Biochemistry MCAT
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
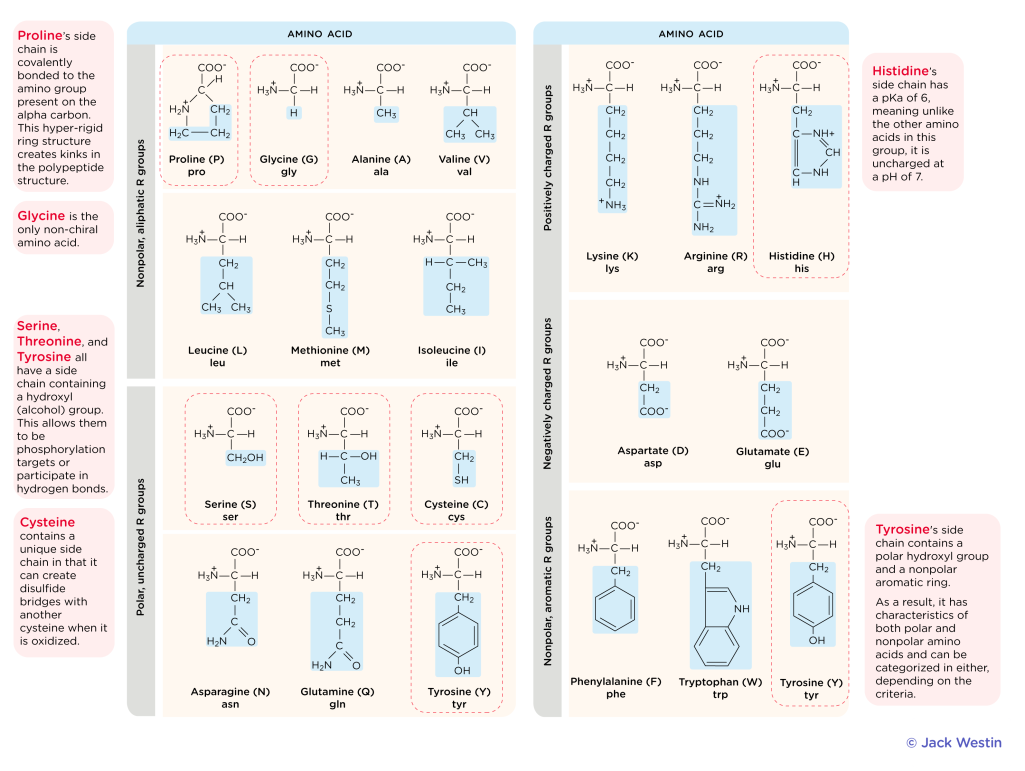
Amino Acids
Building Blocks of Proteins
Amino acids with long alkyl chains are hydrophobic, and those with charges are hydrophilic; many others fall somewhere in between.
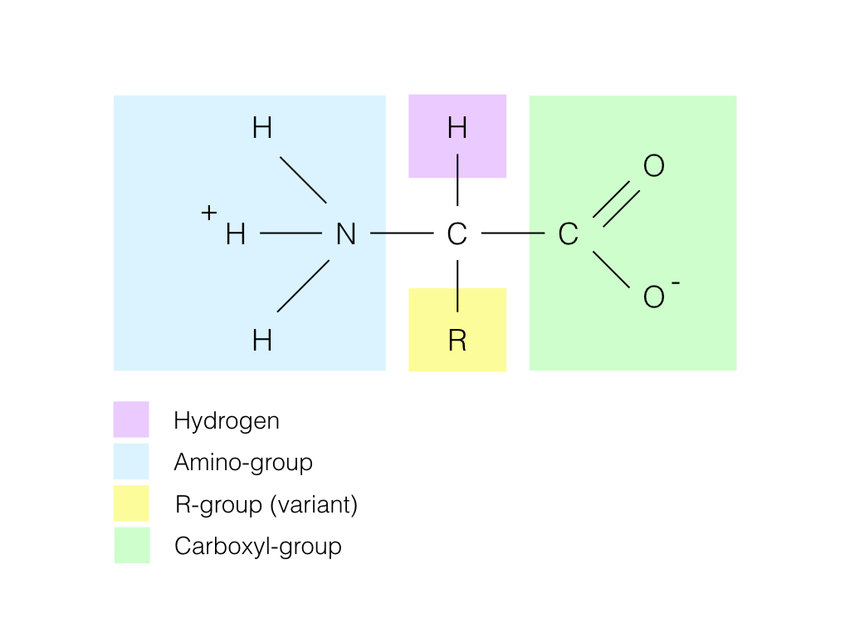
Amino Acid Structure
Carboxyl Group (COOH)
Amino Group (NH3)
Hydrogen (H)
R Group (Varies)
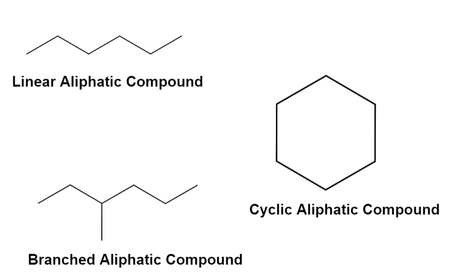
Alkyl Chains
Amino acids with long alkyl chains are hydrophobic,
Alkyl chains are hydrocarbon chains, meaning they are composed primarily of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
Amino acids with alkyl side chains are classified as Aliphatic and they include:
Alanine
Valine
Leucine
Isoluecine
Aliphatic
Amino Acids with side chains consist of carbon and hydrogen atoms, forming straight or branched hydrocarbon chains
Amphoteric
Amino acids can accept or donate protons.
