Somatic and Addictive Disorders
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
102 Terms
somatization
psychological and emotional expression of stress through physical symptoms
holistic approach to somatization
multidimensional interplay of biological, psychological, and sociocultural needs and its effects on somatization
somatic symptom disorder
characterized by a focus on somatic (physical) symptoms, such as pain or fatigue, to the point of excessive concern, preoccupation, and fear
one or more distressing symptoms lasting longer than 6 months
somatic symptom disorder
3 multiple choice options
excessive thoughts, anxiety and behaviors around symptoms, or health concerns without significant medical findings or health concerns
somatic symptom disorder
3 multiple choice options
clients are often resistant to seeking psychiatric assistance
somatic symptom disorder
3 multiple choice options
illness anxiety disorder
misinterprets physical manifestations as evidence of a serious disease process, which can lead to obsessive thoughts and fears about illness
preoccupation with having or acquiring serious illness for at least 6 months
illness anxiety disorder
3 multiple choice options
high anxiety about health, excessive health-related behaviors or maladaptive avoidance
illness anxiety disorder
3 multiple choice options
clients may be care-seeking or care-avoidance
illness anxiety disorder
3 multiple choice options
conversion disorder
neurological symptoms in the absence of a neurological diagnosis
presence of deficits in voluntary motor or sensory functions
conversion disorder
3 multiple choice options
clinical manifestations: conversion disorder
paralysis, blindness, movement disorder, gait disorder, numbness, paresthesia, loss of vision or hearing, episodes resembling epilepsy, la belle indifference (lack emotional concern about dramatic symptoms)
factitious disorder
consciously pretend to be ill to have their emotional needs met and achieve the status of patient; artificially, deliberately, and dramatically fabricate symptoms or self-inflict injury with the goal of assuming the sick role
