Fluids & Electrolytes & Acid-Base Balance
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
Functions of Body Fluids:
Transport gases, nutrients, & waste
Helps generate electrical activity to power body functions
Takes part in the transformation of food → energy
Environmental stresses and disease affects balance
How is Body Water distributed?
Through:
Intracellular water
Extracellular/Plasma water
Interstitial water
Total Body Water (TBW):
60% of total human weight
Intracellular fluid: 2/3 of water
Extracellular fluid: 1/3
Extracellular fluid is divided into:
Interstitial fluid: around cells; most of the bunch
Intravascular: plasma & lymph fluid
Transcellular fluid: low amount; synovial, intestinal, CSF, sweat, urine, pleural, peritoneal, intraocular fluids; joint spaces
Low # but important
TBW in Peds:
75-80% of body weight
Susceptible to significant changes in body fluids; dehydration in newborns
Aging in TBW:
v % of TBW
v free fat mass & v muscle mass & renal decline
Diminished thirst perception
Intracellular Compartment (ICF)
Fluid contained within all of the cells in the body
Higher concentration of K+
Almost no Ca
Moderate # of magnesium
Small Na+
Extracellular Compartment (ECF):
Contains all outside cell fluid; interstitial or tissue spaces & b.v.
Higher concentration of Na+
Moderate # of bicarbonate
Small K+
Osmolarity:
of the extracellular fluid almost entirely due to Na+
of the intracellular fluid almost due to K+ as the primary electrolyte
measure of the total number of solute particles dissolved in a fluid
If ECF/ICF changes in concentration _______
fluid shifts from lesser → greater concentration
Kidneys’ involvement with fluid-electrolyte balance:
Maintains & excretes body fluids
Selectively retains substances needed & excretes unneeded ones (like electrolytes, metabolic waste & toxins)
Regulates pH via excretion/maintaining hydrogen ions & bicarbonate
Lungs’ involvement with fluid-electrolyte balance:
Rids 300mL of fluid/day out of body & plays role in Acid-Base Balance
Regulates CO2 conc.
Heart’s involvement with fluid-electrolyte balance:
pumps blood with sufficient force → perfuse the kidneys → kidneys work ^ effectively
Adrenal gland involvement with fluid-electrolyte balance:
Secretes aldosterone: Na+ retention (water retention) & K+ excretion
Parathyroid’s involvement with fluid-electrolyte balance:
Regulates Ca & P balance
PTH: ^ Ca & v PO4 (phosphate)
Pituitary gland’s involvement with fluid-electrolyte balance:
Secretes ADH (vasopressin) → ^ water reabsorption in kidneys
posterior part
Tonicity:
Tension/effect that effective osmotic pressure of a solution w/impermeable solutes exerts on cell size due to water movement across cell membrane
Isotonic: neither shrink/swell
Hypotonic: Swell; high osmolarity inside
Hypertonic: shrink; high osmolarity outside
Water movement between fluid compartments depend on:
Osmolality: measure of the conc. of dissolved particles (solutes) in solution
Osmotic forces: force driving water low → high conc.
Aquaporins: protein that selectively transports water
Starling forces: water leaving capillary site → lymph → venae cava
Net filtration = forces favoring filtration - forces opposing it
Hydrostatic pressure:
caused my water, more water → ^ hydrostatic psi
Colloidal osmotic/oncotic pressure:
Have more proteins → attract water
Filtration:
caused by capillary hydrostatic psi (35mm Hg) + blood colloidal psi (25mm Hg)
Arterial end net filtration psi = +10 mmHg
No Net movement:
capillary hydrostatic psi (25mm Hg) = blood colloidal osmotic psi (25mm Hg)
Mid Capillary net filtration psi = 0 mm Hg
Reabsorption:
Fluid re-enters capillary due to capillary hydrostatic psi (18 mmHg) < blood colloidal osmotic psi (25 mm Hg)
Venous end net filtration psi = -7 mm Hg
Net Filtration:
Forces favoring filtration:
Capillary hydrostatic psi (BP)
Interstitial oncotic psi (water pulling)
Forces favoring reabsorption
Plasma (capillary) oncotic psi (water-pulling)
Interstitial hydrostatic psi
Edema:
Accumulation of fluid within interstitial spaces
Causes:
^ in capillary hydrostatic psi
v in plasma(capillary) oncotic psi
^ in capillary permeability
Lymph obstruction
Localized vs generalized:
Pitting Edema
Assessing via daily weight, visual assessment, measuring affected part, finger pressor for pitting edema
What are the causes of decreased capillary oncotic psi that would lead to Edema?
