patient with joint replacement
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
artho
a prefix meaning joint
arthroscopy
the repair of joint problems through the operating arthroscope or open joint surgery
arthroplasty
forming a “new joint”
hemiarthroplasty
the replacement of one of the articular surfaces (ex half of hip joint)
osteotomy
surgical cutting of the bone
prosthesis
artificial substitute for a missing part of the body (replacement)
THA/THR
total hip arthroplasty/total hip replacement
TKA/TKR
total knee anthroplasty/total knee replacement
hip, knee, finger joints
replaceable parts
shoulder, elbow, wrist, ankle
less frequently replaced
arthritis
d/t damage to joints can lead to pain and decreased mobility and function
osteoarthritis: more common in older adults
rheumatoid arthritis: can happen in children
(individual that gets joint replacement)
trauma → functional joint damage
from fractures
certain hip fractures
ex break hip at trochanter area which cuts off blood supply leads to necrosis of that joint
(individual that gets joint replacement)
congenital deformity → functional joint damage
hip dysplasia: incorrectly formed/not fully formed hip joints (not formed properly)
(individual that gets joint replacement)
tumors
__ can invade and cause death of bone
(individual that gets bone replacement)
avascular necrosis
if any joint is w/o blood supply, it will not get O2 or nutrients = joint death/necrosis
sickle cell anemia: clotting from sickle cells and no longer distribute O2 and nutrients
(individual that gets bone replacement)
replacing a joint with an artificial one can __
increase mobility, use, joint stability, & relieve pain
(mobility, functionality, stability, comfort)
when do people get joint replacement?
after all other, more conservative therapies for healing and health have failed
PT physical therapy
medication (pain control/decrease inflammation)
joint injections
weight loss
activity modification (using a cane)
(people try other options first and last resort is surgery for joint replacement)
R hip prosthesis
joint stem important bc this depends on the person (tall vs short)
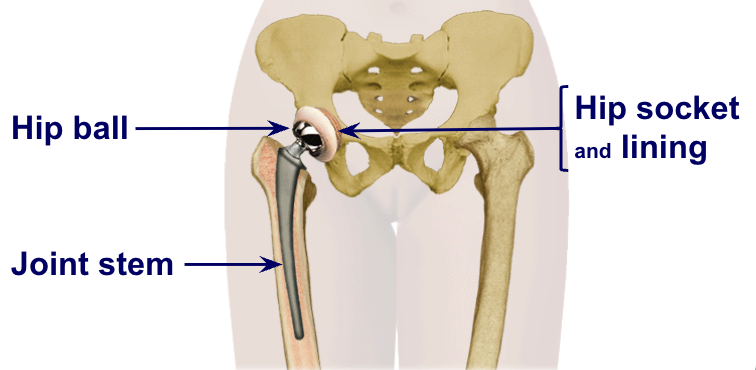
component material
plastic (polyethylene): particularly for the cup (hip socket & lining) to make it smooth for rotation
metal: cobalt chrome or titanium (for joint stem)
ceramic: actually a metal oxide (ball of new hip; seems to last longer)
cement: actually more of a filling compounds; hold “after market parts” in place
problem with cement, over years it can dry, flake off and you can get loosening of parts
cementless prosthesis
more common now; prosthesis is hammered into more precisely bored hole in the femur
see far fewer disadvantages
cementless hip prosthesis advantages
avoid cement relate problems (flaking or dried cement)
minimal risk of prothesis bone bond loss
prosthesis has porous coating so the actual bone grows into the porous coating which allows overtime for a stable joint since it becomes united
cementless hip prosthesis disadvantages
risk of bone marrow chuncks forced into circulatory during shaft replacement
potential need for weight bearing restriction
thigh pain (larger prosthesis)
loosening of fibers from porous coated surface
requires good circulation to injury site so it may not be appropriate
