ib econ - 2.8: Market failure (externalities and common pool resources)
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
credits https://www.econinja.net/microeconomics/2-8-market-failure-externalities-common-pool-resources
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What is allocative efficiency?
Where equilibrium meets at the socially optimum output - at this point, the added benefits for society (marginal social benefits) equal the added costs for society (marginal social costs)
what does ‘social’ mean when referring to marginal social benefits or costs?
the combination of producers and consumers. hence, the socially optimum output is where the combined value of consumer and producer surplus is largest. this happens at the optimal price and quantity.
draw the allocative efficiency diagram
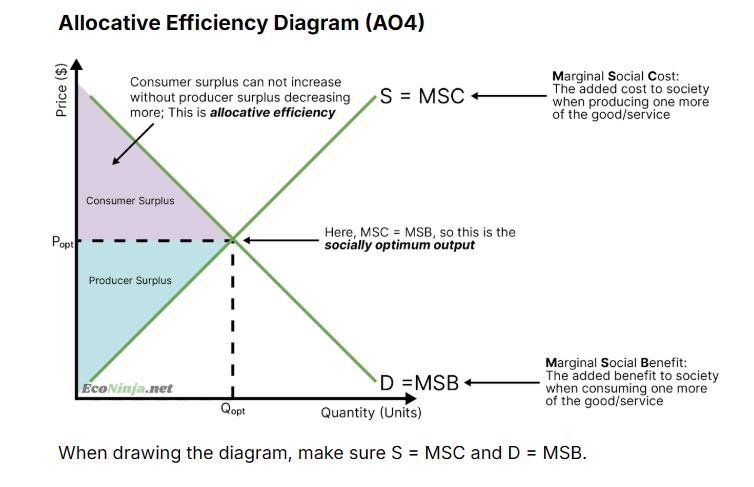
what is a positive externality?
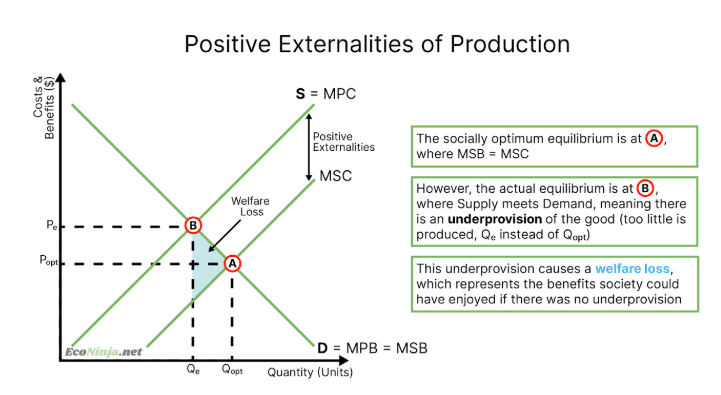
benefits caused by producers or consumers but passed onto a third party. for example, healthy foods cause positive externalities of consumption (society benefits from a less strained health system) and public infrastructure causes positive externalities of production (society benefits from being able to use a fast form of transport)
what are goods that create positive externalities called?
merit goods (examples include the education system, healthcare system, vaccinations, healthy food)
what is the market failure when it comes to merit goods?
there is an under provision or underconsumption of the good
what do msc, msb, mpc and mpb mean?
