Rheumatology
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
important autoantibodies
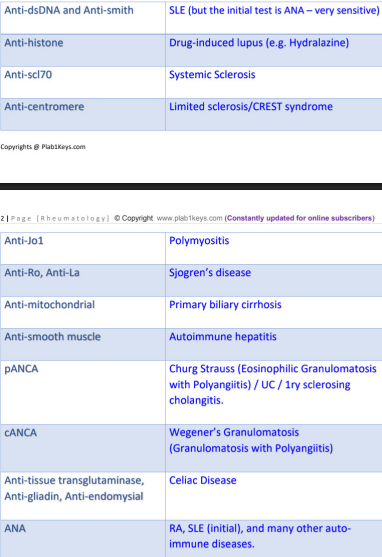
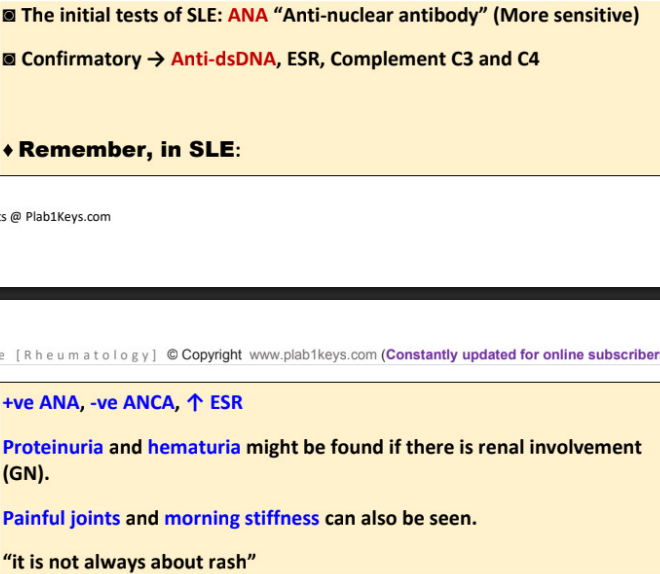
initial screening test for SLE →
confirmatory →
Anti Nuclear Antibody (ANA)
Anti-dsDNA
systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
_____system, _______ disorder, presents in _________, more common in _______ and ________ origin.
general features (5), skin (4), musculoskeletal (2), cardio (2), respiratory (2), renal (2), neuro (3)
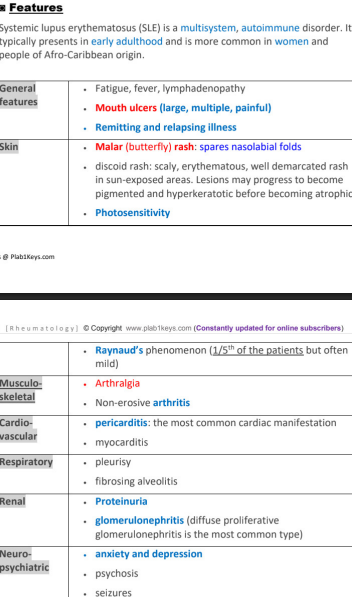
SLE (ANA, ANCA, ESR, initial and confirmatory test)
anti histone antibodies →
(due to ________ used for ______ along with ________)
other DX (3)

chronic fatigue syndrome
diagnosed after _____ months of fatiguability affecting mental and physical function more than ___% of time in absence of __________.
more common in M/F
no past _________ as RF
other features (9)
DX (to exclude other pathology) (12)
TX (2)
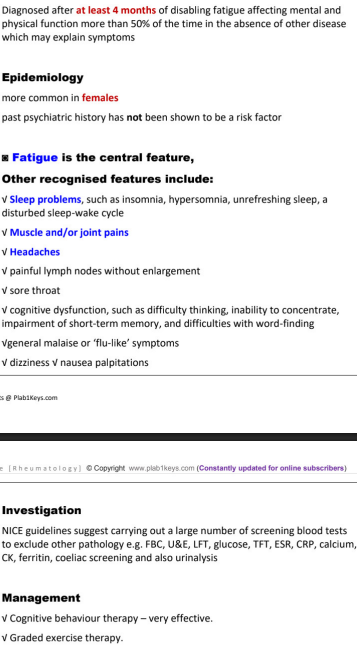

chronic fatigue syndrome
myopathies
features (3)
causes (4 subs)

polymyositis
features (2)
common in _______ muscles (6)
DX (2) confirmatory (1)

