Touch, Temperature, & Pain
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
The Vestibular Sense
Detects the position and the movement of the head. Directs compensatory movements of the eye and helps to maintain balance.
Consists of the Saccule and Utricle and 3 Semicircular Canals
True or False: Movement of cilia causes action potentials in the 8th cranial nerve, which has axons connecting to the brain stem and cerebellum
True
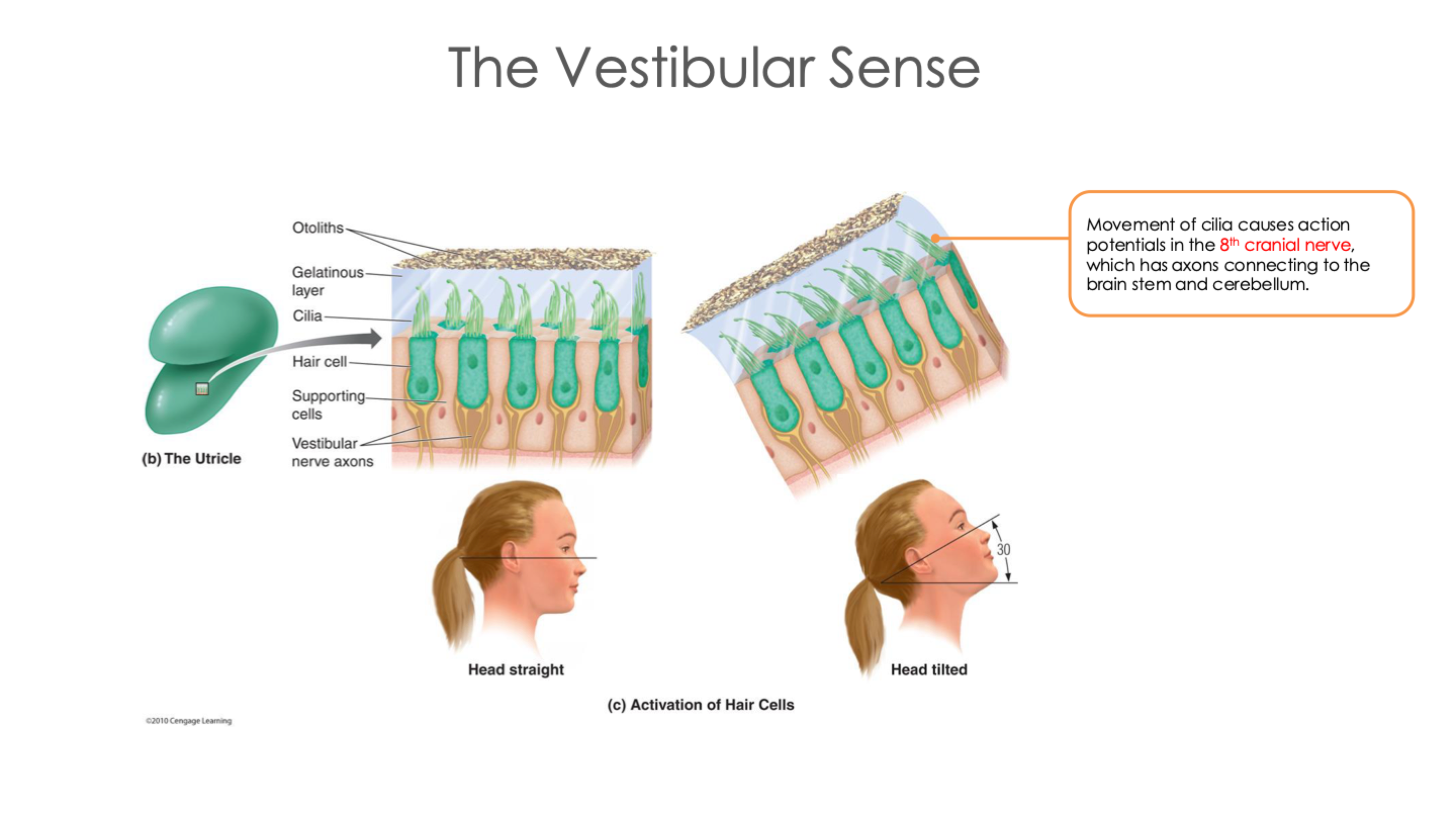
The Vestibular Sense: Saccule and Utricle
Saccule and Utricle
Register angle of head and linear acceleration
Contains calcium carbonate particles called otoliths which move, causing hair cells to bend
The Vestibular Sense: Three Semicircular Canals
Register head rotation
Oriented in perpendicular planes
Are filled with a fluid and lined with hair cells
Somatosensory System
The sensation of the body and its movements, is not one sense but many, including touch, deep pressure, the position and movement of joints, pain, and temperature
What 3 Groups does Somatosensation break into?
Exteroception
Interoception
Proprioception
Somatosensation: Exteroception
Sensation from skin provides information about external world
Somatosensation: Interoception
Sensation from internal organs provides information about internal functions
Somatosensation: Proprioception
Sensation from muscles and tendons to convey body position
Somatosensory Receptors
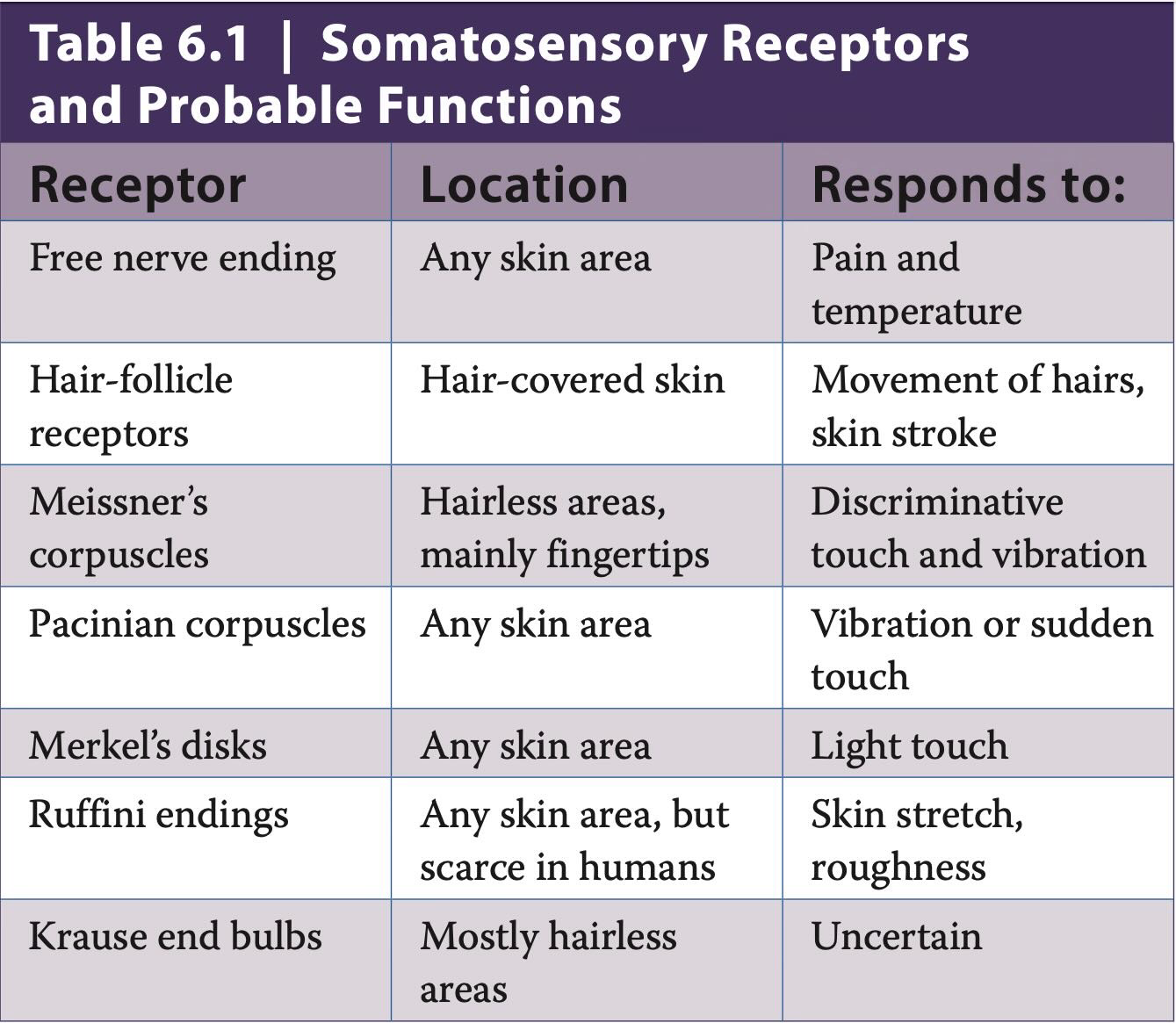
What somatosensory corpuscle detects vibrations or sudden displacements on the skin?
