Organ Systems
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
The Organ System
Serves a particular purpose within the organism (living thing) in which they exist
they serve a variety of different particular purposes within the human body, but many of these organ systems also exist in a variety of other organisms
The Circulatory System
Responsible for pumping blood to all the tissues of the body
The Heart (diagram is usually drawn in reverse)
Oblique positioned diagonally
Heart divided into two parts by a cellular wall (Spetum) and has four chambers
The Upper Cavities
Right Atrium and Left Atrium
Starts in the left ventricle where the deoxygenated blood and nutrients enter the heart
Starts at the Largest most Powerful Chamber of the Heart
The Left Ventricle.
It pushes blood out to the body
Pushes it out through the biggest artery; the Aorta
The aorta then branches out into smaller arteries
Arties take blood out
Veins bring blood back in
These arteries branch out to large arteries like the femoral artery (runs down the leg) then branches into smaller and smaller arteries until branches into capillaries
Aorta
Biggest artery in the heart
Then branches out into smaller arteries
Arteries
take blood out
Veins
bring blood back in
Capillaries
Very small, tiny even blood vessels connected to the arteries with veins and cells
Part 2
The capillaries weave throughout the tissues and allows cells to absorb the oxygen and the food that the red blood cells are carrying
Then waste product is picked up by other capillaries and is fed back into the veins
These veins pass by organs such as the kidneys that can filter out toxins and eventually, the blood is brought back to the right atria
Part 3
So the blood depleted of oxygen comes back to the right atria and is pushed through a Valve
The valve one directional so the blood cannot go back through the other way. It gets pushed into the right ventricle
The right ventricle then pushes the blood out again to the lungs to be reoxygenated
The lungs alveoli are where capillaries that weave through lungs can be absorbed
Valve
“doors”
Alveoli
are where capillaries that weave through lungs can be absorbed
Part 4
The re-oxygenated blood comes backup and goes into the left atrium
It gets pushed through another one directional valve and into the left ventricle
Now we have oxygenated blood that can go back out into the body again and this circles around in this cycle
White Blood Cells
used to fight disease, sort of the protectors of the body.
Think of them as defenders
e.g. cops on a highway
Red Blood Cells
Transports Hemoglobin, oxygen food supply
Think of them like truckers on highway
police protect them
Where are White and Red Blood Cells Produced?
Both in the BONE MARROW
The Nervous System
Central Nervous System: the brain and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System: all other components of the nervous system such as nerves throughout the body
The Brain
Cerebral Cortex: wrinkly outter layer made up of 4 lobes. It’s responsible for a variety of different higher functioning behaviors like spatial awareness, conscious thought and reasoning, language and vision
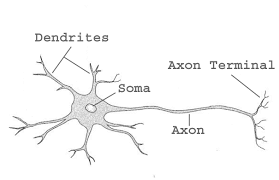
Dendrites and Axon
Nerve cells that make up the nervous system that look like brooms
Dendrites catch messages from other neurons and bring them to the main part of the cell. They help neurons talk to each other!
Axons are like long wires that send messages away from the neuron to other neurons, muscles, or body parts. They help messages travel far and fast!
The axon is wrapped in a myelin sheath
Myelin Sheath to Synaptic Gap
Holds in energy
It’s a special coating that wraps around nerve cells (neurons) to help messages travel quickly and smoothly
that energy gets transmitted through the axon up to the next nerve cell across a gap called the SYNAPSE/SYNAPTIC GAP
Then, the next set of dendrites receives that message and relays it again
We see this occur in the brain, nerves of the spinal cord, and nerve cells that go out to your fingers
When you feel something
Something presses on that nerve and it relays it through millions of nerve cells back to your brain
which itself is made of the same types of nerve cells
The Cerebral Cortex
The wrinkly outer layer (what we picture when we think of a brain)
Made up of 4 lobes
Responsible for a variety of different higher-functioning behaviors like
Spatial awareness
conscious thought,
reasoning,
language ability,
vision
Within the CC, there are Inner Cortical structures (hippocampus, thalamus, hypothalamus) things that process our
satiation,
feeling full,
fear responses, and memory
The Cerebellum
Responsible for the timing of motor movements
It sits at the back of your brain, right under the big part of your brain (the cerebrum).