Either
Loss of plasma protein to interstitial space from increased capillary permeability
Lower synthesis of plasma proteins from cirrhosis or malnutrition
Increased loss of plasma proteins from nephrotic syndrome
Increased plasma Na- and water retention from dilution of plasma proteins
What are the causes of increased capillary permeability that would lead to Edema?
Burns or inflammation
causes loss of plasma proteins to interstitial space
What are the causes of increased tissue oncotic pressure that would lead to edema?
Loss of plasma proteins to interstitial space
Lymph obstruction → v transport of capillary filtered protein
What are the causes of increased capillary hydrostatic psi that would lead to edema?
Venous obstruction, salt & water retention, and heart failure
Causes fluid movement to tissues
Lymph obstruction and its effects on edema:
Fluid movement to tissues
lower transport of capillary filtered proteins
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH):
^ water reabsorption → plasma
^ plasma osmolarity → detected by receptors → either fluid intake (will lead to v osmolarity straight up) or hypothalamus detects it → PP pars nervosa → ADH → aquaporins ^ → renal water retention → v plasma osmolality
v plasma volume → detected by receptors → hypothalamus detects it → PP pars nervosa → ADH → aquaporins ^ → renal water retention → ^ plasma volume
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP):
^ plasma volume → atrial stretching detected by endocrine cells → ANH release → (glomerulus starts to ^ Glomerular Filtration Rate → excrete more water) or (proximal tubule lowers Na+ reabsorption → excrete ^ Na)
High amounts suggest heart failure
Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System (RAAS):
either v extracellular fluid/arterial BP → kidneys sense low # of fluid → Juxtaglomerular cells secrete Renin → turn angiotensinogen to angiotensin 1 → converting enzymes in lungs turn 1 to Angiotensin 2 → (goes to adrenal cortex → induce aldosterone → ^ Na+ reabsorption of kidney thus water too → ^ Vascular volume & arterial BP) or/and (goes to arterioles → vasoconstriction of systematic arterioles → ^ arterial BP)
Osmolarity Alterations:
All occur in interstitial compartment; normal osmolarity is from 275-295 mm Hg
Can either be:
Isotonic
Hypertonic
Hypotonic
Isotonic Alterations:
TBW change w/proportional electrolyte & water change (no conc. change)
Isotonic fluid loss/excess
Hypertonic alterations:
Na gain & water loss → intracellular dehydration & hypernatremia
ICF → ECF
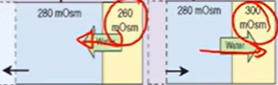
Hypotonic alterations:
v osmolality → cells expand & hyponatremia
water moves into cells via osmosis
Fluid Volume Deficit:
in the Interstitial compartment
Isotonic Dehydration
Hypertonic Dehydration
Hypotonic Dehydration:
Isotonic Dehydration:
Inadequate intake of fluids & solutes
Excessive losses of isotonic body fluids
Hypertonic Dehydration
Excessive perspiration, hyperventilation, ketoacidosis, prolonged fevers, diarrhea, diabetes insipidus all lead to ^ fluid loss
Hypotonic Dehydration:
Chronic illness, renal failure, chronic malnutrition
To assess body fluid losses measure:
HR, BP, venous volume/filling, capillary refill rate
Conditions that predispose Na + water loss, weight loss or body functions indicate v fluid volume
Fluid Volume Excess:
Interstitial compartment
Isotonic Overhydration
Hypertonic Overhydration:
Hypotonic Overhydration:
Isotonic Overhydration
Hypervolemia
Excessive fluid in extracellular compartment
fluid does not shift
Causes circulatory overload & interstitial edema
Hypertonic Overhydration:
Rare, excess Na intake
fluid is drawn from ICF
Hypotonic Overhydration:
Water intoxication
Fluid moves into ICF → expansion
Proportionate changes in Na & H20 in Interstitial compartment
Loss of water & sodium → fluid loss in ECF
Gain of water & sodium → fluid excess in ECF

Disproportionate changes in Na & H20 in Interstitial compartment:
Loss of sodium or gain of water → Hyponatremia
Gain of sodium or loss of water → Hypernatremia
What are all the electrolytes?