Pacinian Corpuscle
There is a neuron membrane
The onion-like outer structure provides mechanical support that resists gradual or constant pressure, insulating the neuron against most touch stimuli
Only a sudden or vibrating stimulus bends the membrane, enabling sodium ions to enter and start an action potential
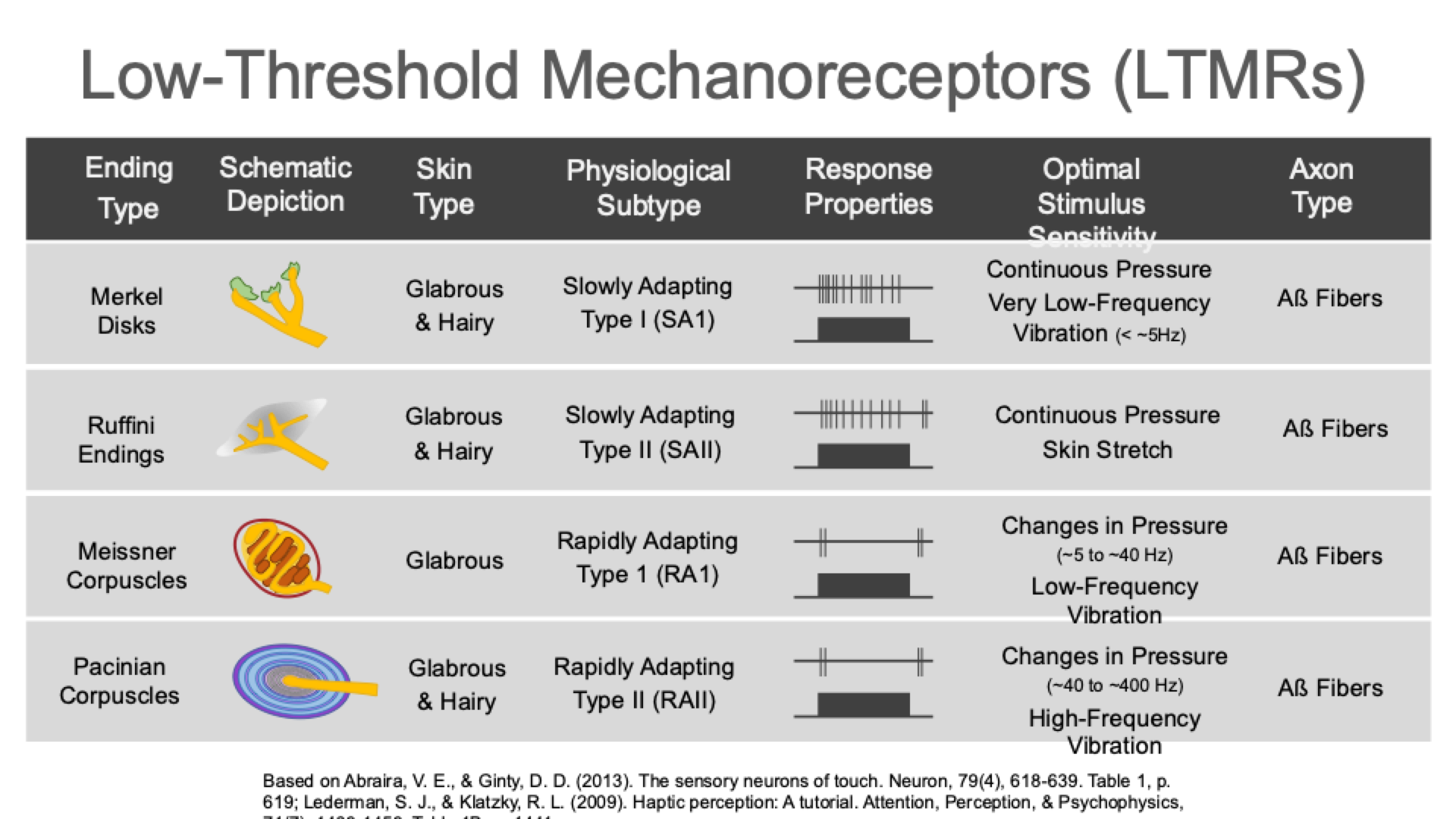
Low-Threshold Mechanoreceptors (LTMRs)
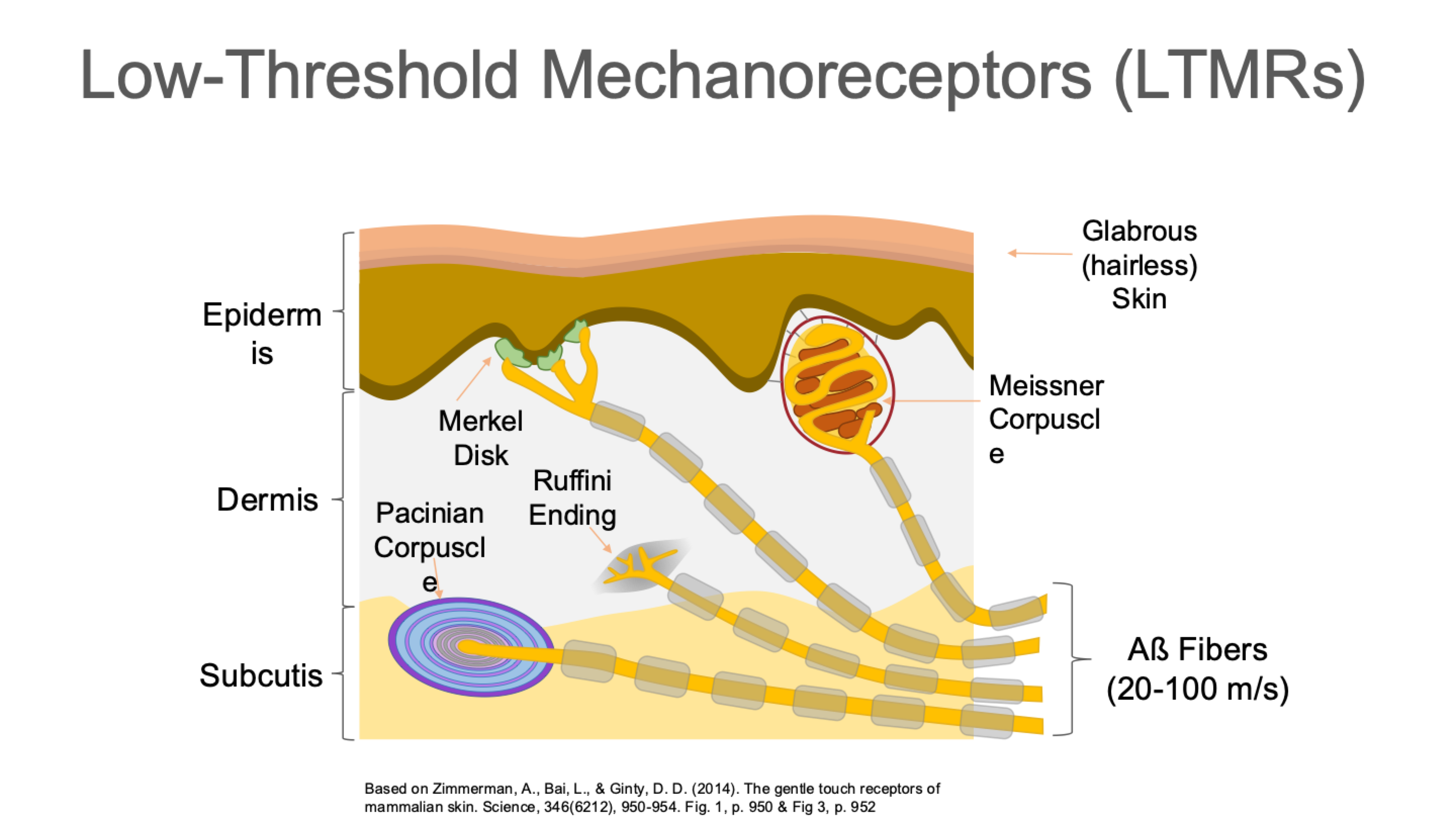
Types of LTMRs
Fill in The Blank: The body has _____________ for _______________, a critical variable because overheating or overcooling the body can be fatal
receptors, temperature
