Chapter 2 Study Guide: The Chemistry of Life
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 1: Unit 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
What is the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of that specific type of matter?
Atom
What is a substance that cannot be broken into another substance by a chemical reaction?
Element
What occupies space and takes up mass?
Matter
What term describes substances with two or more elements in a fixed ratio?
Compound
What is the attractive force that holds two atoms together?
Chemical bond
What are the four classes of large biological molecules?
Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, Nucleic Acids
What are the building blocks (monomers) of carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides
What is the unique property of water that allows it to dissolve many important substances?
Polarity
What type of chemical bond involves the sharing of electrons between atoms?
Covalent bond
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats?
Saturated fats contain no double bonds between carbon atoms, while unsaturated fats have one or more double bonds.
What role do enzymes play in chemical reactions?
Enzymes speed up chemical reactions.
What happens to an enzyme's shape after a chemical reaction?
An enzyme's shape does not change permanently after a reaction.
Which type of bond is characterized by the unequal sharing of electrons?
Polar covalent bond
What is the function of cholesterol in the cell membrane?
Cholesterol helps maintain the structure of the cell's membrane.
What are triglycerides?
Triglycerides are the main form of fat storage in the body.
What will likely happen to unsaturated fats when they undergo hydrogenation?
They will turn into a solid or semisolid state.
What do you call a chain of amino acids?
Polypeptide.
What are lipids characterized by?
They are hydrophobic (do not mix with water).
In the context of nutrition, what type of fat typically remains liquid at room temperature?
Unsaturated fat.
What are acids?
Substances that can donate protons (H+) in a solution, typically having a pH less than 7.
What is the active site of an enzyme?
The specific region on an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction.
What is adhesion in biological terms?
The tendency of molecules to stick to other substances, important for processes like water transport in plants.
What are amino acids?
Organic compounds that serve as the building blocks of proteins, containing an amino group, carboxyl group, and a side chain.
Define atomic number.
The number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom, determining the element's identity.
What are bases in chemistry?
Substances that can accept protons (H+) or donate hydroxide ions (OH-) in a solution, typically having a pH greater than 7.
What are buffers?
Solutions that resist changes in pH when acids or bases are added, helping to maintain stability in biological systems.
What is the structure of carbohydrates?
Organic molecules composed primarily of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, often in the ratio of 1:2:1, including sugars and starches.
What is cellulose?
A complex carbohydrate that forms the cell wall of plants, providing structural support.
Define chemical bonds.
Forces that hold atoms together in molecules, including ionic, covalent, and hydrogen bonds.
What is chitin?
A structural polysaccharide found in the exoskeletons of arthropods and fungal cell walls.
What is cholesterol?
A type of lipid that is a key component of cell membranes and is involved in the synthesis of hormones and vitamin D.
What is cohesion?
The attraction between molecules of the same substance, essential for phenomena like water surface tension.
What are compounds?
Substances formed when two or more different elements chemically bond together.
What are covalent bonds?
Chemical bonds formed by the sharing of electron pairs between atoms.
What is a disaccharide?
A carbohydrate composed of two monosaccharides joined by a glycosidic bond.
What is a double bond?
A type of chemical bond where two pairs of electrons are shared between two atoms.
What are electrons?
Negatively charged subatomic particles that orbit the nucleus of an atom and are involved in chemical bonding.
What are elements?
Pure substances that consist of only one type of atom and cannot be broken down into simpler substances.
Define enzymes.
Biological catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions in living organisms without being consumed.
What is glucose?
A simple sugar and primary source of energy for cells, classified as a monosaccharide.
What is glycogen?
A polysaccharide that serves as a form of energy storage in animals, primarily found in the liver and muscles.
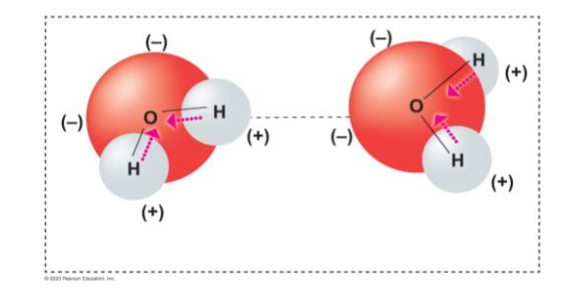
What defines a hydrogen bond?
A weak attraction between a hydrogen atom already bonded to an electronegative atom and another electronegative atom.
What is hydrogenation?
The chemical process of adding hydrogen to unsaturated fats to make them more saturated, often used in food processing.
What does hydrophobic mean?
Referring to molecules that repel water and do not mix well with aqueous solutions.
What are ionic bonds?
Chemical bonds formed through the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions.
What are ions?
Atoms or molecules that carry an electrical charge due to the loss or gain of one or more electrons.
