Structure and Function of Skeletal Muscle
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
What percentage of total body weight do skeletal muscles comprise?
40-50% of total body weight.
What is the scientific study of muscles called?
Myology.
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
Skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle.
What are the characteristics of skeletal muscle?
Skeletal muscles are striated, voluntary, multinucleated, and part of the somatic nervous system.
What is the primary function of skeletal muscle?
To move bones of the skeleton.
What distinguishes cardiac muscle from skeletal muscle?
Cardiac muscle is striated, involuntary, and the fibers are attached by intercalated discs.
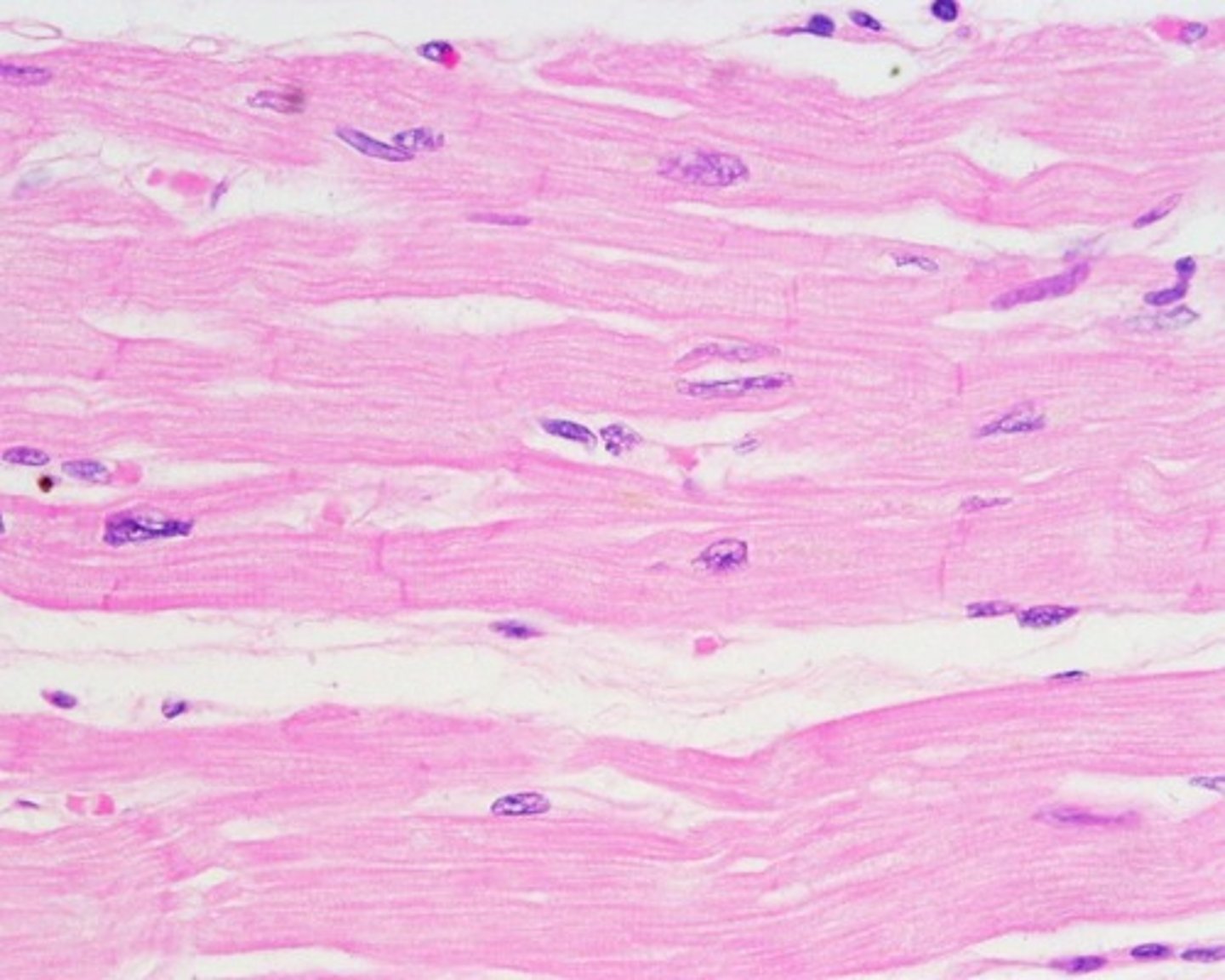
Where is smooth muscle found in the body?