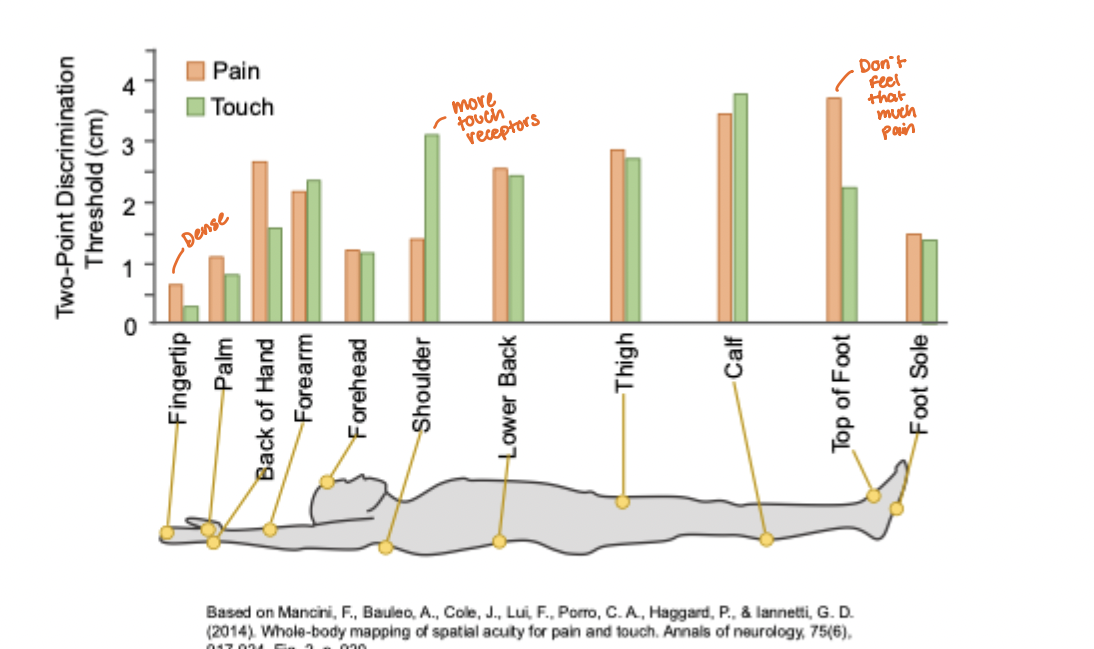
Simultaneous Two-Point Discrimination Task
Discrimination Threshold: The distance between two stimuli at which people are just able to tell they are being touched by two stimuli rather than one stimulus
Participant is poked with 2 sharp needles and asks the person whether they felt pain in 2 places or one
Tells you about how many receptors are in the area
If the needles are far apart there are more receptors

Two-Point Discrimination Threshold
Better to get injury in shoulder or calf
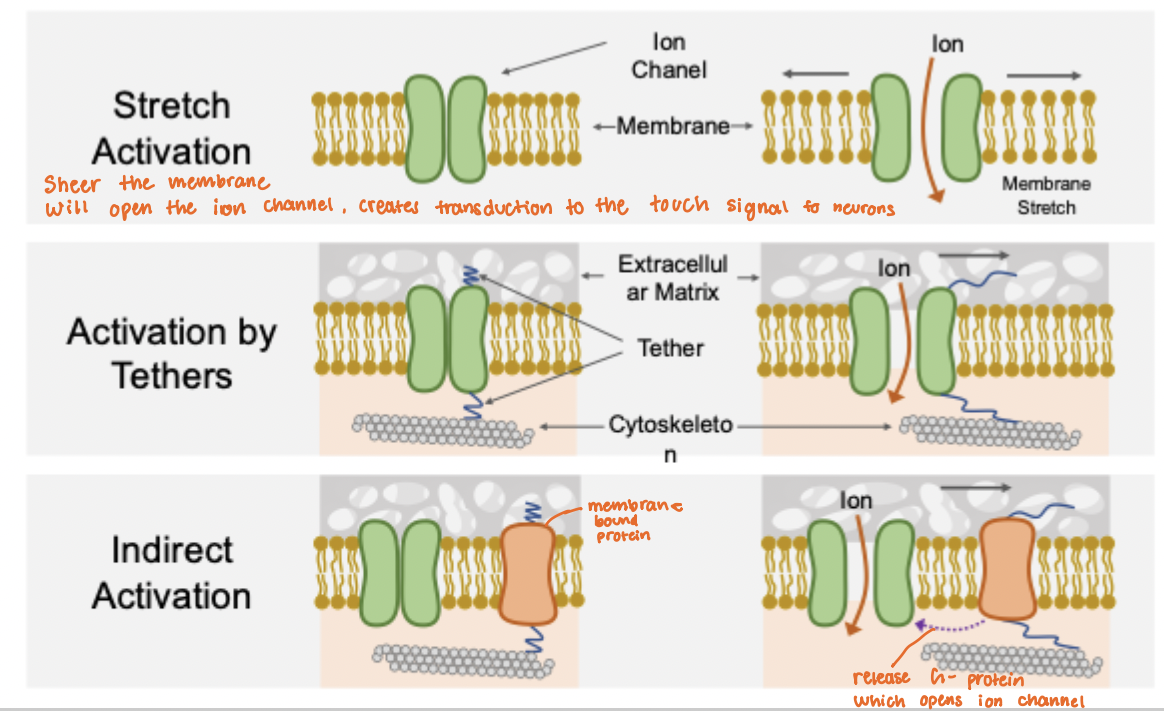
Ion Channels
What to heat-sensitive neurons respond to?
