CLAS241 - Middle Bronze Age (2000 - 1550 BCE)
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms

Wasp pendant. Middle Bronze Age. 2000 - 1550 BCE.
Bees are important in Minoan culture (antimicrobial and makes honey)
Shows that Minoans are good in metal working
Metal-working techniques
Relief: how far an image stands up from the surface (high or low)
Repoussé: achieving relief through hammering from behind
Filigree: decoration made with thin wire
Granulation: soldering globules of gold/silver onto jewellery
The wasp pendant uses relief, repoussé, filigree, and granulation.
Relief is how far an image sticks out. The wasp pendant has high relief because it sticks out a lot from the back. Relief was done through repoussé, which hammers the image from behind. Filigree is decoration made with thin wire, which was used for stuff like the legs. Granulation solders globules of gold or silver onto jewelry. Droplets can be seen on the wasp’s honeycomb for example.
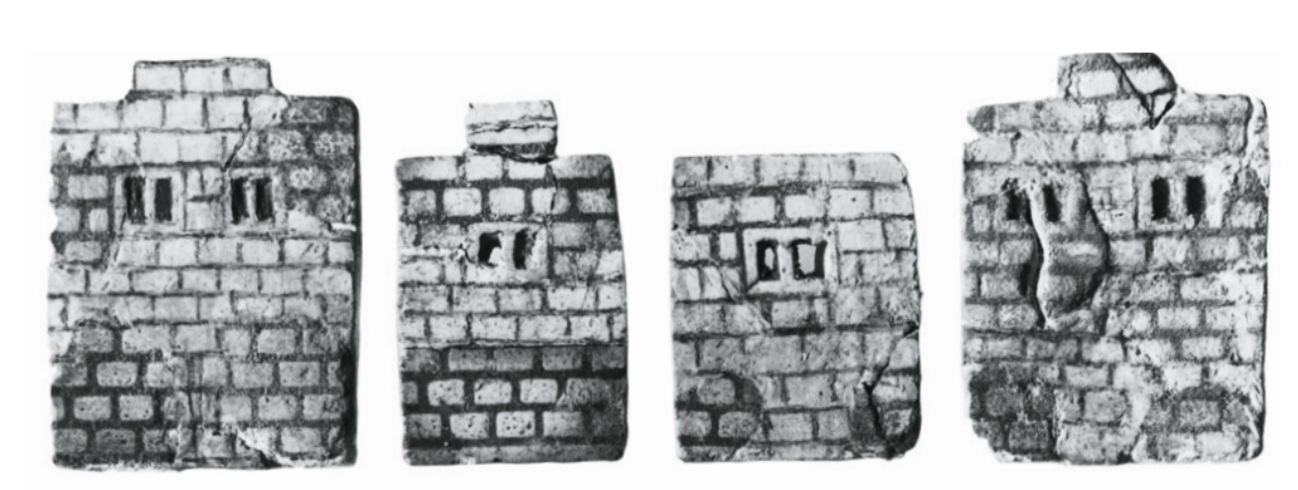

Plaques in the shape of houses. Middle Bronze Age. 2000 - 1550 BCE.
In Malia, Crete
Earliest example of domestic middle bronze age architecture
These plaques may have decorated the sides of chests
Represents the external face or elevation of the private houses at Mallia
Probably owned by rich people
Found beneath the flooring of the rebuilt palace of Knossos (these plaques date the time the first palace was there)
Illustrates the houses with two or three stories, a symmetrical arrangement of windows (showing Minoans interest in air and light for ventilation), shutters, flat roofs
Built of brick and timber

Model of a house. Middle bronze age. 2000 - 1550 BCE.
Another version of the house shaped plaques
Owned by wealthy people
This is the terracotta model of a house
Gives more evidence for upper stories of houses and staircases opening out onto the flat roofs

Figurines. Middle Bronze Age. 2000 - 1550 BCE.
Earliest examples of Minoan sculpture, made of terracotta
Figurines represent humans, animals, or human limbs, which are offerings to the divinity
Both figures are geometrically similar, carries on into later Crete
Faces lacking detail, except nose and chin
Man figure
Looks like a warrior
Standing to attention
Wearing only codpiece, belt, and dagger
Arms raised to chest to show respect (possible religious context)
Man is less detailed than woman
Female figure
Arms raised extended in front of them
Wearing flounced shirt, hat
Has bare breasts
Inherent difference in status
Woman figure looks like she’s in a position of power, suggests more equal society
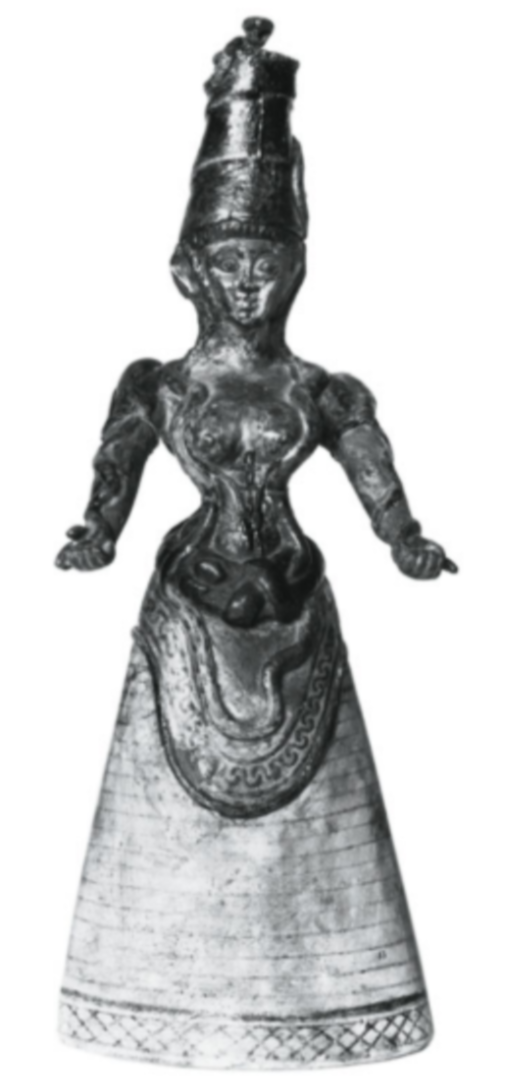

