Lesson 5.2: Business Cycles
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards made from a presentation segment created as a lesson on business cycles.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
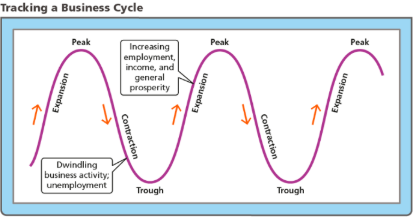
Business cycle
The alternation between economic downturns, known as recessions, and economic upturns, known as expansions
Often affected by specific economic variables that bring about the next phase; however, forecasting is difficult

Business investment
Factor in the business cycle where businesses spend more money, increasing GDP and economic expansion
Office buildings are one manifestation of this

Credit cost
Factor in the business cycle describing the cost of borrowing money
Higher levels of this may result in decreased consumer spending or business investment

External shocks
Factor in the business cycle describing those outside of a business’s control that positively or negatively affect growth
Wars and global pandemics are examples of this

Consumer expectations
Factor in the business cycle describing predictions made by consumers about the future that affect present spending
Recessions
Periods of economic downturn when output and employment are falling with dwindling business activity
Defined as 2 consecutive quarters of falling real GDP
Usually lasts from 6 to 18 months with 6 to 10 percent unemployment

Depressions
Deep and prolonged downturns
No precise definition; usually defined as a recession with high unemployment and low economic output
Stagflation
A decline in real GDP (output) combined with a rise in the price level (inflation)
Expansions
Periods of economic upturn when output and employment are rising with general prosperity
Measured by a rise in real GDP
Peak
The time when real GDP stops rising and the economy has reached the height of an economic expansion
Unemployment and inflation are low
Contraction
The time after a peak marked by a decline in falling real GDP and higher unemployment
Trough
The time after a contraction when the economy has “bottomed out” as real GDP stops falling and expansion begins