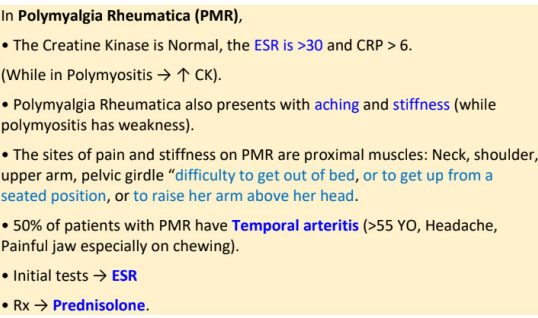
polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) is often differentiated with _________.
important differentiating point
-creatinine kinase, esr, crp
-symptoms (2)
-sites of pain
-50% patient have…
-initial test (1)
-TX (1)
polymyositis
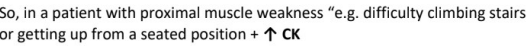
suspect →
polymyositis
sjogren’s syndrome is an _________ disorder affecting ___________ resulting in _________.
1ry or 2ry to ______, ______
more common in M/F
features (main 3)
SX (5)
TX (2)


likely diagnosis


likely diagnosis

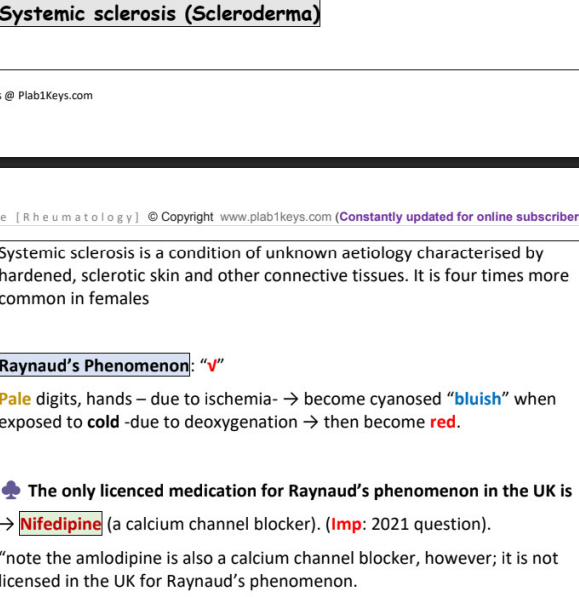
systemic sclerosis (________)
etiology →
characterized by →
more common in M/F
_______ phenomenon (description and only med in UK)
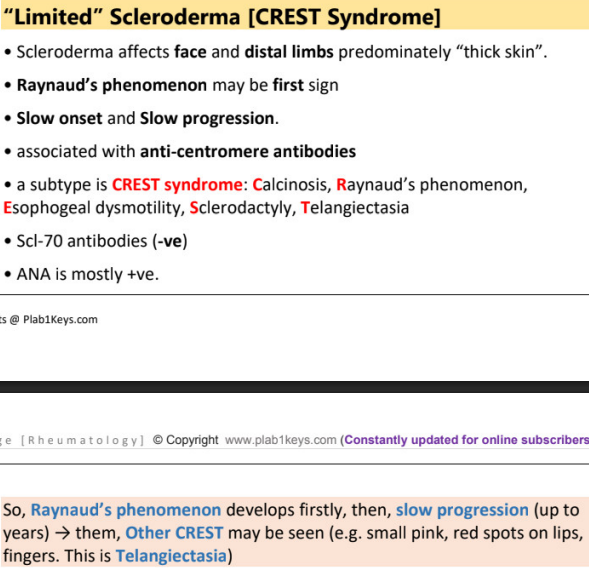
limited scleroderma (crest syndrome)
affects _____ and ______ predominantly
__________ may be first sign
onset and progression
subtype : C.R.E.S.T. syndrome
scl-70 Ab
ANA
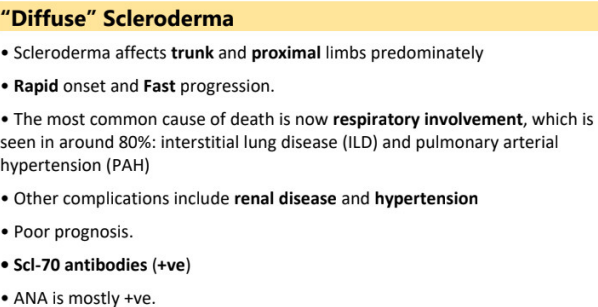
diffuse scleroderma
affects _____ and _____ predominantly
onset and progression
commonest cause of death is ______ (i.e _____ and ______)
other complication (2)
prognosis
scl-70 Ab
ANA

