Chapter 3 Review: Crystal Structures, Densities, and X-Ray Diffraction
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
VOCABULARY-style flashcards covering crystalline vs noncrystalline materials, crystal structures (SC/BCC/FCC/HCP), packing factors, density, polycrystalline vs single crystals, anisotropy/isotropy, polymorphism, and X-ray diffraction concepts.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
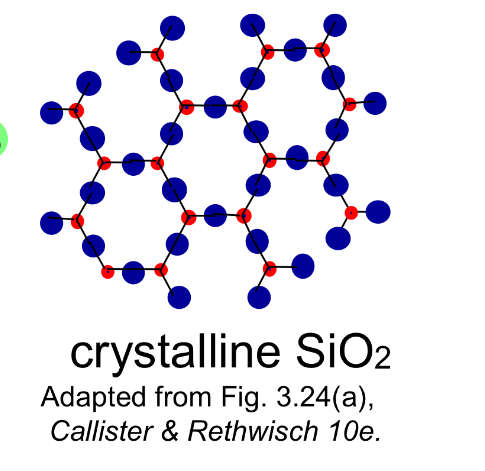
Crystalline materials
Materials with atoms arranged in a periodic 3D array (long-range order).
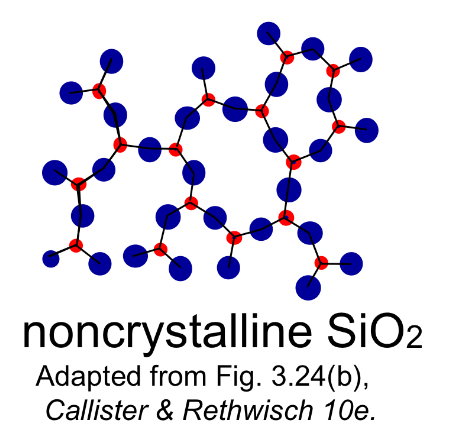
Noncrystalline materials (Amorphous)
Materials lacking long-range order; atoms arranged irregularly, often formed by rapid cooling.
Amorphous
Noncrystalline; lacking long-range order.
Lattice
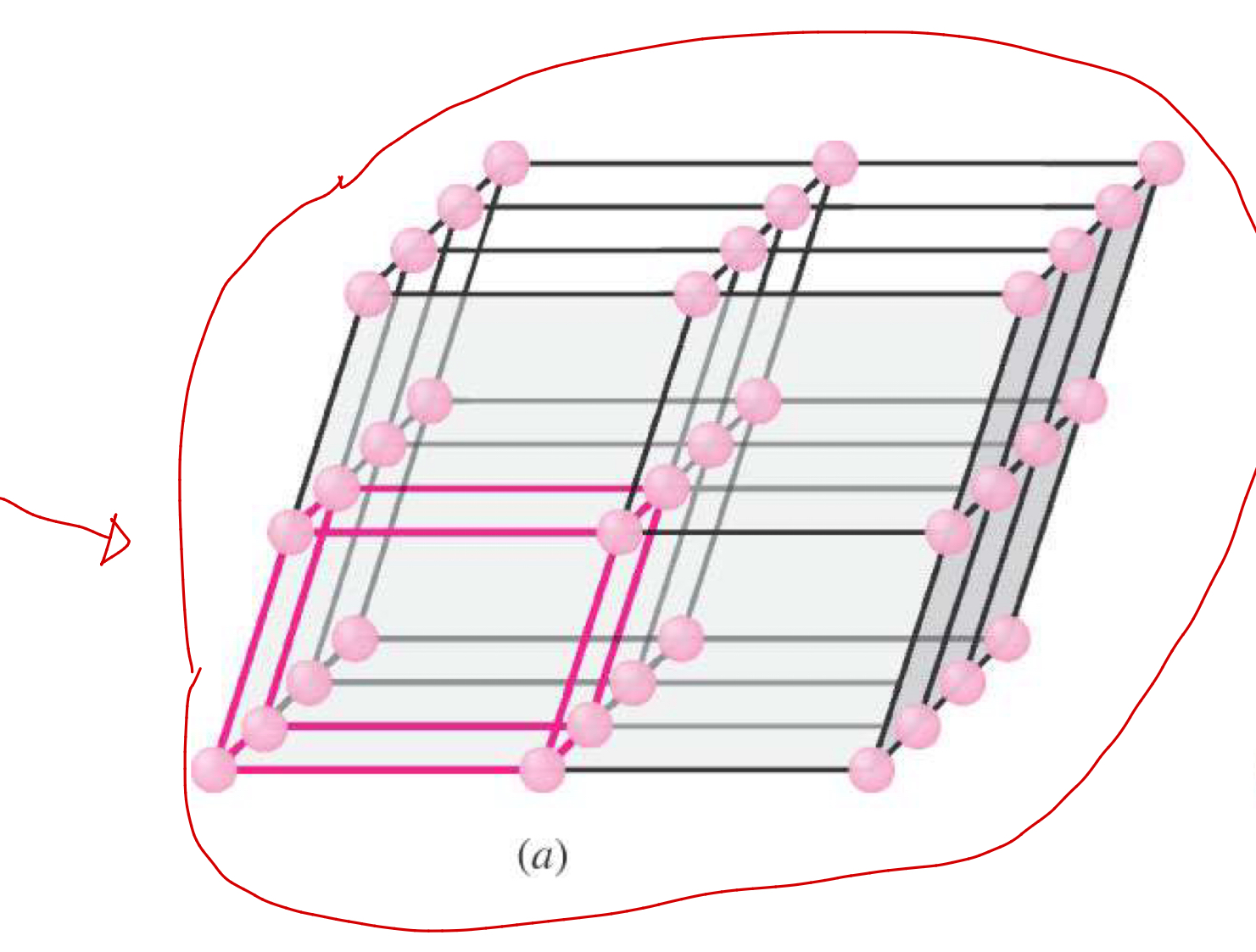
Three-dimensional array of points representing atom positions in a crystal.
