Water and The Environment
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Structural formula of water
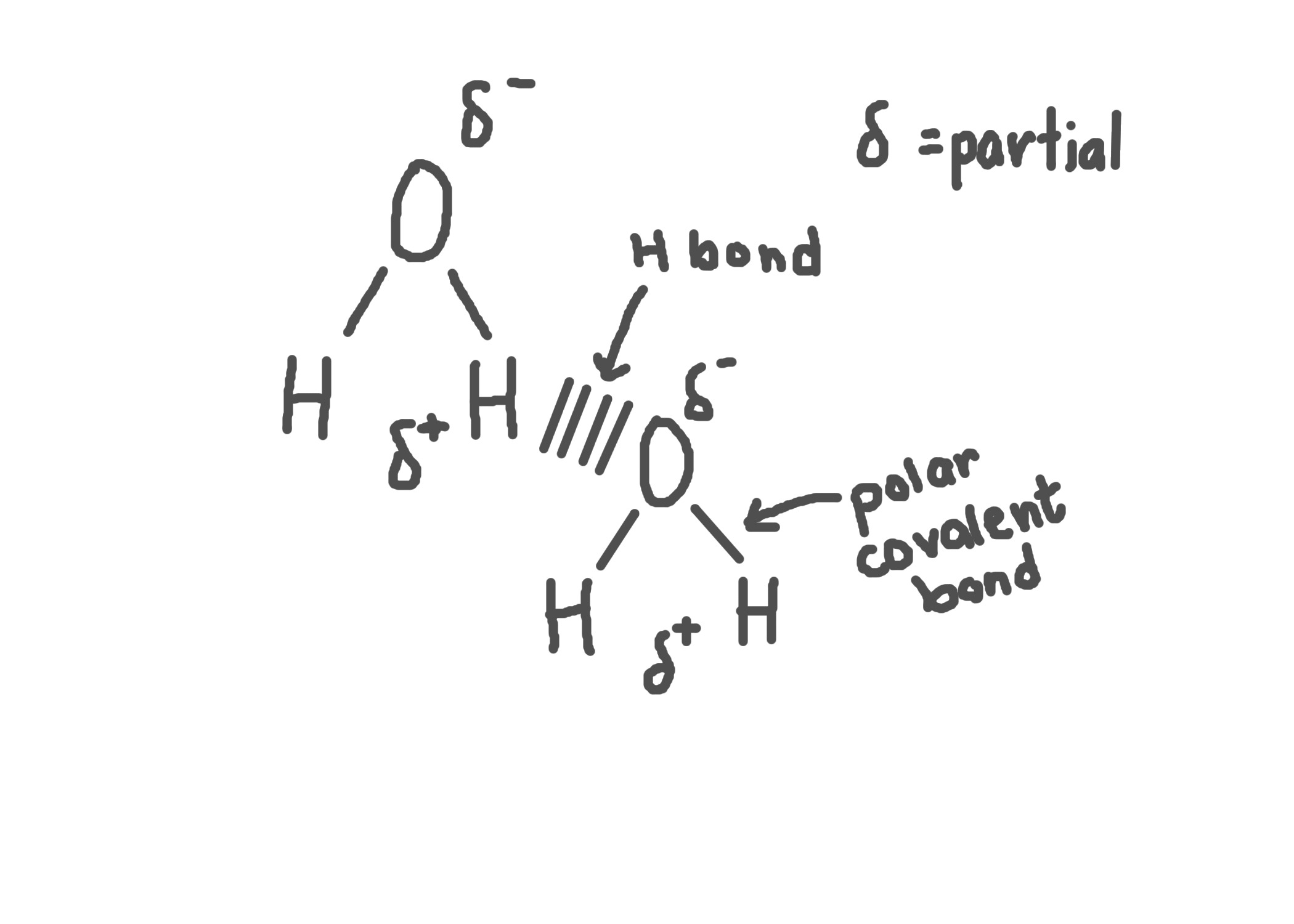
Properties of water are caused by…
-Polar molecule→ unequal sharing of electrons (dipolarity)
-Hydrogen bonds with adjacent water molecules
Properties of Water that Make Life Possible
-Cohesion/adhesion
-Water is a good solvent
-Water moderates the temperatures on earth
-Ice floats
-pH
-Extraplanetary water
Cohesion
water molecules “stick” together because of H bonding
Adhesion
-water molecules stick of other surfaces
-leads to the meniscus, water droplets sticking to surface
Practical applications of cohesion
-movement of water up xylem of plants (transpiration)→ cohesion pulls water column upwards due to evaporation out the leaf
Practical applications of adhesion
-capillary action/effect: water moves upwards against gravity due to adhesion to a surface (cellulose, glass, paper)
Surface tension
adhesion leads to surface tension→ film on the surface of water, water droplets
Surfactant
-substance that lowers surface tension and keep water from sticking together
-Ex: detergents, emulsifiers
-in lungs, keep alveoli (air sacs) from collapsing
Is water a universal solvent?