malingering
a consciously motivated act of fabricating an illness or exaggerating symptoms; done for secondary gain to become eligible for such things as disability compensation, committing fraud against insurance companies, obtaining prescription medications, evading military service, or receiving a reduced prison sentence
factitious disorder by proxy
the client deliberately causes injury or illness to a vulnerable person

nursing interventions: factitious disorder by proxy
- keep careful, detailed records of visitation and events
- interact with patient frequently during visiting hours
- sitter in the room may be required
psychological factors affecting other medical conditions
a link between a client's psychological state and their physical condition
Freud's psychoanalytic theory
psychogenic complaints of pain, illness, or loss of physical function is a cover up for conflicted feelings and/or unwelcome experiences
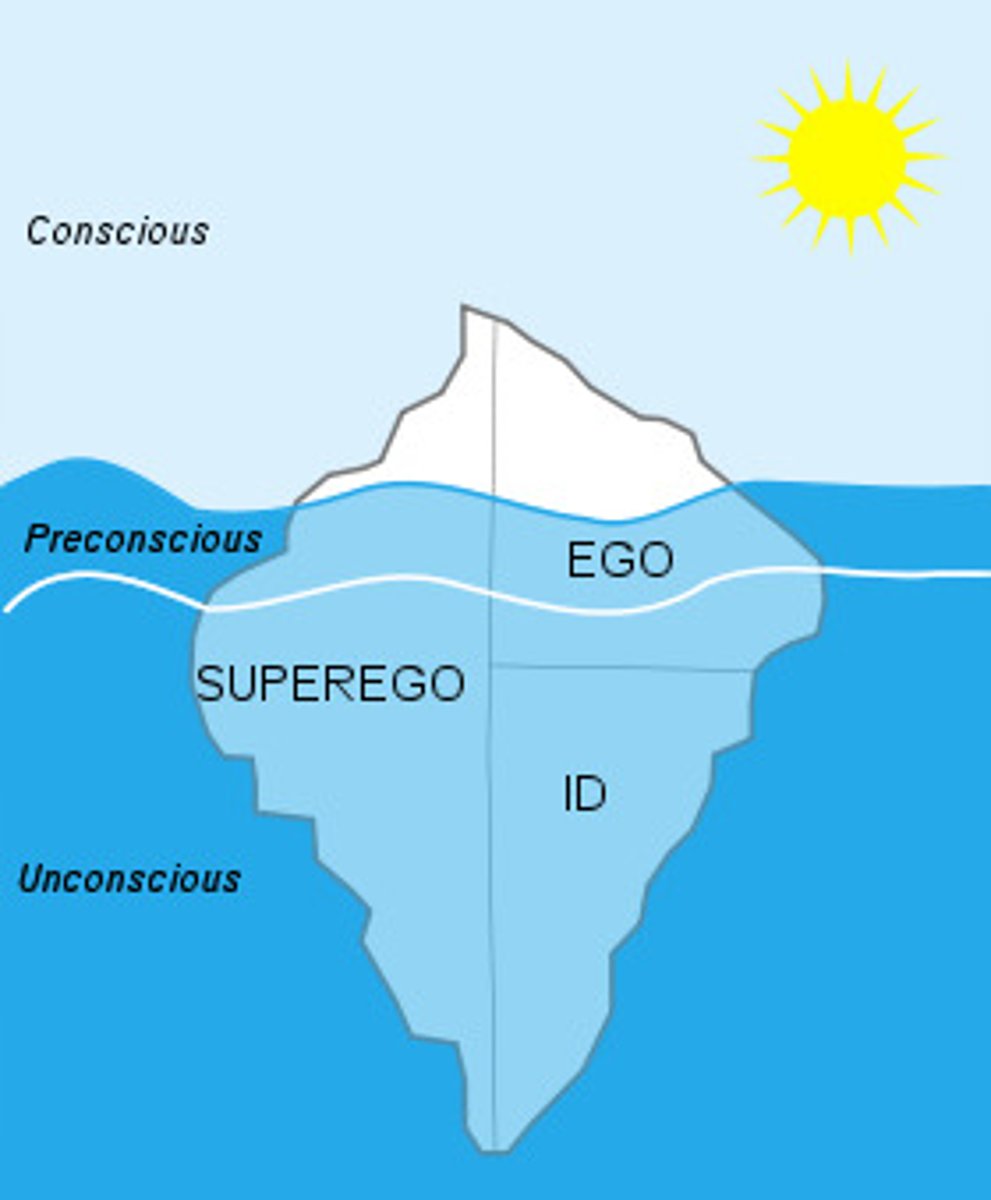
behavioral theories
- communication of helplessness
- attention-seeking behavior.
cognitive theories
- negative, distorted, catastrophic thoughts
- focus on body sensations and misinterpret their meaning, responding with excessive
assessment of somatic disorders
- assess for nature, location, onset, characteristics, and duration of the symptom(s).
- explore past history of adverse childhood events.
- identify symptoms of anxiety, depression, and past trauma that may be contributing to somatic symptoms and ability to meet basic physical, and safety/security needs.
- determine current quality of life, social support, and coping skills including spirituality.
- identify any secondary gain that the patient is experiencing from symptom(s).
- explore the patient’s cognitive style and ability to communicate feelings and needs.
- assess current psychosocial and biological needs.
- screen for misuse of prescribed medication and substance use.