cemented hip prosthesis
the prosthesis is placed into a bored opening in the femur and surrounded by the bone cement
bored opening does not have to be precise
cemented hip prosthesis advantages
surgical skill deviations
early weight bearing
is smaller, lighter prosthesis
is more cost effective
cemented hip prosthesis disadvantages
cement may cause circulatory interruptions
with age, cement can crack → bonding loss between prosthesis and bone → joint instability
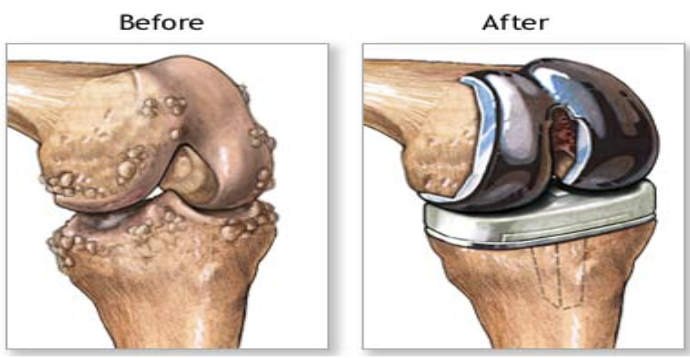
knee prosthesis
before: left has lost its cushioned plate between bones and now there’s friction (bones are right on top of each other)
the bump = bone spurs are inflammation of bone → causes excess bone growth
after: joint prosthesis allowing for smooth movement
smooth base (plasticky base) on bottom portion; metallic piece fitted over the top of femur
complications of joint replacement
dislocation/loosening (osteolysis) of artificial joint (inflammation in the area that does not allow for it to be stable)
infection at surgical site
thromboembolism
complications of immobility
long term
heterotopic ossification: extensive bone growth
avascular necrosis: lack of blood supply to the area d/t damaging of blood vessels
loosening of the joint: may not loosen at first but can in many years down the line
nursing goals
minimize discomfort/pain
prevent infection of surgical site (do not change sterile dressing frequently as it actually helped prevent infection; maybe air out site for faster healing)
prevent/minimize negative consequences of immobility
prevent dislocation/loosening of prosthesis (certain position can prevent this)
post op nursing responsibilities
vital signs/neurovascular checks as ordered (q 1-2 hours)
maintain body/limb alignment (to prevent stress on other joints)
home health/social service for rehab referrals
control pain
medications: IV, PO, PCA (patient controlled analgesia), nerve block
as needed and before planned activities
nerve block: local anesthetic and less pain (usually for knee replacement) more likely to participate in therapy = more likely to progress
became a part of procedure rather than giving lots of analgesics
individualized strategies
reposition
(postop nursing responsibilites)
respiratory toilet
prevent atelectasis, pneumonia through coughing, deep breathing, incentive spirometer, OOB, fluid
C-DB, IS
(postop nursing responsibilities)
monitor incision
infection, bleeding, record/drainage, drain output, maintain clean/dry dressing (no damp dressing because it can cause bacteria growth)
(post op nursing responsibility)
prevent DVT
thrombus preventive therapy
Lovenox, Coumadin, Aspirin, others
AE hoses/SCDs
activity and weight-bearing as allowed by surgeon
OOB ASAP, with order
PROM (passive range of motion)
assess skin integrity
investigate:
complaints of itching, burning (especially heels)
redness of bony prominences
OOB to promote healing
(postop nursing responsibilities)
nutrition/hydration
balanced diet for healing
energy for PT/activity
(postop nursing responsibilities)
neurovascular assessment/concerns
surgery can damage nerves and vessels; need to assess beyond surgery
if replaced shoulder → check hands
if replaced knee → check feet
neurovascular assessment/concerns (early ~ 3Ps)
pain: unrelieved with medication or repositioning/elevation
