ACLS
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What is the drug action of epinephrine/adrenaline?
peripheral vasoconstriction
Indications for the use of epinephrine?
VF/pulseless VT
asystole
What is the recommended dose for epinephrine?
Dose for 1:1,000 = 1 mg/mL every 3-5 mins
Dose for 1:10,000 = 0.1 mg/mL
these should be given every second loop of CPR
What is the drug action of amiodarone?
prevents conduction of unwanted electrical activity by blocking potassium channels to prevent a second action potential from being generated
Indications for the use of amiodarone?
VF/pulseless VT
What is the initial and additional dose for amiodarone?
300mg then 150mg
Drug action of verapamil?
Verapamil is a calcium-channel blocker that slows conduction through the AV node which reduces heart rate and contractility
Drug action of atropine?
blocks the effect of the vagus nerve on the heart to increase our heart rate
Indications for atropine?
bradycardia
What is the initial dose for atropine?
0.6 mg IV
What is the drug action of adenosine?
prevents tachycardias which originate above the ventricles
Indications for adenosine?
supraventricular tachycardia
Initial and additional dose for adenosine?
6mg then 12mg after 1-2 mins
What is the drug action of calcium?
Increases myocardial excitability and contractility
Indications for calcium?
hypocalcaemia
hyperkalaemia
overdose of calcium channel blocking drugs
What is the dose range for calcium?
5-10 mL
What is the drug action of lidocaine?
blocks sodium channels to prevent depolarisation and nerve conduction
Indications for lidocaine?
VF/pulseless VT
What is the initial and additional dose range for lidocaine?
1mg/kg then 0.5 mg/kg
What is the drug action of vasopressin/ADH?
increases water and sodium retention and causes vasoconstriction
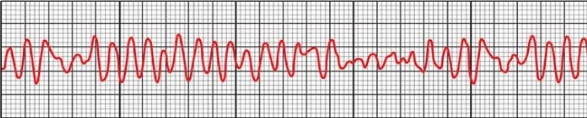
What arrhythmia is this?
Ventricular fibrillation
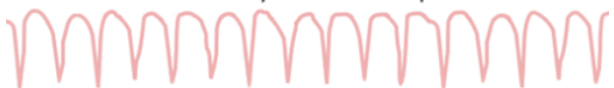
What arrhythmia is this?
Pulseless ventricular tachycardia
What arrhythmia is this?
asystole
What are the 2 shockable rhythms?
ventricular fibrillation
pulseless ventricular tachycardia
What are the 2 non-shockable rhythms?
asystole
pulseless electrical activity (PEA)
Where are the top and bottom paddles placed for defibrillation?
top paddle= right parasternal area, bottom paddle= midaxillary line
What are the 4 H’s?
hypoxaemia, hypovolaemia, hypo/hyperkalaemia, and hypo/hyperthermia
What are the 4 T’s?
Tension pneumothorax, tamponade, toxins, thrombosis
What is a tension pneumothorax?
Build-up of air in the pleural space which places pressure on our lungs, trachea, and heart
What is a cardiac tamponade?
Build-up of blood in the pericardial space which causes compression of the heart
What is an acute coronary syndrome (ACS)?
a syndrome in which there is an imbalance between the supply and demand of oxygen to the heart due to an occlusion of the coronary arteries
What is unstable angina?
chest pain which occurs during rest as a result of a partial occlusion of the coronary artery
What are the common symptoms of ACS?
central chest pain with or without radiation to the neck, arm, and back
SOB
diaphoresis
tachycardia
What is the treatment for ACS?
maintain an SpO2 >94%
administer NGT and morphine for vasodilation and pain management
attach electrodes for ECG monitoring
fibrinolytic therapy
What is a STEMI?
ST elevation myocardial infection caused by complete occlusion of the coronary artery
What is a cardiac arrest?
when the heart suddenly stops beating
Common causes of hypovolaemia?
anaphylaxis
bleeding
sepsis
Hypovolaemia presentation
flat neck veins
hx of bleedings
Treatment for hypovolaemia
fluids
bloods
Common causes of hypoxia
drowning
opioids/sedative overdose
Hypoxia presentation
cyanosis
SOB
compromised airway
Hypoxia treatment
oxygen
ventilation
CPR
Common causes of hypo/hyperkalaemia?
renal failure
vomiting/diarrhoea
hypo/hyperkalaemia presentation
on dialysis?
diabetic?
on diuretics?
Treatment for hypo/hyperkalaemia
hypokalaemia: potassium fluid replacement
hyperkalaemia: glucose with insulin as this pulls potassium into cells
Thrombosis (coronary) treatment
MONA: morphine, oxygen, NGT, aspirin
What is IgE mediated hypersensitivity?
A food allergy which is immediate
What are the common symptoms associated with a IgE mediated allergy?
hives
swelling
itchiness
watery nose and eyes
difficulty breathing and swallowing
vomiting
LOC