Anatomy and Physiology: Key Concepts, Terminology, and Body Organization
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Space it out
Studying in short sessions over time is more effective than cramming.
Mix it up
Incorporating new information with older material and other subjects.
Science
A way of observing and measuring natural phenomena to explain them.
Human Anatomy
Study of the structure or form of the human body.
Human Physiology
Study of the body's functions.
Surface anatomy
Examines surface markings.
Regional Anatomy
Examines the body in separate areas such as head or neck.
gross anatomy
Examines structures that can be seen with the naked eye.
Microscopic Anatomy
Examines cells (cytology) and tissues (histology) with the use of a microscope.
Systemic Anatomy
Examines individual organ systems.
Cardiophysiology
Study of the physiology of the heart.
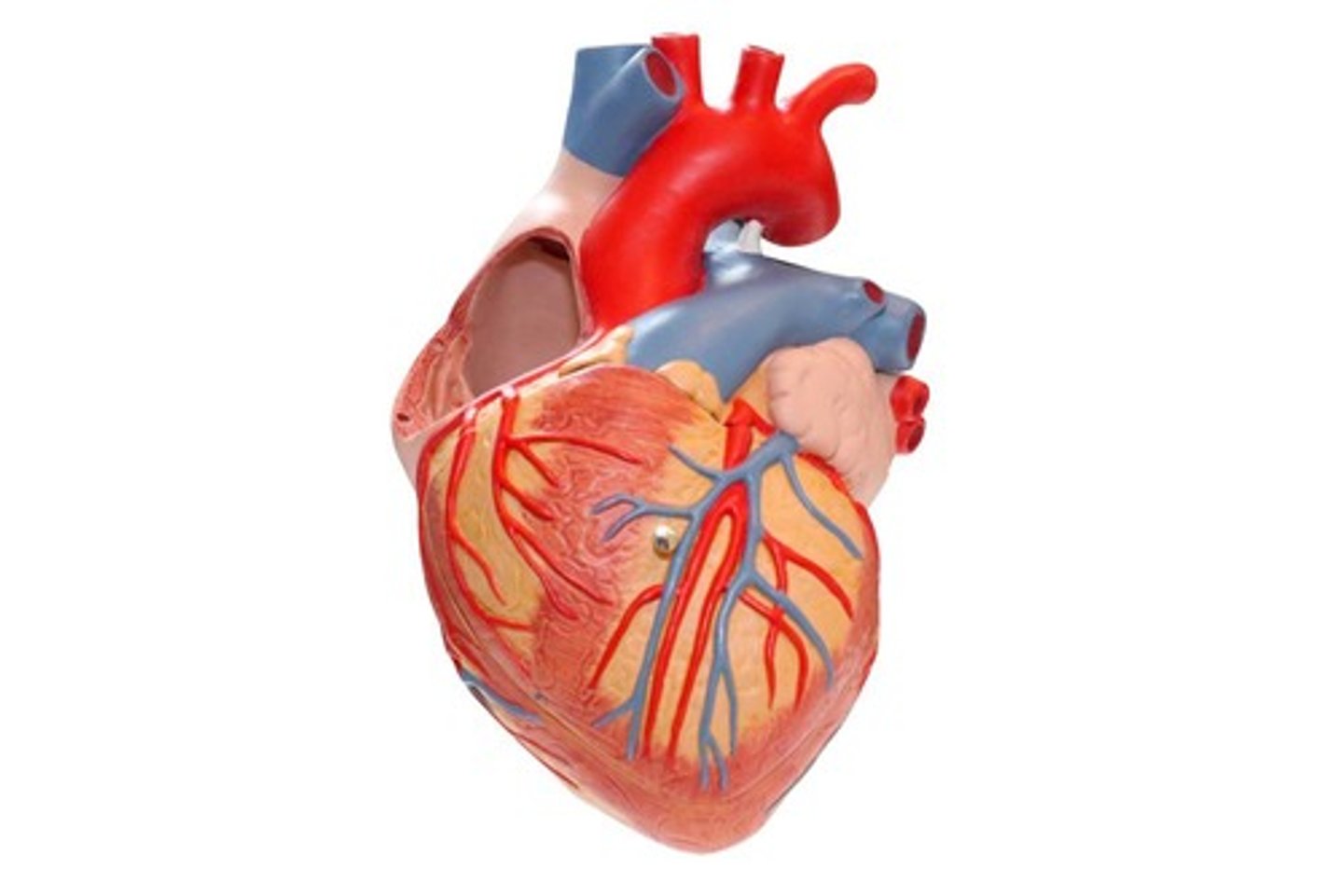
Neurophysiology
Study of the physiology of the nervous system.
Characteristics of living organisms
Includes cellular composition, metabolism, growth, excretion, responsiveness, movement, and reproduction.