No, water is a good solvent
Why is water a good solvent?
-Like dissolves like→ polar substances dissolves polar, ionic; nonpolar dissolves nonpolar
Chemical reaction
Solute+ solvent→ solution
Aqueous solution (aq)
water is the solvent; a solution dissolved in water
Solvation
process of solvent molecules surrounding and interacting with solute molecules
Hydrophilic
-substances (water loving)
-dissolve in water like polar (sugar) or ionic (salt)
-substances dissolve because water surrounds them; often attracted to opposite charges
Hydrophobic
-will not dissolve in water
-Ex: non-polar (oil) or large polar substances too big to dissolve (cotton)
Application of water is a good solvent
-substances (glucose, salt (ions), amino acids) are carried in blood plasma and transported around the body.
-cell membranes are hydrophobic and won’t dissolve, keep cells separate
Water moderates the temperatures on earth
-polar substances have stronger intermolecular forces if attraction than nonpolar substances
-more energy released to form or absorbed to break H bonds
-keeps temperatures on earth stable
H bonds in water lead to…
high heat capacity, high specific heat, and high seat of vaporization
High heat capacity
-water has to absorb a large amount of energy before its temperature increases
-Ex: metals=low specific heat=heat up quickly; water=high specific heat=heats up slowly
High specific heat
amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1g of water by 1°C (high heat of vaporization)
High heat of vaporization
-water absorbs a great deal of heat before evaporating
-absorbs the heat from the surface below
Application of water as a temperature moderator
-water acts as a heat sink→ absorbs heat all day, gives off heat at night