In the walls of hollow internal structures such as blood vessels, airways, and organs in the abdominopelvic cavity.
What type of muscle tissue is involuntary and non-striated?
Smooth muscle.
What are the functions of muscle tissue?
Producing body movement, stabilizing body position, regulating organ volume, moving substances within the body, and producing heat.
How do sphincter muscles function in the body?
They sustain contraction to prevent outflow of contents from hollow organs, such as the stomach and urinary bladder.
What role does cardiac muscle play in the circulatory system?
It pumps blood through the body's blood vessels.
What is the significance of muscle contraction in terms of heat production?
Muscle contraction produces heat, and shivering increases the rate of heat production.
What is electrical excitability in muscle tissue?
The ability to respond to certain stimuli by producing electrical signals.
What is contractibility in muscle tissue?
The ability of muscle tissue to contract forcefully when stimulated by an action potential.
What does extensibility refer to in muscle tissue?
The ability of muscle to stretch without being damaged.
What is elasticity in muscle tissue?
The ability of muscle tissue to return to its original length and shape after contraction.
What is the basic cellular unit of skeletal muscle?
Muscle fibers.
What is fascia in the context of muscle tissue?
A sheet or broad band of fibrous connective tissue.
What are the two types of fascia associated with skeletal muscle?
Superficial fascia and deep fascia.
What is the function of superficial fascia?
It separates muscle from skin, provides a pathway for nerves and blood vessels, stores triglycerides, and serves as an insulating layer.
What is deep fascia?
Dense, irregular connective tissue that allows free movement of muscles and carries nerves and blood and lymphatic vessels.
What are the three layers of connective tissue that protect and strengthen skeletal muscle?
Epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium.
What does the epimysium surround?
It surrounds the entire muscle.
What does the perimysium surround?
It surrounds bundles of muscle fibers (fascicles).
What does the endomysium surround?
It surrounds individual muscle fibers.
What is an aponeurosis?
A broad and flat tendon.
What is the blood supply like for skeletal muscles?
Skeletal muscles are well supplied with nerves and blood vessels.
What are muscle fibers also called?
Myofibers.
What are myoblasts?
Cells that produce muscle fibers.
What are satellite cells?
Unspecialized cells that multiply and produce muscle fibers.
What is sarcoplasm?
The cytoplasm of the muscle fiber, located within the sarcolemma.
What important protein does sarcoplasm contain for oxygen binding?
Myoglobin.
What are glycosomes?
Granules that contain glycogen, providing glucose during periods of muscle cell activity.
What is the sarcolemma?
The muscle cell membrane.
What is a sarcomere?
The contractile unit of muscle fibers, located between two Z discs.