Heat-sensitive neurons in the spinal cord respond to the absolute temperature, and they do not adapt
A cell that responds to 44°C will respond the same way regardless of whether the skin was hotter, cooler, or the same temperature a minute or two ago
These ion channels are polymodal, responding to both temperature and a ligand
When they’re exposed to a certain temperature, they open ion channels
Also have a binding sight for a chemical, capsaicin (spicy food)
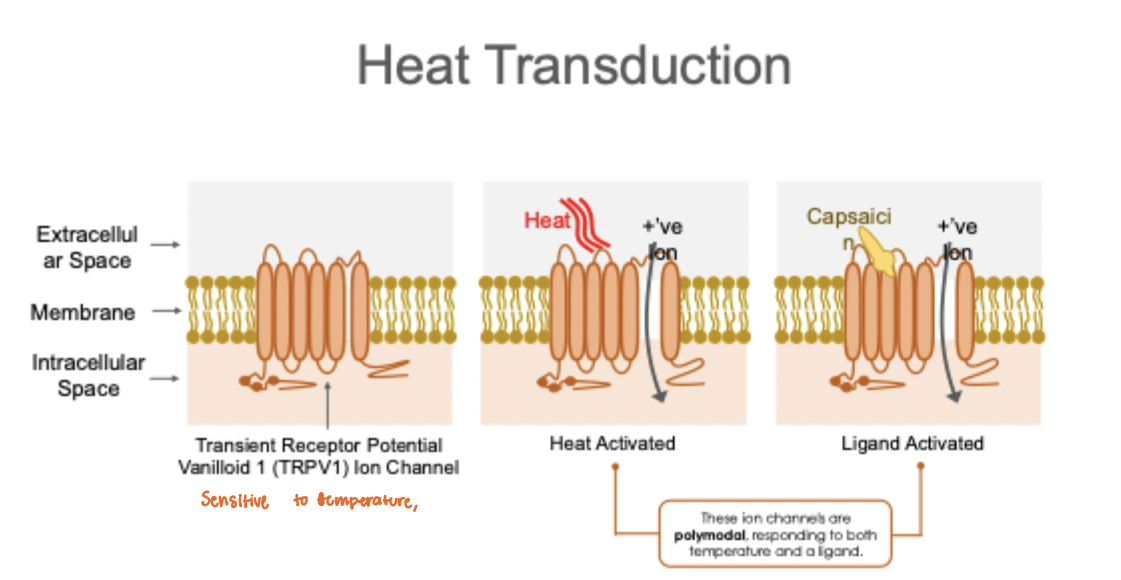
Capsaicin
Found in jalapeños and other hot peppers, stimulates the receptors for painful heat
Can produce burning or stinging sensations on many parts of your body, as you may have experienced if you ever touches the insides of hot peppers and rubbed your eyes
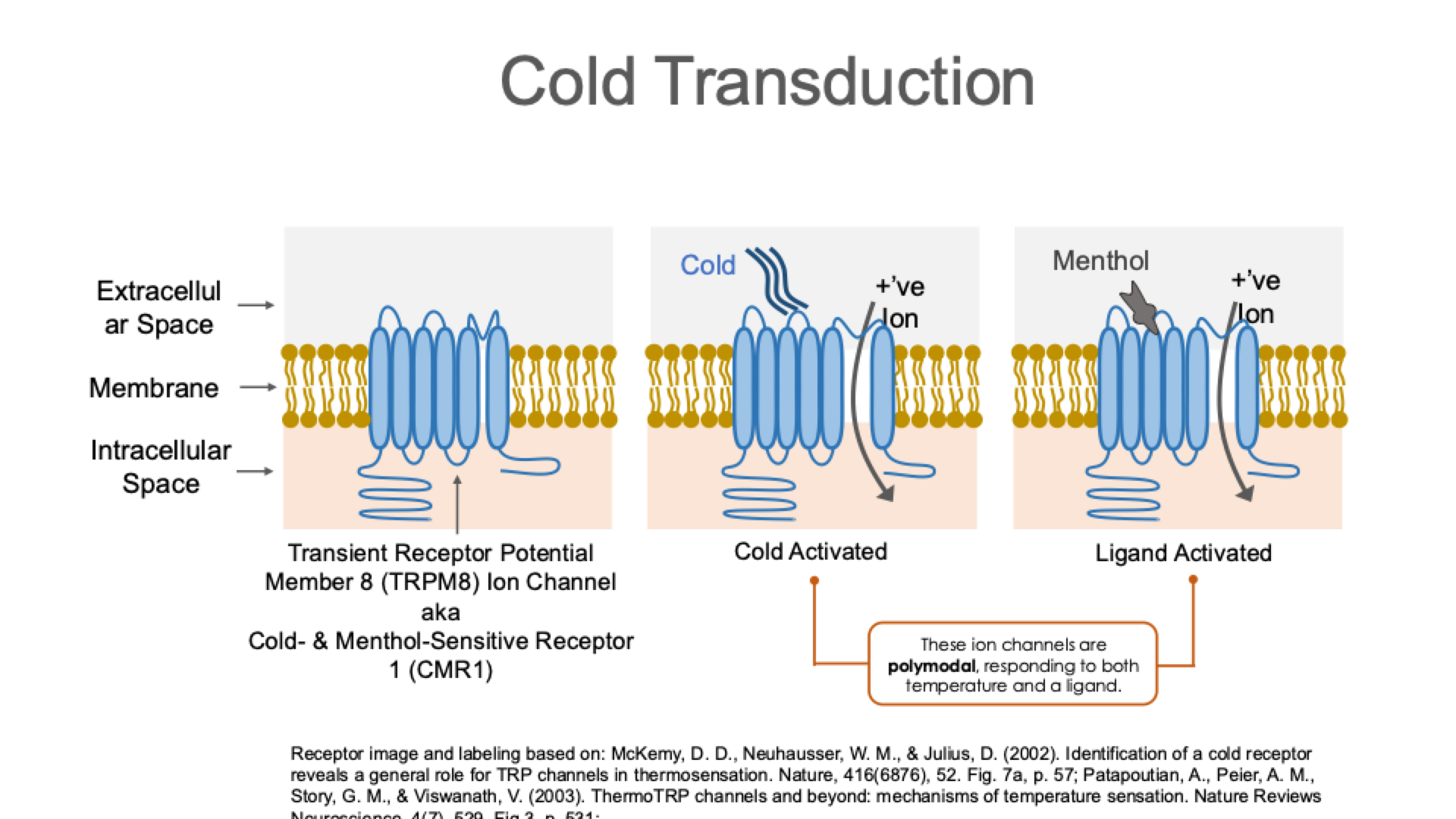
What do cold-sensitive neurons respond to?
