2: radiation physics and x ray Machine
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
Matter
Anything that has mass and takes up space
The fundamental unit of matter
atom
Components of an atom
protons, neutrons, electrons
Mass Number
the sum of the number of neutrons and protons
atomic number
number of protons
How are atoms arranged on the periodic table?
by increasing atomic number
Electrons
revolve around the nucleus in defined paths - orbits or shells
Maximum shells contained by an atom
7 shells
K shell
the orbital shell closest to the nucleus
Lettering of shells
K, L, M, N, O, P, Q
binding energy
electrons are held in orbit by electrostatic attraction between the positive nucleus
Is binding energy different for each shell?
Yes
What is binding energy dependent on?
the distance from the nucleus
Binding Energy (BE) Units
electron volts or kilo electron volts
Ionization in a neutral/stable atom
# of protons = # of electrons
Ionization
removal of an electron from an atom
the energy required to remove an electron must exceed...
the binding energy of the election
What is an ion pair?
positive ion and ejected electron
What is radiation?
the emission and propagation of energy through space
What are the two types of radiation?
particulate and electromagnetic
examples of particulate radiation
-electrons (beta particles and cathode rays)
-protons
-neutrons
-alpha particles
What is electromagnetic radiation?
movement of wave-like energy as a combination of electric and magnetic fields
Examples of electromagnetic radiation (7)
- x rays
- y rays
- UV
- visible light
- IR Radiation (AKA heat)
- microwaves
- radio waves
ionizing radiation
radiation w/enough energy to free electrons
non-ionizing radiation
Radiation that has enough energy to move atoms, but not enough to remove electrons
ionizing radiation examples
x-rays and gamma rays
(some UV)
non-ionizing radiation examples
Microwaves, Radio Waves, Infrared light and the visible light spectrum
(and some UV Rays)
3 properties of electromagnetic radiation
1) does not have mass or weight
2) no electrical charge
3) travels at the speed of light
Wilhelm Roentgen
discovered x-rays
Components of X ray Tube
- cathode
- anode
- leaded glass housing (vacuum)
- power supply
What is the cathode made of?
Tungsten wire filament
Molybdenum focusing cup
where cathode is placed -
focuses electrons on target (in a narrow beam)
Is the cathode negatively or positively charged?
negatively charged
what happens when the cathode is heated?
electrons are produced and accelerate towards a positive anode
What are the two types of anodes?
stationary and rotating
Are rotating anodes used in dental units?
NO
Is the anode positively or negatively charged?
positively charged
What is the anode made of?
a small tungsten target 2-3 mm thick that is embedded in a copper stem
Why is the anode embedded in a copper stem?
because copper is a better heat conductor than tungsten
Focal spot
area on the anode that electrons hit during x-ray production
Metal housing of x-ray tube head characteristics
Has transformers
Filled with insulating oil
Metal housing of x-ray tube head function
Protection of x ray tube
grounds the high voltage components
insulating oil (tubehead)
Surrounds x-ray tube and transformers, prevents overheating
Transformers (tube head)
alter voltage
Tube head seal
ALUMINUM or LEADED glass covering of the tube head that permits the exit of x-rays
Aluminum disks (tube head)
1. Filter out the non penetrating, longer wave length X-rays
2. sheets of 0.5 mm thick (aluminum)
X rays consist of a....
continuous spectrum of photon energies
only photons with sufficient energies can...
penetrate through anatomic structures and reach image receptors or sensors
Low energy photons cannot...
reach image receptors and cause unnecessary exposure to patients
how are low energy photons removed?
small metallic disc or filter
Types of filters
Inherent
Added
Examples of inherent filters
X ray tube housing
glass envelope
oil
Example of added filter
sheets of aluminum
Required total filtration for 1.5mm Aluminum
50-70 kVp
Required total filtration for 2.5mm Aluminum
Above 70 kVp
Collimator
lead plate with a hole that fits directly over the opening of metal housing
restricts the size of x ray beam
Position indicating device (PID)
lead lined cylinder that extends from the metal housing of the tubehead
aims and shapes the X-ray beam.
what do collimators regulate?
the shape and size of beam
What is most dental equipment collimated at? (measurement)
2.75 inches or 7 cm
step down transformer
a transformer that decreases voltage
110-220V to 3-5V
Step up transformer
a transformer that increases voltage
65,000 to 100,000 voltage
Autotransformer
voltage compensator that corrects minor fluctuations
Tube current
flow of electrons through the tube from cathode to anode
What is tube current controlled by?
mA
Tube voltage is controlled by
kVp
Timer (x ray unit)
controls duration of x ray exposure
thermionic emission
the release of electrons from the outer shell of tungsten filament
What are the two types of interactions when high energy electrons interact with the tungsten target?
Bremsstrahlung or Breaking Radiation
Characteristic Radiation
Bremsstrahlung radiation
1) electron passing close to a tungsten atom is attracted towards the nucleus
2) the electron changes direction
3)The kinetic energy lost by this electron is emitted as radiation
Most x rays are produced by what reaction?
