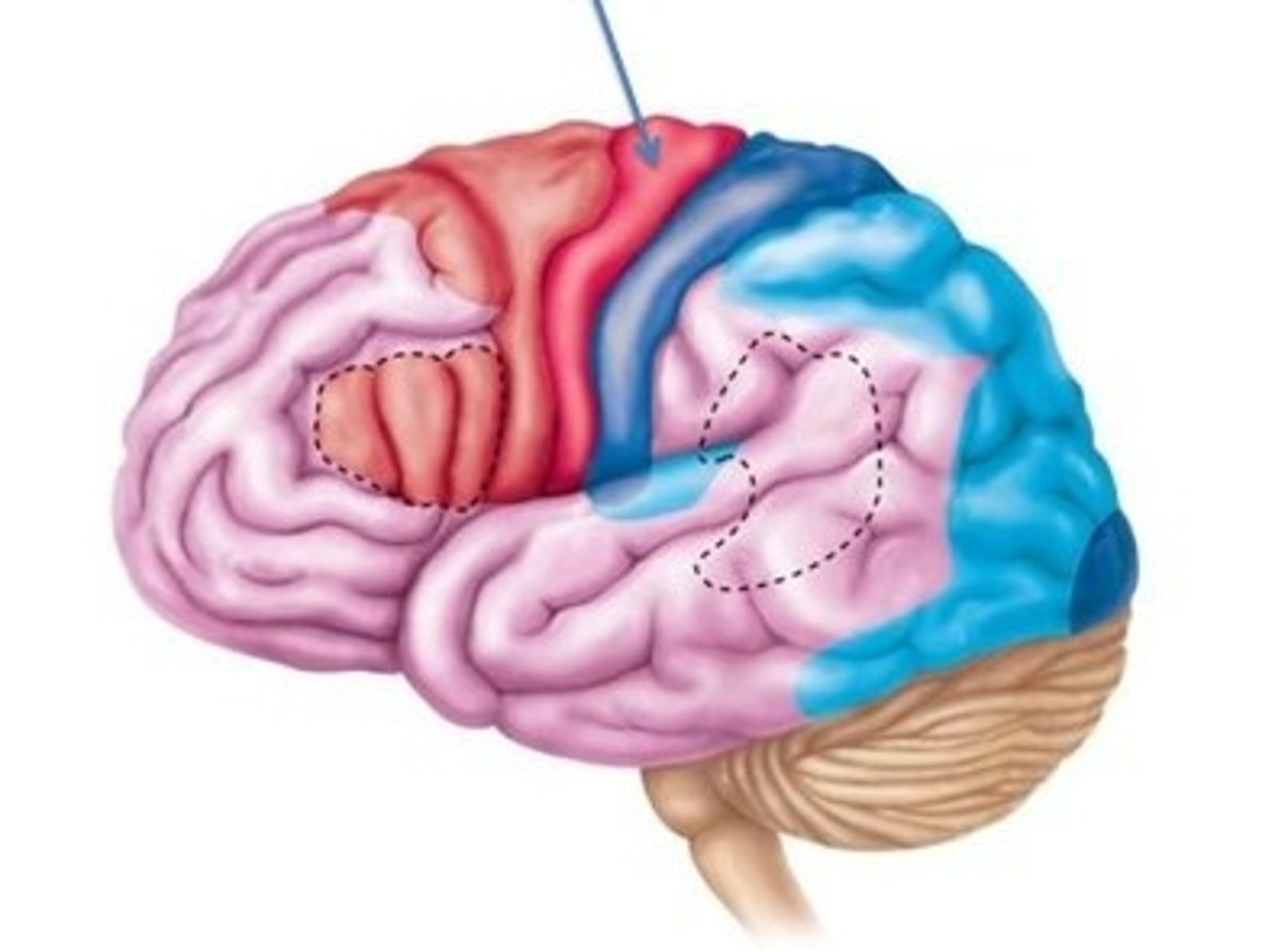
sensory areas of cerebral cortex
Primary somatosensory, Primary visual, Primary auditory, primary olfactory, primary gustatory
motor areas of cerebral cortex