Cold-sensitive neurons in the spinal cord exhibit little response to a constant low temperature, but they respond to a drop in temperature.
A cell that responds from 39°C to 33°C would also respond to a drop from 33°C to 27°C
Thus, on a very hot day, you might detect a breeze as “cool,” even though the air in the breeze is fairly warm
These ion channels are polymodal, responding to both temperature and a ligand
This is why things feel cold, because stimulate the cold
Cough drops, gum
Temperature Ranges of TRP Ion Channels
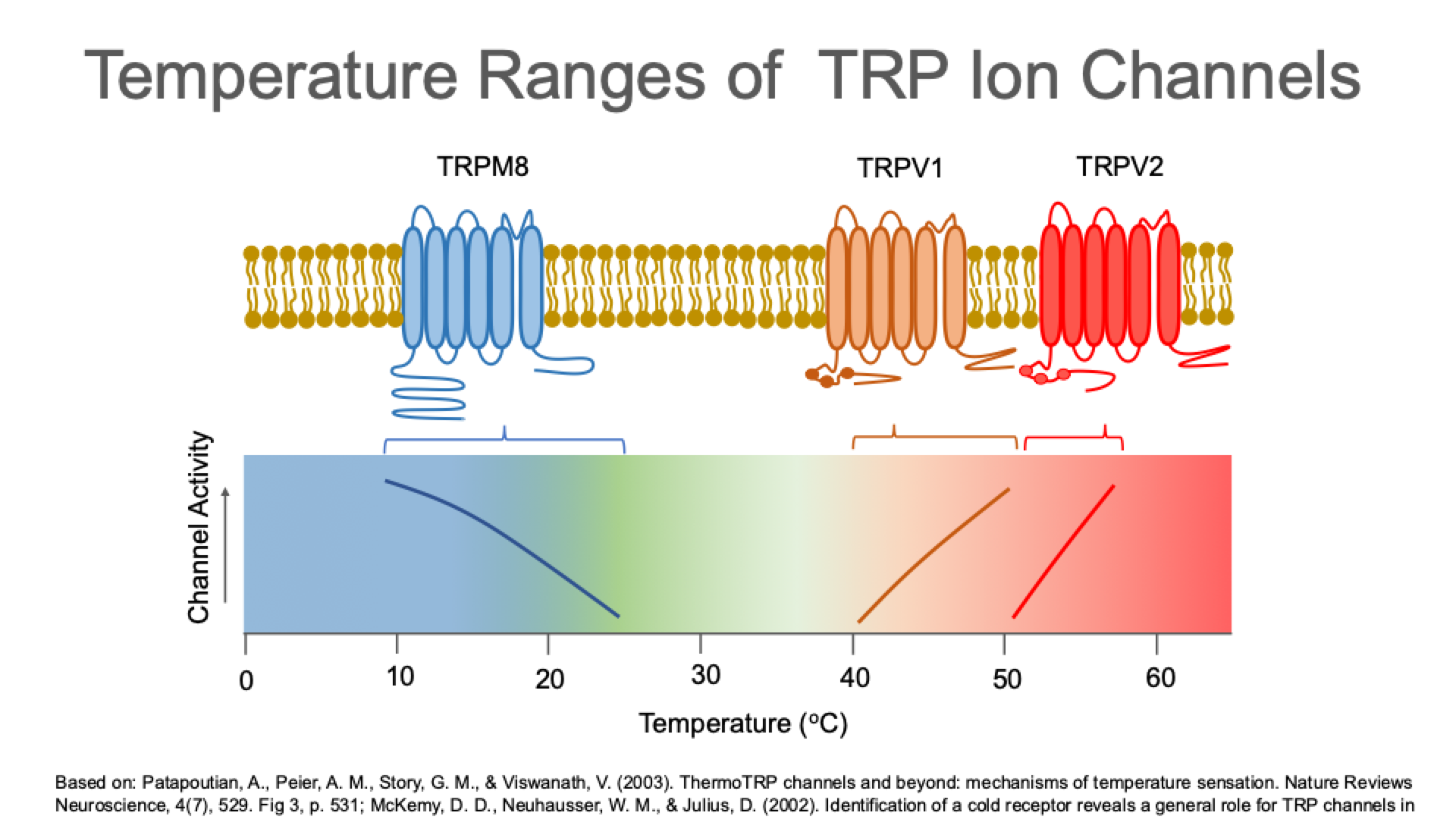
10 - 20: Less sensitive as it gets warmer
If you burn your skin, you’re killing the receptor
Somatosensation in the Central Nervous System
Information from touch receptors in the head enters the central nervous system through the cranial nerves. Information from receptors below the head enters through the 31 spinal nerves.
