BIOL500 Test 2
1/82
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Mendel’s Laws of Inheritance
Law of segregation, Independent assortment, Law of dominance
Law of Segregation
During gamete formation, the two alleles for each gene segregate randomly so that half of the gametes receive one allele and the rest receive the other.
Independent assortment
During gamete formation, alleles of different genes assort independently of each other, resulting in genetic variation.
Law of Dominance
When contrasting alleles are crossed, only the dominant trait appears in the next generation.
Monogenic trait
A trait influenced by one set of alleles.
Monogenic trait example
Freckles; Widows Peak; Cystic fibrosis
Polygenic trait
Trait influenced by more than one gene
Polygenic trait example
Eye colour; Hair colour; Height
Pedigree
Chart used to trace inheritance patterns in a family
Karyotyping
Examination and analysis of an individual’s chromosomes
Aneuploidy
Abnormal number of chromosomes
Trisomy
Extra chromosome
Monosomy
Lack of chromosome
Polyploidy
Additional set of chromosomes present
Central dogma
Genetic information flows from DNA to RNA to protein
DNA replication
DNA molecule is replicated before cell division
Semi-conservative replication
Each new DNA molecule contains one old and one new strand
Steps of DNA replication
Initiation, elongation, termination
DNA replication initiation
Helicase unwinds double helix at origin of replication, SSBP keep strands separate, Topoisomerase reduces increased coiling, Primase synthesises RNA primer
DNA replication elongation
DNA polymerase adds complementary nucleotides from 5’ to 3’ resulting in leading and lagging strands, removes RNA primers and proofreads, DNA ligase joins okazaki fragments
DNA replication termination
Replication forks meet, new DNA molecules separate
Eukaryotic DNA replication
Occurs in nucleus; Linear DNA has multiple origins of replication; Slower replication rate
Prokaryotic DNA replication
Occurs in nucleoid region; Circular DNA has a single origin of replication; Faster replication rate
Types of RNA
mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
Gene
Section of DNA containing information for molecule synthesis; Unit of heredity