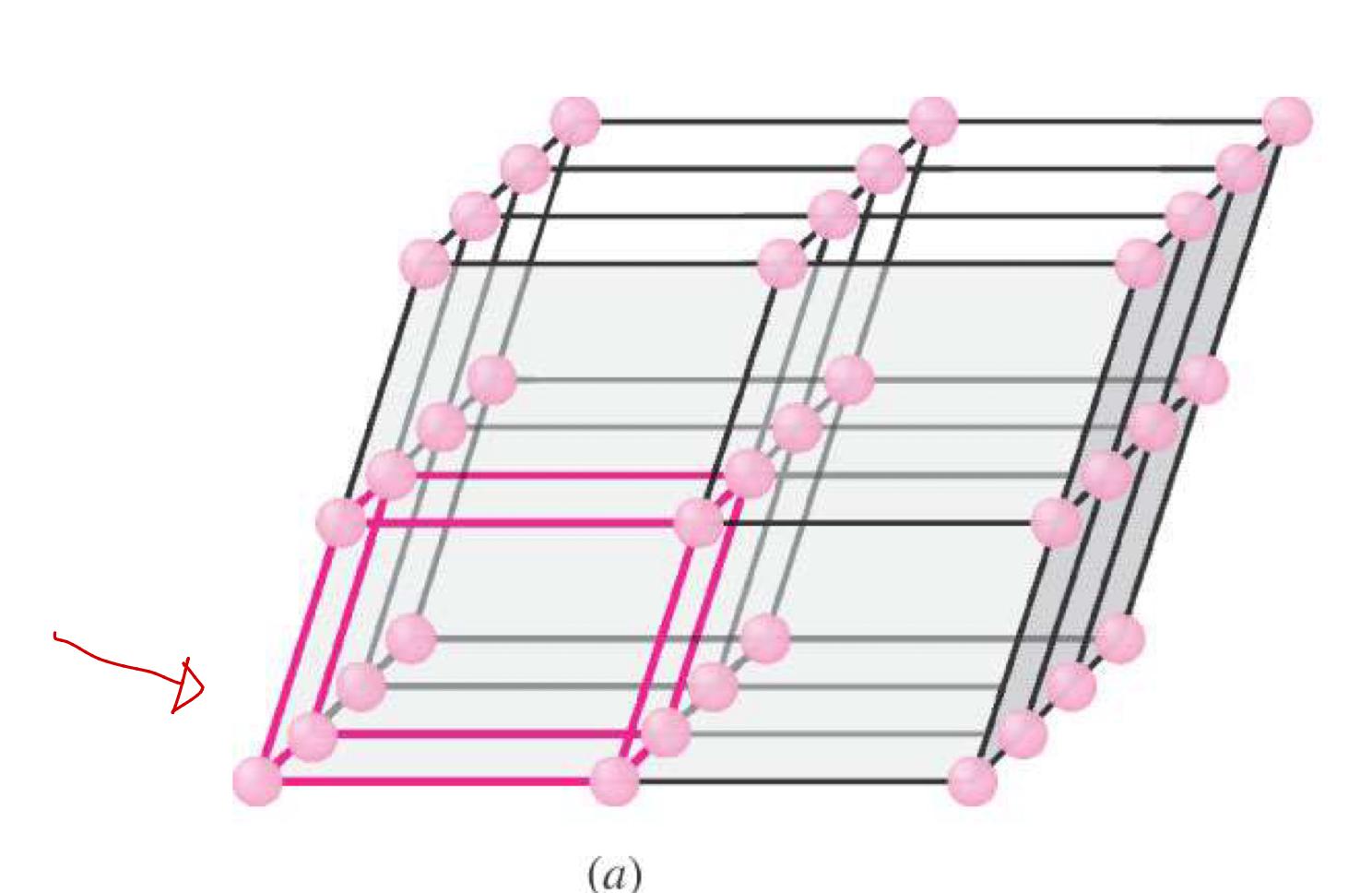
Unit Cell
The basic structural building block of a crystal; defines structure by geometry and atom positions.
