Ch. 11 - Nervous System
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
What are the 3 divisions of the nervous system?
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Enteric Nervous System (ENS)
What does the central nervous system contain? Its function?
CNS; brain and spinal cord
Function; Information processing, integrates, coordinates sensory and motor
What does the peripheral nervous system contain?
PNS; any nervous tissue leaving the spinal cord
What is the enteric nervous system?
ENS; nervous controls GI tract
What are the subdivisions of the peripheral nervous system?
Sensory (afferent) division: brings info. to brain (CNS)
Motor (efferent) division; carries motor commands AWAY from CNS
nerve impulses toward muscles
What does the sensory (afferent) division include?
Sensory receptors
Special sensory organs
What are the sensory receptors?
Sensory (afferent) division
Position, touch, pressure, pain, temperature
What are the special sensory organs?
Sensory (afferent) division
Smell, taste, sight, balance, hearing
What does the motor (efferent) division include?
Somatic nervous system (SNS)
Autonomic nervous system (ANS)
What is the somatic nervous system?
Motor (efferent) Division
Voluntary, conscious control
skeletal muscle
What is the autonomic nervous system?
Motor (efferent) Division
Involuntary, automatically regulates activities
smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands, adipose
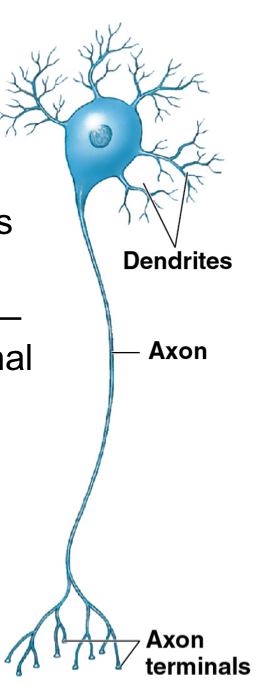
What are the main 3 regions of a neuron?
Dendrites
Cell body
Axon
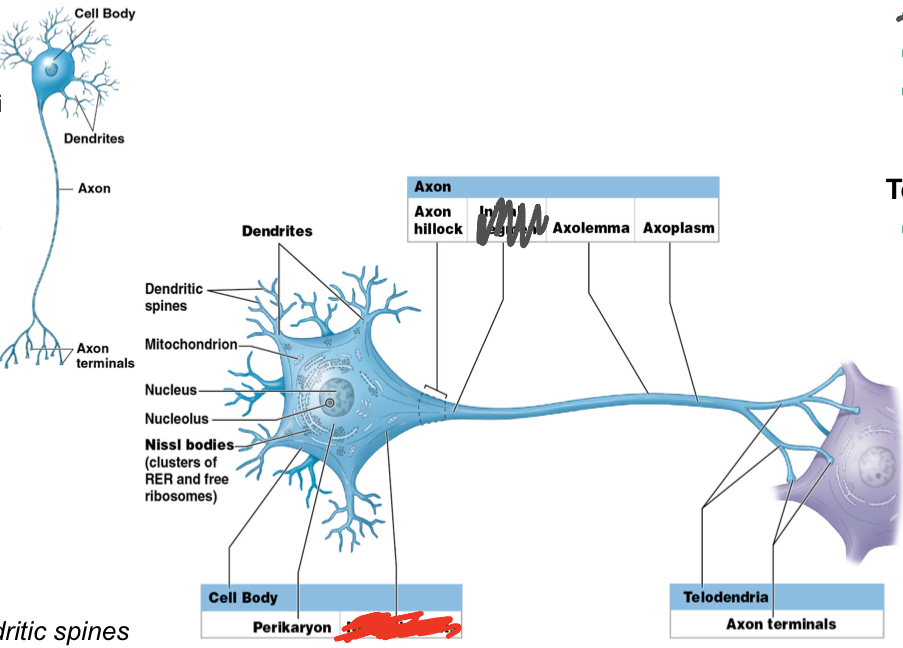
What is the function of dendrites? What is their structure?