Each spinal nerve has a sensory component and a motor compononent
Dermatome
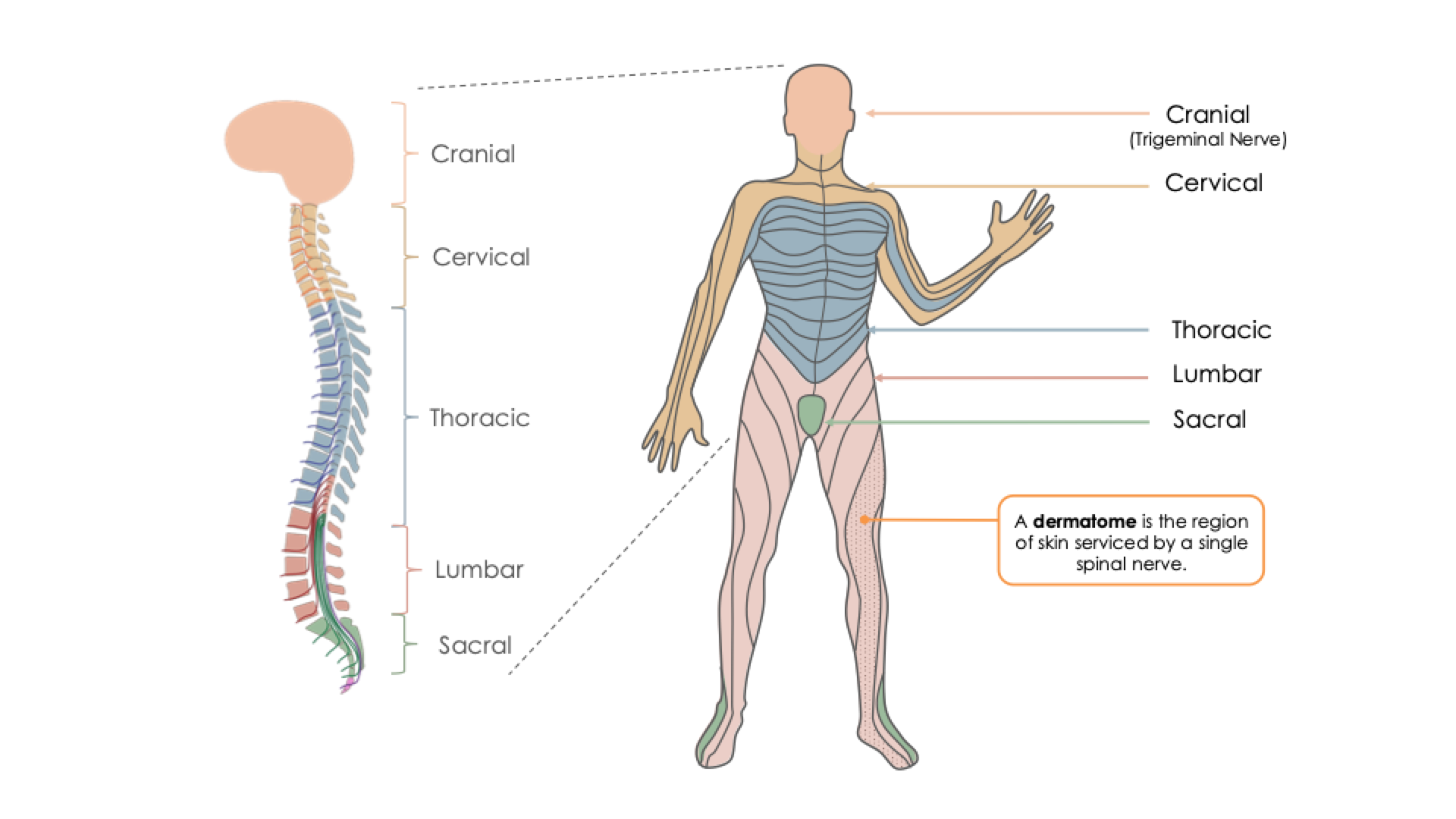
Each spinal nerve innervates a limited area of the body called a dermatome
For example, the third thoracic nerve (T3) innervates a strip of skin just above the nipples as well as the underarm area
Spinal Cord (C8)
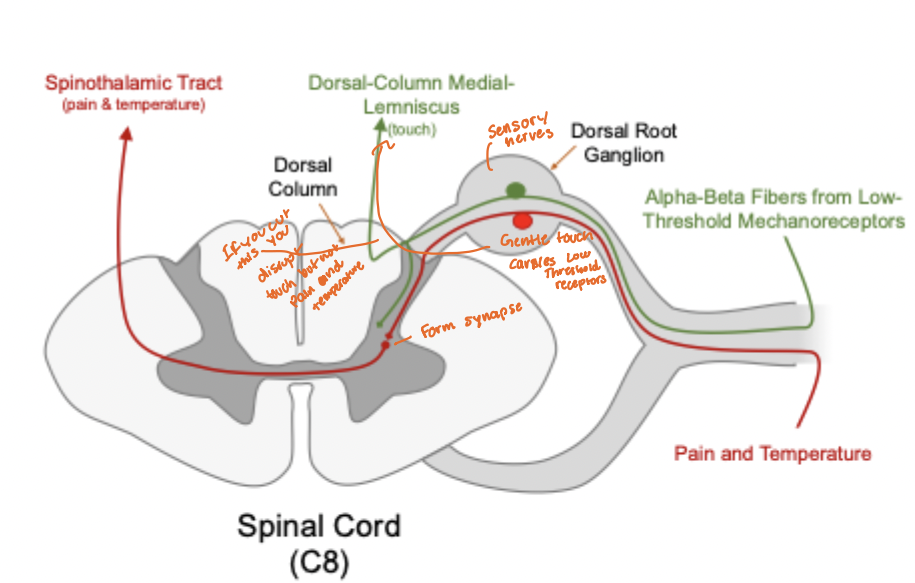
Stimuli and Spinal Cord Paths
The thicker and faster axons convey sharp pain, whereas the thinner ones convey duller pain, such as post surgical pain
Mild pain releases the neurotransmitter glutamate, whereas stronger pain releases both glutamate and neuropeptides, including substance P and CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide.)
