Forage Crops Exam 3 Forage Selection/Forage Establisment/Forage Management
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
What 3 Sections are we Overview for this quiz
Forage Selection
Forage Establishment
Forage Managememt
Fertility
Weeds
Irrigation
5 main criteria for forage selection
Livestock selection
Calving
Yield Distribution
Forage Quality
Planyt Persistence
Livestock Selection
3 types of livestock kinds
Grazers (cattle)
Browers (Goats)
Mix Feed (Sheep)
Why is selecting livestock for you forage important for forage selestion?
Different types of animals require different types of physiological states, nutrients, health types, forage preference, etc.
All forage must meet nutritional needs for the ANIMAL
Calving
At peak lactation (spring or fall)
The mother must have the highest nutrient requirement/energy/diet because calving takes up a lot OF energy usage
Spring Calving
Fall Calving
BOTH USING TALL FESCUE: due to its high nutritive value
Why is determining forage selection when calving very important?
Choosing the right forage when calving is very important because it affects productivity.
Good-quality forage gives the cow enough energy and protein for calving
Yield Distribution
Being able to identify gaps in growing seasons and replace/changing the forage type based on the animal’s nutrition requirements
An example of a gap would be filling C4 grasses with C3 grasses during the summer slump period
Why is Yield Distribution important for forage selection?
it shows when the forage grows best, helping ensure feed is available throughout the year, not just at one time.
Forage Quality
Feeding the animal forage that has high quality (high protein/high digestibility) to fill out the animal’s dietary requirements
MY, ADG, BW, BCS goals to be reached
Why is Forage Quality important for forage selection?
Importance refers to the nutrient value in the forage, and based on what we want the animals’ performance to look like we need the appropriate amount of quality nutrients in the forage
Plant Persistance
Basically, how “strong” the plant is based on structure, longevity, and its ability to regrow itself
If a plant has good persistence, what is one way that it can regrow itself?
Through seed production, plants can regrow themselves
Stolon & Rhizomers are good examples of plant that are persistent plants
Why are Stolon and Rhizomes good examples of plants that are persistant?
They have nodes that are under grown and can be unharmed by the climate, mowers, livestock, and other issues that can delay persistance
Why is plant persistence important for forage selection.
Persistent plants survive for many years, reducing the need for reseeding and keeping pastures productive and cost-effective over time.
What is one thing that can severely damage plant persistence even though the plant is in a good enviroment?
EDAPHOCLIMATIC Conditions
What is an edaphoclimatic and how does it affect longevity in persistent plants
Disrupts Soil content
Removes H2O from plant roots (causes droughts)
Makes the plant cold
Why does forage region matter for forage selection?
Depending on the forage region, choosing the appropriate region means choosing the proper plant for the proper climate, temp, elevation, etc for long-term persistence
Each forage type has a specific environment for it to thrive/grow/reproduce in
Each forage also has a type of animal species to graze on it
What region do C4 grasses primarily thrive in?
What region do C3 grasses primarily thrive in?
C4: Hot summers
C3: cool springs and falls
Before introducing a new forage specific to a new area, WHY is it essential to evaluate whether its invasive or toxic?
Invasive plants immediately spread and cause soil disturbances in the area
Toxic plants pose risks to the ecosystem
Selecting forages that are well-suited to the specific area or state—and that do not present invasiveness or toxicity issues—helps maintain ecological balance and animal health.
What are the 3 main forage selection management strategies?
Grazing Frequency
Residual Leaf Area
Rest Period
What is Grazing Frequency and why is it important?
The rate that livestock grazes on a forage affects constant growth and plant persistence
controlling how often animals graze, farmers can determine the regrowth and recovery of desirable plants which can improve longevity of the plant
What is residual leaf area and why is it important for forage selection management?
Leaving an adequate amount of leaf area for grazing for photosynthesis for regrowth and for the plant to have enough energy to continue growing
What is rest period for plant and why is it important for forage selection management?
Leaving pastures with a rest period in between grazing, which promotes healthy root growth, which gives grasses time to replenish energy storage, repair damage, and for future grazing
Within Forage Establishment, what 2 types of renovations are there?