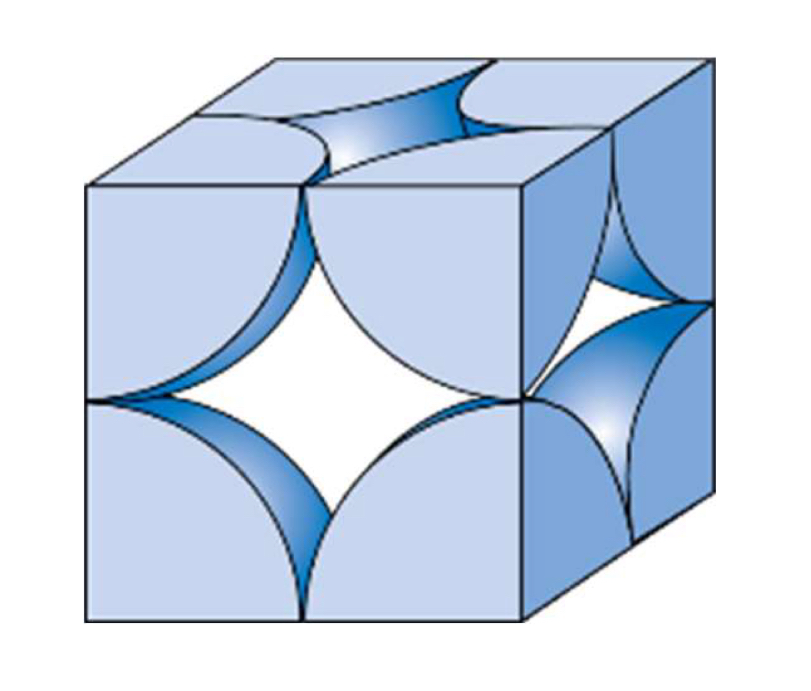
Crystal structure
SC
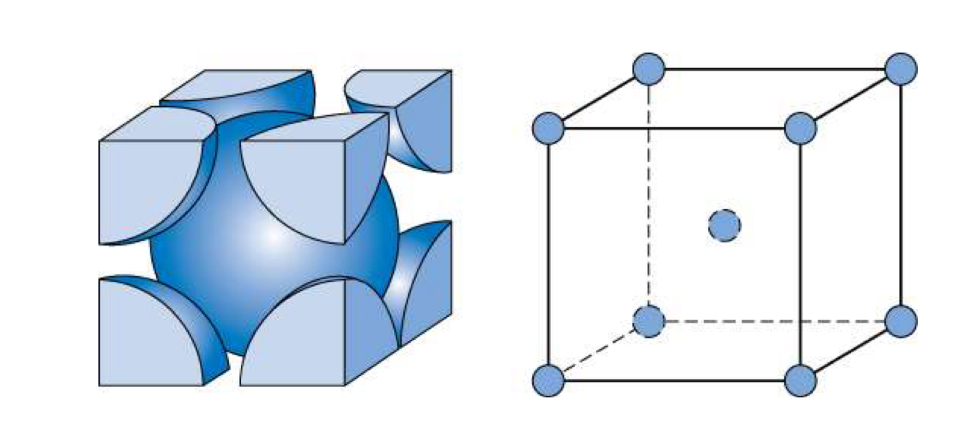
Crystal structure
Body-Centered Cubic (BCC)
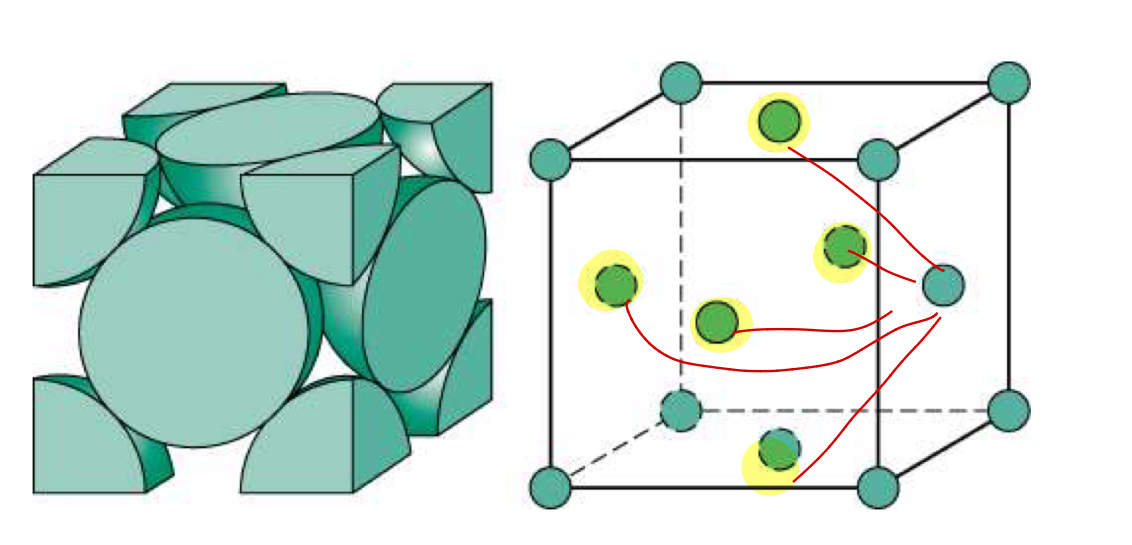
Crystal structure
Face-Centered Cubic (FCC)
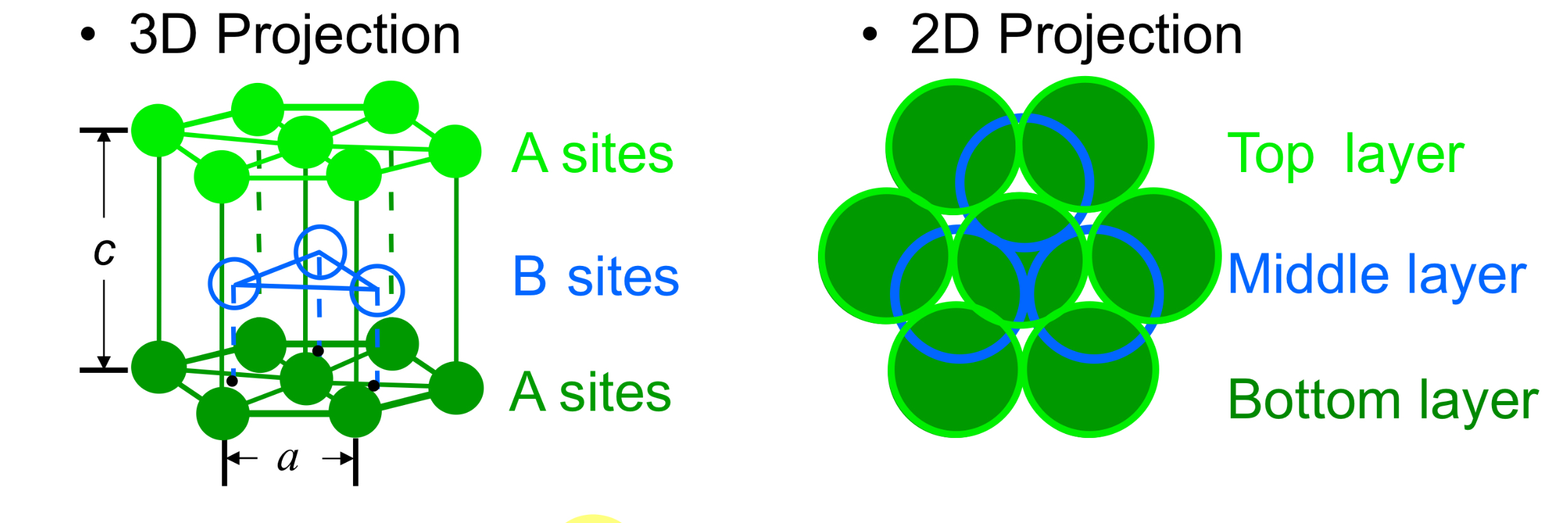
Crystal structure
HCP
SC Structure a vs r