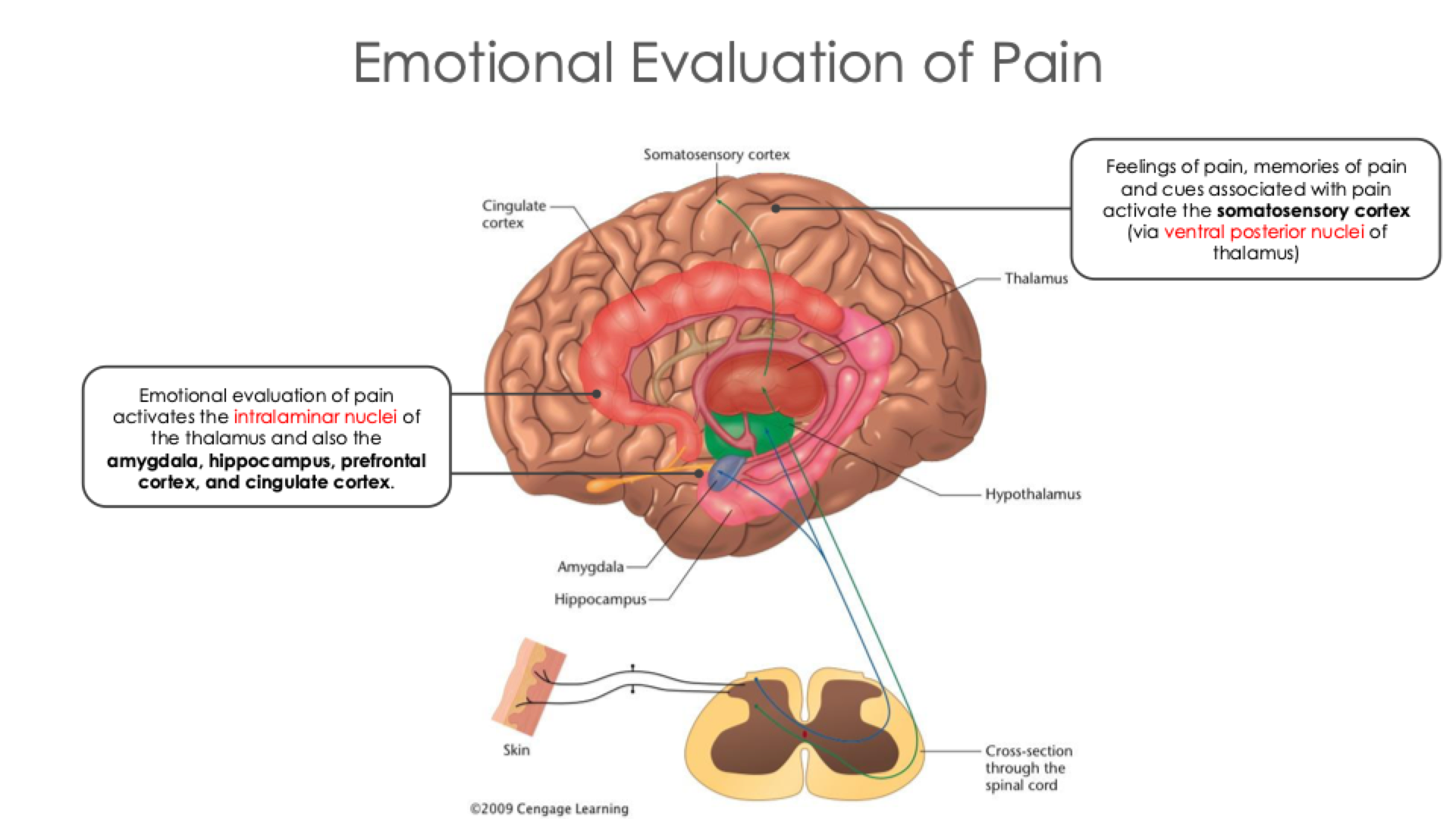
Input from the pain/temperature pathway to the thalamus and then to the somatosensory cortex reports the intensity and location of the pain
After damage to the somatosensory cortex, people have trouble localizing the pain
Fill in the Blank: Information from skin sensations also goes to the ____________ and __________, which respond to the pleasantness or unpleasantness of the sensation
anterior cingulate cortex, insular cortex
What is the primary somatosensory cortex, S1 essential for?
Touch experiences
When the fingers touch something, people are conscious of only those that produce enough arousal in the primary somatosensory cortex
What does damage to the somatoseonsry cortex impair?
Perceptions
A patient had an illness that destroyed the myelinated somatosensory axons from below his nose but spared his unmyelinated axons.
He still felt temperature, pain, and itch, because they depend on the unmyelinated axons.
He had no conscious perception of touch, which depends on myelinated axons.
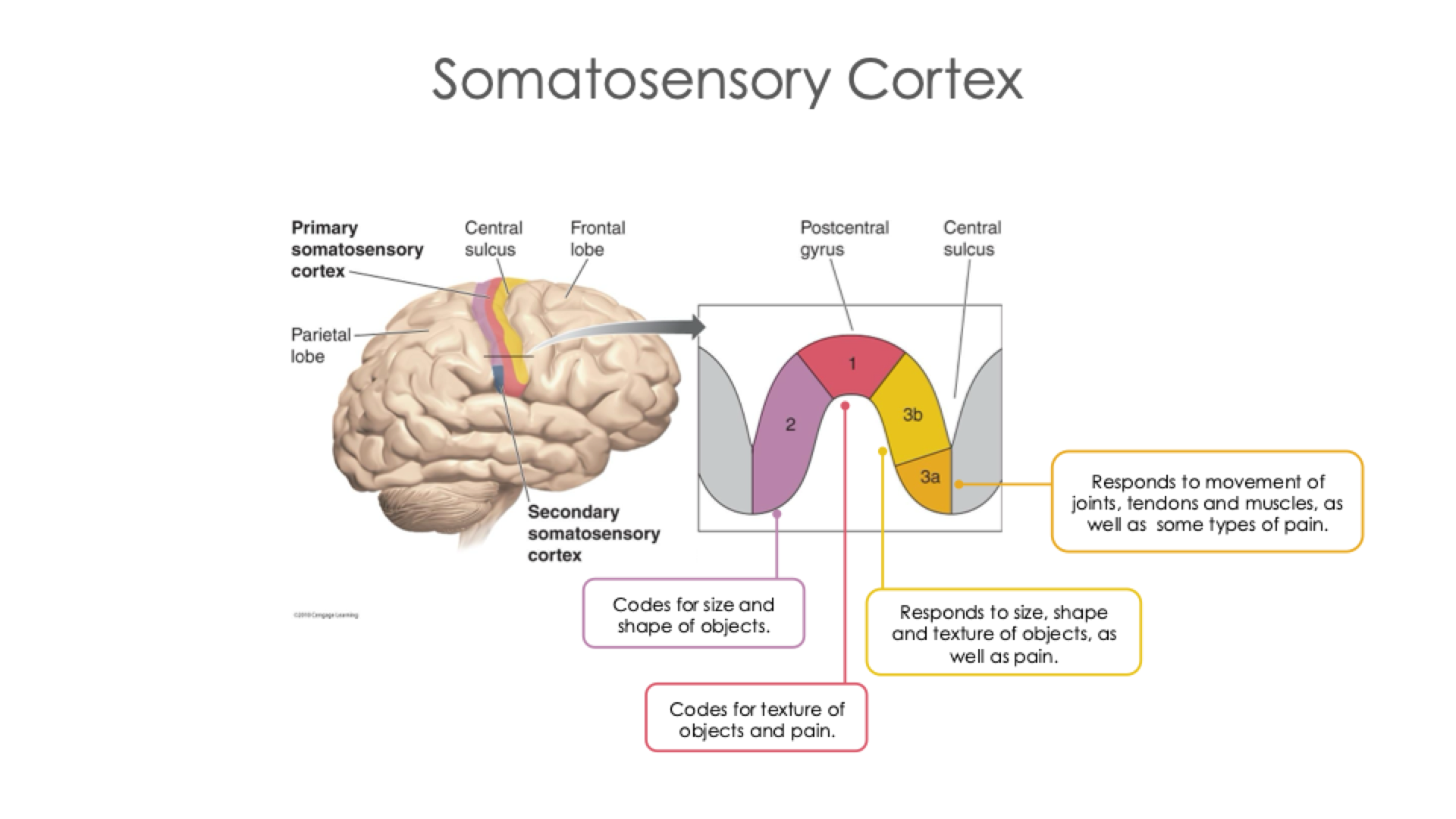
Somatosensory Cortex Diagram
Emotional Evaluation of Pain
Pain Relief
Pain and Depression
More common in women than males
Most of the biological research on pain has relied on just males because women are assumed to be more variable, because of their hormonal cycles
The problem is males and females do not react the same way to pain
Activating certain neurons in the midbrain decreases pain sensitivity in male mice, but not in females
Pain Relief: A Placebo
(A drug or other procedure with no pharmacological effect; your reducing side effects which reduces pain) can reduce pain responses in the brain and in the spinal cord
Placebos have little influence on most illnesses, but they often relieve pain, depression, and anxiety
True or False: People who receive placebos do not just say the pain increases; scans of the brain and spinal cord also exhibit a increased response
People who receive placebos do not just say the pain decreases; scans of the brain and spinal cord also exhibit a decreased response
Nocebo Effect
Nocebo effect, the opposite of placebo
If someone expects an unpleasant reaction to a drug, the nervous system increases that response
Cannabinoids (in marijuana)
Block plain in the periphery of the body (as well as the CNS)
Gabapentin: inhibits neurotransmitters
The pain-relieving effects of opiates and cannabinoids differ between males and females. Researchers are beginning to pay more attention to male-female differences in pain
Cannabinoids: Neuropathic Pain
Cannabinoids have demonstrated promise for treating neuropathic pain, a condition of chronic pain that lasts long after the original cause of pain has ended
Damaged tissue release histamine, nerve growth factor, and other chemicals that help repair the damage but also magnify the responses of nearby heat and pain receptors
Emotional Pain: Break-up Study
A study with more intense hurt feelings, based on remembering a recent romantic breakup, while looking at a photo of the ex, activated not only the cingulate cortex but also the sensory areas responsive to physical pain
What effect does acetaminophen exhibit in the cingulate cortex?