Zwitterion
At pH near the pI of the amino acid, the amino acid is a neutral

L/D Configurations
All Amino Acids in Human Body are “L”
R/S Configuration
All Amino Acids are “S” Except Cystine “R”
Protonation OR Depronation Of AA
Amino acids exist in different forms at different pH values;
At low (acidic) pH, the amino acid is fully protonated (More H+)
At high (alkaline) pH, the amino acid is fully deprotonated (More OH-)
If pKa is higher than pH, a molecule is Protonated
If pKa is less than pH, a molecule is deprotonated
Pka’s
PKa of a group is the pH at which half of the species are deprotonated (OH-); [HA] = [A − ] and half are protonated (H+)
Carboxylic Group (COOH) ≈ 2
Amine Group (NH3) ≈ 10
R - Group ( Varies)
![<p class="has-focus">PKa of a group is the pH at which half of the species are deprotonated (OH-); [HA] = [A − ] and half are protonated (H+)</p><ul><li><p class="has-focus">Carboxylic Group (COOH) ≈ 2</p></li><li><p class="has-focus">Amine Group (NH3) ≈ 10</p></li><li><p>R - Group ( Varies)</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/547b3c8b-b300-4e38-b3d8-26e284efc299.jpg)
Pka Equation
Non Polar, Aliphatic "R" Groups
Glycine Gly (G)
Alanine Ala (A)
Proline Pro (Pro)
Valine Val (V)
Leucine Leu (L)
Isoleucine Ile (l)
Methionine Met (M)
Glycine
Gly (G)
R — H
Not a Chiral/Not Enantiomer
Very Small, Too Flexible and disturbs alpha Helix