a = 2R
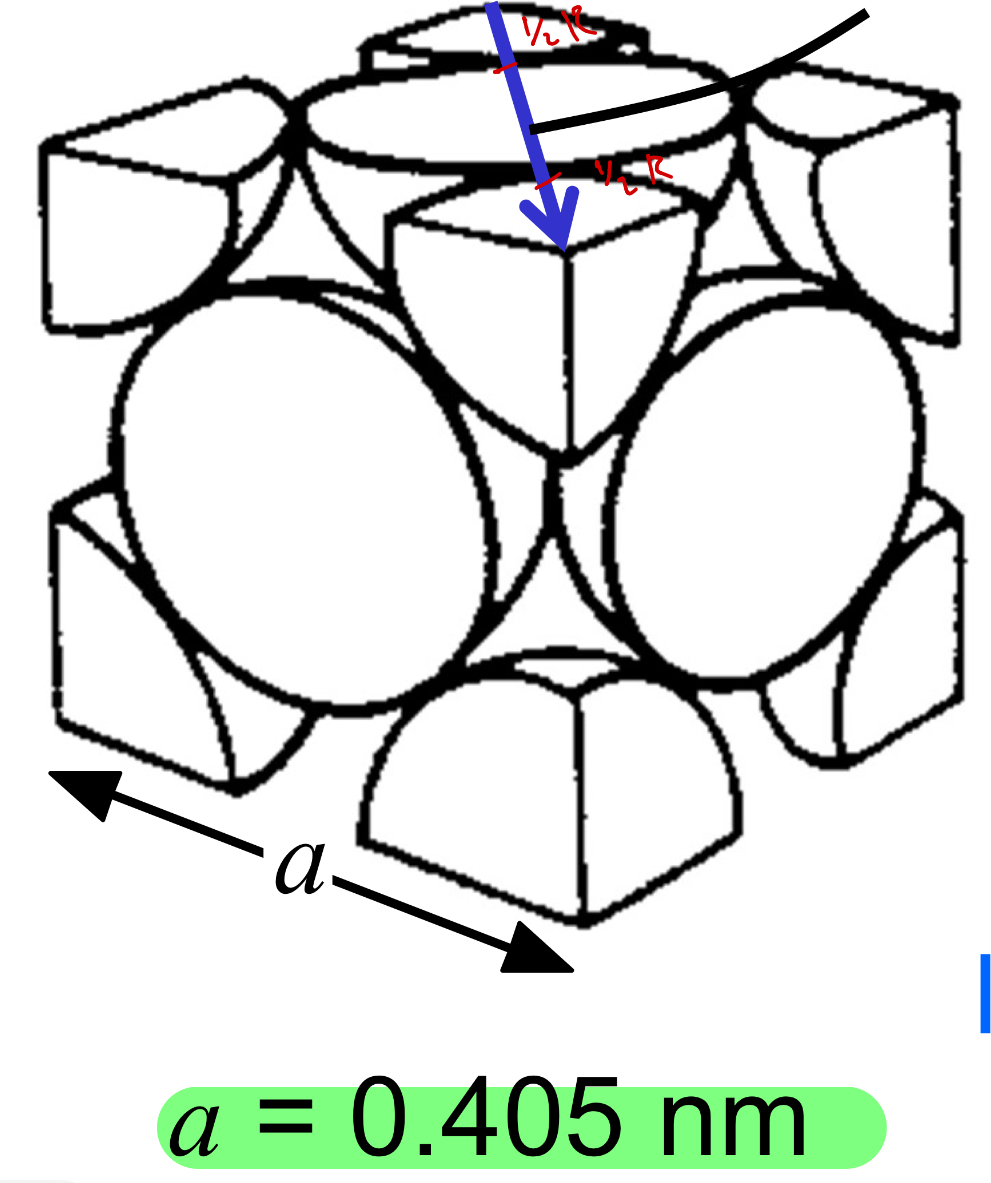
BCC Structure a vs R
a =4R /sq 3
FCC Structure a vs r
a = 4R/sq2
HCP Structure a vs r
A=2R
c = 1.633a
SC Atoms/Cell
1
BCC Atoms/Cell
2
FCC Atoms/Cell
4
HCP Atoms/Cell
6
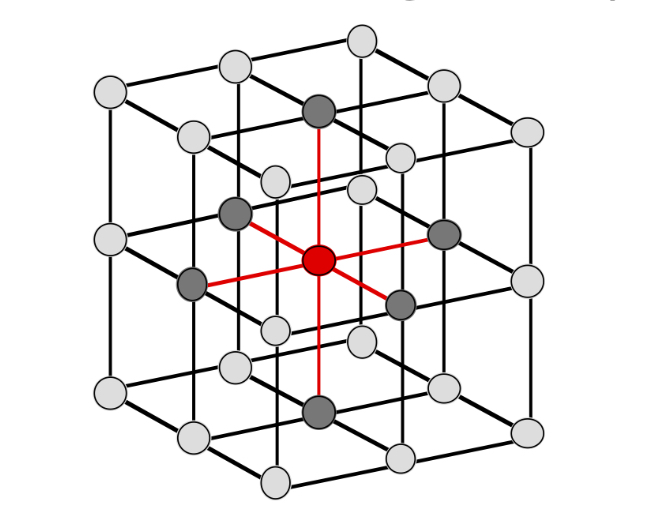
SC Coordination number
6
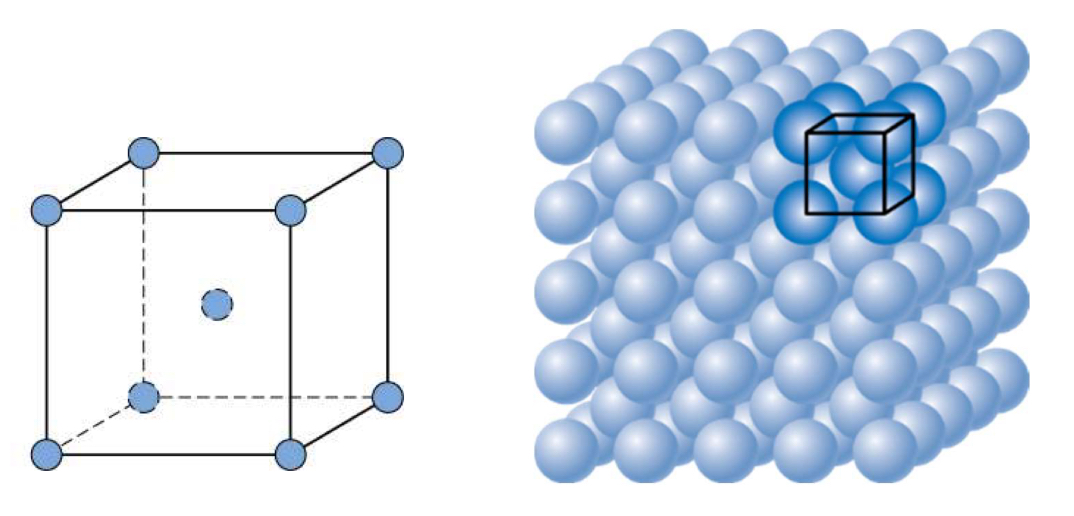