secondary gain
reward value of having a psychological or physical symptom, such as release from ordinary responsibilities
implementation for somatic disorders
- help patient to explore feelings
- cognitive reframing
- establish therapeutic relationship
- educate patient regarding treatment
- refer to support groups or systems
- teach effective coping
- focus on strengths and reinforce skills
cognitive reframing
questioning client to determine other potential causes of feared disease
6 key elements for effective treatment of somatic disorders
1. provide continuity of care
2. avoid unnecessary procedures
3. provide frequent, brief, and regular visits
4. always conduct a physical exam
5. avoid disparaging comments
6. set reasonable therapeutic goals
psychosocial interventions for somatic disorders
- promotion of family involvement
- setting limits
- promotion of self-care activities
- assertiveness training
- self-esteem enhancement
pharmacological interventions for somatic disorders
- no FDA approved medications
- off label uses: TCAs, SSRIs, SNRIs
cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)
a popular integrative therapy that combines cognitive therapy (changing self-defeating thinking) with behavior therapy (changing behavior)
substances that lead to use disorders
- alcohol
- caffeine
- cannabis
- hallucinogen
- inhalants
- opioids
- sedative-hypnotics
- stimulants
- tobacco
- gambling
addiction
compulsive, uncontrollable dependence on a chemical substance, habit, or practice to such a degree that either the means of obtaining or ceasing use may cause severe emotional, mental, or physiologic reactions
intoxication
the process of using a substance to excess
tolerance
when a person no longer responds to the drug in the way that the person initially responded
withdrawal
a set of physiological symptoms that occur when a person stops using a substance
caffeine intoxication symptoms
- restlessness
- nervousness
- flushed feeling
- GI upset
- tachycardia
caffeine withdrawal symptoms
- headache
- drowsiness
- irritability
- poor concentration
treatment for caffeine addiction
abstinence; resolves within a week
cannabis intoxication symptoms
- heightened senses
- depersonalization
- derealization
- delirium
cannabis withdrawal symptoms
- irritability/anger
- restless/anxiety
- depression
- GI upset/fever/chills/HA
treatment for cannabis addiction
- abstinence
- support therapies
- SSRIs
hallucinogen intoxication symptoms
- paranoia
- impaired judgement
- derealization
- pupil dilation
- tachycardia/tremors
- can cause medical emergency
hallucinogen withdrawal symptoms
- re-experiencing symptoms of use that can be distressing
- can last weeks, months, or years
treatment of hallucinogen addiction
- reassurance of safety
- benzodiazepines
- restraints
inhalants intoxication symptoms
- disinhibition
- euphoria
- illusions/hallucinations
- nystagmus
- N/V
- decreased reflexes
inhalants withdrawal symptoms
not considered under DSM-5
treatment of inhalant addiction
abstinence; resolves quickly
opioid intoxication symptoms
- constricted pupils
- drowsiness/slurred speech
- impaired memory and attention
- psychomotor retardation
- respiratory arrest
opioid withdrawal symptoms
- mood dysphoria/anxiety
- N/V/D
- diaphoresis
- hyperreflexia
treatment of opioid addiction
methadone program, medication assisted treatment (MAT)
stimulants intoxication symptoms
- elated, euphoric
- hypervigilant/anxious
- dilated pupils (short term)
- weight loss/confusion
- seizures
- chest pain/arrhythmias
stimulants withdrawal symptoms
- tiredness/insomnia
- vivid nightmares
- depression/suicidal
- paranoia/irritability
treatment of stimulants addiction
- inpatient (for amphetamine use)
- outpatient (for cocaine use)
- antipsychotics
- diazepam (Valium)
intoxication symptoms of sedatives, hypnotic, anti-anxiety med use disorder
- slurred speech
- impaired thinking
- incoordination
- nystagmus
- coma
withdrawal symptoms of sedatives, hypnotic, anti-anxiety med use disorder
- rebound hyperactivity
- tremors/insomnia
- anxiety/seizures
treatment of sedatives, hypnotic, anti-anxiety med use disorder
gradual reduction (taper)
overdose of of sedatives, hypnotic, anti-anxiety med use disorder is treated with
gastric lavage, activated charcoal
tobacco withdrawal symptoms
- irritability
- anxiety
- depression
- difficulty concentrating
- restlessness
- insomnia
treatment of tobacco addiction
- behavioral therapy
- bupropion (Zyban)
- clonidine (Catapres)
- varenicline (Chantix)
overdose
taking an excessive amount of a drug that leads to coma or death
medication assisted treatment (MAT)
strategy for treating substance use disorders that involves using medications and teaching a person how to handle cravings and avoid abusing the substance again
1st opioid use disorder (OUD) medication that can be prescribed in a doctor's office
buprenorphine/naloxone (Suboxone)
3 multiple choice options
buprenorphine/naloxone (Suboxone)
decreases feelings of craving and can be effective in maintaining compliance
given only in a clinic for opioid use disorder
methadone
methadone
used to decrease the painful symptoms of opiate withdrawal, also blocks the euphoric effects of opiate drugs
the only MAT that can be safely used during pregnancy
methadone
3 multiple choice options
taken daily for a minimum of 12 months
methadone
3 multiple choice options
first line treatment for opioid use disorder (OUD) and alcohol use disorder (AUD)
naltrexone
3 multiple choice options
naltrexone
binds to endorphin receptors and blocks effects of opioids and cravings of alcohol
treatment lasts for 3-4 months
naltrexone
3 multiple choice options
risk of taking pill form of naltrexone daily
reduces tolerance for opioids, increasing the risk of overdose
requirements for a client with AUD to begin naloxone
must have withdrawn from alcohol, must maintain sobriety
IM vivitrol q28 days for OUD
must wait at least 7 days from last opioid use for short-acting and 10-14 days after long-acting
drug only for alcohol use disorder (AUD)
disulfiram/Antabuse
3 multiple choice options
disulfiram/Antabuse
blocks enzyme involved in processing alcohol which creates severe discomfort and is a deterrent to drinking
side effects of disulfiram/Antabuse
SEVERE nausea/vomiting, chest pain, tachycardia, flushing, dizziness
important consideration for disulfiram/Antabuse
never use with any alcohol containing products (mouthwash, deodorant, hand sanitizer, perfume, etc.)