What are isotopes?
Variants of the same chemical element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
What is lactose?
A disaccharide sugar found in milk, composed of glucose and galactose.
What are lipids?
A diverse group of hydrophobic organic compounds, including fats, oils, and phospholipids, important for energy storage and cell membranes.
What are macromolecules?
Large complex molecules essential to biological functions, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids.
What is matter?
Anything that has mass and takes up space, comprising atoms and molecules.
What are monomers?
Small structural units that can join together to form larger compounds called polymers.
What are monosaccharides?
The simplest form of carbohydrates, consisting of single sugar units like glucose and fructose.
What are neutrons?
Uncharged subatomic particles found in the nucleus of an atom, contributing to the atomic mass but not the charge.
What is a non-polar bond?
A type of covalent bond where electrons are shared equally between atoms, resulting in no partial charges.
What is the nucleus?
The central part of an atom that contains protons and neutrons, containing most of the atom's mass.
What are omega-3 fatty acids?
Essential fatty acids found in fish and flaxseeds, important for heart and brain health.
What are organic compounds?
Compounds primarily made of carbon atoms, often containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and other elements.
What are peptide bonds?
Covalent bonds that link amino acids together in a protein, formed through a dehydration reaction.
What is the periodic table of elements?
A tabular arrangement of all known chemical elements organized by their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring properties.
What is the pH scale?
A logarithmic scale used to measure the acidity or basicity of a solution.
What are phospholipids?
Molecules that form the structural foundation of cell membranes, consisting of hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails.
What are phospholipid bilayers?
Structures formed by two layers of phospholipids, creating the cell membrane with hydrophilic surfaces and a hydrophobic core.
What is a polar bond?
A covalent bond between two differing atoms where electrons are shared unequally, leading to a dipole moment.
What are polymers?
Large molecules made up of repeated subunits (monomers), forming structures like proteins and nucleic acids.
What are polysaccharides?
Carbohydrates consisting of long chains of monosaccharides, such as starch, cellulose, and glycogen.
What are products in a chemical reaction?
The substances formed as a result of a chemical reaction, following the transformation of reactants.
What are proteins?
Large biomolecules composed of amino acids, essential for structure, function, and regulation of the body's cells, tissues, and organs.
What are protons?
Positively charged subatomic particles found in the nucleus of an atom, determining the element's identity and atomic number.
What are reactants in a chemical reaction?
The starting substances that undergo a chemical change to form products.
What is RNA?
Ribonucleic acid, a nucleic acid involved in protein synthesis and genetic information transfer.
What are saturated fats?
Fats that contain only single bonds between carbon atoms in their fatty acid chains, typically solid at room temperature.
What is a single bond?
A covalent bond where a single pair of electrons is shared between two atoms.
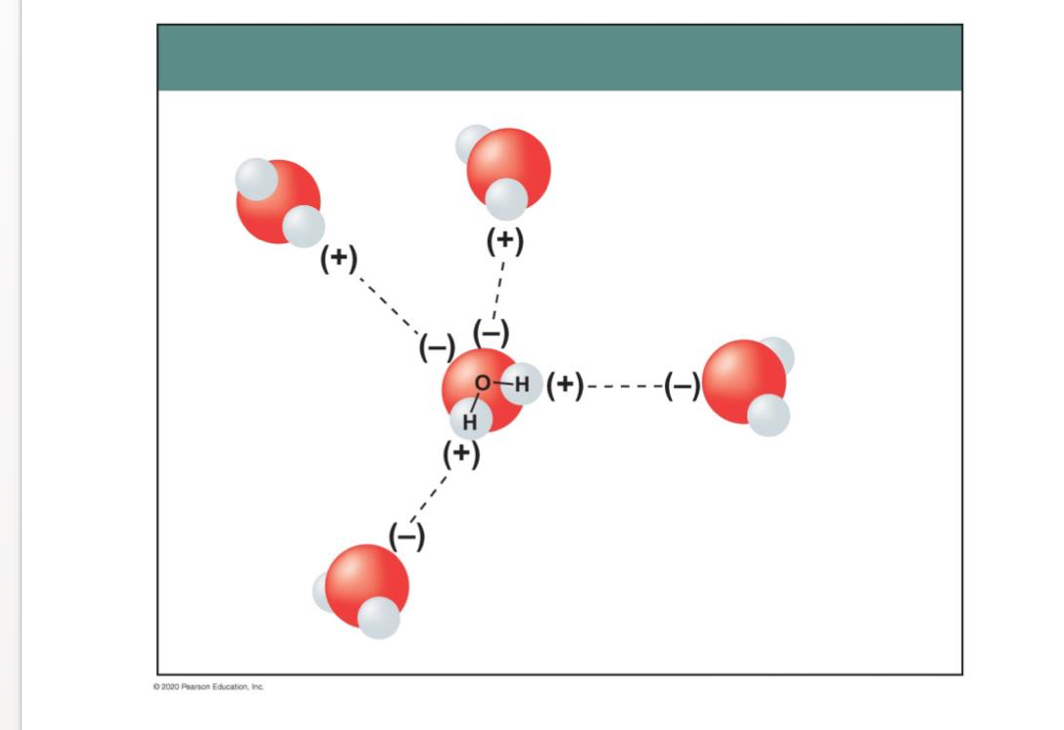
A. _________________ are substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by _______________ reactions.
Elements
_________________ are substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by B. _______________ reactions.
chemical reactions
What elements are in the compound NaCl (table salt)?
sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl).
Is H2O (water) an element? If not, briefly explain your answer.
No, it is not an element; it is a compound made up of two hydrogen atoms (H) and one oxygen atom (O), which are elements.
Where can you find all of the elements listed by their atomic number?
atomic number can be found on the periodic table.
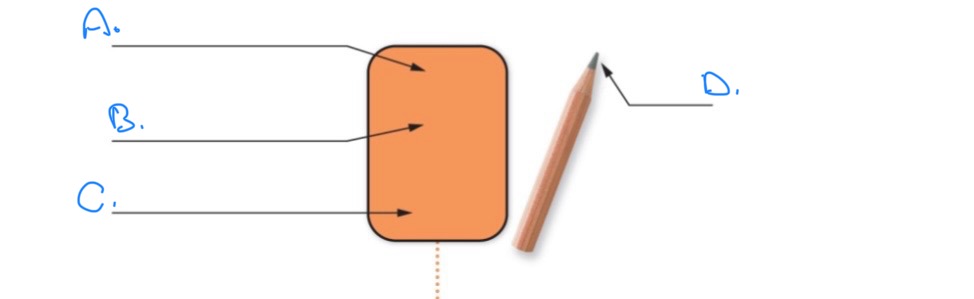
Label the Element of Carbon:
A.
Atomic number 6
Label the Element of Carbon:
B.
Symbol: C
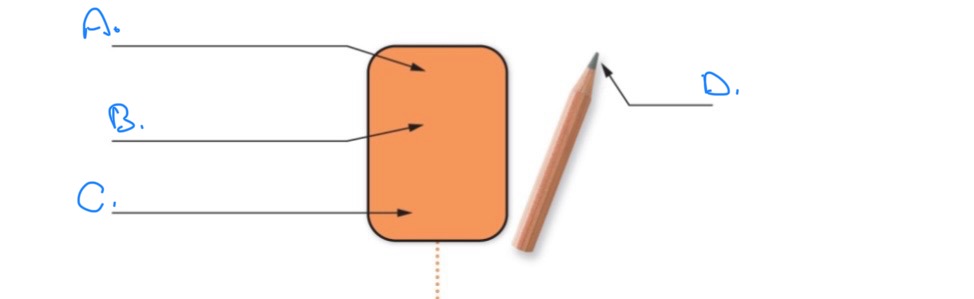
Label the Element of Carbon:
C.
Ex: Graphite carbon
True or False: No two elements on the periodic table have the same atomic number. If false, please correct the statement.
true
Which of the following elements does not make up the bulk of organisms?
A) Carbon
B) Hydrogen
C) Oxygen
D) Magnesium
E) Nitrogen
Magnesium
What are the three ways in which atoms can interact with one another (during chemical reactions) with respect to their electrons?
Ionic Bonds, Covalent Bonds, and Metallic Bonds:
The one feature common to all lipids is that they are __________________________.
hydrophobic, meaning they do not mix well with water.
A cell’s membrane consists, in large part, of a molecule called a phospholipid. Does a phospholipid “love” or “fear” water? Briefly explain your answer.
Phospholipids have a hydrophilic head (loves water) and hydrophobic tails (fears water).
True or false: Cholesterol is used within the cell to help maintain the structure of the cell’s membrane.
True
Which of the following is not a lipid?
A) Triglycerides
B) Cholesterol
C) Anabolic steroids
D) All of the above are lipids.
All of the above are lipids.
Are both steroids and triglycerides located in your body? If so, give a function performed by each.
Yes, they do. Steroids regulate metabolism and immune response, while triglycerides store energy.