Na, K, Ca, P, Mg
Sodium (Na):
Major cation(+ charged atom that lost electrons) in ECF
135-145 mEq/L normal serum lvl
Determinant of plasma osmolarity; works with Cl-
Nerve impulse transmission, muscle contraction, movement of glucose & amino acids
Hyponatremia:
sodium lvl <135 mEq/L → plasma hypoosmolality & cellular swelling
Imbalances of Na+ → fluid volume imbalances
Most common electrolyte disorder; older age ^ risk
Causes of Hyponatremia:
Pure sodium loss
Low intake
Dilutional hyponatremia: gain lots of water → Na+ diluted
Diuretics, diaphoresis, GI loss
Manifestations of Hyponatremia:
Cellular swelling occurs
Early signs: muscle cramps, weak, fatigue (heavy exercise)
N.S. most seriously affected: lethargy, disorientation, confusion, seizures, comma
Loss of ECF & hypovolemia → hypotension, tachycardia, v urine output
Dilutional from excess water (hypervolemic hyponatremia) → weight gain, edema, ascites, jugular vein distention
Hypernatremia:
Serum sodium> 145mEq/L
Causes of Hypernatremia:
Decreased Na excretion
Cushing syndrome: too much cortisol → retains water & sodium → excrete K
Renal Failure: problem excreting waste
Hyperaldosteronism: retains sodium & water
^ Na intake
Excessive oral sodium ingestion
Hypertonic saline solutions
v water intake
NPO: nothing per oral
Infants, elderly, comatose
^ water loss
severe burns/fever
Diabetes insipidus: too low ADH → unable to retain water → peeing lots
Water diarrhea
Manifestations of Hypernatremia:
Thirst- early symptom
v urine output
^ urine & serum osmolality
Dry skin & mouth
Seizures
Tachycardia
Potassium:
Major ICF cation
Normal serum levels 3.5-5.0 mEq/L
Concentration maintained by Na+/K+ AtPase Pump
Transmission & conduction of nerve impulses, normal cardiac rhythm, skeletal/muscle contractions
Derived from diet
Regulated by renal & transcellular buffer systems
Changes in pH affect K+ balance
Aldosterone, insulin & epinephrine influence lvls
Kidney most efficient regulators
Hyperosmolality:
Water leaves cell → intracellular K + → K+ moves out of cell
Metabolic Acidosis/Alkalosis:
Metabolic Acidosis:
H moves into cell for buffering; K moves out to ECF
Metabolic Alkalosis:
H moves out of cell → K moves into cell
Epinephrine. Albuterol, & insulin: Move K → cell
Repeated muscle contractions: Moves K → out of cell
Hypokalemia:
K levels <3.5
K Balance described by changes in plasma potassium lvls
Causes:
v K intake
^ K entry to cells (hyperinsulinism), steroids, cushing syndrome
^ K loss (GI, renal, skin, diuretics, diarrhea, vomiting, NG suction
s/s of Hypokalemia:
(depend on rate & severity):
Membrane hyperpolarization → v in neuromuscular excitability, skeletal muscle weakness, smooth muscle atony, cardiac dysrhythmias
