Carotid Treatment (vascular unit 1 )
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What are the medical treatments that control risk factors?
Control risk factors
Exercise regularly
Lose weight
Quit smoking
Change dietary habits
Control diabetes
what are the medications that control carotid disease and what do each do?
Medications
Blood thinners, Lowers platelet aggregation, Aspirin / plavix / persantin
Statins, Lowers cholesterol
ACE inhibitors, Control blood pressure
what are the surgical treatment
Stent
Endarterectomy
Bypass
For carotid Artery stenting (CAS), how effective is this treatment? what are the clinical trials and what are the limitations?
Has gained in prominence
Treatment just as effective as endarterectomy
Clinical trials
CREST
CAVATAS
SAPPHIRE
Limitations
Contrast allergies
Angioplasty
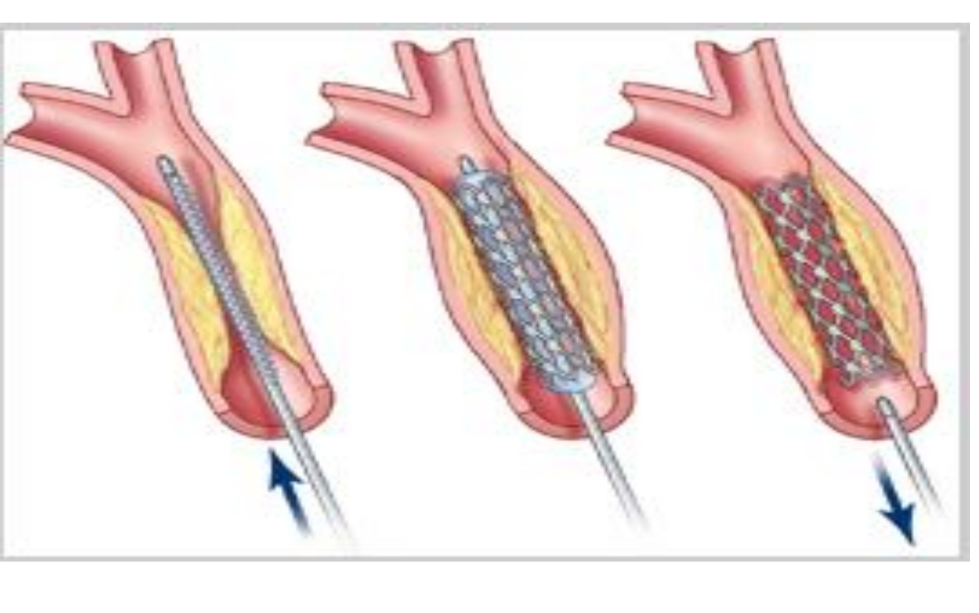
what type of technique is this? what is used to image the vessel, how is it placed?
Angioplasty
Angioplasty
Seldinger technique
X-ray dye is used to image vessel
Catheter manipulation
Open the vessel – balloon
angioplasty
Deploy the stent
Stent is placed in where and what does it have a potential for (risk?)
Stent is placed in the narrowed
region
Potential for emboli; basket “placed”
above narrowed region to catch any
emboli
what are the abnormal findings for stent (3?)
Residual / Recurrent stenosis
Myointimal hyperplasia
Stent malposition
what is Residual / Recurrent stenosis
Atheromatous plaque formation
what is Myointimal hyperplasia
Growth of what? develop at where? replaces what layer and what can it lead too? lower risk for what?
Growth of cells
Develop at the stent site over a
period of time
Replaces the removed intimal layer
Can lead to stenosis
Lower risk for stroke / occlusion
what is Stent malposition
Not in correct position
Stent has peeled away from the wall
Abnormal findings
Duplex US
both carotid systems evaluated, interval testing is 1-2 years
every 6 months is indicated if what?