BCC Coordination number
8
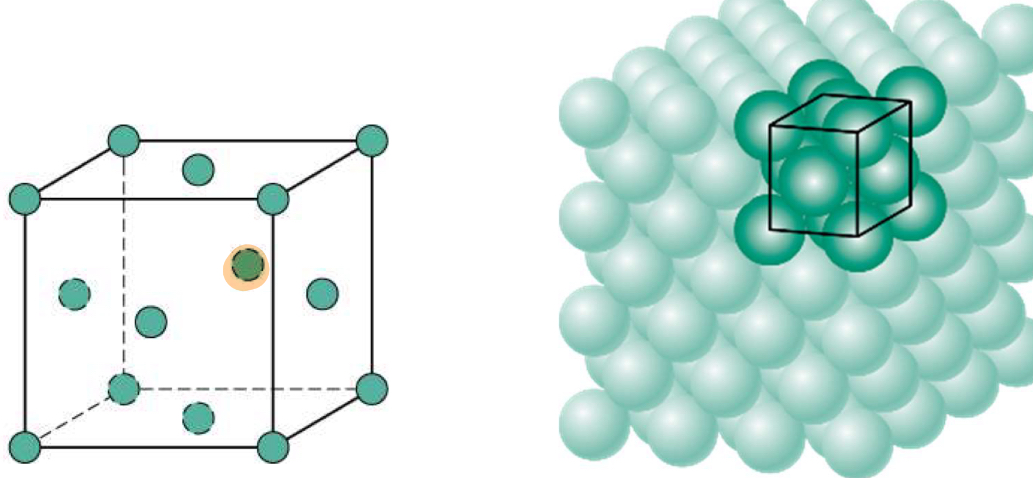
FCC Coordination number
12
HCP Coordination number
12
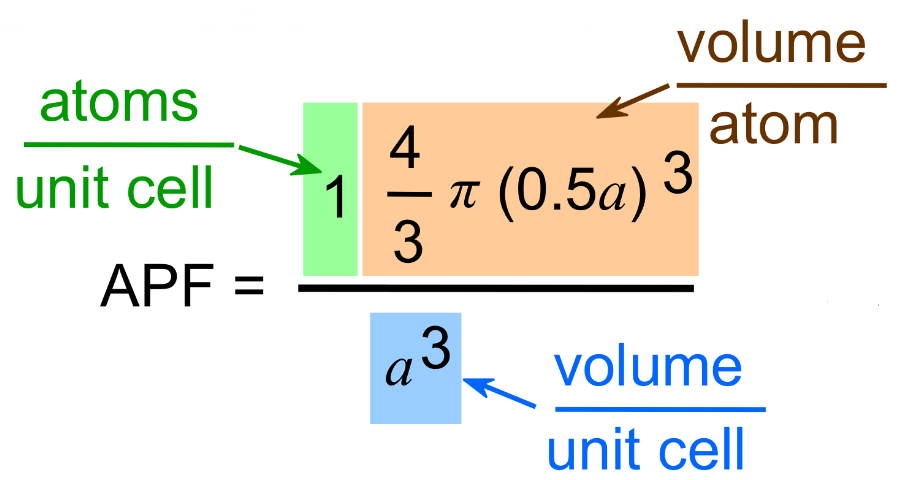
SC APF
0.52
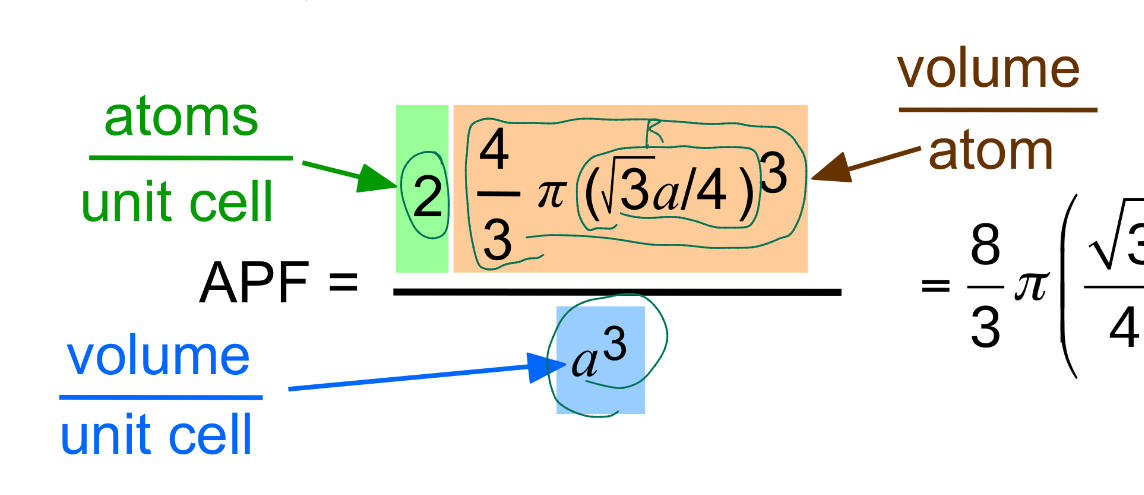
BCC APF
0.68
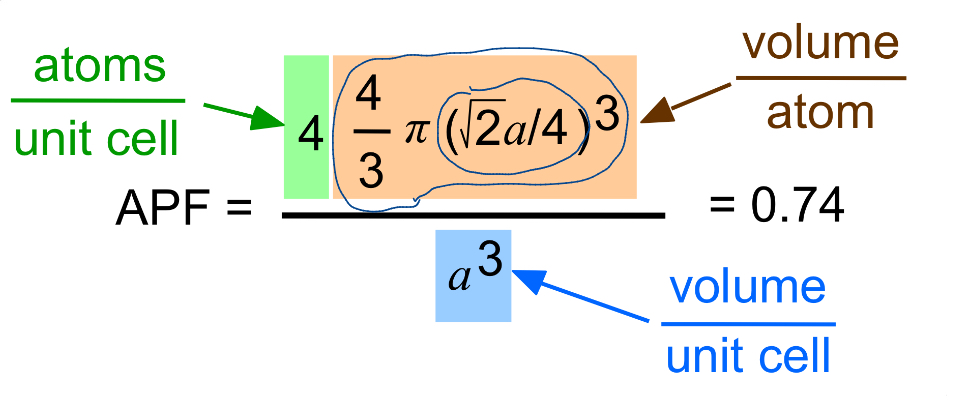
FCC APF
0.74
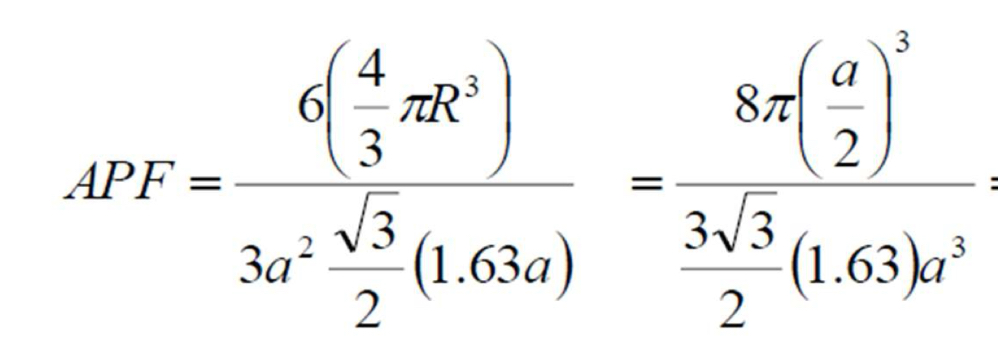