msc: marginal social cost
msb: marginal social benefit
mpc: marginal private cost
mpb: marginal private benefit
draw the diagram for a positive externality of consumption
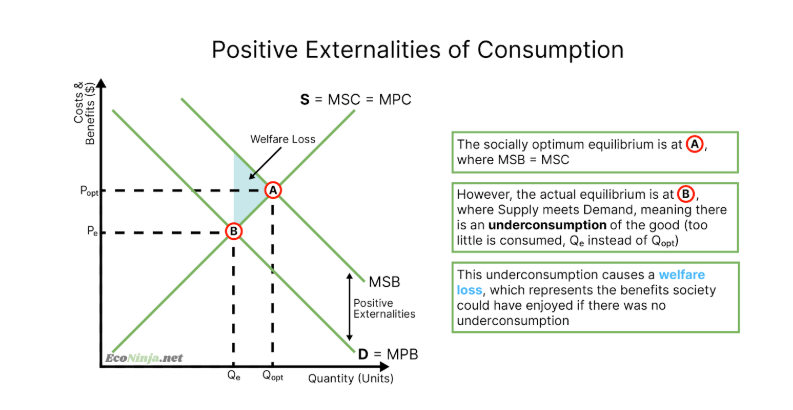
draw the diagram for a positive externality of production
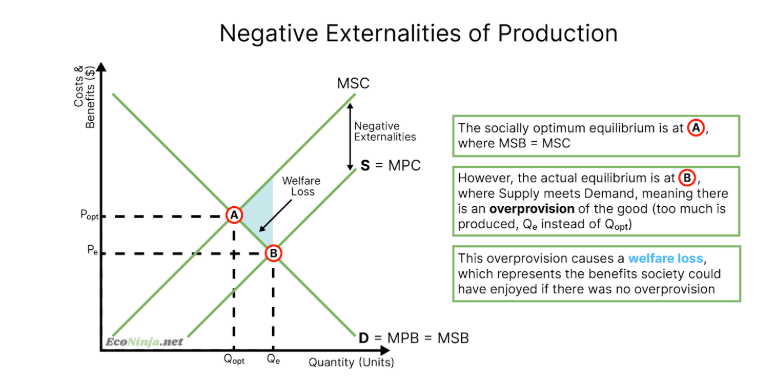
what is a negative externality?
costs caused by producers or consumers that are passed on to a third party (e.g. smoking = negative externality of consumption as society has to pay for your lung cancer treatment, or petrol = negative externality of production (society gets to suffer from the pollution the oil refineries create)
what is a good that creates a negative externality called?
demerit good (such as fast food, tobacco, addictive drugs, petrol)
what is the market failure when it comes to demerit goods?
there is an overprovision or overconsumption of the good
draw the diagram for a negative externality of consumption
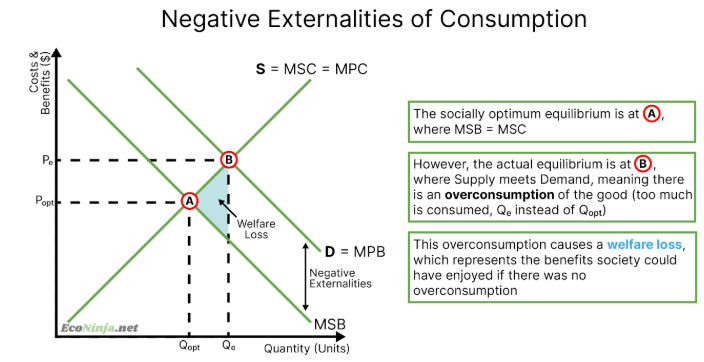
draw the diagram for a negative externality of production
what are the characteristics of common pool resources?
non-excludable: not possible to prevent others from using the resource
rivalrous: if one person/firm uses the resource, the amount others can use is reduced (limited supply)
what do common pool resources create?
a tragedy of the commons, where individuals prioritise themselves over others, causing the depletion of the resource
what is an example of the tragedy of the commons?
You, and the rest of your village, live near a lake with fish in it. The fish is a common pool resource, because:
You cannot prevent others from fishing (non-excludable)
The more you fish, the less others will get (rivalrous)
You know that if everyone fishes too much, the fish population will die out and your village will run out of food. However, you think that if the population will eventually deplete, you should probably fish lots now so you have some spare when the resource runs out.