Velocity numbers
– >75% DR, what is the PSV, EDV, ICA:CCA Ratio
every 6 months is indicated if residual / recurrent ipsilateral or contralteral lesions (>50% DR)
Velocity numbers
– >75% DR
PSV = >300cm/s
EDV = 125-140cm/s
ICA:CCA ratio = >4:1
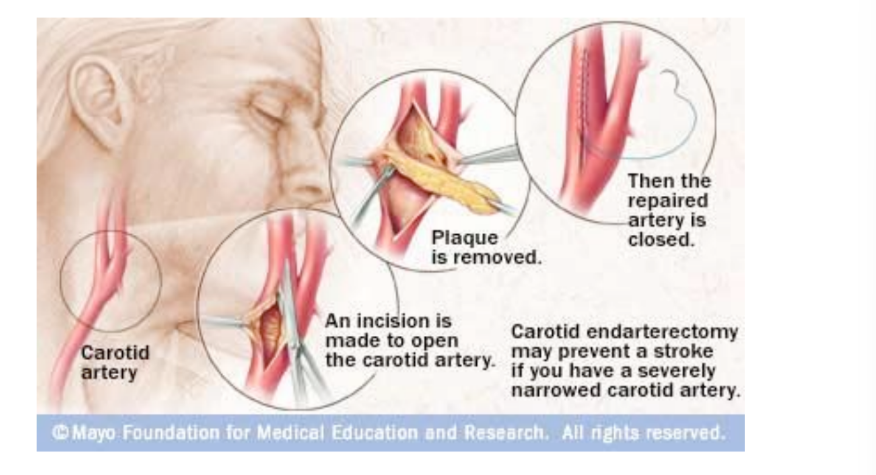
what is Endarterectomy explain the procedure and what layers are removed
Surgical procedure
Plaque is removed from the artery
Carotid is opened length-wise
Temporary shunt is placed to bypass
disease segment
Plaque is removed
Intima and media layers
Carotid is sewn back together using
a synthetic patch
Endarterectomy sonographic appearance
what layers do you not see?
sutures can appear how?
wall thickening can occur-2 types
doppler appearance how
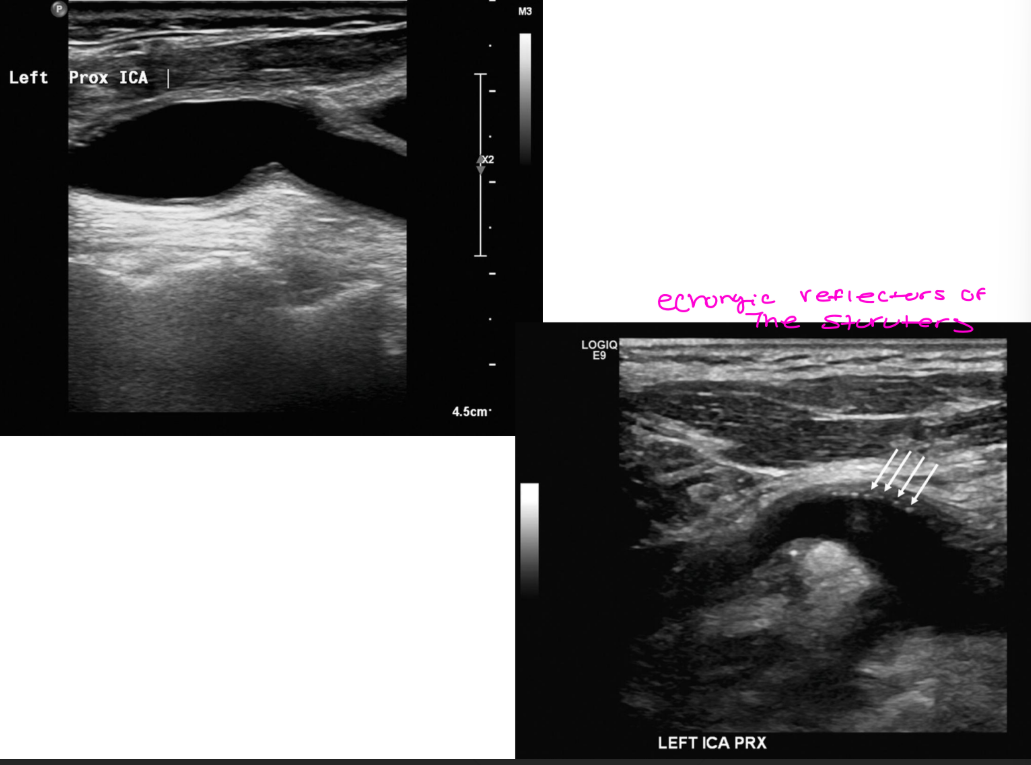
Sonographic appearance
Absent intima / media stripe
Sutures can appear as echogenic
reflector
Wall thickening can occur
Intimal hyperplasia
Re-stenosis can occur
Doppler appearance
Color – disturbed/flow
separation
Spectral – low velocity, disturbed
waveform
what are the abnormal findings for Endarterectomy… explain what its due too and what are the potential to cause
Abnormal findings
Residual / recurrent stenosis
Due to atheromatous plaque
Intimal hyperplasia
Intimal flap
Distal end of endarterectomy site
Cause flow disturbances
Potential to cause
Dissection
Thrombosis
Restenosis
Endarterectomy abnormal findings more
Myointimal hyperplasia
Causes focal / diffuse
narrowing
Overgrowth of tissue layer
that replaces the removed
intima
Occur within the first 3