HCP APF
0.74
Plane Stacking sequence (FCC)
ABCABC… arrangement
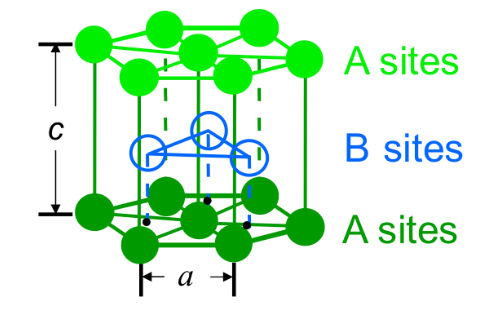
Hexagonal Close-Packed (HCP)
ABAB stacking sequence
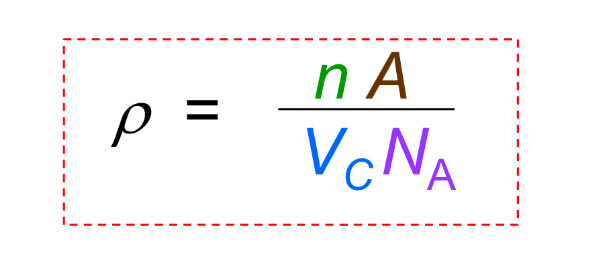
Theoretical Density
Density calculated from unit cell data, commonly ρ = (Z × M) / (N_A × a^3) for cubic crystals.
