Community Ecology
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
what is a community?
a group of organisms of multiple species interacting with each other either directly or indirectly in a specified place or time
How is species richness defined/determined?
count of the number of species in an area; does not consider how many of each species
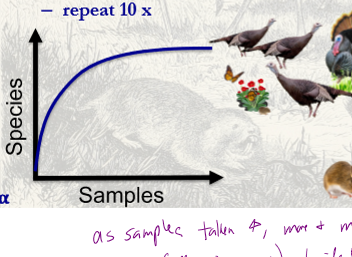
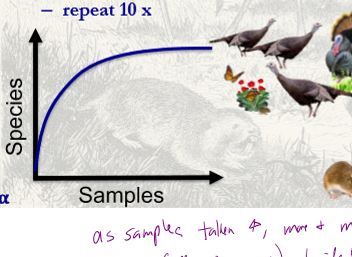
What happens to the number of identifed species in an area as more and more samples are taken?
as samples taken increases, more and more species will be idenitifed until max number of species (all species present) to identift is reached
What is trait/functional diversity?
measures how different species are in terms of their traits/functions (ex. leaf size, body mass, nutrient cycling, pollination, predation)
What is beta diversity?
measures the difference in species composition between sites
What is the food chain? How is energy transferred?
pathway from photosyntethci producers through the various levels of animals
energy lost as move higher in the food chain (about 10% transferred up)
simplistic
bottom up process
What is a food web?
diagram of energy flow
involves harvesting energy from multiple steps in the food chain
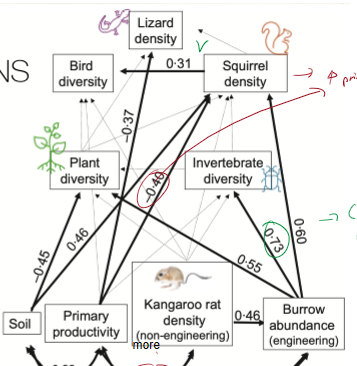
What is structural equation modeling? What do positive and negative numbers indicate?
helps estimate relative importance of each community component to each other
(-) = more of beginning of arrow reduces end of arrow
(+) = more of beginning of arrow increases end of arrow
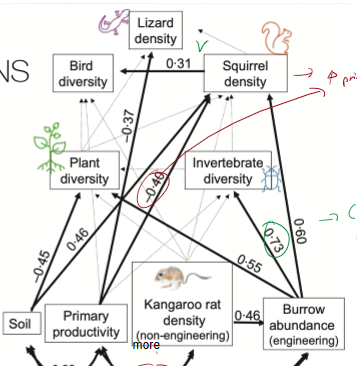
What effect does more primary productivity have on kangaroo rat density?
more primary produces reduces kangaroo rat density
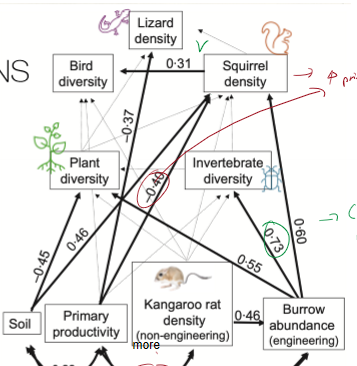
What effect does higher kangaroo rat density have on burrow abundance?
more kangaroo rats equals higher burrow abundance
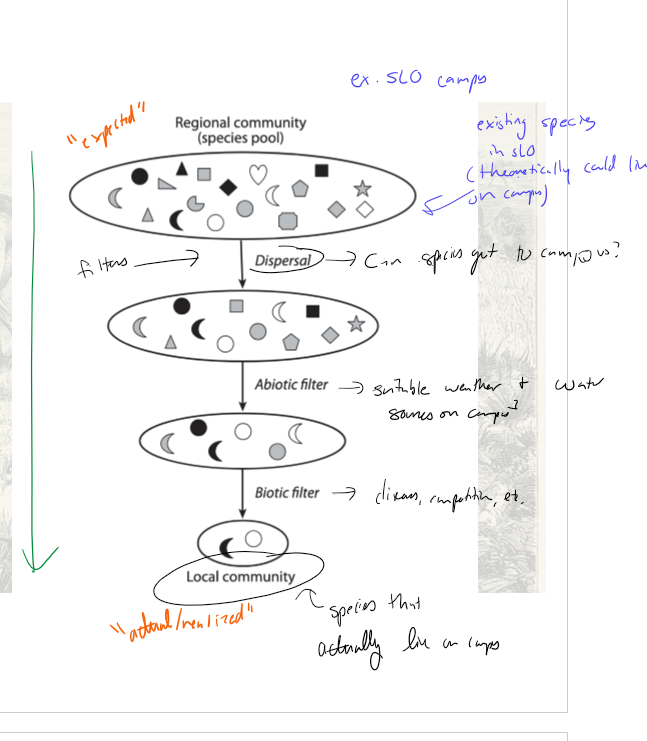
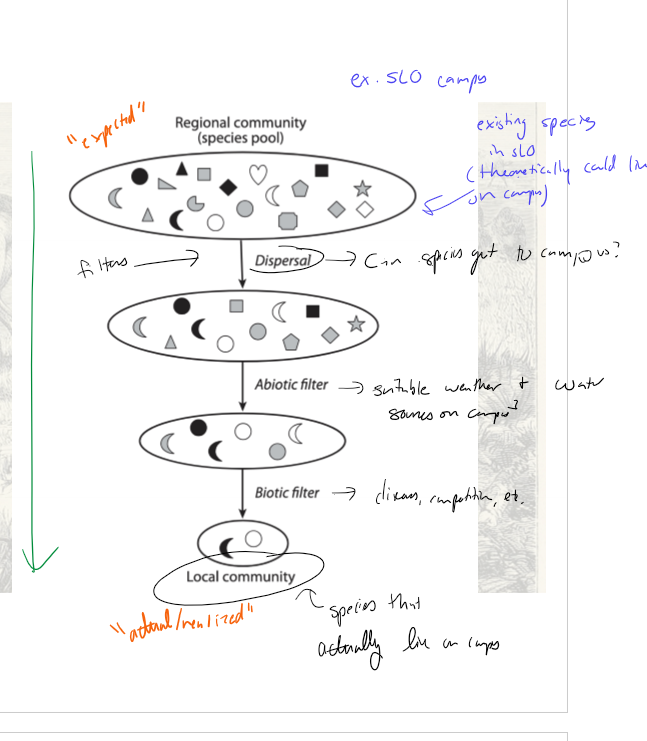
What is the filter model and how does it work?