likely diagnosis →
limited systemic sclerosis (CREST syndrome)


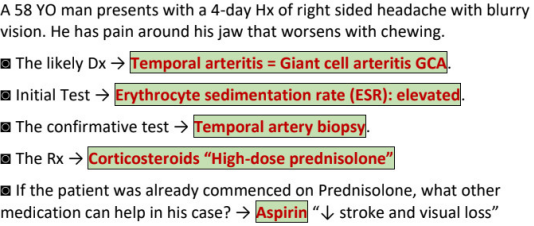
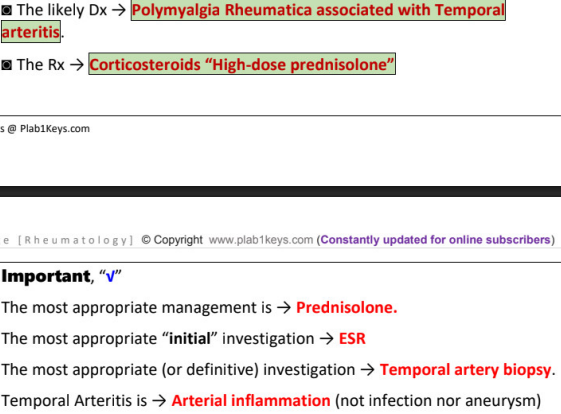
temporal arteritis = ________ = _________
50% of patients with _______ have temporal arteritis
histology showing
features (7)
DX initial, confirmative + finding, normal _____ and ______
TX main, add on, kawasaki case, other add on, specialist


likely diagnosis →
initial test →
confirmative test →
TX → + if patient already commenced on it

likely diagnosis →
TX →
gout (gouty arthritis) = high _______
main features (3)
first presentation (1) commonest area (3)
risk factors (3)
question hints (3)
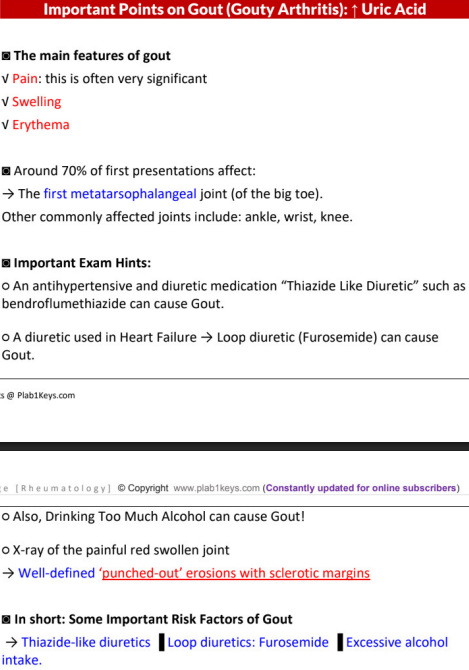
gout
DX main (+ if no fever)
TX acute 1st and 2nd line, long term (3)
radiological features of gout (6)

septic arthritis
monoarthritis
symptoms (5) + a RF (4)
commonly affected area (2)
commonest causative organism (1) (+ if young sexually active)
DX (2)
TX first line start when, if allergic, if causative organism, if still not responding