Bremsstrahlung (70%)
Characteristic radiation
- results when the electrons bombarding the target eject inner orbit electrons
- removal of electrons from tungsten atom makes it positively charged
- the atom returns to neutral stage by emitting excess energy as radiation
(10-28% of x rays)
No interaction (patient)
area top 1/4 of head
9%
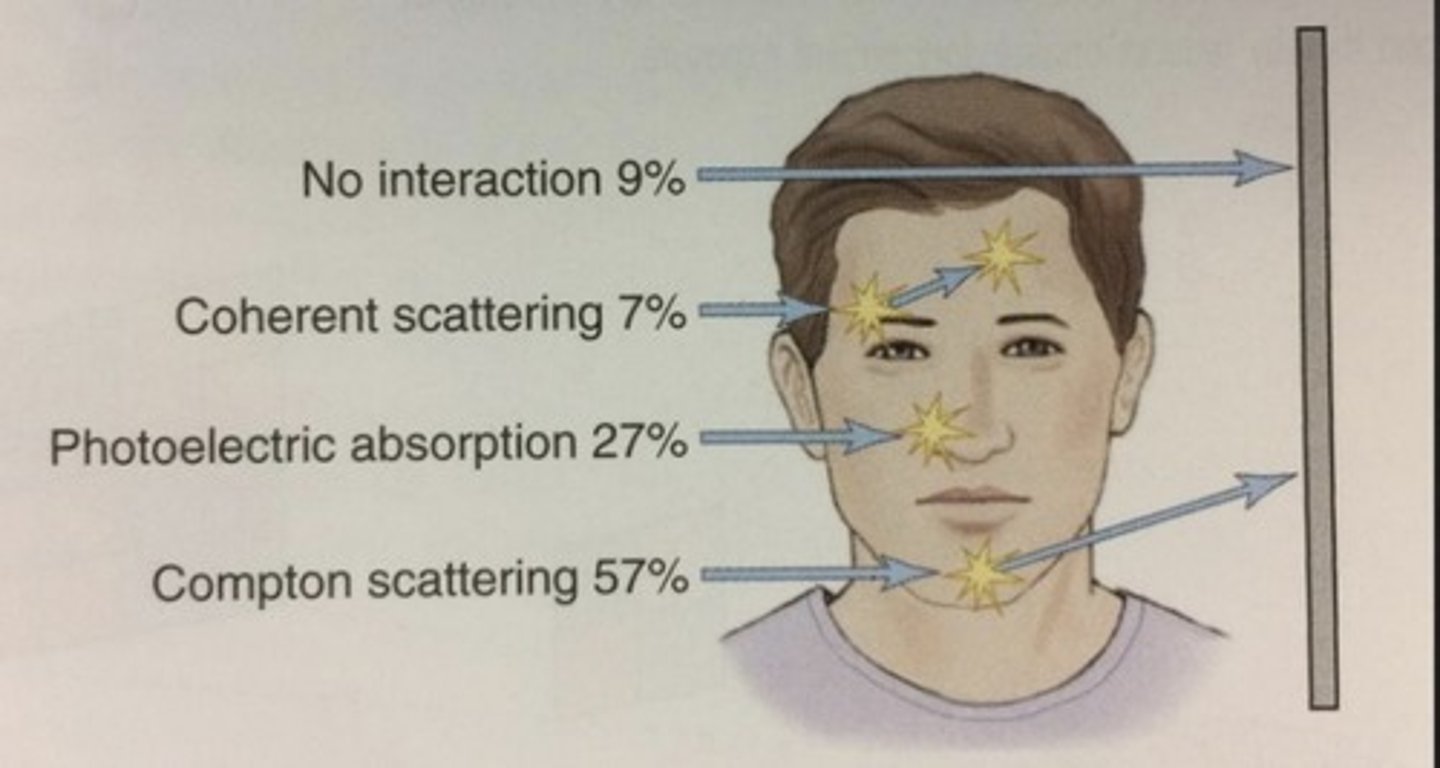
Coherent scattering (patient)
eyebrow/forehead region
7%
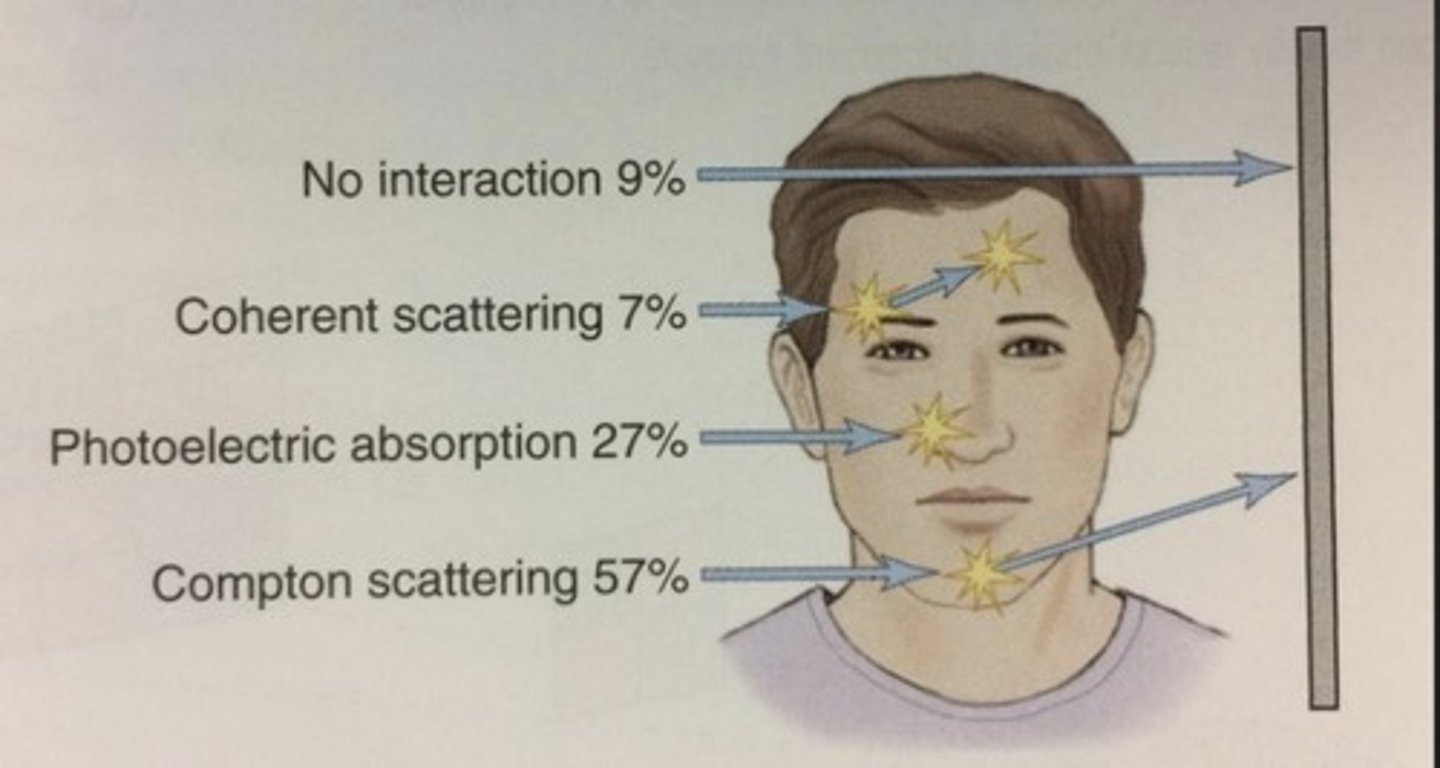
Compton Scatter (patient)
chin region
57%
Photoelectric absorption/effect (patient)
nose/center of face region
27%
what is the primary contributor of image formation?
photoelectric absorption
what happens during photoelectric absorption?
incident photon interacts with the inner shell electron of an atom in the patient's tissues
the photon gives all of its energy and disappears
incident photon has energy greater than...
the binding energy of the electron with which it interacts
Compton scattering
1) higher energy photon strikes a loosely bound outer electron
2) electron is removed it from its shell
3) the remaining energy is released as a scattered photon
does coherent scatter contribute to diagnostic imaging?
NO
Coherent scattering
(occurs with low energy x-rays, typically below the diagnostic range.)
1) The incoming photon interacts with the atom
2) atom becomes excited
3) The x-ray does not lose energy but changes direction.
X-ray beam quality
mean energy or Penetrating ability of the x-ray beam
Shorter wavelength x rays
more energy
more penetrating
Longer wavelength x rays
low energy
less penetrating capability
What does tube voltage control?
quality
wavelength
energy
Tube voltage
The potential difference between the cathode and the anode
(makes electrons move from cathode to anode)
what does voltage determine?
speed of electrons
What happens if speed of electrons increases?
electrons strike target with greater force and energy
the beam is penetrated with shorter wavelength/higher energy
Dental radiography voltage
65 to 100kV
What happens if:
85 to 100kV
Shorter wavelength
more energy
over penetration
What happens if:
65 to 75kV
Longer wavelength
less energy
under penetration
when is a higher kVp used?
when the area that needs to be examined is dense or thick
Amperage
determines the amount of electrons passing through the cathode filament
Ampere
the unit used to measure number of electrons or current flowing through cathode filament
1mA is how many amperes?
1000 amperes
1 milli ampere is how many amperes?
1/1000 of an ampere
Does a change in mA change the kinetic energy of electrons?
NO, only quantity is changed
how many mA required in dental radiography
7 to 15 mA
exposure time
time during which x rays are produced
how is exposure time measured
in impulses as x rays are created in a series of bursts rather than a continuous stream