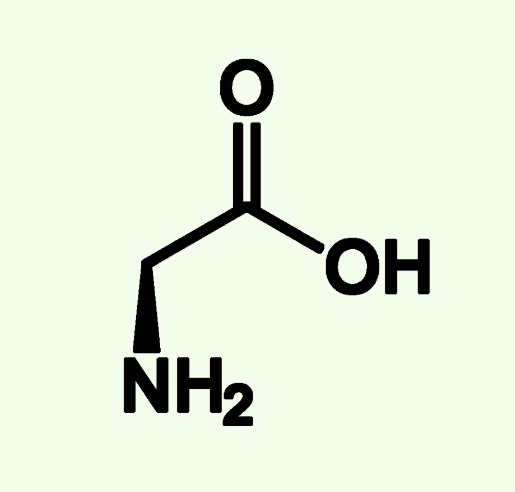
Alanine
Ala (A)
Non Polar
Alkyl Chain
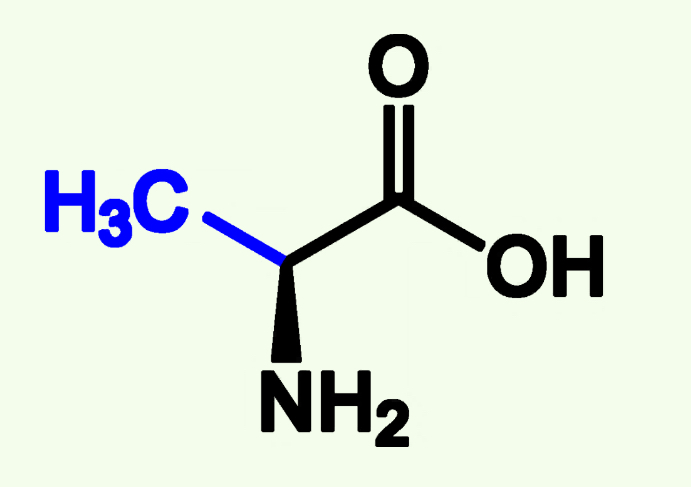
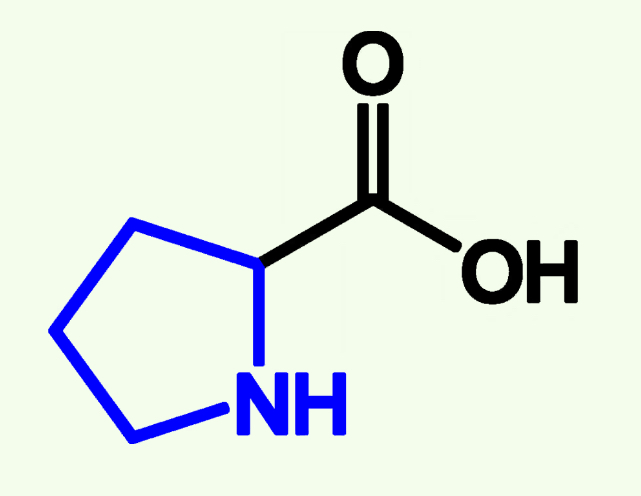
Proline
Pro (P)
Non - Polar
Too Rigid
Creates Kinks Alpha helix and Beta Sheets and that distubs them
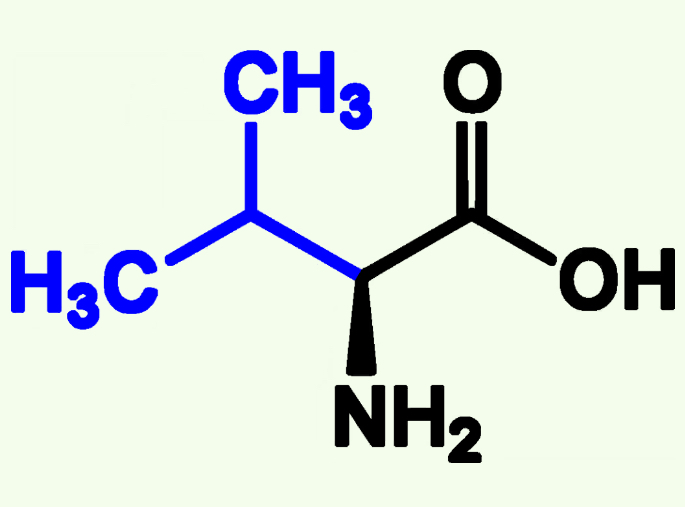
Valine
Val (V)
Non- Polar
Alkyl Chains
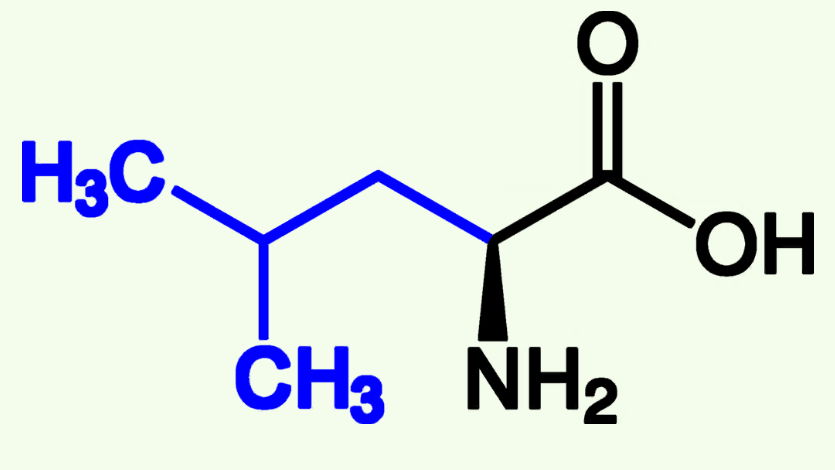
Leucine
Leu (L)
Non-polar
Alkyl Chains
Isoleucine
Ile (I)
Non- Polar
Alkyl Chains
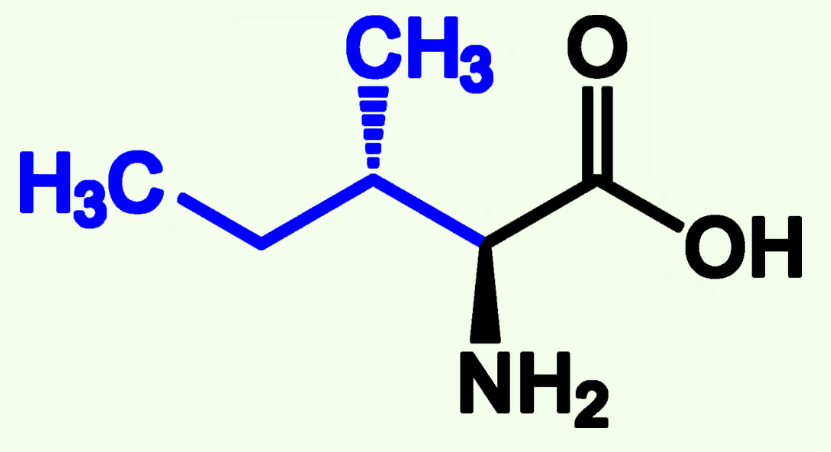
Methionine
Met (M)
Non-Polar
Start of three letter Amino Acids and can also be found at other pistions
Contains Sulfide Group (Can be Oxidized)
Polar, Uncharged R groups
Serine Ser (S)
Threonie Thr (T)