In other words, you act in your own best interest, at the expense of others. The fish (the common pool resource) eventually die out, as you have over-consumed the shared resource.
how does the tragedy of the commons link to negative externalities?
tragedy of the commons is a result of either overproduction of overconsumption of a certain resource
the use of the resource disproportionately causes negative effects on society
common pool resources are exploited, causing tragedy of the commons, an example of a negative externality of either production or consumption.
what are the four umbrella types of way that the government can intervene to correct externalities?
financial intervention (indirect taxes, carbon taxes, subsidies)
legal intervention (regulation, legislation, tradable permits, international agreements)
soft intervention (education, awareness, collective self-governance)
last resort (direct government provision)
what is an indirect (pigouvian) taxes?
those that are put on goods and services rather than individuals or firms. they make goods more expensive. they are used to correct both types of negative externalities (although they are better suited to production)
draw the diagram for a pigouvian tax on a negative externality of production
because an indirect tax decreases the equilibrium output, it can also be used for negative externalities of consumption, as the end goal is the decrease q.
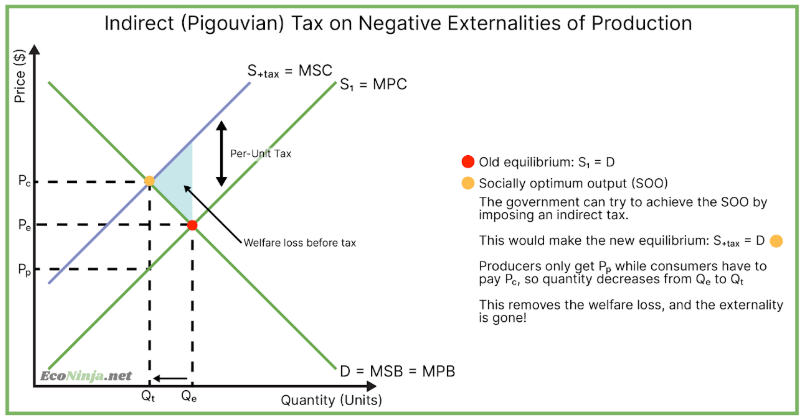
how can we evaluate the effectiveness of an indirect tax?
the effectiveness of an indirect tax depends on the elasticity of the good, but most demerit goods are inelastic, meaning that taxes aren’t super effective.
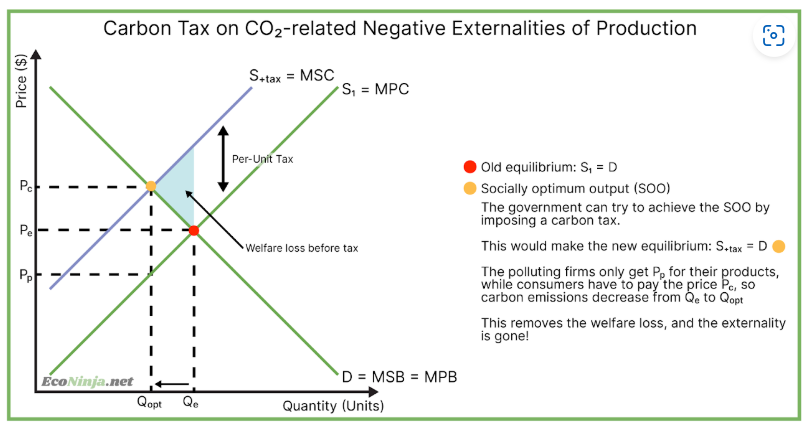
what is a carbon tax?
similar to an indirect tax, but specifically targets sources of carbon emissions, such as polluting factories. this tax is imposed on polluting firms, who then hopefully emit less carbon. used to combat negative externalities of production.