voluntary muscle movements
primary motor cortex
located in the frontal lobe; is the key motor control center responsible for initiating and coordinating movements
premotor cortex
located immediately anterior to the primary motor cortex, responsible for movements such as typing
integrative areas of the cortex
higher cognitive functions; association areas, prefrontal cortex, wernickle's area, broca's area
association areas of cerebral cortex
integrate diverse information
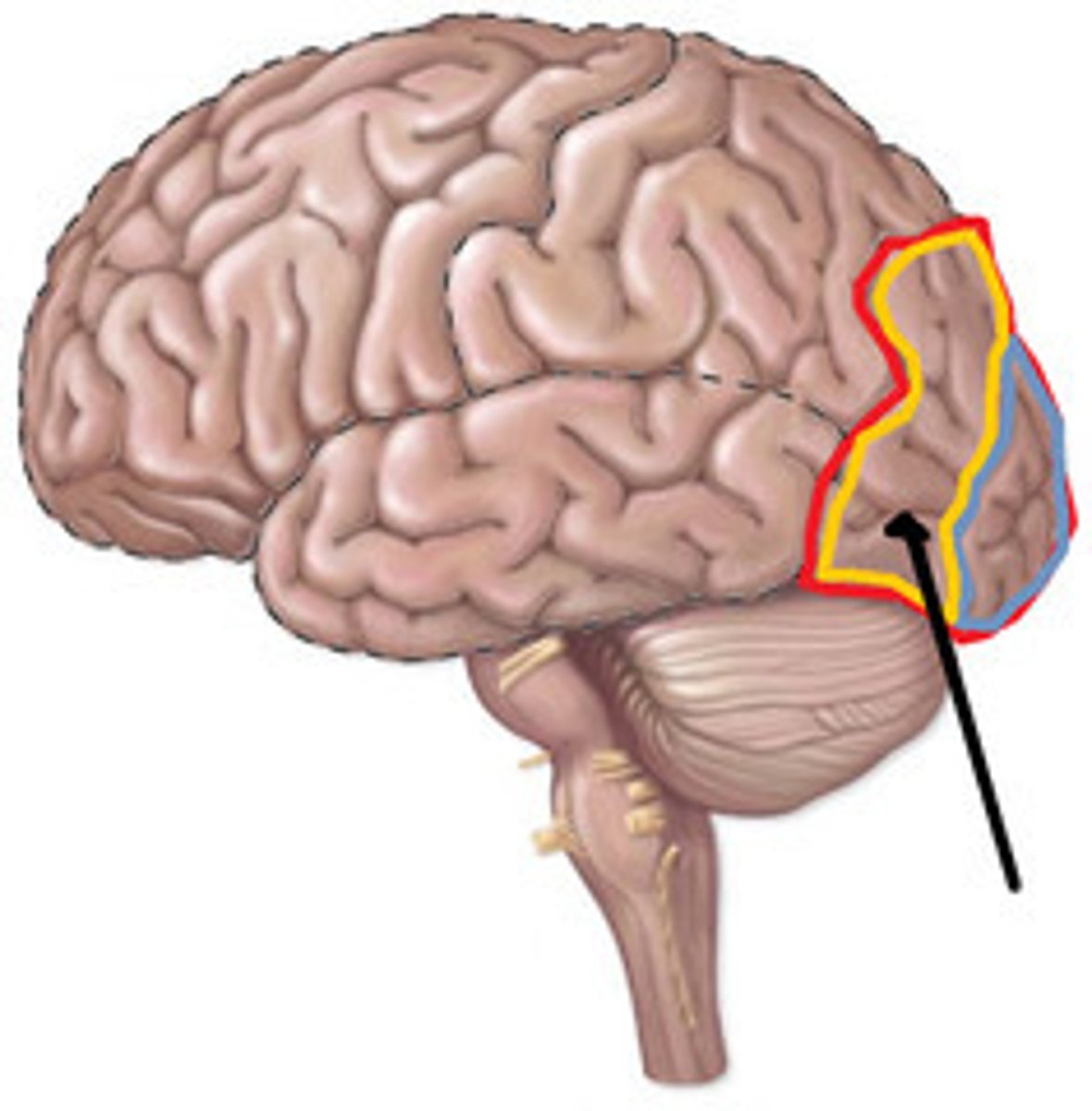
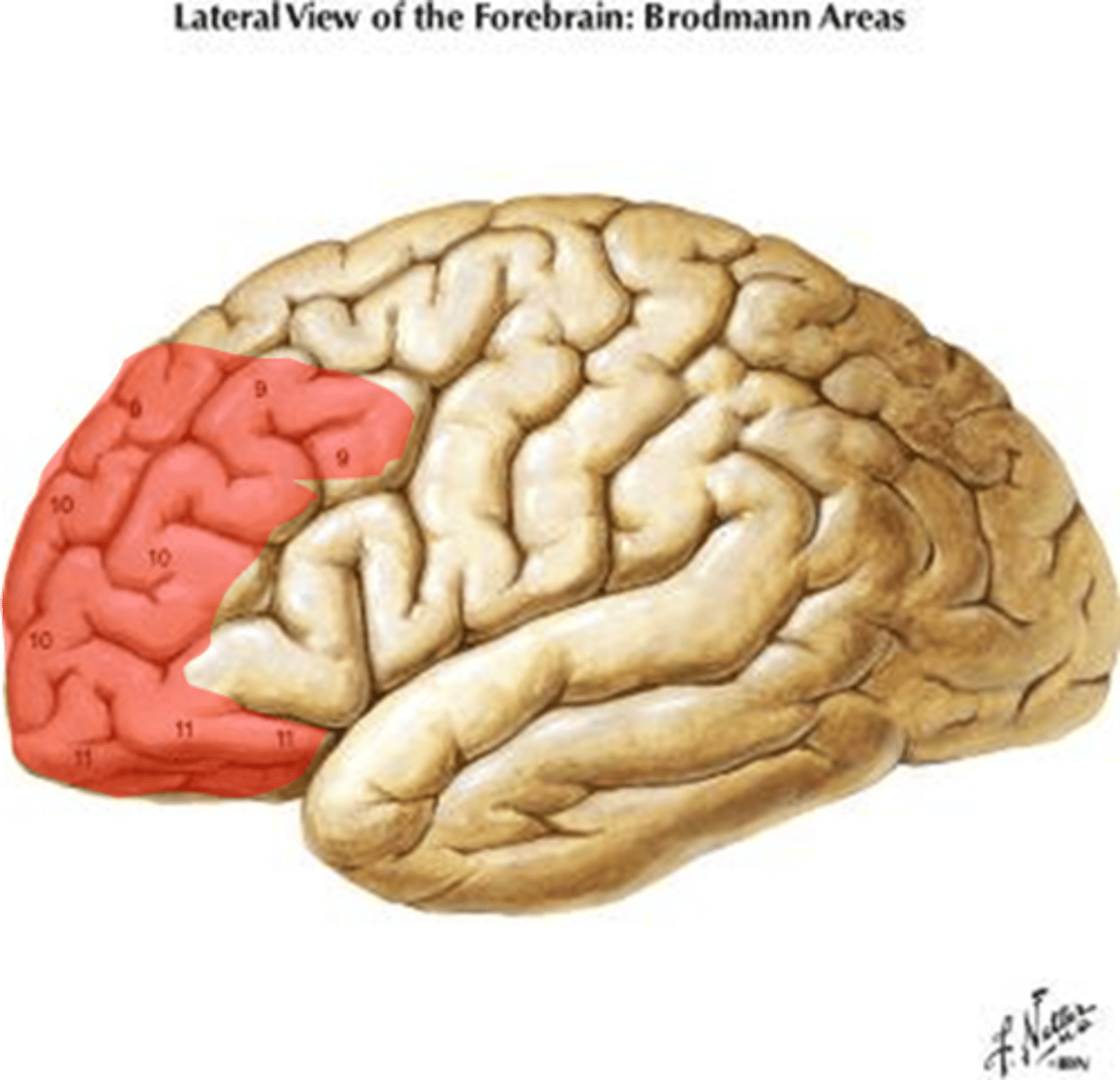
prefrontal cortex