Cysteine Cys (S)
Asparagine Asn (N)
Glutamine Gln (Q)
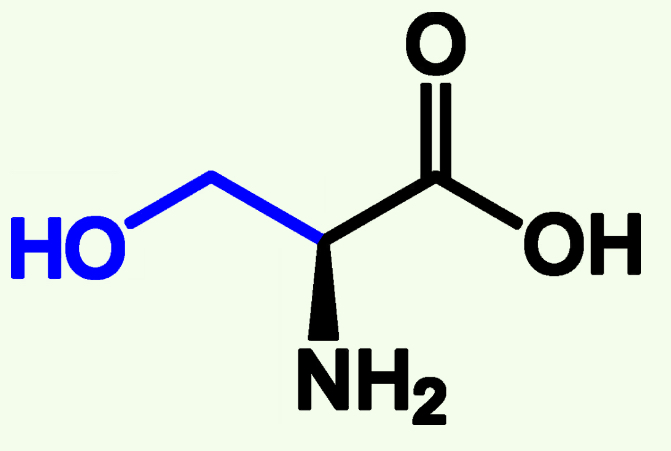
Serine
Ser (S)
Polar
Hydroxyl group (OH)
Capable of Phosphorylation
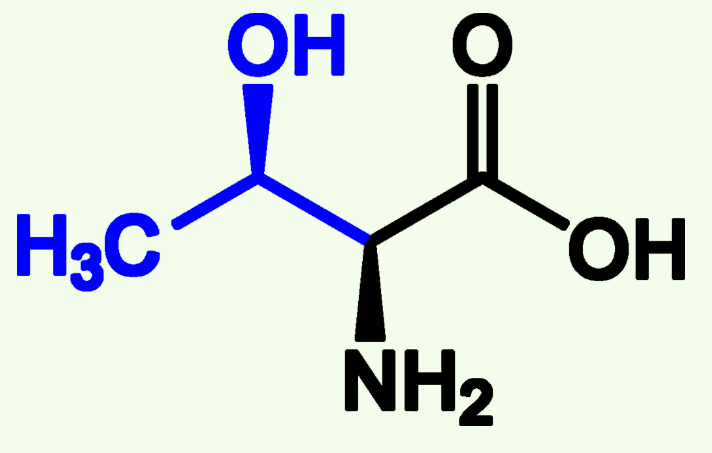
Threonine
Thr (T)
Polar
Hydroxyl group (OH)
Capable of Phosphorylation
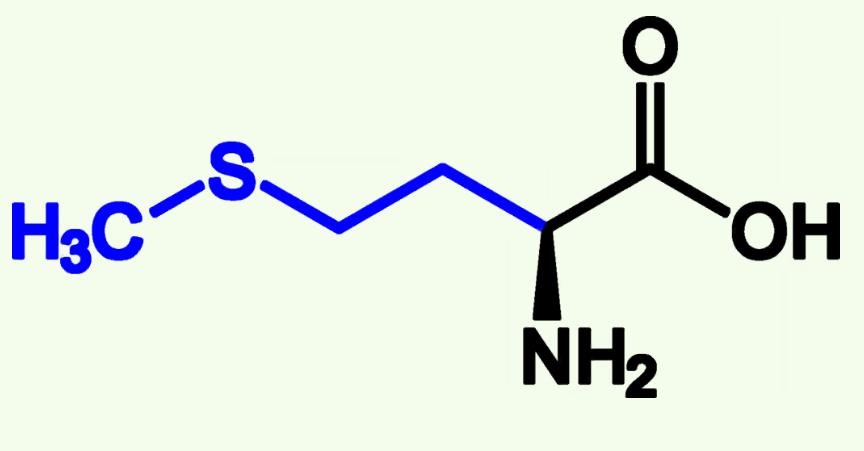
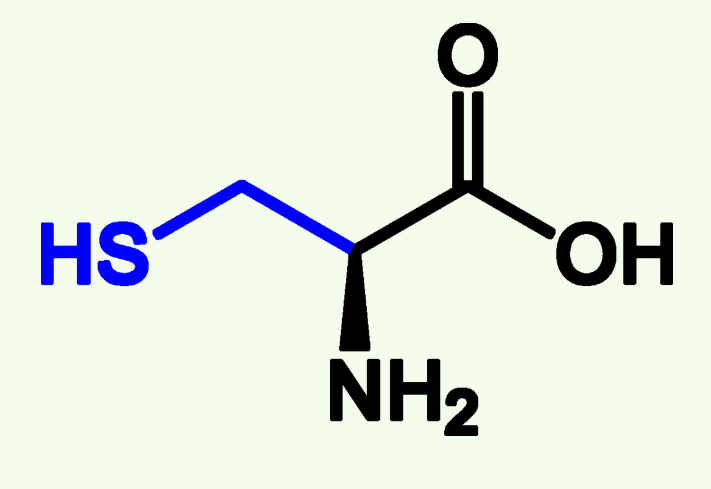
Cysteine
Cys (C)
Thiol Group (—SH)
Covalent Bonds Between two Cysteine; Disulfide Bonds
Can be Oxidized
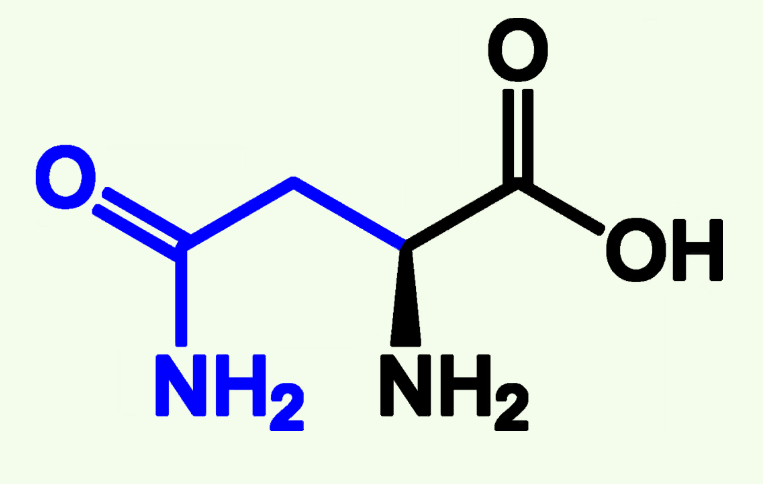
Asparagine
Asn (N)
Amide Side Chain
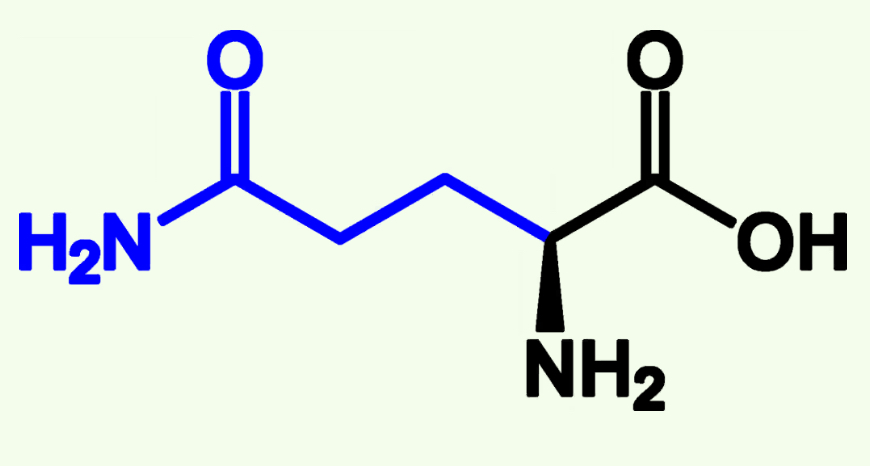
Glutamine
Gln (Q)
Amide Side Chain
Aromatic R Groups
Phenylalanine
Tyrosine
Tryptophan
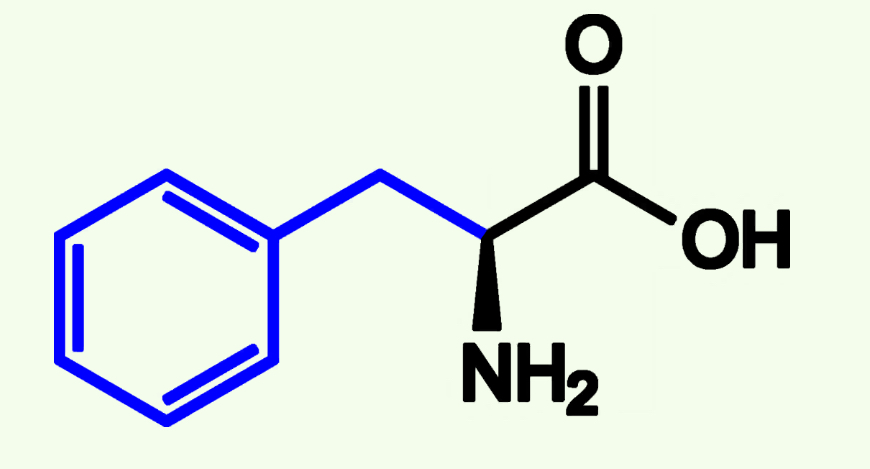