tobacco cessation options
- patches
- lozenges
- gum
- hypnosis
- medications: bupropion (Zyban, Wellbutrin), varenicline (Chantix)
bupropion (Zyban, Wellbutrin)
NDRI antidepressant that decreases nicotine craving and manifestations of withdrawal
varenicline (Chantix)
a nicotinic receptor agonist that promotes the release of dopamine to simulate the pleasurable effects of nicotine; reduces cravings for nicotine as well as the severity of withdrawal manifestations; reduces the incidence of relapse by blocking the desired effects of nicotine
Narcan (naloxone)
reverses respiratory depression secondary to opioid overdose
legally intoxicated blood alcohol concentration (BAC)
0.08% (80 mg/dL)
3 multiple choice options
blood alcohol concentration (BAC) that can indicate acute toxicity and/or death
0.40% (400 mg/dL)
3 multiple choice options
systemic effects of alcohol use disorder (AUD)
- peripheral neuropathy
- alcoholic myopathy and cardiomyopathy
- esophagitis, gastritis, pancreatitis
- alcoholic hepatitis
- cirrhosis of the liver
- leukopenia
- thrombocytopenia
- cancer (head and neck)
minor alcohol withdrawal symptoms (6-8 hours after)
N/V, shaky, jitters, HA, mild perceptual changes
moderate alcohol withdrawal symptoms (8-10 hours after)
- psychotic and/or perceptual symptoms begin (hallucinations)
- can lead to seizures, delirium, or unconsciousness
treatmtent of moderate alcohol withdrawal
ativan, librium
severe alcohol withdrawal symptoms (12-24 hours after)
generalized and tonic-clonic seizures
treatment of severe alcohol withdrawal
diazepam (Valium)
delirium tremens (alcohol withdrawal delirium)
a medical emergency that may occur within 72 hours of withdrawal; causes delusions, hallucinations, and physiologic problems and puts the patient at a danger to self
nursing interventions: delirium tremens (alcohol withdrawal delirium)
- prevention
- monitor vital signs
- notify provider of changes
SBIRT
screening, brief intervention, and referral to treatment
- included in routine wellness screenings
- reduces risk drinking and related harms
- promotes safer drinking
- increase help-seeking among individuals who need it
AUDIT
alcohol use disorders identification test

CAGE
4 questions to identify alcohol abuse
CAGE-AID