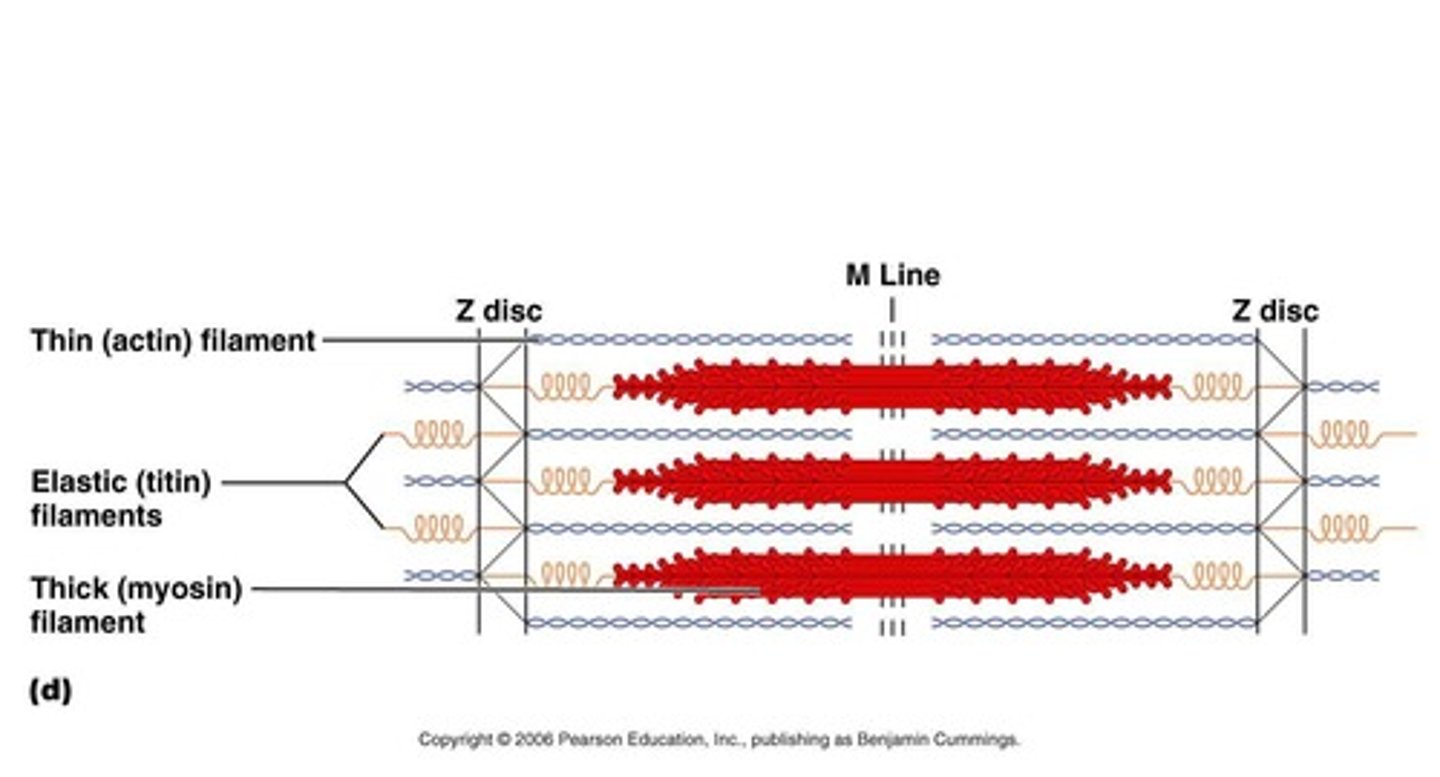
What are the components of a sarcomere?
A band, I band, H zone, and M line.
What are myofibrils?
Contractile elements that contain sarcomeres and myofilaments.
What are the two types of filaments found in myofibrils?
Thin filaments (actin) and thick filaments (myosin).
What is the role of tropomyosin in muscle contraction?
It helps stiffen and stabilize the actin.
What is the function of troponin?
A globular protein that binds to actin, tropomyosin, and calcium ions.
What is titin?
A giant protein that holds thick filaments in place and helps muscle cells spring back into shape after being stretched.
What is dystrophin?
A protein that keeps thin and thick filaments in proper alignment and gives myofibrils elasticity and extensibility.
What is the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
An elaborate smooth endoplasmic reticulum that contains calcium.
What are T tubules?
Invaginations of the sarcolemma that open to the outside and are filled with extracellular fluids.
What is the neuromuscular junction?
The site where a motor neuron meets the muscle fiber, separated by a gap called the neuromuscular cleft.