Dendrites: receive stimulus/information (in CNS)
branched; dendritic spines
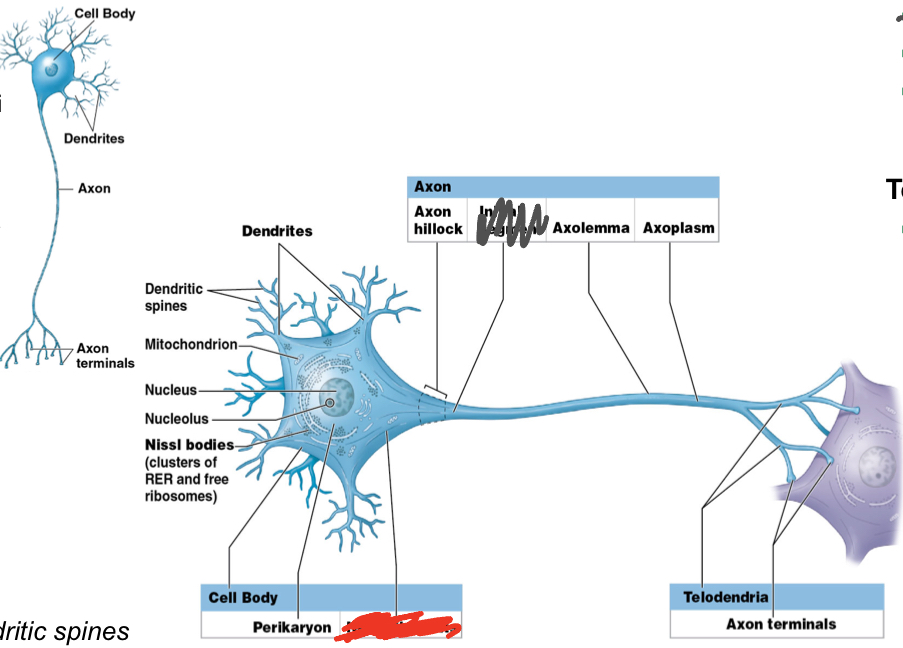
What does the cell body contain?
Perikaryon (cytoplasm surrounds nucleus): contains organelles and synthesizes neurotransmitters/ATP
contains nucleus
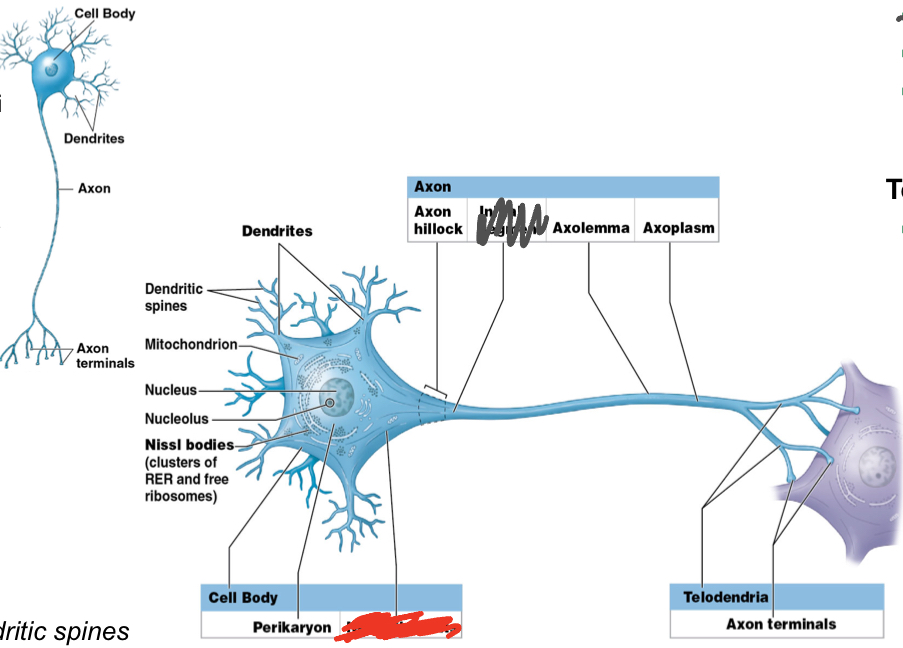
What is the function of the axon?
Axon: carries information AWAY/TOWARD other cells
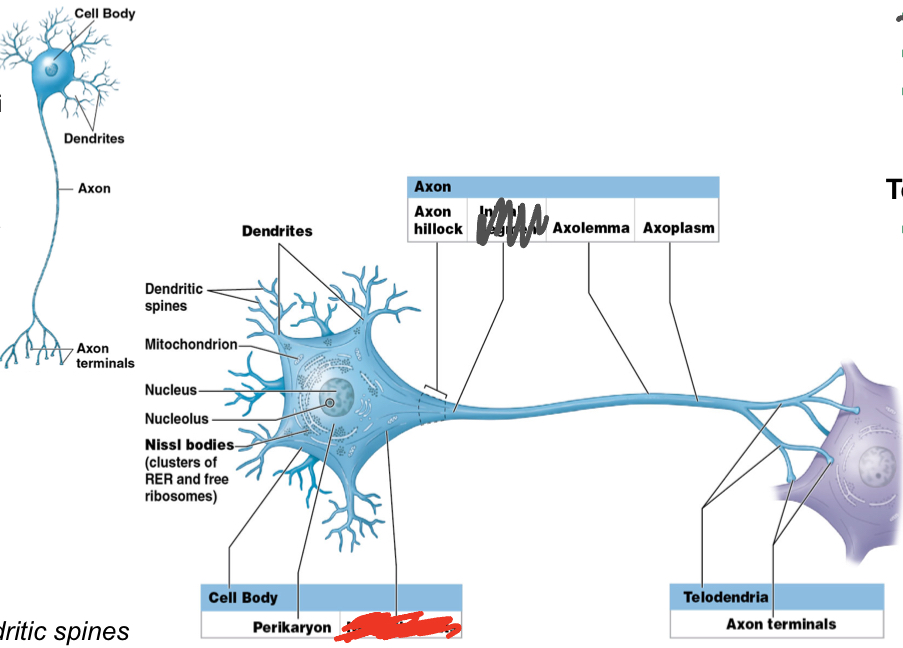
What are the components of the axon? Their function?