Snake goddess. Middle Bronze Age. 2000 - 1550 BCE.
Geometric form like Cycladic figurine
Slim waist, bare, breasts, flounced skirt
Common dress in Minoan culture
Made of faience (quartz ceramic)
Snake goddess figurines were found in Knossos in stone-lined pits, sealed below debris from the later earthquake
Shows formality, naturalism, symmetry, geometry, and elaborate design

Snake goddess. Middle Bronze Age. 2000 - 1550 BCE.
Geometric form like Cycladic figurine, which is seen in the cones and cylinders
Brightly coloured
Slim waist, bare, breasts, flounced skirt
Common dress in Minoan culture
Made of faience (quartz ceramic)
Similar posture, display, and clothing (brightly coloured - red, green, blue)
Snake goddess figurines were found in Knossos in stone-lined pits, sealed below debris from the later earthquake
Shows formality, naturalism, symmetry, geometry, and elaborate design

Beak Shaped Kamares Ware Jug. Middle Bronze Age. 2000 - 1550 BCE.
Bright colours, high contrast
Pairs of spirals and oval motifs that wrap diagonally around the jug
Naturalistic and represents a sea animal (a seabird)
Pellets of spout meant to look like bird eyes, like the Vasilike ware
Painted before firing clay
Sometimes kamares ware designs look as complicated as fireworks
After palace reconstruction, Kamares ware designs became more naturalistic yet stiff, vegetal designs were popular, and kamares ware was popular/shipped out of crete

Minyan ware goblet. Middle Bronze Age. 2000 - 1550 BCE.
Named by Schliemann
Grey, monochrome, no decor
Fired very hard so it doesn’t have any big clay particles
Sharply profiled due to the use of the fast wheel
Similar to the two-handed tankards from Troy, which shows material influences between cultures due to trading.
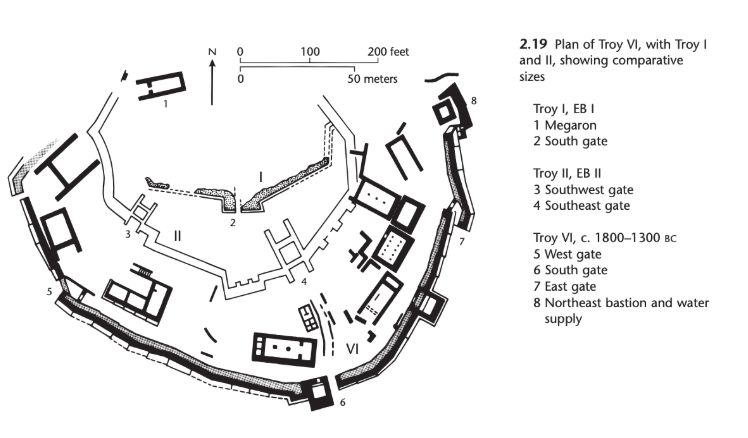
Plan of Troy. Middle Bronze Age. 2000 - 1500 BCE.
Troy
Discovered by Schliemann from Homer’s poems
In a commanding position
Migrants traveled here because it’s at the end of the land route from Asia to Europe
A recognizable channel for cultural ideas
Near the Black Sea and Aegean/Mediterranean
Controlled trade flow
Placed high taxes on people
The more you dig, the older the architecture
Troy I
Big stone walls
Inside the walls, people lived in dwellings of a rectangular plan with a porch
Megaron: a rectangular building with two rooms and an entrance and porch on the short side
Corridor type house influences architecture for Mycenaeans
Troy II
Big stone walls fortified by towers and bastions
There was a megaron larger than the House of Tiles which overshadowed smaller residences
Inhabitants were potters and great metalworkers
Troy III and IV
These short-lived citadels show decline in prosperity from the brilliance of Troy II
Troy V
Final stage of the EB citadel
Troy VI
Survives because of the big defensive walls
Enclosed houses that stood individually