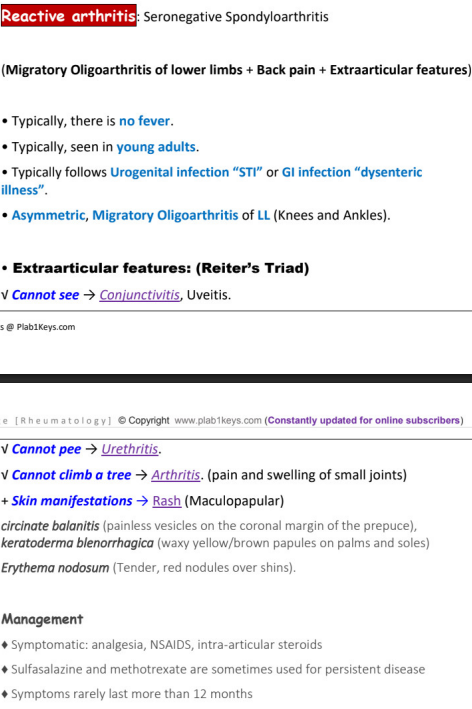
reactive arthritis = __________
__________ + ___________ + extraarticular features
fever, age category, typically follows (2)
extraarticular features (_______ triad) (4)
TX (3)
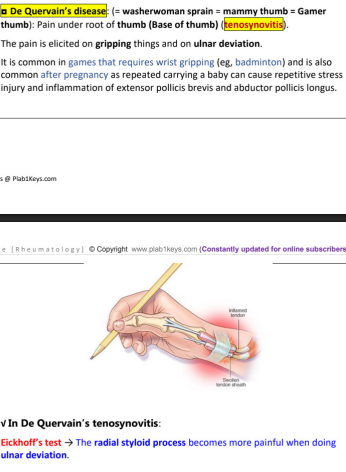
De Quervain’s disease
other names (3)
definition
pain elicited on ________ and on _________
DX
lateral epicondylitis
medial epicondylitis

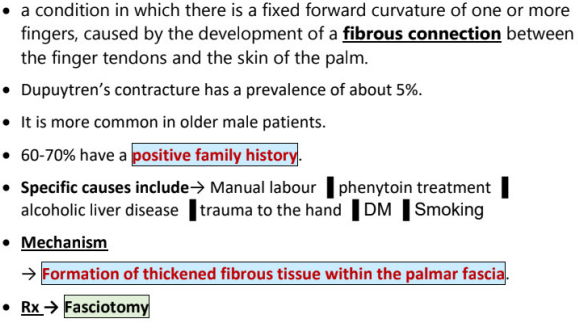
dupuytren’s contracture
definition and cause
more common in M/F
60-70% have __________
specific causes (6)
mechanism
TX
trigger finger = _________
commonest fingers (3)
features (3)


diagnosis
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis

diagnosis
De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis
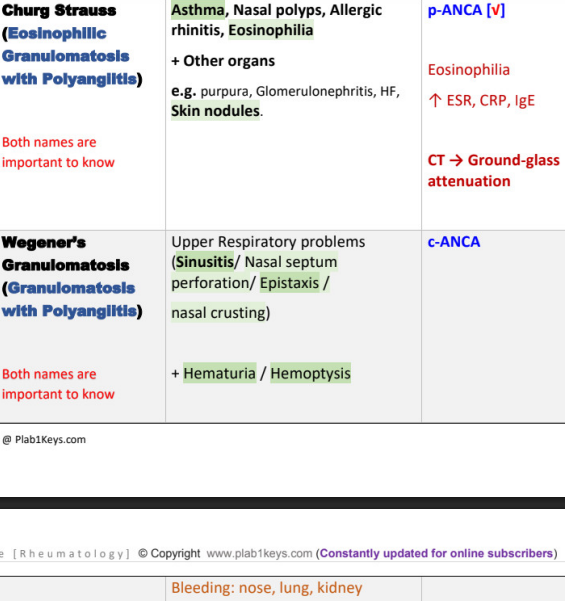
churg strauss vs wegeners granulomatosis
other name, symptoms, DX