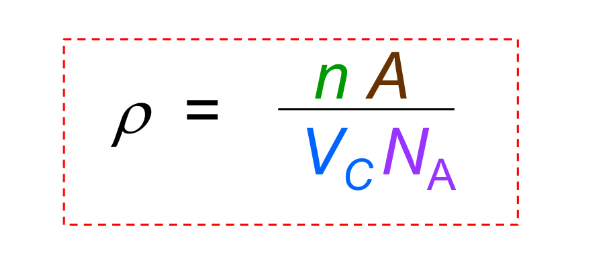
Theoretical Density what is A
atomic weight
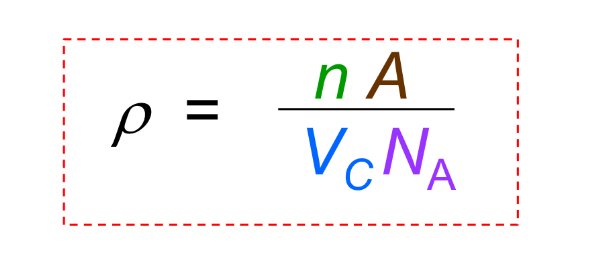
Theoretical Density what is Vc
Volume of unit cell = a^3 for cubic
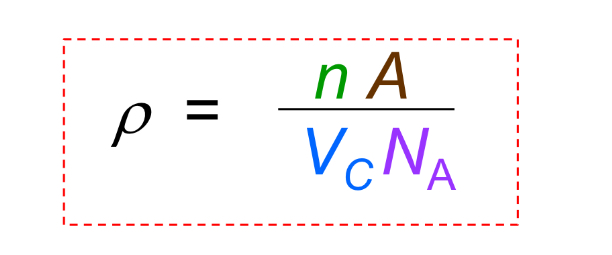
Theoretical Density what is NA
Avogadro’s number = 6.022 x 10^23 atoms/mol
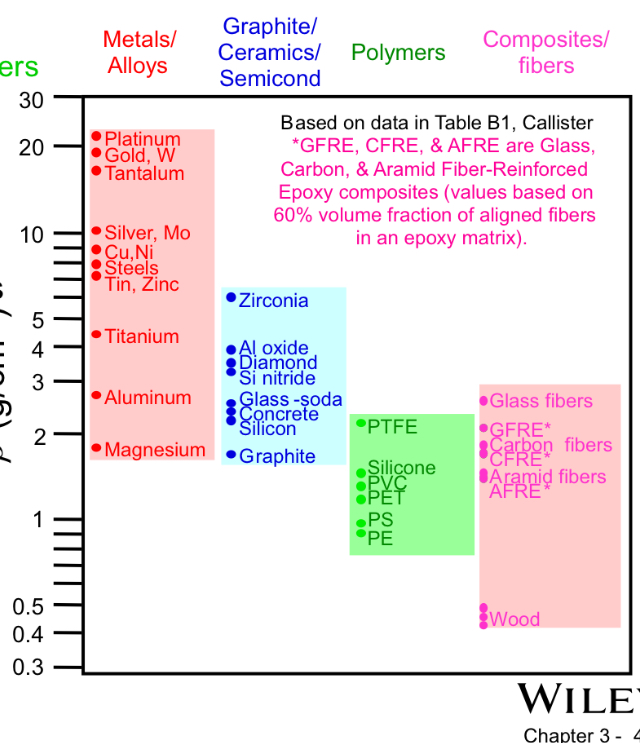
Densities by material type
Metals generally have higher densities than ceramics, which are higher than polymers (ρmetals > ρceramics > ρ_polymers).
Linear Density of Atoms (LD)
= 2/sq2 a
Planar Density of Atoms (PD)
1/a²
Single crystals
A crystal that extends without interruption through the entire specimen; no grain boundaries.
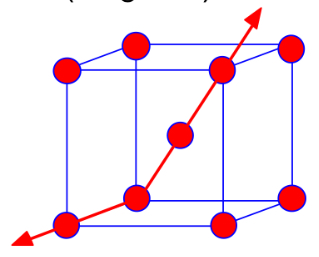
Anisotropy
Property values depend on crystallographic direction; commonly seen in single crystals.
เกรนเรียงทิศเดียวกัน สมบัติเปลี่ยนตามทิศทาง (อาจดีในบางทิศ)
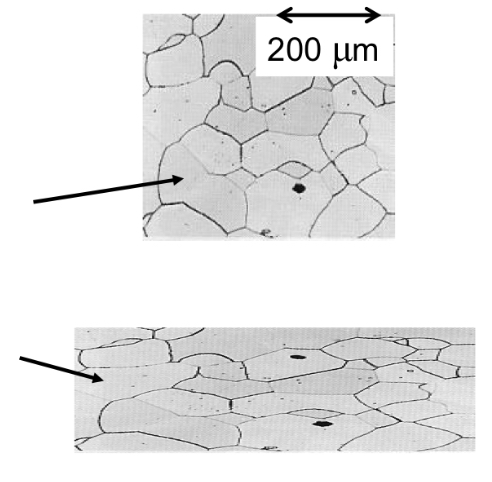
Isotropy
Properties are the same in all directions; occurs when grains are randomly oriented.