Muscle paralysis if life-threatening respiratory v (<2.5)
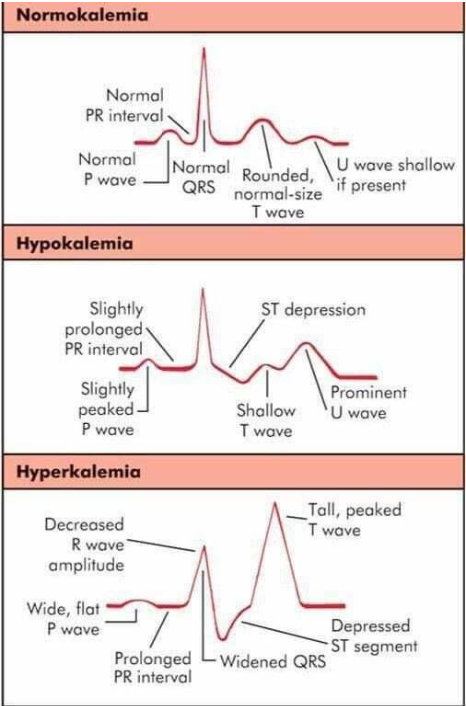
EKG changes: ^ PR interval, depression of ST segment, flat t wave, prominent U wave; lower stimulus (voltage) → not enough to reach threshold for action potential
Hyperkalemia:
K levels >5.0
Rare due to efficient renal excretion
Causes:
^ intake
shift of K+ ICF → ECF (acidosis)
v renal excretion (renal failure, Addison’s disease (OPP of Cushing disease))
Many blood transfusions
Cell Trauma
s/s of Hyperkalemia:
Mild attacks: membrane cell depolarization → initial ^ neuromuscular irritability (restless, diarrhea, intestinal cramps
Severe: EKG: peaked narrow T waves, wide QRS, cardia arrest; v resting membrane potential; weakness, loss of muscle tone, paralysis
EKG of Potassium:
Calcium & Phosphate:
Both controlled by parathyroid hormone (PTH), vitamin D, & calcitonin
Vitamin D : controls normal plasma lvls of Ca & PO4 via ^ intestinal absorption
Calcitonin acts on kidney & bone → removes Ca from extracellular circulation
Approx 99% of calc, 85% of P & 50-60% of Mg is found in bone
Calcium:
Bones, teeth, blood clotting, hormone secretion, cell receptor function, plasma membrane stability & muscle contraction (nerves)
Normal serum conc. 8.6-10.5 mg/dl
ECF Calcium exists in 3 forms:
Protein bound: 40% bound to albumin
Complexed: 10% chelated in citrate, PO4, Sulfate
Ionized: 50% in ionized form
Parathyroid Hormone:
maintains calcium conc in ECF, can also decrease PO4 lvls whilst ^ Ca lvls
If plasma Ca ^ → PTH inhibited → calcium stores in bones
If plasma Ca v → PTH secretion ^ & Ca mobilized from bone
Secretion, synthesis, & PTH action influenced by Mg: cofactor in cellular ATP generation
Hypoparathyroidism:
v Ca
caused by hyposecretion of PTH
May be congenital
Can occur after neck surgery (removal of parathyroid tissue in a thyroidectomy)
Hypocalcemia:
<8.5mg/dl Ca
Causes:
Inhibition of Ca absorption from GI tract
Inadequate oral intake
Lactose intolerant
Malabsorption (Chrons)
^ Ca Excretion:
Renal failure
Diarrhea
Steatorrhea: attached to fat instead of intestinal oxalate
Conditions that v ionized fraction of Ca:
Hyperphosphatemia
Removal/destruction of PT glands
Hypocalcemia s/s:
Chvostek’s sign: twitch of facial nerve in response to tap of nerve
Trousseau’s sign: Spasm of forearm on blood supply obstruction (BP cuff)
Tetany: spasm in muscles; Worst form is laryngospasm (prevents breathing)
Muscle Twitching
Later signs:
Arrhythmias: prolonged ST & QT interval
Hypercalcemia:
>10.5 mg/dl
Causes:
^ intestinal absorption
Excessive oral intake of Ca & Vitamin D
v Ca excretion
Use of thiazide diuretics
^ Bone resorption of Ca:
^ PTH
Malignant neoplasm
Prolonged immobilization