paresthesia: numbness, tingling, pins/needle sensation
pallor: cap refill time > 3 secs, bluish fingers/toes
neurovascular assessment/concerns (late ~ 3Ps)
polar: skin temperature - cool/cold finger/toes
paralysis: unable to move fingers/toes
pulses: palpable pulses, doppler pulse, no pulse
dislocation of hip prothesis human response
increased pain, swelling, immobilization
shortening of affected leg
abdominal internal/external rotation (sign that hip is no longer in its socket)
restricted movement
“popping” sensation of affected hip
prevent prosthesis dislocation
PROPER POSITIONING: maintain abduction for some replacements
put a wedge between 2 legs (abductor pillow) because when you keep legs together/crossed legs → increases chance of hip dislocation
sometimes instruction to not flex hip > 90 degrees (hip higher than knee)
when you try to pick up something from the floor or tying your shoes
no internal or external rotation of the affected leg/hip
knee pointing up straights
depends on the type of procedure; more common for posterior approach procedures
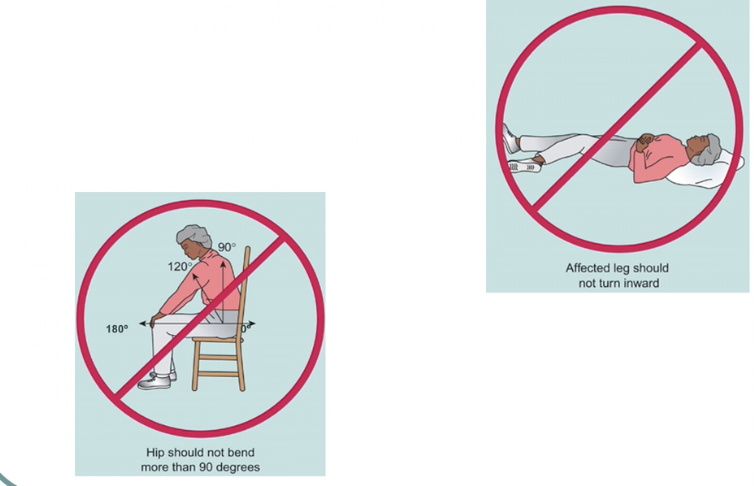
hip dislocation risk
greatest during the first 3 months post-op
other risk factors: age, bone loss, RA, cognitive impairment, implant issues
may not remember all the precautions
important to know the SPECIFIC precautions from surgeon (depends on surgical approach)
give printed literature with pictures to patient and review BEFORE discharge
dislocation of knee prosthesis
human response
pain or swelling after/with movement
an obvious deformity of the knee (no longer aligned properly, looks strange)
numbness in the foot d/t pressure on the nerves
no pulses in the foot (decrease pulse) d/t pressure on the blood vessels
(less common than hip dislocation)
nursing intervention - prevent knee dislocation
proper positioning
maintain leg in full extension (fully straight)
towel roll under ankle of operative leg
reposition towel roll frequently to prevent nerve damage
knee immobilizer (aka POKI: post operative knee immobilizer)
foam wrapped around leg with hole for knee
has rigid back and keeps legs straight to maintain joint stability when OOB
nursing interventions- maintain joint function
polar pack (aka bio chill)
wrap that goes around the knee attached to cooler via tube
cooling circulates through wrap
decreases inflammation and pain (provides comfort)
nursing interventions- maintain joint function
CPM (continuous passive motion)
put leg and slowly extends & flexes knee
can wear at night since it promotes venous return and prevents stiffening of joint
nursing interventions- maintain joint function
documentation
note and document differences
in time on operative limb
difference between operative limb and nonoperative limb
general discharge instructions
continue with PT as ordered
medication education
education on anticoagulant to prevent blood clot
when to contact PCP/Surgeon
elevated temp/fever, drainage from surgical site, sudden increase in pain, significant changes in ROM, gait instability
general discharge instructions (hip)
follow specific positonig guidelines (approach dependent)
general discharge instructions (knee)
avoid prolonged kneeling positions
no running or involvement in sporting activities requiring high speed running and/or jumping until OK with MD/PT