part of frontal lobe responsible for thinking, planning, and language
Wernickle's area
language comprehension
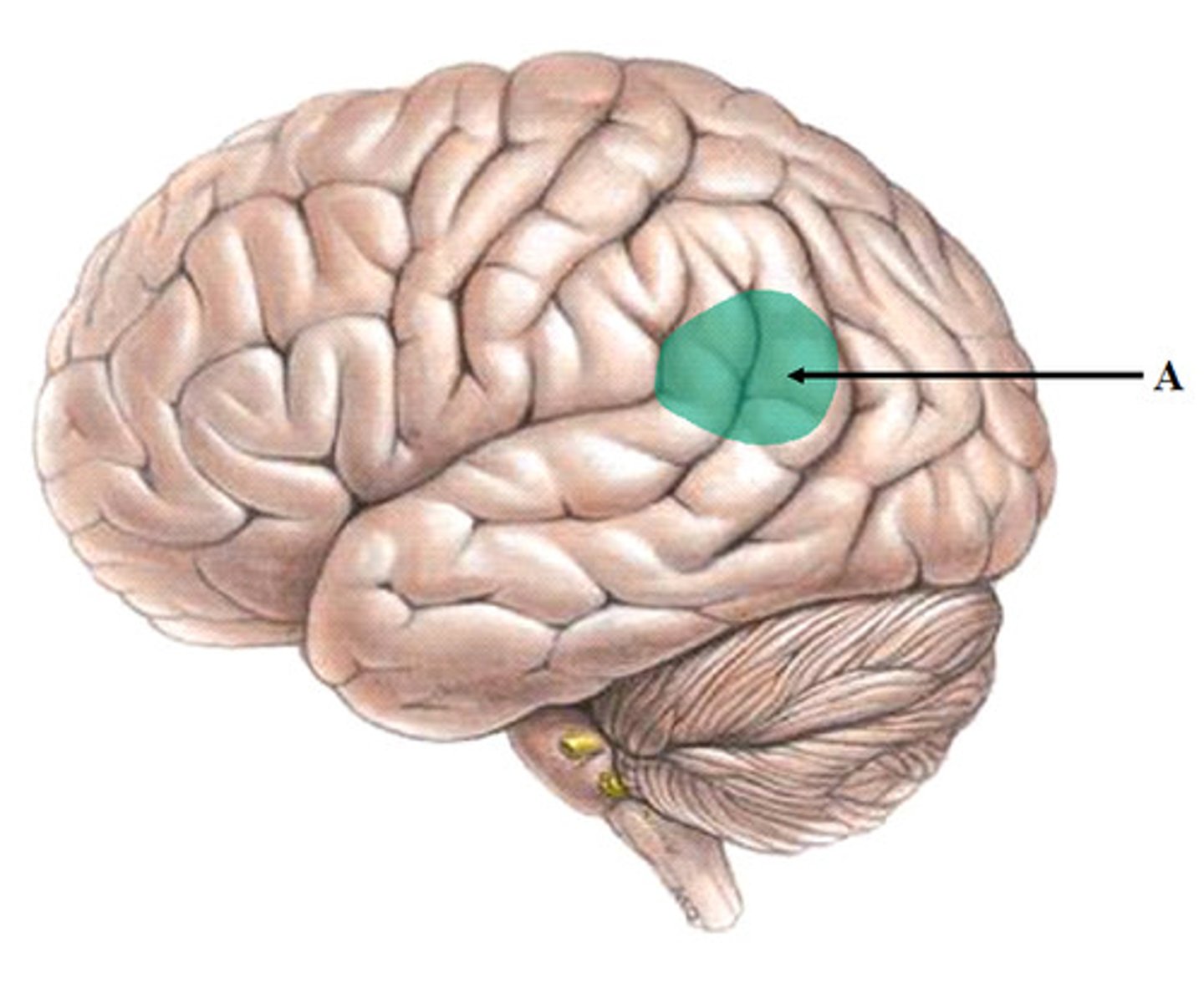
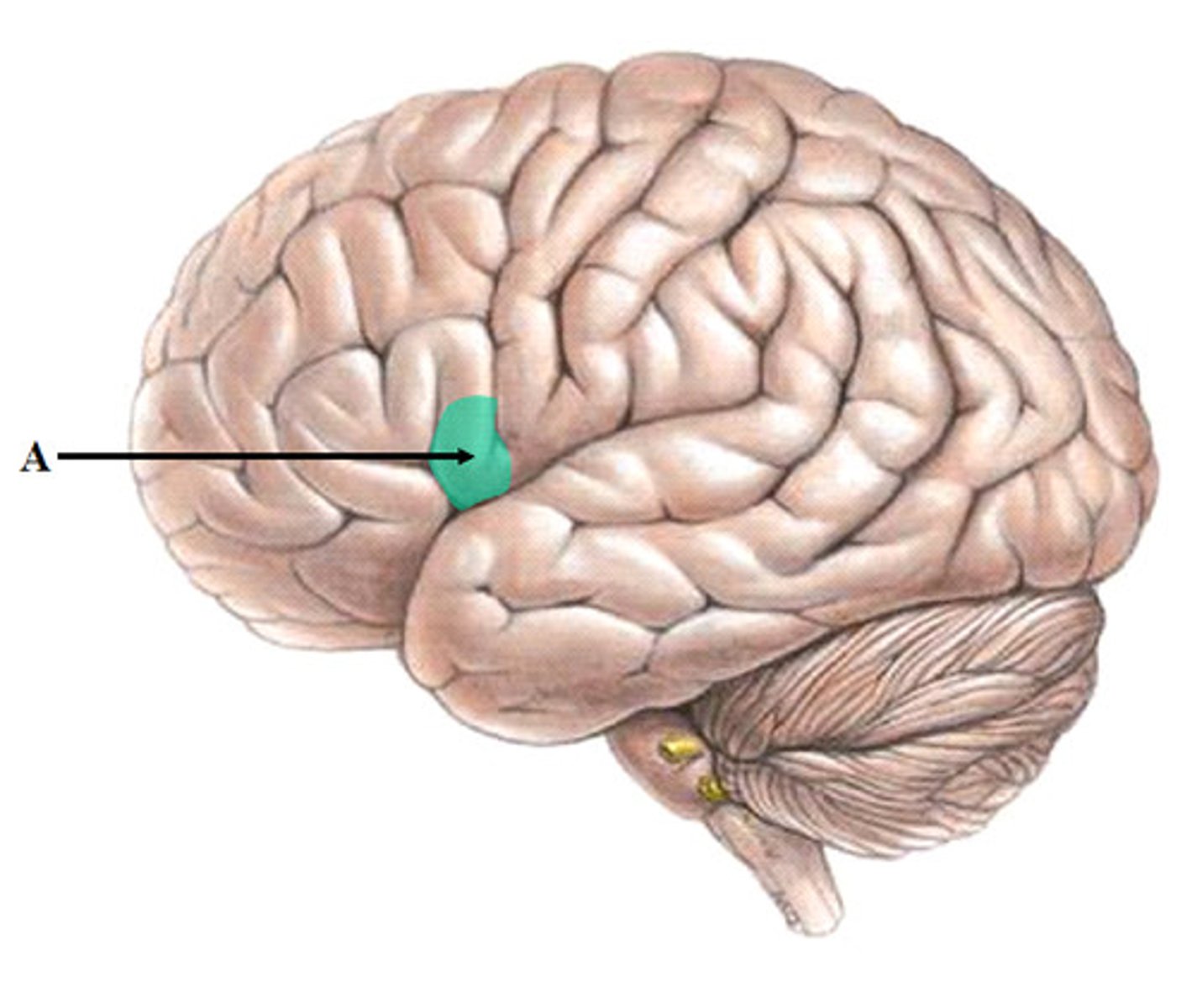
broca's area
speech production