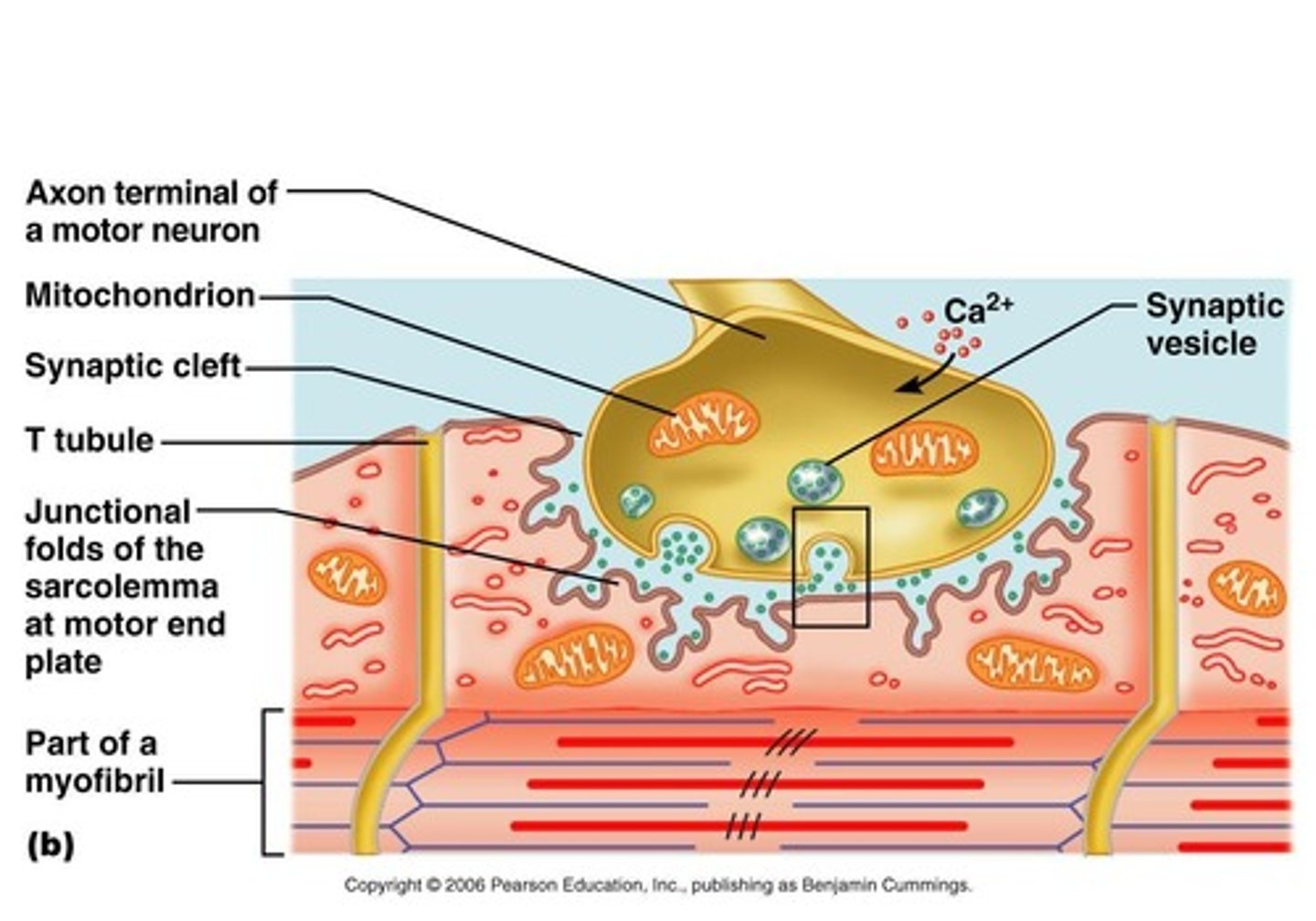
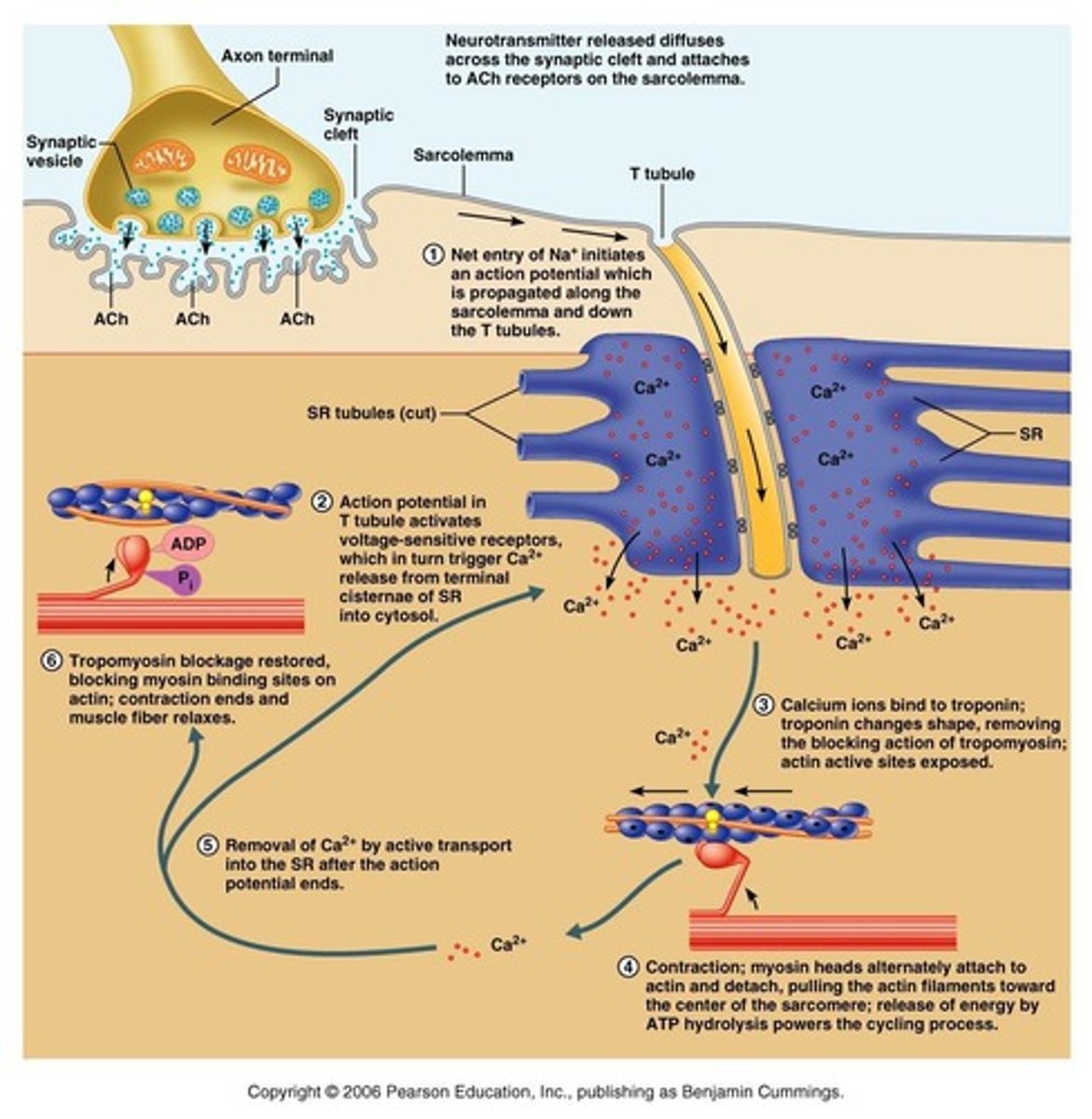
What is the role of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction?