Total Renovation: completely changing the pasture
used when we find K31/endophytes
Partial Renovation: small sections of an already established pasture are changed
used to enhance the pasture without staring over
When talking about Pasture Establishment and Renovation, what 5 main points are involved?
Inventory: Evaluating ground cover and getting forage ready to be planted
Fertility: Proper soil conditions for nutrient growth (P,K, pH)
Timing: the right time is key for successful establishment and long-term productivity
Reducing Competition: Minimizing competition from existing vegetation is crucial for successful pasture establishment, for it ensures proper growth for the plant
Good Seed to Soil Contact: improves germination
What does Phosphorus do for soil conditions?
What does Potassium do for soil conditions?
What does proper pH do for soil cotent?
P: Insures proper root health
K: Disease resistant
pH: maintain nutritive valule
When dealing with timing, when should each Grass be planted
CSP:
CSA:
WSP:
WSA:
CSP: Fall/spring
CSA: Fall
WSP: Winter
WSA: later spring-early summer
Approaches to Reduce Competition
Overgrazing
Mowing
Hay Production
Tillering
Fire
Herbicide
What is frost seeding?
Why do we use it?
Planting seeds late winter to improve germination
Low labor cost and still provides good results
Best plants to use in frost seeding?
Ok plants to use in frost seeding?
Horrible plants to use in frost seeding?
Red/white clover (great)
Annual Lespedeza (ok)
Alfalfa (bad)
Why do we need good seed to soil contact?
Seed germination for optimal plant growth
Characteristics of a No-Till Seeding Method
ADV
DISADV
involves placing seeds directly into the soil with a specialized drill
ADV: Reduces competition from existing vegetation
DISAVD: HEAVY labor and $ cost
Characteristics of Conventional Tilling Methods
ADV:
DISADV
prepares the seedbed by working the soil before planting, then drilling and using a press wheel to close the soil
ADV: good seed to soil contact
DISADV: rick of erosion
Characteristics of Broadcasting
ADV
DISADV
Driving around a pasture, and seeds spin out of the cart onto the ground
ADV: less equipment
DISADV: uneven seed distribution
Seeding Rate example question PLS
lbs/acre x acres = lbs of total seed required
purity% x germination % = PLS
lbs per acre/PLS#
PLS Pure Live Seed
What is pure live seed (PLS)?
The measure of an actual visible seed in a seed lot that is pure and capable of germinating
Equation = Plant germination as a percentage (*) purity = PLS number
Lbs total seed required /PLS number = what our lbs/acre calculation
What is seed preparation Inoculation
What is it important?
Adding beneficial bacteria to the legume species before planting
It ensure proper nitrogen fixation, which improves forage yield and protein content
What is Nodulation in Legumes
Why is it important?
The process of nitrogen fixation occurs in the roots of legumes to form nodules.
So that Rhozomers plants can grow nodules
What are the 4 Developmental Stages of Nodulation in Legumes
Seed Stage
Germination
Young Seedling
Nodularting Seedling
Companion crop Seeding
What is it?
Why is it important?
Seeding a small grain crop planted alongside desired grasses and/or legume to protect soil from erosion and improve soil structure
It provides a temporary grazing source to add income
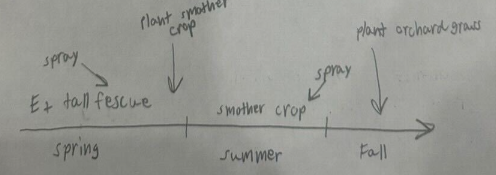
Your K31 tall fescue pastures have thinned due to drought. You decide now is a good time to renovate to orchardgrass. Illustrate the process of replacing your endophyte-infected tall fescue with a fall-planted cool-season forage
What 5 elements are used to have forage management for plant persistence and productivity
Nitrogen (N) (promotes cell division)
Phosphorus (P) Promotes ATP)
Potassium (K) Cycling water, drought tolerance
Calcium (Ca) ( support cell wall structure)
Magnesium (Mg) (enzyme activation
5 Ways HOW TO OBTAIN A QUALITY SOIL SAMPLE
Divide the area for topography
150 ft from Contaminated Areas like trees and water
Collect 15-20 soil cores
Avoid manure/urine spots
Collect sample 3-5 years
What are the 4 levels of how to interpret soil fertility in a test?
