Vertebrates II Bio 1108
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Amniote
Member of a clade of tetrapod vertebrates that include reptiles (including birds) and mammals
Amnion
a protective membrane that encloses the embryo in a fluid-filled cavity
Advantages of an amnion egg
Allows the embryo to develop on land without desiccating and providing a greater degree of protection and facilitating the successful colonization of terrestrial environments
reptiles, birds, and mammals
Traditional classification of 3 living amniotes
Innovations of Amniotes
desiccation resistant skin
thoracic breathing (negative pressure sucks air in)
Water-conserving kidneys- concentrate waste prior to elimination
internal fertilization
Amphibians
Which class did amniotes develop from?
Synapsids and Sauropsids
Two major group of amniotes
Synapsids
Mammals with one temporal fenestrae
anapsids and diapsids
Two groups that make up sauropsids
Anapsids
no temporal fenestrae; turtles
diapsids
two temporal fenestra; birds and reptiles
temporal fenestra
openings in the skull, behind the eye sockets, that are important for the attachment of jaw-closing muscles
300 mya; Carboniferous period
When did reptiles emerge and during which period?
Archosaurs
This group of reptiles includes dinosaurs, crocodile, alligators, bird
Lepidosaurs
This group of reptiles includes lizards, snakes, and tuataras
ecotherm
body heat is dependent on the environment
crocodilia
this order contains crocodiles and alligators
Sphenodontia
This order contains tuataras; two species live in New Zealand
Squamata
This order contains lizards and snakes; largest group of reptiles; found everywhere but Antarctica; diverse
Testudines
This order contains turtles; ventral shell surface called plastron; dorsal shell surface called carapace, forms from ribs
Birds
These animals are:
endothermic
have a high metabolic rate as flight s metabolically expensive
have modifications for flight
Feathers are modified scales
Aid in insulation
Hollow bones
Sternum in the shape of keel
Efficient respiration
Dinosaurs
Birds evolved from small, feathered-covered what? They are also the closest living relative to this animal.
Archaeopteryx
important traditional fossil, intermediate to birds and dinosaurs
Archaeopteryx lithographica
Related to theropods, group of saurischian dinosaurs

Caudipteryx zoui
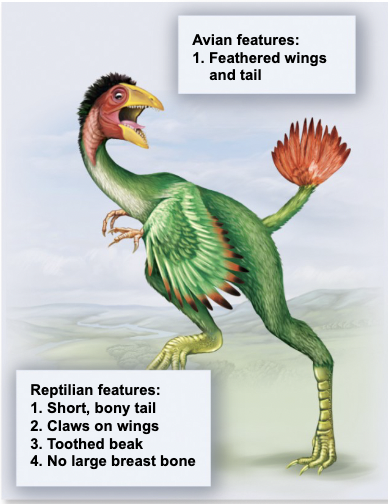
Confuciusornis sanctus
Completely feathered lacking bony tail and toothed jaw

Mammals
This group of animals are:
Endothermic
Have hair
Mammary glands that secrete milk
Only vertebrates with specialized teeth
Large brain contained in a large skull
Single lower jaw bone
Three inner ear bones
External ears
Rodentia
This mammalian order is comprise of about 2277 species including rats, mice, squirrels, beavers, and porcupines; plant eating; gnawing habit with two pairs of continually growing incisor teeth
Chiroptera
This mammalian order consists of about 1116 species including bats; insect or fruit eating; small; have ability to fly; navigate by sonar; nocturnal
Eulipotyphyla
This mammalian order consists of about 452 species including shrews, moles, and hedgehogs; insect eaters; primitive placental mammals
Primates
This mammalian order consists of about 404 species including monkeys, apes, and humans; opposable thumb, binocular vision; large brains
Carnivora
This mammalian order consists of about 286 species including cats, dogs, weasels, bears, seals, and sea lions; flesh-eating mammals; canine teeth
Artiodactyla
This mammalian order consists of about 240 species including deer, antelopes, cattle, sheep, goats, camels, and pigs; herbivorous hoofed mammals, usually with two toes, hippopotamus and others with four toes; many with horns or antlers
Diprotodontia
This mammalian order consists of about 143 species including kangaroos, koalas, opossums, and wombats; pouched mammals mainly found in Australia
Lagomorpha
This mammalian order consists of about 92 species including rabbits and hares; powerful hind legs; rodent-like teeth
Cetacea
This mammalian order consists of about 84 species including whales and dolphins; marine fishes or plankton feeders; front limbs modified into flippers; no hind legs; little hair except on snout
Perissodactyla
This mammalian order consists of about 18 species including horses, zebras, tapirs, and rhinoceroses; hoofed herbivorous mammals with odd number of toes, one (horses) or three (rhinos)
Monotremata
This mammalian order consists of about 5 species including duck-billed platypuses and echidna; egg-laying mammals found only in Australia and New Guinea
Proboscidea
This mammalian order consists of about 3 species one of which are elephants; long trunk; large upper incisors modified as tusks
sensory, camouflage, quills
Types of hair on mammals
biting, grinding, gnawing, tusks, grasping
Types of teeth in mammals
3 main groups of mammals
Subclass Prototheria- Order Monotremata
Sublcass Theria- Clade Metatheria
Subclass Theria- Clade Eutheria
Subclass Prototheria - Order Monotremata
Platypus and echidna lay eggs, lack placenta, poorly developed nipples
Subclass Theria -Clade Metatheria Marsupials
Marsupials:
7 orders
Once widespread, now confined to Australia
Opossum found in North America
Very undeveloped young must make it to marsupium to finish development
Subclass Theria - Clade Eutheria
Placental mammals
Long-lived complex placenta
Prolonged gestation
Hominidae
This family includes humans (Homo sapiens) and related extinct species that are distinguished from apes by their bipedalism and increased brain size