Hypercalcemia s/s:
Cardiovascular: ^ HR (early), Bradycardia (later)
Bounding/full pulse
EKG changes: short ST segment, wide T wave
Respiratory: skeletal weakness → ineffective respiration
Renal:
Polyuria: ^ urine output → dehydration
Renal Calculi (stones)
GI
v motility & bowel sounds
Anorexia
Nausea, vomiting
Abdominal distention
Constipation
Phosphate:
Energy for muscle contraction
PTH, Vitamin D3, calcitonin act together → controls phosphate absorption/excretion
Normal value = 2.5-4,5 mg/dl
Hypophosphatemia:
Causes:
Intestinal Malabsorption
Vitamin D deficiency
Antacids containing Mg & Al
Long term alcohol abuse
Malnutrition
Respiratory alkalosis (intracellular shift)
^ Renal excretion of PO4 associated w/ hyperparathyroidism
Hypophosphatemia s/s:
s/s:
Muscle Pain & weakness
Mental changes: irritated, confused, numb, coma, convulsions
Respiratory Failure
Cardiomyopathies
Hyperphosphatemia:
>4.5 mg/dl
Due to Hypocalcemia
Causes:
v renal excretion (renal failure)
^ intake
Hypoparathyroidism
Hyperphosphatemia s/s:
s/s:
v serum Ca lvls due to ^ PO4 lvls; sim to hypocalcemia results
Magnesium:
Intracellular cation
1.5 - 2.5 mEq/L
Cofactor for intracellular enzymatic enzymes
^ neuromuscular excitability
Hypomagnesemia:
Causes:
Malnutrtion
Gastric Suction
Malabsorption syndromes
Alcoholism
Urinary losses
Hypomagnesemia s/s:
s/s:
Anorexia
Neuromuscular irritability
^ reflexes
Depression
Disorientation
Hypermagnesemia:
Causes:
Renal insufficiency/failure
^ intake of Mg-containing antiacids
Adrenal insufficiency; v renal excretion
Hypermagnesemia s/s:
s/s:
Lethargy & drowsiness
Hypotension
Muscle weakness
v deep tendon reflexes (DTR)
v respirations
Bradycardia
Important in Pregnant woman: checks DTR, respirations
Acid-Base Balance:
Regulated to maintain normal pH via many mechanisms
Normal blood/body pH is from 7.35-7.45 pH
Measured by arterial blood gas (ABG) sampling; take from radial pulse w/needle
Determined by H+ conc in body fluids
3 Systems:
3 Systems of Acid-Base Balance:
Chemical Buffer System (HCO3-H2CO3 [Bicarbonate acid])
Kidneys (HCO3 [Bicarbonate)
Lungs (CO2)
pH:
-log of H+ conc
^ H+ = acidic
v H+ = alkaline
0-14 scale
Acid can be eliminated via:
Lungs → CO2 gas
Renal tubules w/regulation of HCO3-
Secretion regulation of H+ into urine
Buffering systems:
used to control pH
Buffer: chemical that binds excessive H+/OH- w/out significant pH change
Most important plasma-buffer systems: carbonic-bicarbonate pair
20 molecules of HCO3- to 1 H2CO3 (carbonic acid) = 7.4 pH
Acidosis: <7.35; ^H+ & v HCO3
Alkalosis: >7.45; vH+ & ^ HCO3
2 Systems can compensate when pH altered:
Respiratory System: ^/v ventilation → expire/retain CO2
CNS medulla controls & regulates RR