screen for all types of substance abuse; adjusted to Include drugs
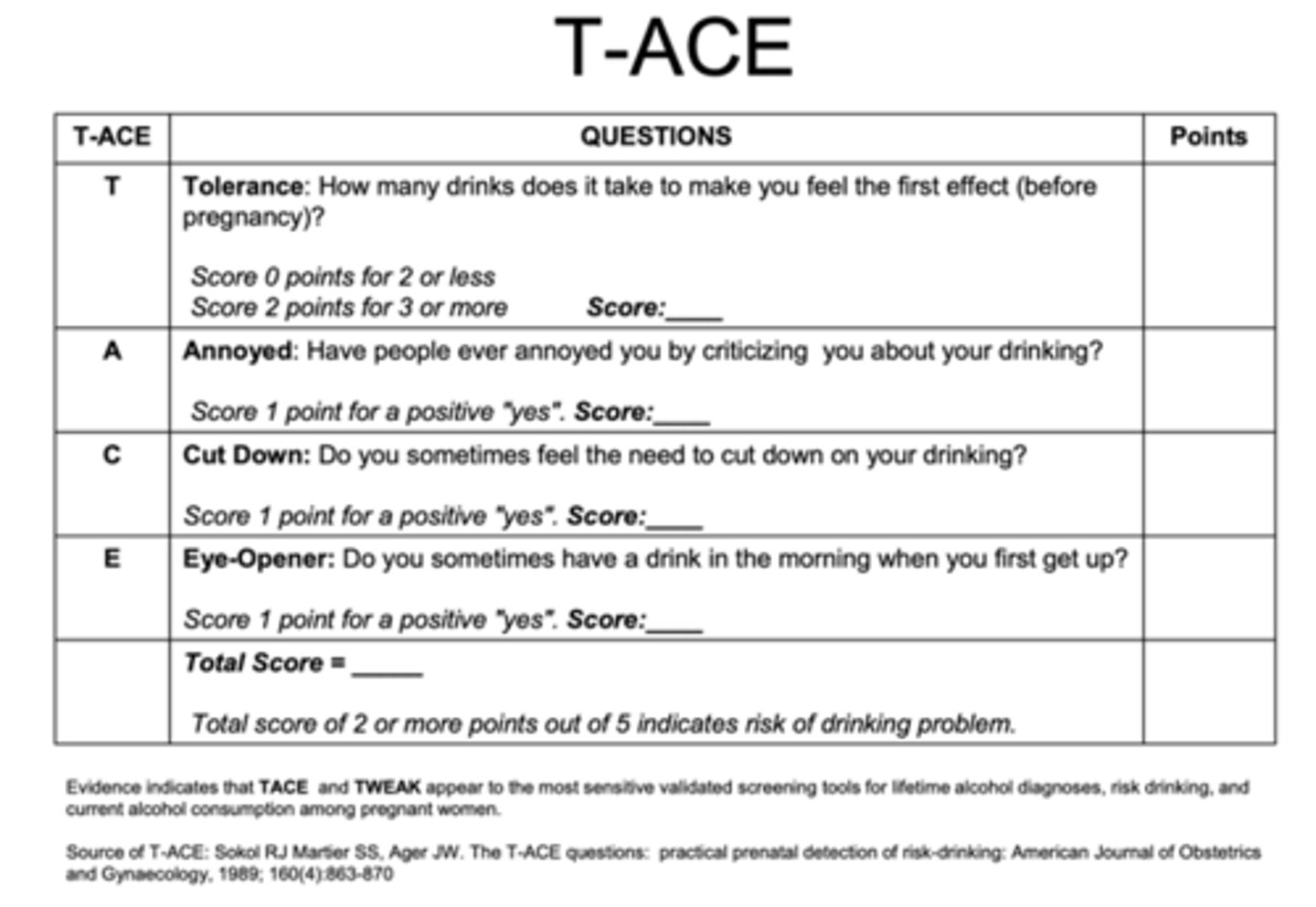
T-ACE
tolerance, annoyance, cut down, eye-opener; identifies risk of drinking during pregnancy
implementation for substance abuse disorders
- achieve psychological stability
- provide an empathetic, supportive environment
- promoting safety and sleep: first-line interventions
- reintroduce good nutrition and hydration
- support for self-care (hygiene)
- exploring harmful thoughts and spiritual distress
care continuum for substance abuse
- detoxification (detox)
- rehabilitation
- halfway houses
- other housing
- partial hospitalization
- intensive outpatient (IOP) treatment
- outpatient treatment
- Alcoholics Anonymous (AA)
- relapse prevention
transtheoretical stages of change theory
a psychological theory that describes how people progress through distinct stages when attempting to change a behavior
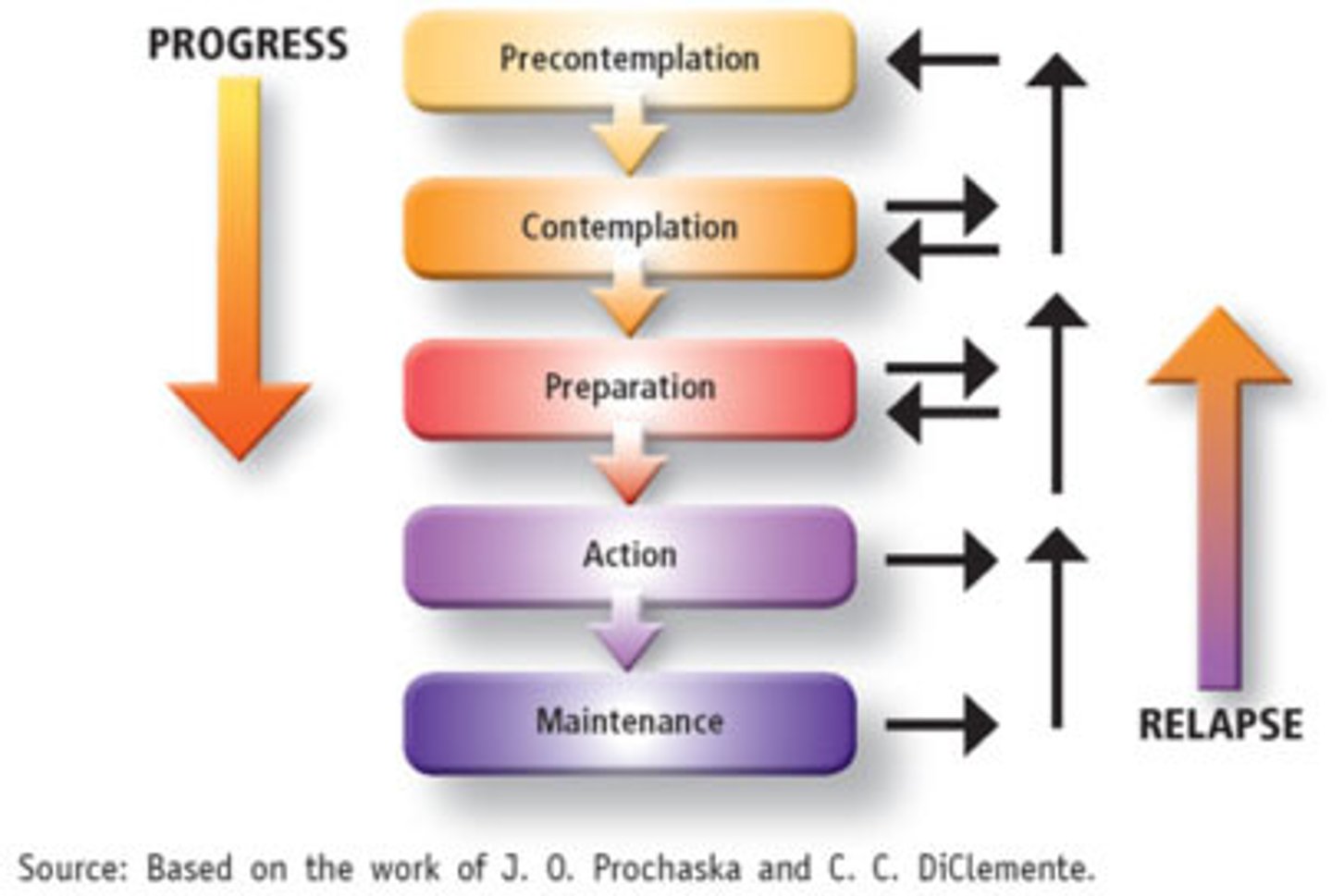
precontemplation stage
stage of change in which people are unwilling to change their behavior
contemplation stage
stage of change in which people are considering changing behavior in the next 6 months