Gene expression in eukaryotes
Transcription occurs inside nucleus; Transcribed mRNA needs to be processed before exiting nucleus; Translation occurs in cytoplasm (rough ER matrix)
Gene expression in prokaryotes
Occurs in cytoplasm; Transcribed mRNA can be translated immediately
Gene structure
Promoter, coding region, terminator
Gene promoter
Region defining where transcription begins
Gene coding region
Encodes RNA and/or protein sequence
Gene terminator
Region defining where transcription stops
Eukaryotic gene structure
Contains introns — non-coding regions spliced out before translation
Prokaryotic gene structure
Lack introns — coding region uninterrupted
Steps of Transcription
Initiation, Elongation, Termination
Transcription initiation
RNA polymerase binds to promoter region, starts at +1 nucleotide, no primer required
Transcription elongation
RNA polymerase adds complementary ribonucleotides to RNA chain (uracil), uses 3’-5’ template while synthesis is 5’-3’
Transcription termination
RNA polymerase, DNA, and mRNA dissociate upon reaching terminator
mRNA in eukaryotes
Transcribed in the nucleus then processed before being transported to cytoplasm for translation
mRNA in prokaryotes
Transcribed directly in the cytoplasm where it is then translated
Coding strand of DNA
Codes for gene of interest
Template strand
Complementary to coding strand, can be transcribed to produce RNA with identical sequence to coding strand
Stages of protein synthesis
initiation, elongation, termination
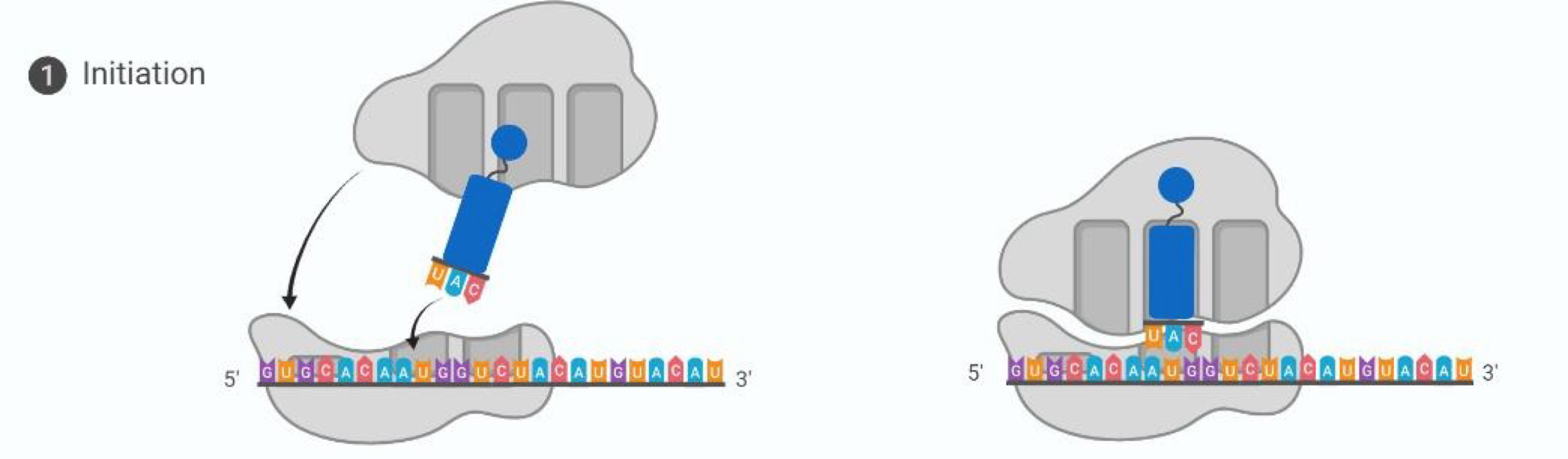
Translation initiation
Small ribosomal subunit attaches to mRNA, large subunit attaches to small subunit, tRNA start codon enters A-site with complementary anticodon
Translation elongation
tRNA with complementary anticodon moves to P-site, AA from first tRNA joins to second AA, used tRNA moves to E-site to be ejected and recycled. Ribosome moves along mRNA
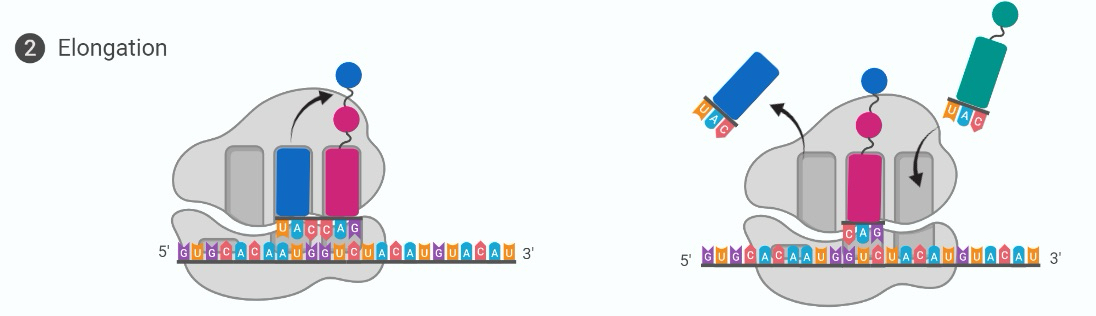
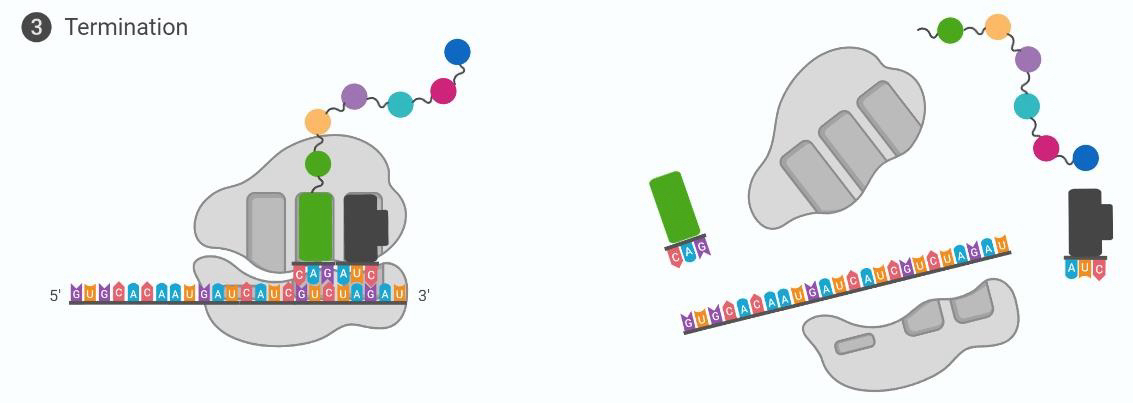
Translation termination
Stop codon encountered in A-site, release factor enters. H2O molecule added to final position, AA releases. Polypeptide chain undergoes further modification.