Those taking acetaminophen exhibited less response in the cingulate cortex and other emotionally responsive areas
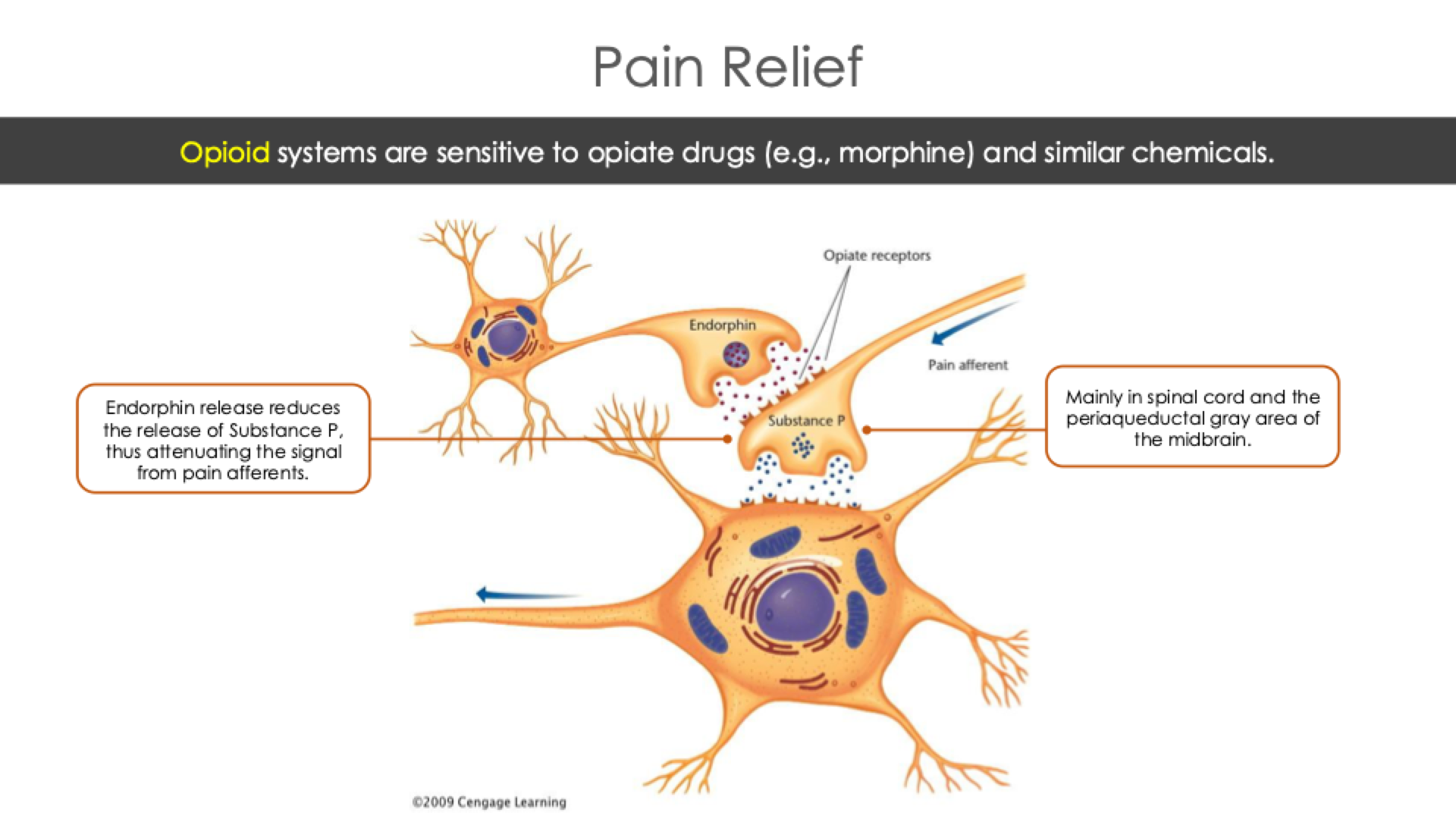
Opioid Mechanisms
The brain puts the brakes on prolonged pain by opioid mechanisms
Opioid Mechanisms: systems that respond to opiate drugs are similar chemicals
Fill in the Blank: Opioids bind to receptors in the spinal cord and the _______________ of the midbrain
Opiates bind to receptors in the spinal cord and the periaqueductal gray area of the midbrain
Endorphins
The nervous system has its own opiate-type chemicals called endorphins
Endorphins: The transmitters that attach to the same receptors as morphine
The brain produces several types of endorphins, which relieve different types of pain, such as the pain from a cut versus the pain from a burn
Inescapable pain is especially potent at stimulating endorphins and inhibiting further pain
Endorphins are released during intense pleasures, such as orgasm
Morphine
Morphine does not affect large-diameter axons that convey sharp pain
Morphine does block messages from thinner axons that convey slow, dull pain such as post surgical pain
Gate Theory
Spinal cord neurons that receive messages from pain receptors also receive input from other inputs that can close the gates for the pain messages
True or False: Is itch a separate sensation?
True
Cause: Tissue Damage
The other cause is tissue damage, such as when your skin is healing after a cut. Your skin releases histamines that dilate blood vessels and produce an itching sensation.
Uses of Itch
Itch is useful because it directs you to scratch the itchy area and remove whatever is irritating your skin
Your brain is not satisfied until you scratch hard enough to produce mild pain, because pain inhibits itch
Opiates, which decrease pain, increase itch
Fill in the Blanks: The inhibitory relationship between ______ and ______ is clear evidence that itch is not a type of pain. Further evidence is the demonstration that blocking itch fibers does not reduce pain
The inhibitory relationship between pain and itch is clear evidence that itch is not a type of pain. Further evidence is the demonstration that blocking itch fibers does not reduce pain