model that filters the “possible” regional community (species pool) down to the “realized/actual” local community through dispersal filters, abiotic filters, and biotic filter
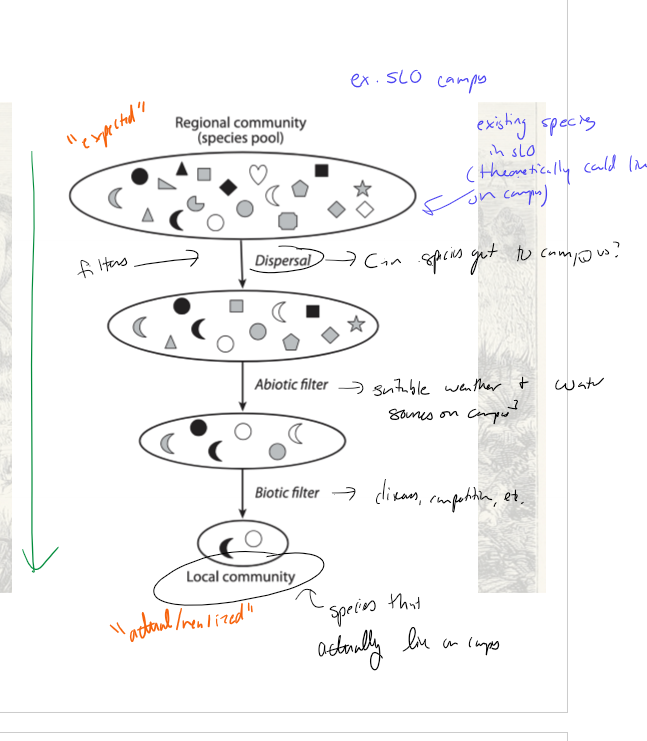
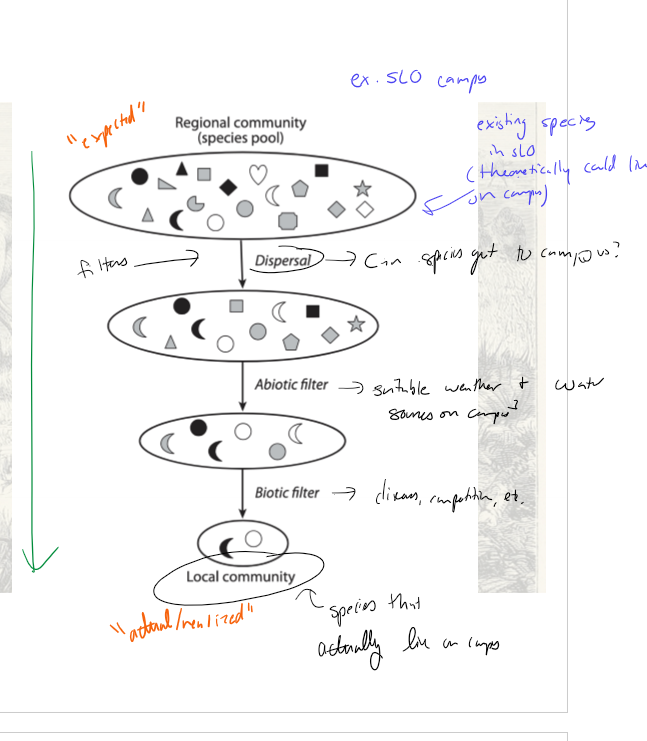
Give an example of the filter model using the cal poly campus
regional community = all species in slo
dispersal filter = can the species get to campus?
abiotic filter = does the species have suitable weather and water sources on campus?
boitic filter = does the species have food? Is it impacted by disease, competition, etc?
local community = actual/realized, species that are actually on campus
What is the unified theory? What are the ways to gain and lose species?
4 high level processes that underly community dynamics when only considering species richness and compisition
gain: speciation, dispersal/immigration
lose: drift, selection