Primary structure
Linear sequence of amino acids joined by peptide bonds — protein backbone
Secondary structure
Alpha helices, Beta-sheets
Tertiary structure
3D shape of protein chain, dependent on amino acid composition
Quaternary structure
Multiple polypeptide chains joined to form one functional molecule with multiple subunits
Enzyme
Protein acting as a biological catalyst
RuBisCO
Most abundant enzyme on earth; Crucial role in photosynthesis
DNA polymerase
Enzyme that synthesises new DNA strands using existing DNA as template
RNA polymerase
Synthesises RNA from DNA template
Ribosomes
Synthesise proteins from amino acids
Electron transport proteins
Transfer electrons
ATP synthase
Enzyme converting energy from proton gradients into ATP
Ion channels
Protein structure in cell membrane regulating movement of ions across membrane.
Cellulose synthase
Enzyme synthesising cellulose
Nitrogenase
Catalyses reduction of dinitrogen N2 to ammonia NH3
Metabolism
Sum of all biochemical reactions involved in keeping a cell alive
Metabolic pathways
Series of biochemical reactions that convert molecules, catalysed by enzymes; Product of one reaction becomes the substrate for the next reaction
Metabolites
Molecules involved in metabolic pathway products
Catabolism
Breaking down large nutrient molecules into smaller molecules with simultaneous energy production
Anabolism
Synthesis of larger molecules from smaller ones, energy input generally required
Acetyl coenzyme A
Roles in krebs cycle, fatty acid synthesis, glyoxylate cycle.
Chemiosmosis
Movement of ions (protons) across membrane to generate ATP.
Glyoxylate Cycle
Modified version of krebs cycle in plants and microorganisms
Glyoxylate cycle purpose
Allows plants to convert lipids into glucose, allows microorganisms to convert lipids or simple molucules into polysaccharides for their cell walls
Fatty acid anabolism
Synthesised from Acetyl-CoA via acetate/malonate pathway, allows conversion of carbs into lipids via glycolysis; Glucose to Acetyl-CoA to fatty acids
Fatty acid catabolism
Broken back down to Acetyl-CoA via beta-oxidation pathway, go to krebs cycle for energy production in mitochondrion
Regulation of metabolic pathways
Biochemical regulation, Regulation of rate-limiting step, Cellular regulation, Gene regulation
Biochemical regulation
Product of pathway influences its own production, inhibits enzyme activity to prevent over-accumulation; Feedback inhibition
Regulation of rate-limiting step
Inhibition or enhancement of rate-limiting step has greatest influence on pathway
Cellular regulation
Done via cell-signalling pathways like hormones
Gene regulation
Turn genes on or off depending on environmental or cellular signals
Photosynthesis
Plants convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen using the energy of sunlight
Respiration
Plants and animals use plant-derived glucose to ‘reverse’ photosynthesis to release energy
Light-dependent reactions
Light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll, used to make ATP and NADPH
Light-independent reactions
ATP and NADPH are used to convert carbon dioxide into glucose
Site of light-dependent reactions
Thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast
Site of Calvin cycle
Stroma of the chloroplast
Chemiosmosis in eukaryotes
Occurs in inner mitochondrial membrane and thylakoid membrane of chloroplast
Chemiosmosis in prokaryotes
Occurs across plasma membrane