Acetylcholine is released from the motor neuron and causes an end-plate potential (EPP), leading to depolarization of the muscle fiber.
What is a motor unit?
A motor unit consists of a somatic motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it stimulates.
How many muscle fibers does a single motor neuron typically contact?
On average, a single motor neuron makes contact with about 150 muscle fibers.
What is the sliding filament model of muscular contraction?
Muscle shortening occurs due to the movement of actin filaments over myosin filaments, forming cross-bridges and reducing the distance between Z-lines of the sarcomere.
What is maximal oxygen uptake?
The rate of oxygen consumption in the body, which is a function of cardiac output.
What does the equation CO = SV x HR represent?
This equation represents cardiac output (CO) as the product of stroke volume (SV) and heart rate (HR).
What is oxygen debt?
Oxygen debt refers to the oxygen that was withdrawn from reserves in hemoglobin and myoglobin, representing the difference between O2 at rest and elevated rates of O2 consumption.
What is the anaerobic pathway in muscle metabolism?
The anaerobic pathway involves glycolysis and lactic acid formation, using glucose as an energy source, producing 2 ATP per glucose without using oxygen.
What is the duration of energy provision for anaerobic metabolism?
The anaerobic pathway provides energy for about 60 seconds or slightly more.
What is the aerobic pathway in muscle metabolism?
The aerobic pathway involves aerobic cellular respiration using glucose, pyruvic acid, free fatty acids, and amino acids, producing 36 ATP per glucose, CO2, and H2O.
What is the duration of energy provision for aerobic metabolism?
The aerobic pathway can provide energy for hours.
What happens during short-duration exercise?
ATP stored in muscles is used first, followed by glycogen breakdown to glucose for ATP generation.
What happens during prolonged-duration exercise?
ATP is generated by the breakdown of several nutrient energy fuels through the aerobic pathway, using oxygen from myoglobin or delivered in the blood.
What are slow oxidative fibers?
These fibers have slow myosin ATPase activity, are smallest in diameter, generate ATP aerobically, have many mitochondria, and are fatigue-resistant, suited for activities like running and marathons.
What are fast oxidative fibers?
These fibers have fast myosin ATPase activity, contain the most myofibrils, can generate ATP both aerobically and anaerobically, and are suited for activities like walking and basketball.
What are fast glycolytic fibers?
These fibers generate the most powerful contractions, have fast myosin ATPase activity, low myoglobin, few mitochondria, and fatigue quickly, suited for short-duration activities like weight lifting.
What is muscle tone?
Muscle tone is the continuous and partial contraction of muscles that helps maintain posture.
What happens when motor neurons serving a skeletal muscle are damaged?
The muscle becomes flaccid, resulting in a state of limpness where muscle tone is lost.
What is isotonic contraction?
Isotonic contraction involves body movement and moving objects, where tension generated overcomes resistance, causing muscle shortening.
What are the two types of isotonic contractions?
Concentric contraction, where the muscle shortens, and eccentric contraction, where the muscle contracts while being lengthened by an external force.
What is isometric contraction?
A type of contraction where tension generated is not enough to exceed the resistance of the object to be moved, resulting in no muscle shortening or joint movement.
What are the three phases of a muscle twitch?
1. Latent period: events of excitation-contraction coupling; 2. Period of contraction: cross bridge formation and tension increases; 3. Period of relaxation: Ca2+ reentry into the SR and tension declines to zero.
What is a twitch contraction?
The contraction of all the muscle fibers in a motor unit in response to a single action potential in its motor neuron, lasting 20-200 milliseconds.
What happens during depolarization in muscle fibers?
Depolarization occurs due to Na+ entry into the muscle fiber.
What happens during repolarization in muscle fibers?
Repolarization occurs due to K+ exit from the muscle fiber.
What is the refractory period in muscle fibers?