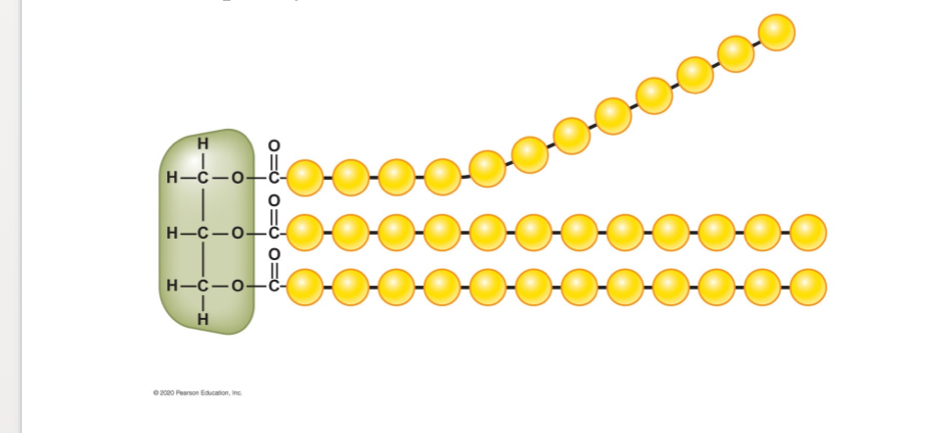
Which fatty acid tail from the following diagram is saturated? Which one is unsaturated?
Unsaturated = bent tail = first one
(at least one double bond)
Saturated = straight tails = second and third
Saturated Fats
are types of fats that are solid at room temperature and are found in animal products and some plant oils.
Unsaturated Fats
are types of fats that are liquid at room temperature and are found in plant oils, nuts, and fish.
An unsaturated fat can be turned into a solid or semisolid state by __________________________.
A) omega-3 fatty acidification
B) hydrophilic
C) hydrogenation
D) unsaturation
hydrogenation
A protein’s __________________ determines its function.
shape or structure.
_____ are the monomers from which large proteins are constructed.
A) Polymers
B) Amino acids
C) Polypeptides
D) Peptide bonds
Amino acids
A protein that speeds up chemical reactions is a (n) __________________.
enzyme
True or false: A chemical reaction changes the shape of the enzyme permanently.
false
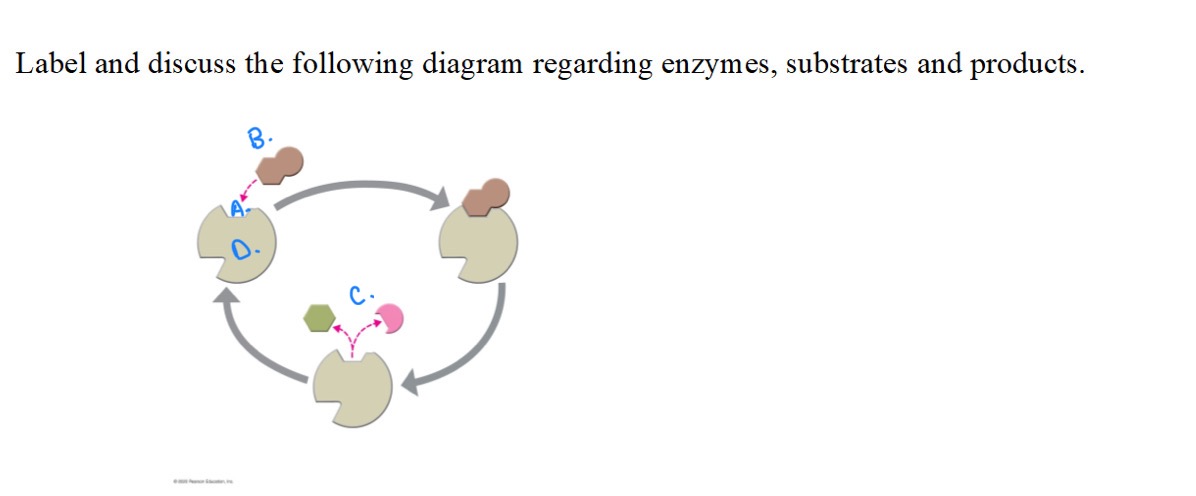
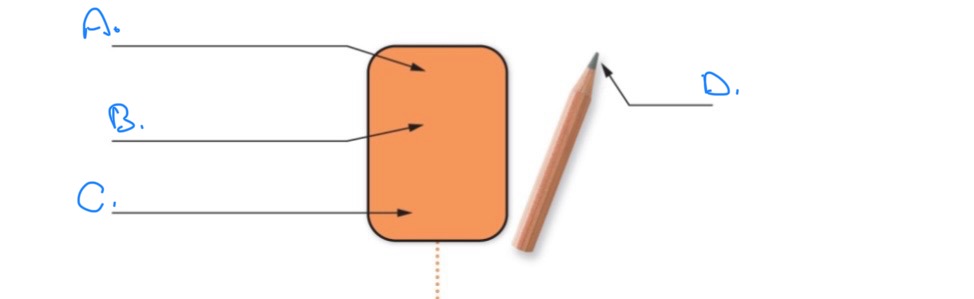
Label and discuss the following diagram:
A.
Active Site