Phenylalanine
Phe (F)
Nonpolar
Aromatic Group
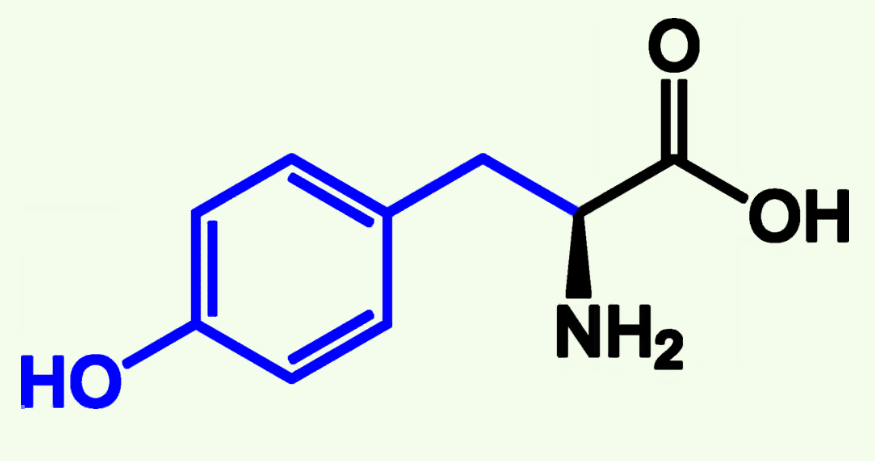
Tyrosine
Tyr (Y)
Aromatic Group
Neutral Polar - more Polar than nonpolar because of Hydroxyl group (OH)
Capable of Phosphorylation
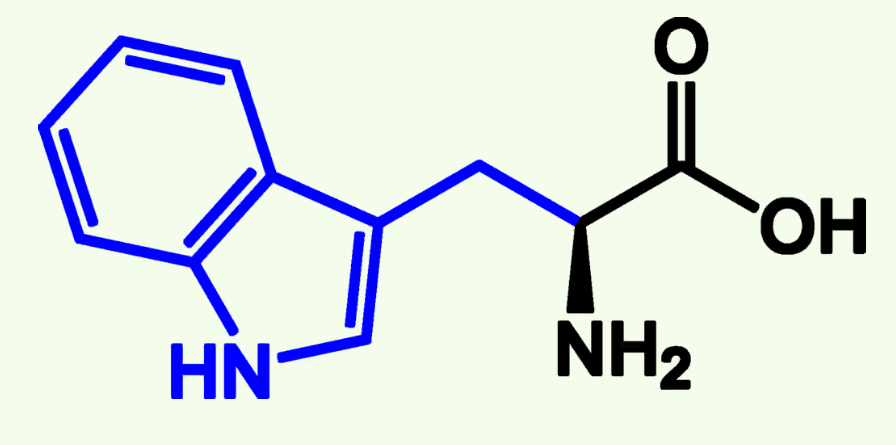
Tryptophan
Trp (W)
Nonpolar
Aromatic Group
Positively Charged “R” Groups/ Basic Polar
Lysine
Arginine
Histadine
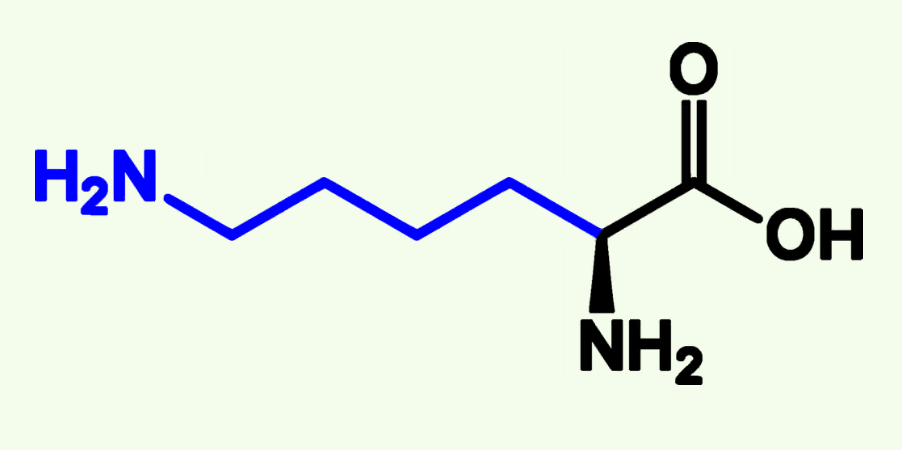
Lysine
Lys (K)
Basic Polar
Pka ≈
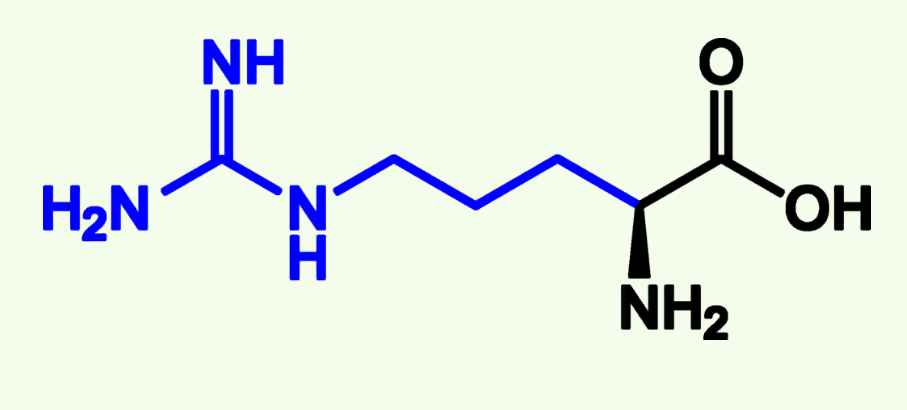
Arginine
Arg (R)
Basic Polar
Pka ≈
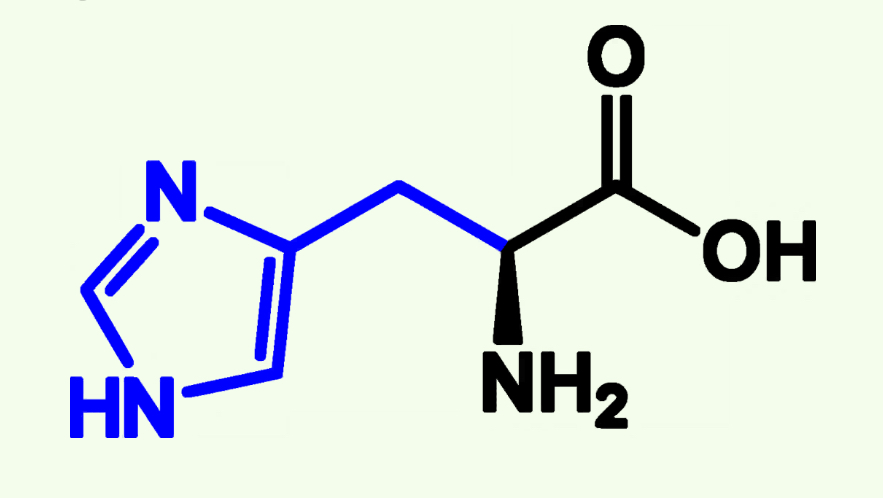
Histadine
His (H)
Basic Polar
Pka ≈ 7
Negativaly Charged “R” Groups/ Acidic Polar
Asparatate
Glutamate
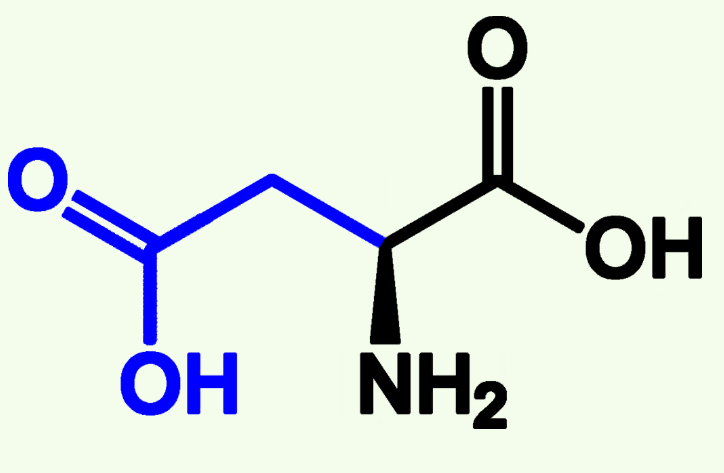