Structural Levels of Organization
Includes chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, and organ system levels.
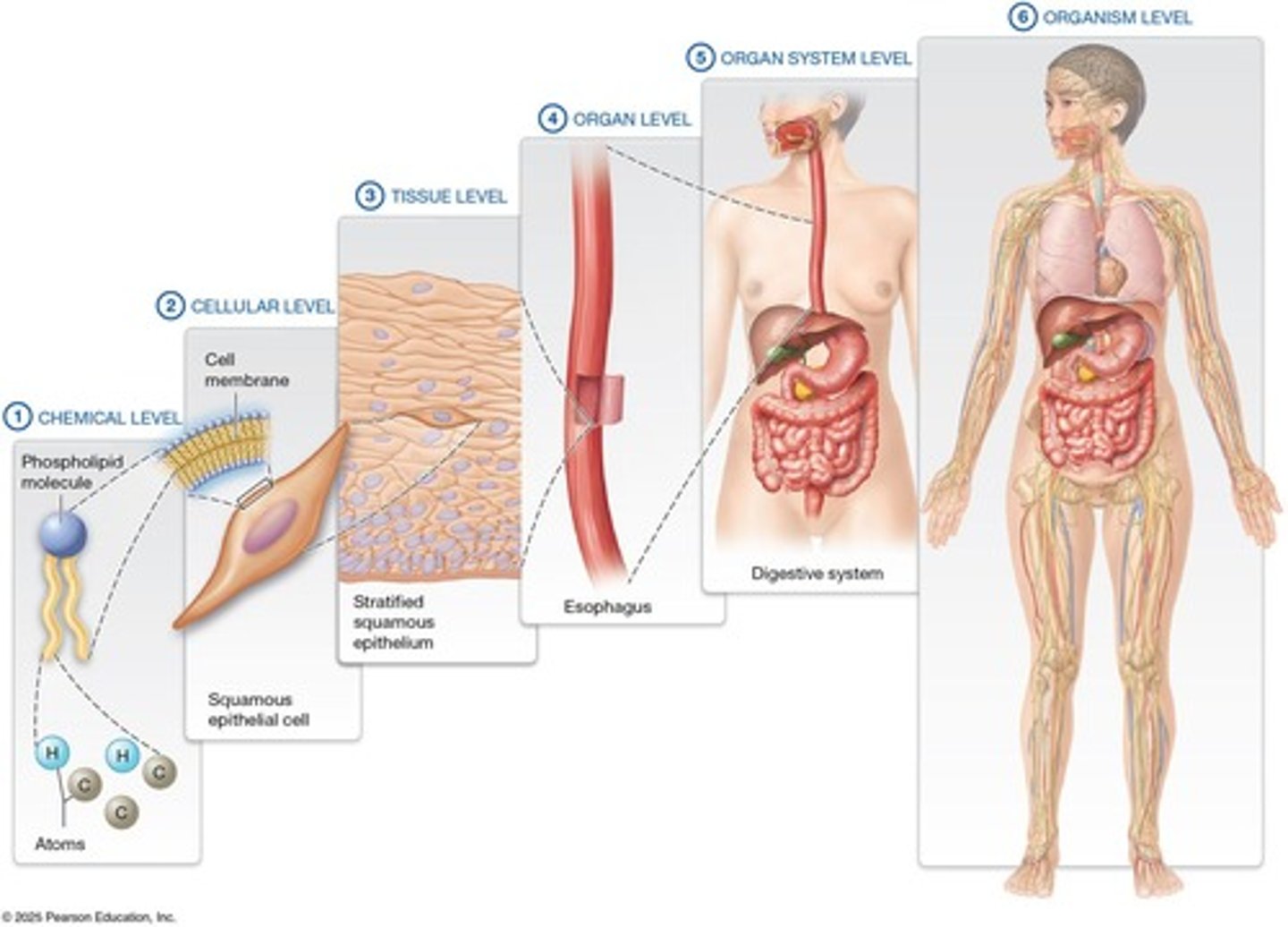
Organism
Word roots
Examples: card/I _______, encephala/o _______, gastr/o _______, hepat/o _______
Prefix
Examples: a/an _______, endo _______, hypo _______, sub _______
Suffix
Examples: genesis _______, it is _______, ology _______, philic _______
Anatomical position
Directional Terminology
Describes relative locations of body parts and markings. Ensures accurate ________________ among scientists and healthcare professionals.