Renal System: produces acidic/alkaline urine (HCO3/H+)
Slow compensatory mechanism
Lungs regulation of Acid-Base Balance:
PaCO2: partial psi of CO2 in arterial blood
35-45 mmHg
Acute rise in PaCo2 is powerful respiration stimulant
Kidneys Roles in Acid-Base Balance
Regulate pH of ECF
If pH low:
Elimination of H+ in urine
HCO3 reabsorption
HCO3 production
NORMAL VALUES of Acid-Base Balance:
pH: 7.35-7.45
PaCO2: 35-45 mm Hg
>45 acidosis ; <35 alkalosis; Respiratory altered
HCO3: 21-28 mEq/L
<21 acidosis; >28 alkalosis; Metabolic altered
PaO2: 80-100 mm Hg
O2 sat: 95%+
Acid-base imbalances:
Respiratory Acidosis: ^ PCO2 due to ventilation depression
Respiratory Alkalosis: v of PCO2 due to hyperventilation
Metabolic Acidosis: v of HCO3/ ^ in noncarbonic acids
Metabolic alkalosis: ^ of HCO3, caused by excessive loss of metabolic acids
Mixed acidosis: resp + metabolic acidosis
Mixed alkalosis: rep + metabolic alkalosis
Metabolic Acidosis:
v HCO3 → v pH
Caused by
^ metabolic acids
Diabetic ketoacidosis (Dka): Usage of fat instead of glucose for energy
Starvation ketoacidosis
Anerobic metabolism
Ferrous sulfate overdose
Renal failure, uremia
Inability of kidneys → excrete acid
Excess loss of HCO3 via kidney/GI
Severe Diarrhea
Pancreatic secretions lost via pancreatic fistulas
Excessive acetazolamide (Diamox)/ammonium chloride
Renal failure
Metabolic Acidosis Compensation:
Compensation:
Ventilating faster
Acidic urine
Therapy: lactate containing solution used in therapy → convert to HCO3 ions in live
Metabolic Acidosis s/s:
s/s:
Headache
v BP
Hyperkalemia
Muscle Twitchin
Kussmaul Respirations
Diarrhea, Nausea
Metabolic Alkalosis:
>7.45 ^ HCO3
Causes:
^ HCO3 loading
Antacids
Ringer’s lactate
Loss of acid
Gastric suctioning: taking H+ out of stomach
Vomiting
Thiazide/loop diuretics
Contraction of ECF
v in ECF due to vomiting/NGT suction → loss of Cl & reabsorption of Na+ & HCO3
Metabolic Alkalosis compensation:
Compensation:
Breathing suppress → hold CO2
Kidney conserves H+ & makes HCO3 urine
Chloride-containing solution → HCO3 replaced by Cl
Metabolic Alkalosis s/s:
s/s:
Compensatory Hypoventilation
Tremors, muscle cramps, finger/toes tingling
Respiratory Acidosis:
^ in CO2 → v pH
Causes:
Hypoventilation
Acute disorders of Ventilation:
Impaired respiratory center function in medulla & pons (overdoses & tumors)
Lung disease
Chest injury
Weak respiratory muscles
Airway obstruction
Chronic Disorders of Ventilation:
COPD
Pulmonary Fibrosis
^PaCo2 production:
Exercise
Fever
Sepsis
Burns
Carb rich diet
Respiratory Acidosis Compensation:
Compensation:
Conserve HCO3 via kidneys
Respiratory Acidosis s/s:
s/s:
Headaches
Hyperkalemia
Dysrhythmias (K+)
Hypoxia ← Hypoventilation