Aspartate
Asp (D)
Acidic Polar
Pka ≈
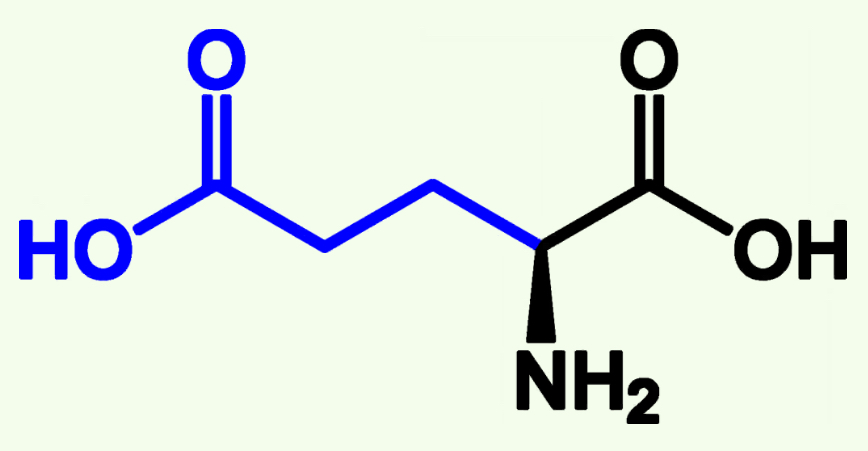
Glutamic Acid
Glu (E)
Acidic Polar
Pka ≈
Amino Acids that can H-Bond
Any amino acid with a
Hydroxyl side chain (Serine, Threonine and Tyrosine),
Amide (Asparagine, Glutamine)
Amine group (Lysine, Arginine and histidine)
Amino Acids With Hydroxyl (OH) side chain
Serine
Threonine
Tyrosine
Amino Acids With Amide Side Chain
Asparagine
Glutamin
Amino Acids With Amine Side Chain
Lysine
Arginine
Histidine)
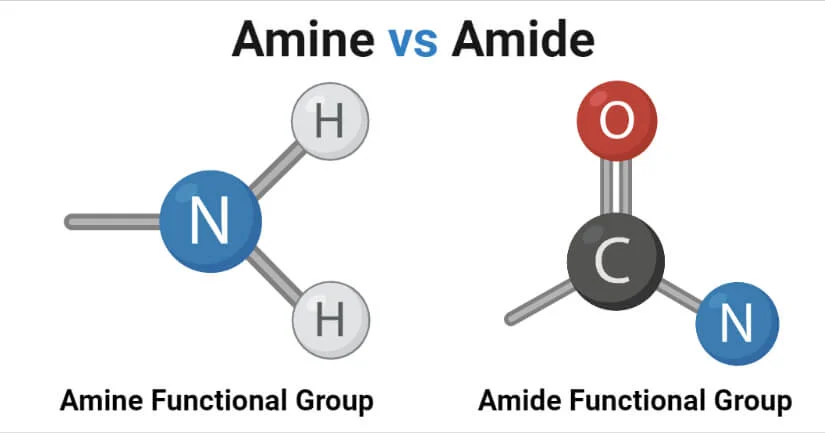
Peptides
Composed of amino acid subunits, Called residues
Dipeptides
Two Residues of Amino Acids
Tripeptides
Three Residues of Amino Acids
Oligopeptide
Amino Acids up to 20 residues
Polypeptides
Long Chain more than 20 residues of AA
Peptide Bond (Amide)
Residues in peptides are joined together through peptide bonds, a specialized form of an amide bond, which form between the −COO− group of one amino acid and the NH3+ group of another amino acid.
Peptide Bond Formation
Condensation/Dehydration Reaction occur; a water molecule (H₂O) is removed from two or more molecules, forming a new bond between them
Peptide Bond Hydrolysis (Breakage)
A water molecule (H₂O) is added to the peptide bond.
The oxygen atom from the water attacks the carbon atom of the carbonyl group in the peptide bond, and the hydrogen atom of the water attacks the nitrogen atom.