Even though it’s small, it works without you even thinking about it, ensuring your body moves just right.
There’s specific nerve fibers: Purkinje fibers are the internal timing mechanisms
Balance
Smooth movement
Coordination
e.g. think rah rah robot
The Brain Stem
Responsible for base life-support functions
Respiration
Heart Rate
Helps w/ digestion
The Digestive System
Responsible for breaking down and absorbing food
Salivary Glands and Esophagus
First, eat food and chew it with your teeth causing it to break down the cell walls (plants) you’re coating the food w/saliva from the salivary glands. It also makes it easier for the food to go down your esophagus to the stomach. This is the beginning process of digestion
Stomach and Pancreas
Once the small pieces of food enter the stomach, the stomach has a mucous lining that protects it from digesting itself.
Then the sphincters at both ends that close the stomach off
It then secretes digestive acids produced by organs such as the pancreas.
Those digestive acids further break down the food
Heartburn
When sphincters fail to close off, the stomach acid can come into the esophagus and starts to digest the esophagus itself
Small Intestine
After break down in the stomach, the food gets passed into the small intense, a long winding tract of intestines
This is where we absorb the nutrition
We absorb the nutrition in the small intense
Large Intestine and Colon
After gliding through the tract of the small intense
the depleted food (after nutrition is absorbed) gets passed into the large intestines 3 different parts
ascending
transverse
and the descending parts (the colon)
Rectum
This is where the depleted good passes through before it’s excreted through the rectum
The reproductive system
Most animals → repo sexually
sperm created in the testes
eggs created in ovaries (ova)
When sperm fertilizes an egg, the two haploid cells combine to form a diploid cell
(two haploid cells, only 1 chromosome each combine to form a fertilized cell that has a pair of chromosomes aka diploid cells)
Key Advantage of Sexual Reproduction
Greater Genetic Variation
because you’re sharing genetic information between two parents
so you get a variety of traits from each
Greater variation can be an advantage in terms of Evolution because
traits that can be MORE or LESS useful in a given environment and t- that extra variation makes organism more chance of having a trait maybe useful
Key Disadvantages of Sexual Reproduction vs Asexual Reproduction
Reproduction requires a mate and fertilization
you have no choice after reproduction has taken place
BUT
An organism that reproduces asexually can choose when it wants to produce offspring.
It can wait for right amount of food, right temperature, and right conditions and then reproduce using its own genetic material
Asexual Reproduction Advantages
Aphids
Aphids can use asexual repo in the summertime when they get a lot of food to reproduce thousands and thousands of offspring
Asexual Reproduction Disadvantages
Aphid doesn’t get to combine DNA with another partner to create variation so flawed gene or other disadvantage, trait, will continue to propagate
Types of Reproduction in Plants
Can occur sexually and asexually
Algae
Fungi
Angiosperms
Gymnosperms
Algae
One of the oldest organisms on Earth
Green, photosynthetic plant and it reproduces asexually
Fungi
Only one in the list in terms plant type that’s not photosynthetic
depends on decaying biological material to feed
e.g. can grow on food in your fridge. It doesn’t need light; think closed fridge door
ASEXUAL REPRODUCER
Ferns
BOTH ASEXUAL AND SEXUAL REPOS
The reason they’ve survived so long
You can see two different plants that look entirely different and they’re the same plant in 2 different phases of its life cycle
one in a sexual phase
one in an asexual phase
Ferns enjoy advantages and variation from sexual repo, but also enjoy ability to repo when needed to when conditions are “just right”
Angiosperms
Flowering plants and have sex organs within the flower so its a
SEXUAL REPRODUCER
Sex organs: PISTOL and the STAMEN
Pistol: Female sex organ
Stamen: Male sex organ
Gymnosperm
SEXUAL REPRODUCERS
They’re “Cone bearing plants”
e.g. Pine trees
In those cones it’s producing a seed that’s being fertilized and after fertilization, it grows into an adult version of that plant