A temporary loss of excitability following sufficient stimulation for contraction.
What is wave summation?
When a second stimulus occurs after the refractory period of the first stimulus is over, but before the muscle fiber has relaxed, resulting in a stronger second contraction.
What is unfused (incomplete) tetanus?
A condition where muscle is stimulated at a low frequency (20-30 times/second), resulting in partial relaxation between stimuli.
What is fused (complete) tetanus?
A condition at high stimulus frequencies (80-100 times/second) where there is no relaxation at all between stimuli.
What is muscle recruitment?
The process in which the number of active motor units increases, responsible for smooth movement rather than jerks.
What are the functional groups of skeletal muscles?
1. Prime movers: provide the major force for a specific movement; 2. Antagonists: oppose or reverse a particular movement; 3. Synergists: add force to a movement and reduce undesirable or unnecessary movement.
What occurs during the latent period of a muscle twitch?
Events of excitation-contraction coupling.
What is the role of Na+ channels during muscle contraction?
Na+ channels open for depolarization due to Na+ entry.
What is the role of K+ channels during muscle contraction?
K+ channels open for repolarization due to K+ exit.
How does muscle tone contribute to muscle function?
Muscle tone maintains a constant, slightly contracted state, which is essential for posture and readiness for movement.
What is the significance of muscle recruitment in movement?
Muscle recruitment allows for graded responses and smooth movements by activating more motor units as needed.
What is the difference between prime movers and antagonists?
Prime movers provide the major force for a specific movement, while antagonists oppose or reverse that movement.
What is the effect of high stimulation frequency on muscle contraction?
At high stimulation frequencies, muscle fibers do not relax between stimuli, leading to fused (complete) tetanus.
What is the duration of a twitch contraction?
A twitch contraction lasts between 20 to 200 milliseconds.
How does wave summation affect muscle contraction strength?
Wave summation increases contraction strength by allowing subsequent stimuli to generate stronger contractions before the muscle has fully relaxed.
What is the function of fixators in the muscular system?
Fixators prevent the bone from moving, such as the rhomboid muscle holding the scapula firmly.
How are skeletal muscles named based on location?
Skeletal muscles are named according to the bone or body region associated with the muscle.
What does the term 'deltoid' refer to in muscle naming?
The term 'deltoid' refers to the shape of the muscle, which is triangular.
What does 'maximus' and 'minimus' indicate in muscle naming?
'Maximus' indicates the largest muscle, while 'minimus' indicates the smallest muscle.
What does the term 'rectus' signify in muscle fiber direction?
'Rectus' signifies that the muscle fibers run straight.
What are the two types of muscle arrangements based on the direction of fibers?
Muscle fibers can be arranged as parallel or at angles to an imaginary defined axis.
What is a convergent muscle and give an example?
A convergent muscle has fascicles that converge toward a single tendon insertion; an example is the pectoralis major.
What is a circular muscle and give an example?
A circular muscle has fascicles arranged in concentric rings; an example is the orbicularis oris.
What is a fusiform muscle and provide an example?
A fusiform muscle is spindle-shaped with parallel fibers; an example is the biceps brachii.
What is the definition of a first-class lever in the body?
A first-class lever has the arrangement of load-fulcrum-effort, like raising your head off your chest.
What is an example of a second-class lever in the body?
Standing on tip-toe is an example of a second-class lever, where the arrangement is load-effort-fulcrum.
Describe the third-class lever system in the body.
A third-class lever has the arrangement of load-effort-fulcrum, exemplified by flexing the forearm with the biceps brachii.
What are the components of a lever system?
The components of a lever system include a lever (bone), effort (force applied), and load (resistance moved by the effort).
What happens to muscle mass as people age?
Aging is associated with a loss of muscle mass, with the rate of loss increasing after 50 years of age.
Can regular exercise training eliminate age-related muscle mass loss?
Regular exercise training can improve strength and endurance but cannot completely eliminate age-related loss in muscle mass.