years of surgery
Lower risk for stroke /
occlusion
Endarterectomy
Abnormal Findings
Duplex ultrasound of bilateral carotid
systems
Duplex surveillance is performed every 1-2
years
6-month interval surveillance with
>50% DR
Velocity numbers for >75% DR
what are the PSV, EDV, ICA:CCA ratio
PSV >300cm/s
EDV > 125-140cm/s
ICA:CCA ratio >4
Bypass procedure explain what it is
Procedure in which blood is rerouted
around a severely diseased section of an
artery
Long segment arterial disease
Aneurysm
Infections
Cancer
Radiation arteritis
Recurrent stenosis post
endarterectomy
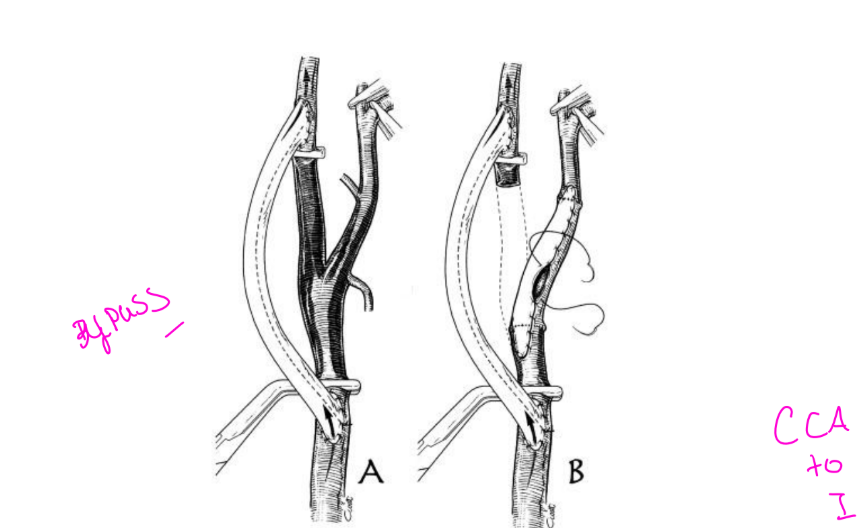
what are the Bypass methods
Graft material
Carotid: performed as a last resort
Much higher incidence of morbidity
Bypass Graft material autogenous vs gortex
Autogenous: using a vessel from the
patient
Gortex: preferred material
for bypass which is performed as a last resort and why would that be ?
Carotid: performed as a last resort
Endarterectomy was unsuccessful
Patient not a viable candidate for
endarterectomy
for bypass Much higher incidence of morbidity
Second surgical procedure
Patients are more critical
Bypass contraindications and what are the types
Underlying and unstable disease
conditions
Poor circulation distally
Poor inflow disease
Types
CCA to CCA ipsilateral
CCA to ICA ipsilateral
CCA to CCA contralateral
Bypass complications are what
Cranial nerve injury
Stroke
Horner Syndrome
Hematoma
Graft thrombosis
Graft infection
what are the Post procedure follow up for bypass
Duplex sonography
CTA
MRA
Conventional angiography