Audit Test 1
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
What factors create the demand for auditing services?
monitoring and/or stewardship
Insurance
Information
Business risk
risk that an entity will fail to meet its objectivies
Information Risk
probability that the info circulated by a company will be false or misleading
Assurance
lending of credibility to info
attestation
when assurance is provided for specific assertions made by management
auditing
when the assertions are embodied in a company’s financial statements
Auditing services
refers specifically to the certification of financial statements
Attest Engagement
providing assurance on other financial info; expanded set of financial info beyond financial statements
Financial Reporting provides
statement of financial position, results of operations, changes in cash flows, accompanying disclosures
Existance
does this cash really exist?
Rights and obligations
does the company really own this inventory?
Valuation
are the depreciation amounts properly valued?
Occurrence
did these sales really take place?
completeness
are all of the expenses included? Are they recorded in the correct period?
ASB Assertions
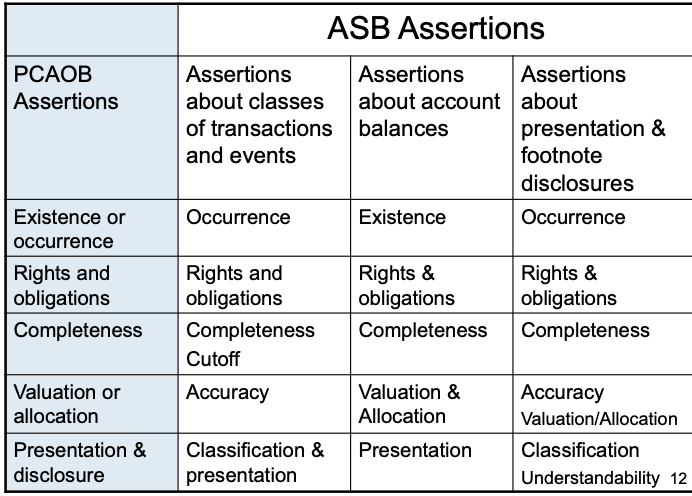
Concern
failure to record something
Professional Skepticism
auditor’s tendency to not accept management assertions without corroboration; “prove it”
Doveryai, no proveryai
trust, but verify
Services provided by CPAs
tax, advisory, assurance, personal financial planning, litigation support services, fraud investigation services
Audits of Financial Statements
systematic examination of financial statements
Operational and Internal Auditing
systematic review of activities. Focuses on effectiveness and efficiency
Compliance or Governmental
adherence to some established criteria, policies, or regulations
External Auditors (independent, public)
engaged by the company. Responsible for reporting whether the financial statements are presented fairly in conformity with GAAP
Internal Auditors
independent, objective assurance and consulting activity designed to add value and improve an organization’s operations
Regulatory or Governmental Auditors
determine compliance with laws, statutes, policies, and procedures
GAO
Government Accountability Office
AICPA
American Institute of CPAs
IIA
Institute of Internal Auditors
AAA
American Accounting Association
SEC
Securities and Exchange Commission
PCAOB
Public Company Accounting Oversight Board
PCAOB
created to oversee and discipline CPAs and public accounting firms that audit public companies
AUD
Auditing and Attestation
FAR
Financial Accounting and Reporting
REG
Taxation and Regulation
BAR
Business Analysis and Reporting
TCP
Tax Compliance and Planning
ISC
Information Systems and Controls
Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002
impacts any CPA actively working, created the PCAOB; requires rotation of lead audit partner and reviewing audit partner every 5 years; statute of fraud to 5 years; harsh penalties; prohibits what work can be done; internal controls
Why are standards importants
standards are established to measure the quality of performance. They represent the minimum rules/principles that a profession’s members have agreed to observe
GAAS
authoritative standards that CPAs must comply with in performing audit engagements
Stages of an audit
obtain engagement, engagement planning, risk assessment, audit evidence, reporting
Competence and capabilities
education, CPE, experience, and ability to develop and apply professional judgement in real-world situations
Independence and due care
comply with appropriate ethical requirements; must maintain an independence in mental attitude (in fact and appearance), must exercise due professional care
Skepticism
a state of mind
Judgement
the application of relevant training, knowledge, and experience in making informed decisions about appropriate courses of action during the audit
Reasonable assurance
a GAAS audit may not detect all material misstatements; auditors are not insurers regarding the fairness of the company’s financial statements
Planning and supervison
prepare a written audit plan, supervise the audit work, obtain knowledge of the client’s business, deal with differences of opinion among the firm’s own personnel
Effective internal control
lower level of control risk → allows auditors to evaluate less evidence and use less effective substantive procedures
Ineffective Internal control
Higher level of control risk → requires auditors to evaluate more evidence and use more effective substantive procedures
High Audit Evidence quality
auditor’s direct, personal knowledge
evidence obtained directly from independent external sources
Mid Audit Evidence Quality
evidence originating outside the client is considered competent when internal control is strong
Low Audit evidence quality
internal evidence consists of documents that are produced, circulated, and stored in the client’s information system
Verbal and written representations given by client
Unmodified Report
means GOOD; not calling attention to anything wrong
Modified Report
presented fairly “except for” some isolated departure or limitation
Adverse Report
not presented fairly
Disclaimer Report
no opinion given
Covered Member
new term that replaces “member”; refers to an individual, firm, or entity capable of influencing an attest engagement
Threats to Independence
familiarity, close relatives, undue influence, self-review, financial self-interest, management participation/advocacy, past employment with the client, future employment with the client
Commissions that are prohibited when the member or firm also performs the client’s
audit or review of financial statements
compilation of a financial statement
examination of prospective financial information
Permitted commissions and referral fees must be disclosed
disclosure must be made prior to the start of the service
must state the amount of the fee or the basis on which the fee will be computed
Common Law (unwritten law)
uses legal precedent to identify the fault and responsibility of parties when there is no violation of a written law or statute.
State-dependent and precedent based
arises due to breach of contract, negligence, or fraud
Statutory Law
legal decisions based on laws passed by legislative bodies and complied in federal, state, and municipal codes
has the law been violated by the actions of the party?
breach of Contract
claim that services were not performed in the manner described in the contract
Tort
cover other civil complaints arising from auditors’ failure to exercise the appropriate level of professional care
Privity of Contract
relationship of direct involvement between parties to a contract
ordinary or simple negligence
failure to exercise due professional care
unintentional breaches of duty
Gross negligence
extreme, flagrant, or reckless disregard for standards of due professional care
lack of minimal care
Fraud
misrepresentation of a material fact
deliberate intent to deceive
other party must prove resulting damages
CPA’s defenses
exercised due care, followed GAAS
not negligent
performed the engagement in accordance with terms of the contract
plaintiff’s loss caused by some other event
plaintiff's contributory negligence
ultramares approach
established an obligation to third parties not in privity with auditors for gross negligence and fraud
Primary beneficiaries approach
auditors know both name and intended use of financial statements
restatement of torts approach
exact identity of these third parties need not be known
rosenblum approach
cover all those whom the auditor should reasonably forsee as recipients of the financial statements