Edexcel IGCSE Chemistry - Electrolysis
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
what is electrolysis?
the breaking down of a substance using electricity
what is electrolyte?
a molten or dissolved ionic compound that electric current passes through during electrolysis
which two process take place during electrolysis?
oxidation
reduction
what are positive ions called?
cations
what are negative ions called?
anion
what is the negative electrode called?
cathode
what is the positive electrode called?
anode
what happens to cations during electrolysis?
they are reduced
what happens to anions in electrolysis?
they are oxidised
what happens when the ions gain or lose electrons?
they form uncharged substances and become discharged from the electrolyte
what equations are used for electrolysis?
ionic half equations
what do ionic half equations show?
show how electrons are transferred
how do you form an ionic half equation?
put one of the things being oxidised or reduced on one side of the arrow, and the things it gets oxidised or reduced to on th eother
balance the numbers of atoms just like in a normal equation
then add electrons to one side to balance up the charges

what are the two types of compounds that can be electrolysed?
molten ionic compounds
aqueous ionic compounds
why can molten ionic compounds be electrolysed?
ions can move freely and carry charge
what is a molten compound broken into when it is electrolysed?
its elements - ions first and then elements when they reach the electrodes
what are electrodes made from?
inert (unreactive metal) so they don’t take part in the reaction
if molten lead bromide is electrolysed, what products will there be?
at the cathode: lead (II) ions become discharged to form lead → silver coating
at the anode: bromide ions become discharged to form bromine → orange solution
what are the half equations for the electrolysis of molten lead bromide?

how would you set up a circuit for electrolysis (carry electrolysis out)?
get two inert electrodes - graphite or platinum
clean the surfaces of the electrodes with emery paper
don’t touch the electrodes form now on
place both electrodes into a beaker filled with your electrolyte - should dip into the solution
connect the electrodes to a power supply using crocodile clips and wires
when you turn the power supply on, a current will flow through the cell
electrolysis will happen
after a few minutes record observations
what ions are present in aqueous solution?
ions from the ionic compound
hydrogen ions (H+)
hydroxide ions (OH-)
how do you determine what is produced at the cathode during the electrolysis of an aqueous compound?
either the metal ion or the hydrogen ion will be reduced at the cathode
whichever is least reactive will be produced → if the metal is more reactive, hydrogen will be produced and vice versa
how do you determine what is produced at the anode during the electrolysis of an aqueous compound?
the non-metal ion or the hydroxide ion could be oxidised at the anode
if the non-metal ion is a halide ion it will be oxidised at the anode, and a halogen will be produced
if the non-metal ion is not a halide ion (is polyatomic), hydroxide ions will be oxidised and oxygen (and water) will be produced
what is the half equation for the production of oxygen at the anode?
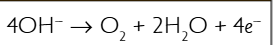
what is the half equation for the production of hydrogen at the cathode?
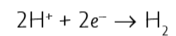
what products are formed when aqueous sodium chloride is electrolysed?
cathode: (hydrogen ions →) hydrogen - bubbles
anode: (chloride ions →) chlorine - green-yellow gas
left behind: sodium hydroxide solution
what are the half equations for the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride?
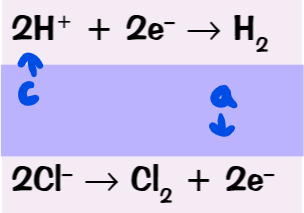
what products are formed when aqueous dilute sulfuric acid is electrolysed?
cathode: hydrogen → bubbles (no metal)
anode: oxygen → bubbles
what are the half equations for the electrolysis of aqueous dilute sulfuric acid?
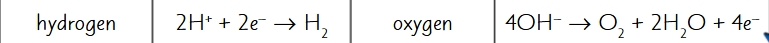
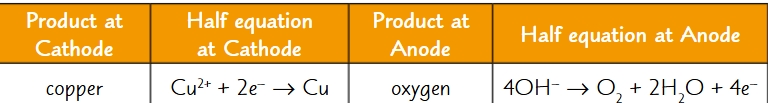
what products are formed when aqueous copper (II) sulfate is electrolysed?
cathode: copper → salmon pink deposit
anode: oxygen → bubbles
what are the half equations for the electrolysis of aqueous copper (II) sulfate?
what is bauxite?
bauxite = Al2O3 = aluminium [(III)] oxide
describe the apparatus for the electrolysis of aluminium oxide (bauxite)
electrodes = made of graphite
aluminium oxide has very high melting point
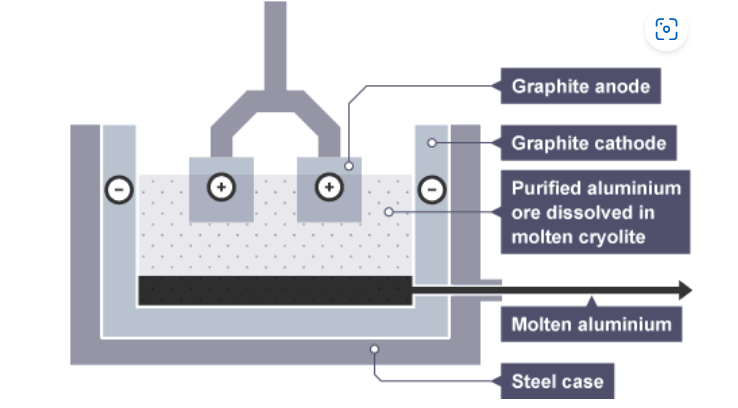
what is cryolite?
a solvent which lowers the boiling point of bauxite
what are the products formed during electrolysis of bauxite?
cathode: aluminium ions → aluminium
anode: oxygen ions → oxygen
what are the half equations for the electrolysis of bauxite?
cathode: Al3++ 3e-.→ Al (l)
anode: 2O2- → O2 (g) + 4e-
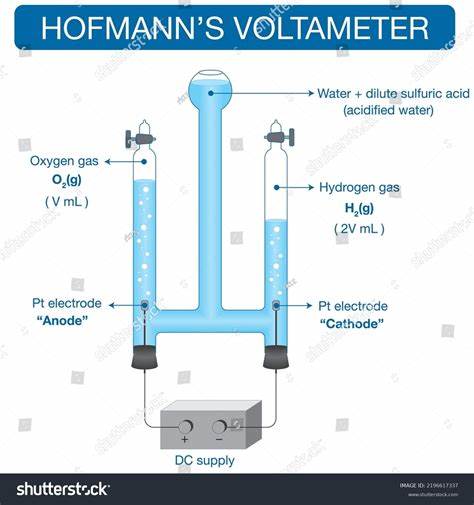
which apparatus is used for the electrolysis of water (with sulfuric acid added)?
hoffman apparatus