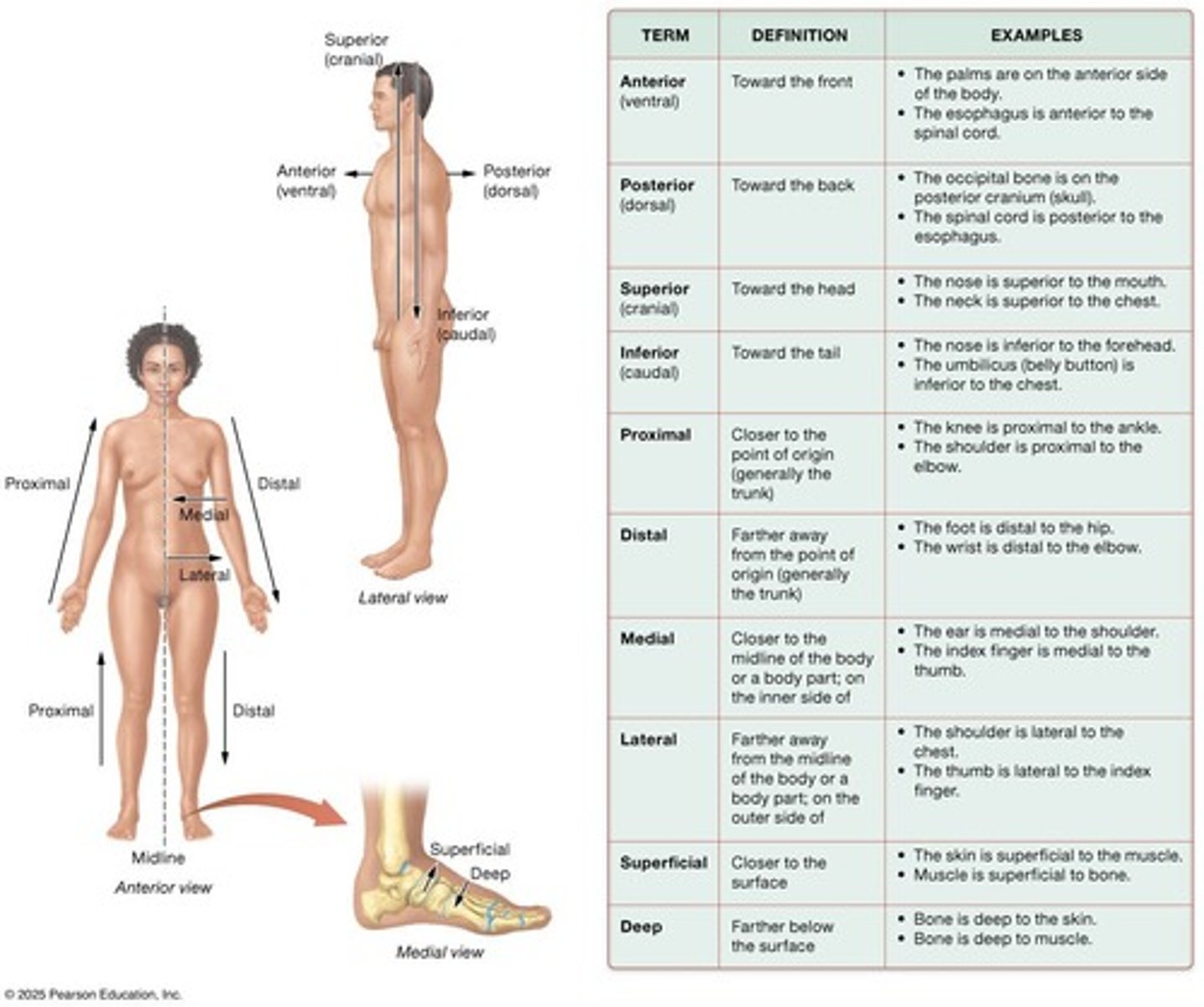
Anterior / Posterior
Superior / Inferior
Proximal / Distal
Medial / Lateral
Superficial / Deep
Axial and Appendicular
2 broad regions of skeleton
Planes of Section
Imaginary lines that ________________________, usually used for examination of more specific areas.
Sagittal Plane
Frontal Plane
Transverse Plane
Oblique Plane
Taken at an angle. Used much less frequently.