draw the diagram for a carbon tax
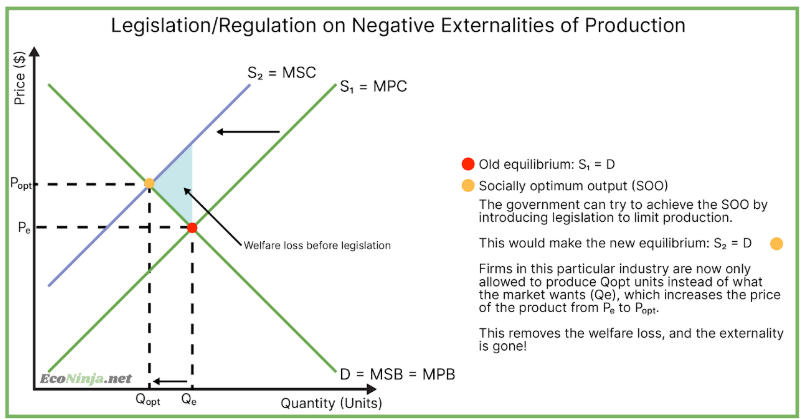
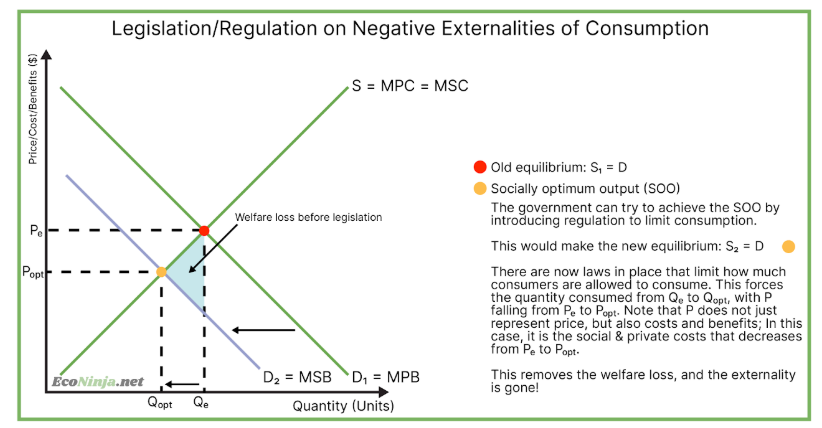
what types of externalities would legislation/regulation help?
any negative externality - laws or policies aim to reduce the welfare loss
what is an example of regulation created by governments to reduce a negative externality of consumption?
in the uk (and many other countries) it is illegal for those under 18 to consume alcohol. this is a regulation created by governments to reduce the negative externalities of consuming alcohol, such as causing a disturbance.
what is an example of legislation created by governments to reduce a negative externality of production?
the eu have laws set against overfishing, where fishing boats are only allowed to catch a certain number of boats per year. this is legislation set by the government to reduce the negative externalities of overfishing, such as the extinction of fish specieis.
draw the diagram for legislation on negative externalities of production.
draw the diagram for legislation/regulation on negative externalities of consumption
how can education and awareness creation correct externalities?
instead of forcing a tax or strict laws, the government can instead encourage more merit goods and less demerit goods by educating its population.
how can tradable permits be used to correct externalities?
tradable permits are permission slips that firms can get in order to be allowed to pollute.
these permits are then able to be bought and sold amongst companies, creating their own markets
this is an effective way to limit negative externalities of production
by limiting the amount of permits issued in the first place, the government can ensure pollution targets are met.
Company A has 1000 permits, allowing them to pollute 1000kg of CO2. They have factories that can in theory pollute less, but don't bother. Company B also has 1000 permits, but desperately needs another 500. Company A can sell 500 of its own permits to B, and they both benefit. A is incentivized to specialize in clean technology, as they make extra money from selling these permits.
how can international agreements correct externalities?
governments can team up and make common taxes, rules and campaigns (as many externalities are worldwide)
an example is the paris agreement, where almost every country worldwide agreed to collectively aim to reduce their carbon emissions (the negative externalities of production). this is much more effective than if just a few countries had done so
how can collective self-governance help to correct externalities?
refers to voluntary actions done by local communities in order to reduce their negative externalities of consumption
for example, beach plastic clean-ups are a form of collective self-governance, where a community reduces the negative externalities of consumption that plastic generates.