-prevents big fluctuations in temperature
-evaporative cooling (sweating)→ leaves the surface behind cooler (from evaporation of sweat)
Ice floats
-solid ice is less dense than liquid water
-H bonding causes crystal lattice to form, keeps water molecules apart
-water is most dense at 4°C
Application of ice floats
-keeps ponds from freezing from the bottom up
-layer of ice insulates water below→ ice releases heat as it forms which makes transitions between seasons less abrupt
-ice formation can disrupt living tissues
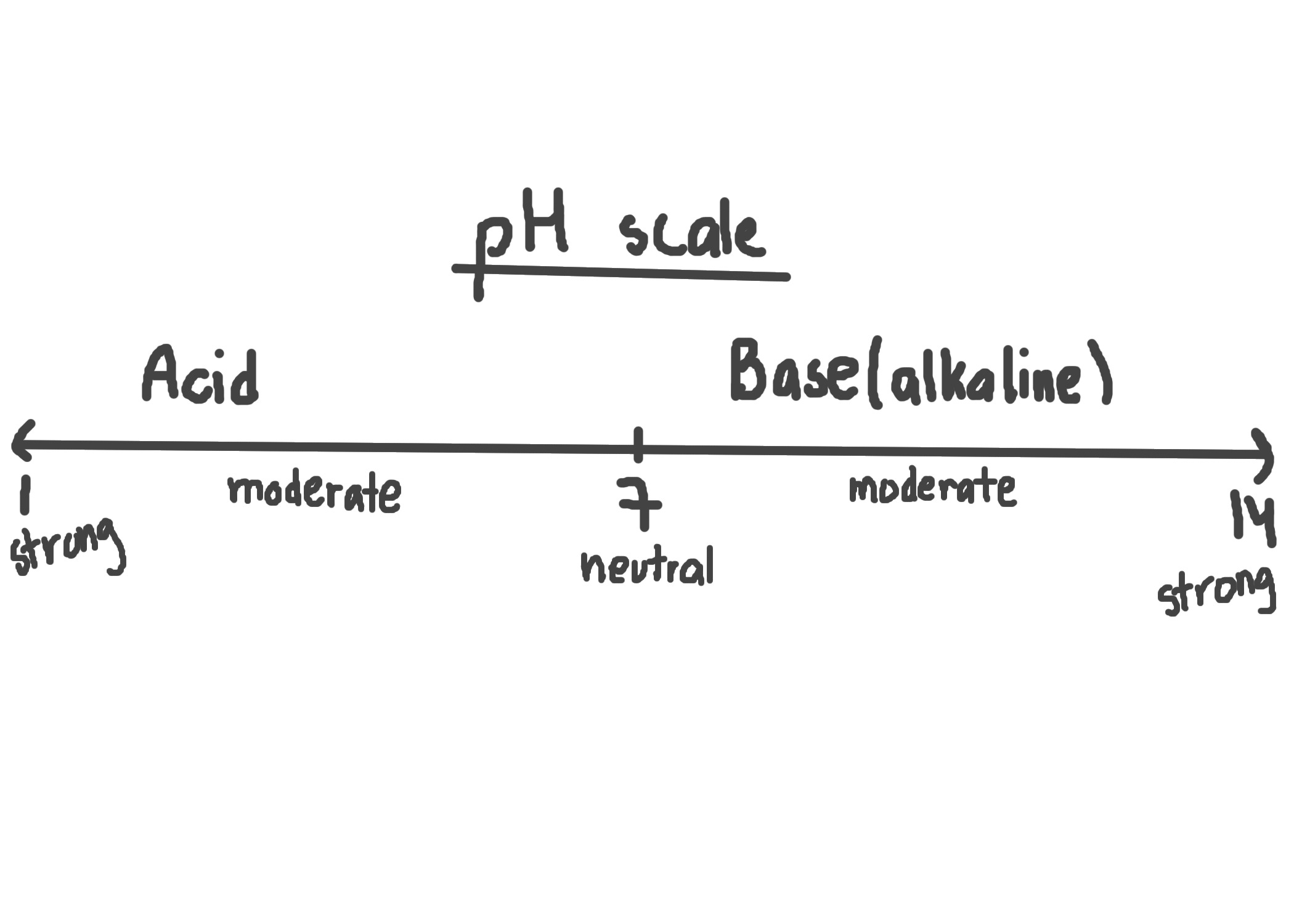
pH
a measure of H+ in an aqueous solution
-can only measure the pH of aqueous solutions
Acid
-anything that adds H+ ions or removes OH- from solution
-Ex: HCl→ H+ + Cl-
Base
-anything that adds OH- ions or removes H+
-Ex: NaOH→ Na+ + OH-
Acid
Base
Neutral
→[H+]>[OH-]
→[H+]<[OH-]
→[H+]=[OH-]
pH scale
Applications of pH
-most human enzymes work best between a pH 7-8
-pepsin (digest proteins) in the stomach works best at a pH of 2
-acidity often prevents pathogen growth
Buffer
a substance that minimizes changes in pH
-human blood is buffered by H2CO3 (bicarbonate)
-reduces fluctuations in blood pH, helps maintain a pH of around 7.35-7.45
-can prevent acidosis or alkalosis
Extraplanetary water
-could water come from outer space on asteroids, comets, or from another planet?
-If so, a long distance from the sun would prevent it from boiling away; would condense to form a liquid in cooler temps; gravity would hold water to earth
Goldilocks effect
just right for water to exist in all three states (solid, liquid, and gas) on earth if it came from another planet
Making Dilutions
-using a known concentration and volume of solution
-written as M1V1=M2V2 or C1V1=C2V2