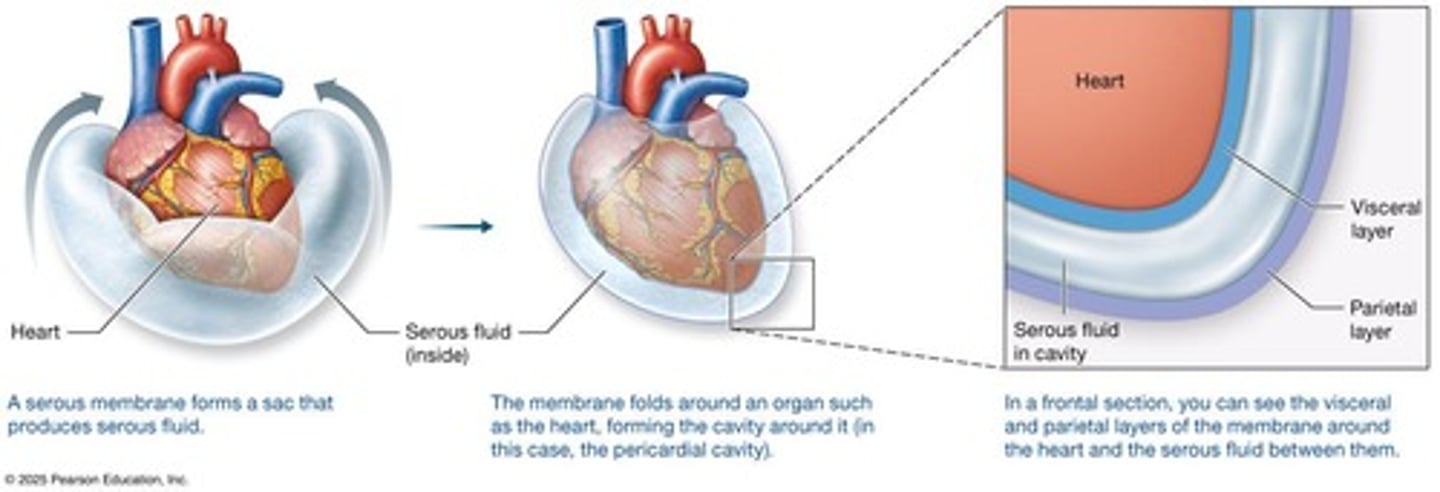
Serous membranes
Thin sheets of tissue that fold over to form a continuous double-layered structure filled with serous (clear/yellow watery) fluid to lubricate organs in the cavity.
Visceral layer
thin membrane lining the outer surface of organs in body cavities
Parietal layer
the outer layer of a serous membrane that lines the walls of a body cavity
Posterior Body Cavity
Located on the posterior side of the body.
Cranial Cavity
(within the skull, includes the brain).
Spinal Cavity
(within the vertebral column, includes the spinal cord).
Anterior Body Cavity
Thoracic cavity
Pleural cavities
(surround left and right lungs).
Mediastinum
(btw pleural cavities; houses heart, great vessels, trachea, and esophagus).
Pericardial cavity
(within mediastinum; serous membrane that surrounds heart).
Abdominopelvic cavity
(contains organs from digestive, lymphatic, urinary, and reproductive systems).
Abdominal cavity
Extends from the diaphragm to the bony pelvis.
Peritoneal cavity
Largest serous membrane in the body; surrounds some abdominal organs.
Pelvic cavity
Located within the bony pelvis.
Medical Imaging
Used to look inside patients without surgery.
X-ray
Uses ionizing radiation - radiation that carries enough energy to free electrons from atoms or molecules, resulting in ionization.
Computed Tomography (CT)
Uses ionizing radiation. A 3D image is computer generated from data.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Uses a magnetic field to computer generate a 3D image from data.
Core Principles in Anatomy and Physiology
Basic concepts of anatomy and physiology that you will repeatedly encounter when studying the human body.
Feedback loops
A change in a regulated variable causes effects that feed back and in turn affect that same variable.
Negative Feedback
Negates the initial change and reduces the output; promotes stability by negating any stimulus that moves a variable away from homeostasis.
Positive Feedback
Enhances the initial change and increases the output; less common than negative feedback and will eventually shut off in response to an external stimulus.
Homeostasis
The condition in which the body develops and maintains a relatively stable environment.
Steps of a feedback loop
1. Stimulus - information that a regulated variable is outside the normal range. 2. Receptor or Sensor - cellular structure that registers the stimulus. 3. Control center - stimulus is sent to the control center (brain or gland) by the nervous or endocrine systems. 4. Effector - the cells or organ that will react. 5. Response - effector causes the response that will return the variable to the normal range.
Homeostasis: Blood Sugar
Refers to the regulation of blood sugar levels in the body.
Positive Feedback Loop: Childbirth
1. Stimulus - baby's head stretches the cervix. 2. Receptors - nerves in the cervix send signals to the brain. 3. Control center - brain, which received the signal from nerves in cervix. 4. Effector - uterus, which produces the hormone oxytocin which stimulates uterine contractions. 5. Response - uterine contractions. This response is continuously amplified until baby is born, which stops the feedback loop.
Pitocin
A synthetic version of oxytocin that is used when labor needs to be artificially started, or induced.
Structure and Function
The form of a structure is such that it best suits its function.
Gradients
Present any time more of something exists in one area than another and the two areas are connected; often drives many physiological processes.
Cell to cell communication
Cells communicate with each other in order to maintain homeostasis.