Why is this important?
Low, Medium, High Very High
Your soil fertility must match or exceed the need of your selected forage and the proper level of fertility will affect plant persistance, longevity, and soild nutrient level.
What does soil pH pertain to?
Why is this important?
The concentration of hydrogen ions is in the soil sample
The number of hydrogen ions affect how available different nutrients are for plant uptake
If you collect a soil sample that has a pH value of 4.8:
What is the general consquence of not correct this pH value of the soil?
What do you need to do to your pasture to correct this pH value?
low pH in a pasture will result in low availability of nutrients
Come up with a rate of lime and apply it to raise pH
Why do we have to be careful when determining soil fertility between hay fields or pastures.
Hay fields and pastures require different fertilizer inputs
Hay fields: consistent fertilizer input to replace nutrients
Pastures: recycle nutrients through grazing animals and experience gradual leakage
Why producers must regular replace hay when harvest from the ground?
When hay is removed from a pasture, valuable nutrient come with it (K,P,Ca,Mg,N) resulting in the soil bad fertility.
3 Main Forage Management Implications
Regular Soil Testing
Using fertilizers to replace valuable nutrients
Avoid overharvesting without replenishing
How does Excretion from Livestock effect nitrogen cycling?
Since animal feces/urine has a lot of Nitrogen, it influences nutrient recycling and environmental loss
Ways to manage manure Distribution
Rotate water and shaded locations
Use rotational grazing
Test soill frequency
As part of your new fertility management program, your goal is to use your livestock to achieve greater uniformity of nutrient distribution. What grazing management techniques should be implemented to achieve your goal?
Using rotational grazing
Rotate water/shaded locations
You are interested in improving nutrient distribution during your upcoming winter hay feeding. What hay feeding practice can you use to improve manure distribution compared to traditional hay feeding practices?
Varying the hay feeding areas across the pasture and increasing the distribution of manure/fertilizer
How does N fertilization affect persistence of legumes in pastures?
High nitrogen fertilization reduces biological N fixation along with limiting persistance and long-term pasture sustainability
Since feralization should match our periods of high forage, When soul you fertlize (sping, fall spring/fall, none)
30% legumes__
Stockpiling tall fescue for a stocked cow calf operarion___
Mananging a cow-calf grazing with stocker calves in April____
In the tall fescue hay buiness ___
None
Fall
Spring and Fall
Spring
5 ways that weeds can be harmful to pasture
Decrease palatability
Decrease nutritive Value
Decrease Yield
Increase toxicity
Affect native/benefical plants
5 Conditions that Promotes Weeds in Pasture
Overgrazing
Poor soil fertility
Movement of weed seeds
Main Considerations when trying to plant a weed
Identifying the weed
Annuals, biennials, perennials
Controlling the weed
Annuals, biennials, perenials
How to cultural control weeds?
Prevention
Pre-bolt Stage Management
Multi animal species grazing
What is “Ounce of Prevention, Is Worth a Pound of Cure?”
This is to control well-managed pasture practices by:
Avoids overgrazing
Provide rest periods
Maintin proper soil ph and fertility
What is irrigation?
Supply water through technology in regions natural rainfall is insufficient for forage production
common in high drought areas
Types of Irrigation systems
Pod-line
Low Pressure system
Hose-pull traveler
Enter pivot
Inputs and Outputs of Irrigation
Input: Rainfall
Output:
Transpiration
Runoff
Root Storage
Evaporation
6 Objectives of Irrigation
Adequate moisture
Distribute water evenly
Minimize Water Loss (evaporation/runoff)
Root O2
Prevet Leaching
Prevent soil erosion
4 Soil Moisture Levels and Irrigation Scheduling Growth Stages
Saturation: soil is full of water
Field Capacity: Ideal Water content in soil
Refill Point: Low soil moisture
Permanent Wilting: extremely dry soil
Goal of irrigation: Keep soil moisture between field capacity and refill point for ideal plant growth and efficient water use.
What 3 factors can affect Irrigation efficiency?
Edaphic (soil water storage, not too much not to little)
Forage Species (WUE)
Atmospheric Conditions (Precipitation/Evaporation)
Goal: Maximize water use while minimizing waste and plant stress.