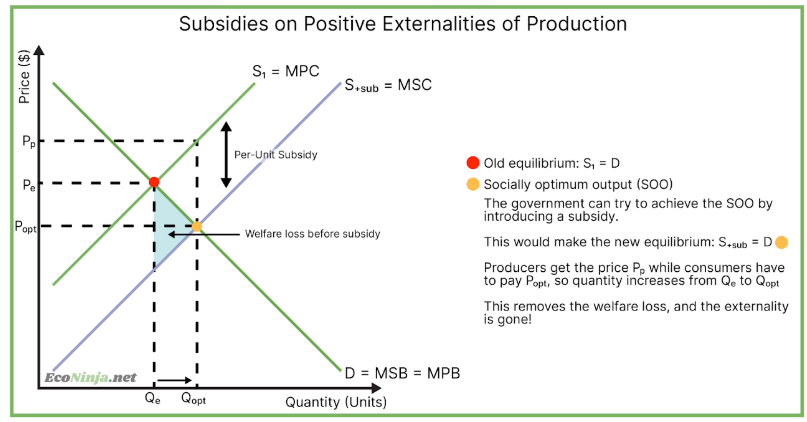
how can subsidies be used to correct externalities?
forms of monetary government assistance for firms or an industry - they reduce the price of goods. they can be used for both types of positive externality.
draw the diagram for a subsidy on a positive externality of production
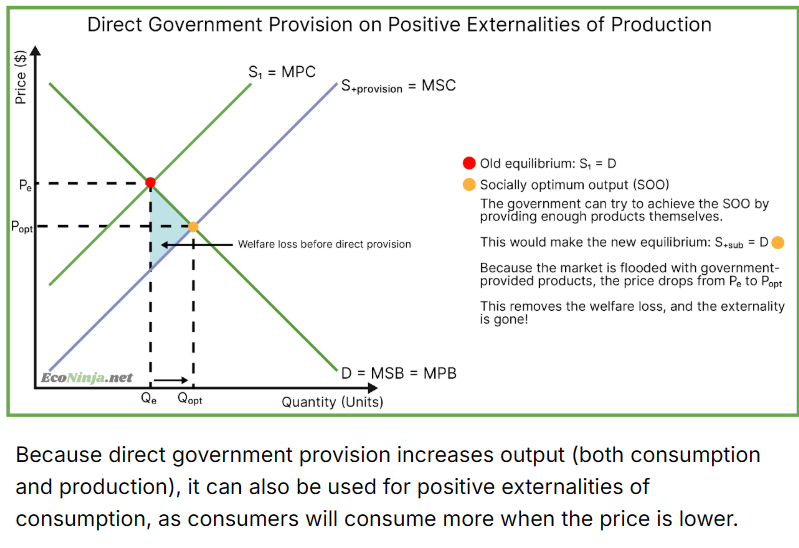
how can direct government provision be used to correct externalities?
when the government ensures there is enough of an underprovided merit good
for example, the gov. builds most schools and parks, because the private market would not provide enough themselves
draw the diagram for direct government provision on positive externalities of production
what are the strengths and limitations of government policies?
challenges involved in the measurement of externalities: very hard to measure the value of social benefit - how much value does a park bring?
degree of effectiveness: government policy is not always perfect (e.g. because someone is aware of the dangers of smoking, doesn’t mean they won’t do it)
consequences for stakeholders: everyone with a stake in the affected market will be affected in different ways by government intervention. for example, large firms may have an easier time adapting to new regulations than smaller firms, decreasing competition
what is the importance of international cooperation (relating to the global nature of sustainability issues)?
many issues relating to externalities are global
climate change caused by co2, for example, cannot be solved by one country as it affects every country
therefore, when dealing with externalities of international scale, it is important that collaboration happens beyond borders
what are the challenges faced in international cooperation?
countries have different priorities
whilst some want to gradually ban the use of oil and gas, others such as saudi arabia and russia profit massively from these industries and are unwilling to cooperate on this issue
what is the importance of international cooperation (relating to monitoring and enforcement)?
some of these international agreements are relatively easy to monitor, such as carbon emissions, which can be detected by satellites in space
however, others are not, as certain countries may provide insufficient or tampered statistics to pass regulations
furthermore, how can rules be properly enforced on a global stage?