เกรนหันคนละทิศ สมบัติเท่ากันทุกทิศ (ดีต่อการใช้งานทั่วไป)
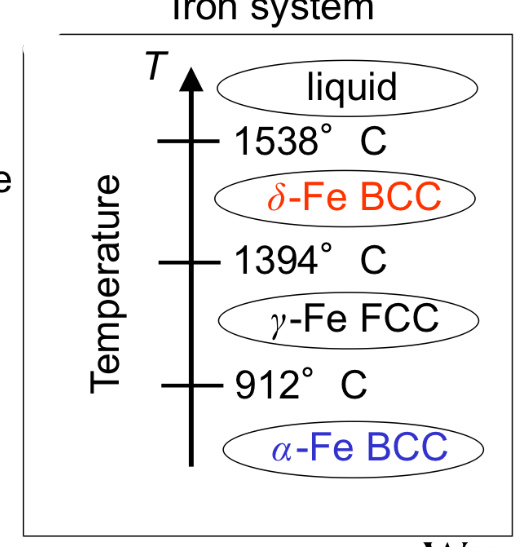
Polymorphism/Allotropy
Two or more crystal structures for the same material depend on temperature
X-ray Diffraction
Analytical technique to determine crystal structure using X-ray scattering.
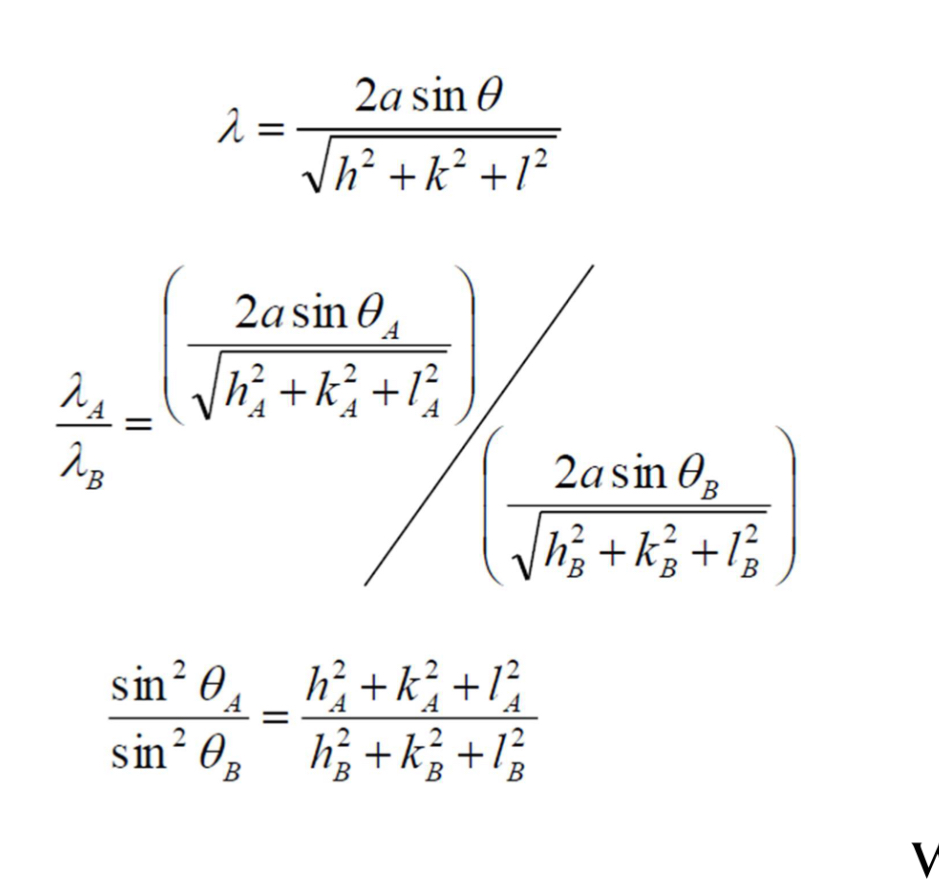
Bragg’s law
n lambda = 2d sin0
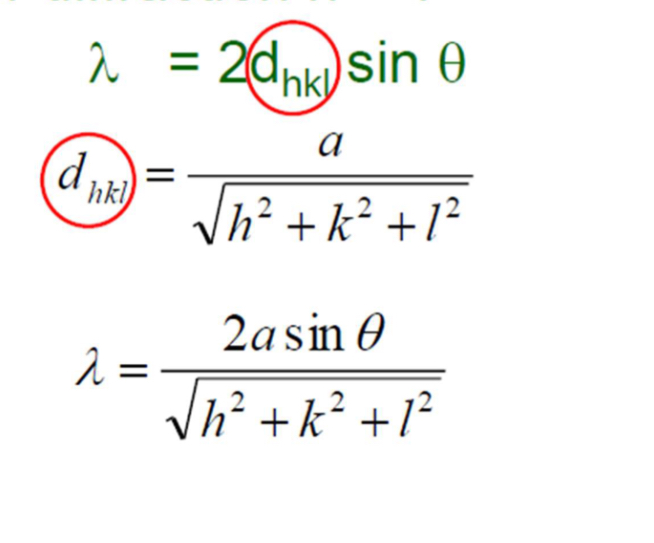
What condition must be met for X-ray reflections to be present in a BCC lattice?
The sum h^2 + k^2 + l^2 must be even.
When are reflections absent in a BCC lattice?
When h^2 + k^2 + l^2 is odd
What condition allows reflections to be present in an FCC lattice?
The Miller indices (h, k, l) must be all odd or all even
When are reflections absent in an FCC lattice?
When the indices (h, k, l) are not all odd or all even.