Axon hillock: origin of axon from cell body
Axolemma; axon's plasma membrane
Axoplasm: axon’s cytoplasm
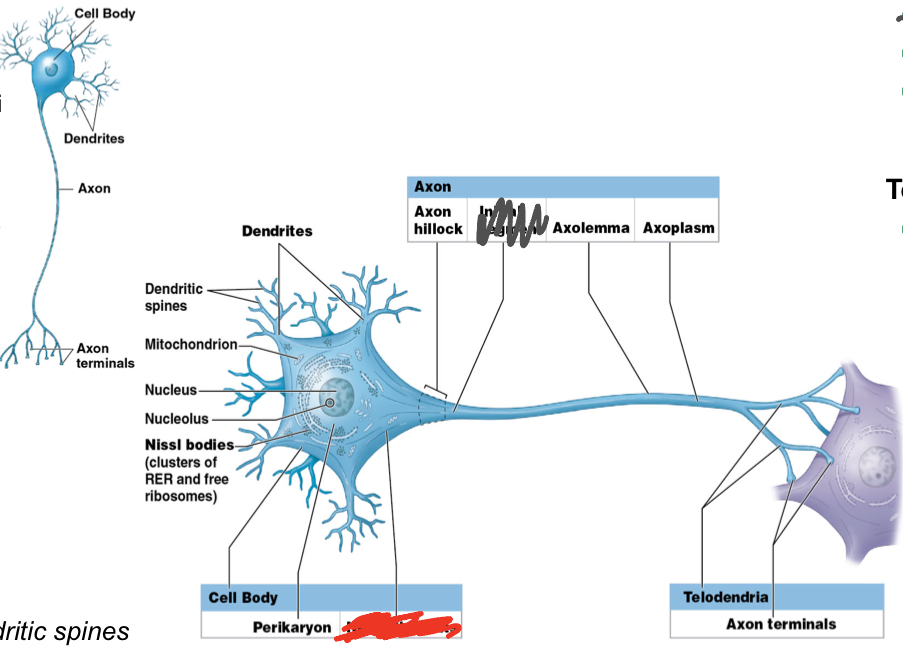
What is the telondendria?
Component of Axon
Telondendria; fine extensions
end at Axon Terminals
What is a synapse?
Synapse: a presynaptic cell connects with a post synaptic cell
What are the 3 types of synapses?
Synapses with another neuron; neuron + neuron
Neuromuscular junction; neuron + muscle fiber cell
Neuroglandular synapse; neuron + gland cell
What occurs when neurotransmitters are released from the presynaptic membrane?
Neurotransmitters (like ACh); released into synaptic cleft and bind to receptors on post synaptic membrane
relaying AP
What are synaptic vesicles of synapses?
Synaptic vesicles: store neurotransmitters (in presynaptic cell)
fuse with membrane
What are collateral branches of synapses?
Collateral branches: allow single neuron to communicate with many cells
e.g. motor units
What do CNS neurons lack?
Lack centrioles; cannot be replaced
What structures contain neural stem cells?
Olfactory epithelium
Retina of eye
Hippocampus
What are the classes of neurons?
Anaxomic neuron
Bipolar neuron
Unipolar neuron
Multipolar neuron
KNOW WHAT they look like
What is an anaxomic neuron?
Not understood
What is a bipolar neuron? Where do they occur?
Cell body in the way
Occur in special sense organs
What is a unipolar neuron? What is their structure?
Cell body off one side
Initial segment: where dendrites separate
What is a multipolar neuron? What is an example?
Multiple dendrites and single zon
Most common (e.g. motor neurons)
What is the function of neuroglia or glial cells? How much volume do they compromise?
Neuroglia: cells support/protect neurons
compromise; half of total volume of nervous system
What are the 4 types of CNS glial cells?
Ependymal cells
Microglia
Astrocytes
Oligodendrocytes
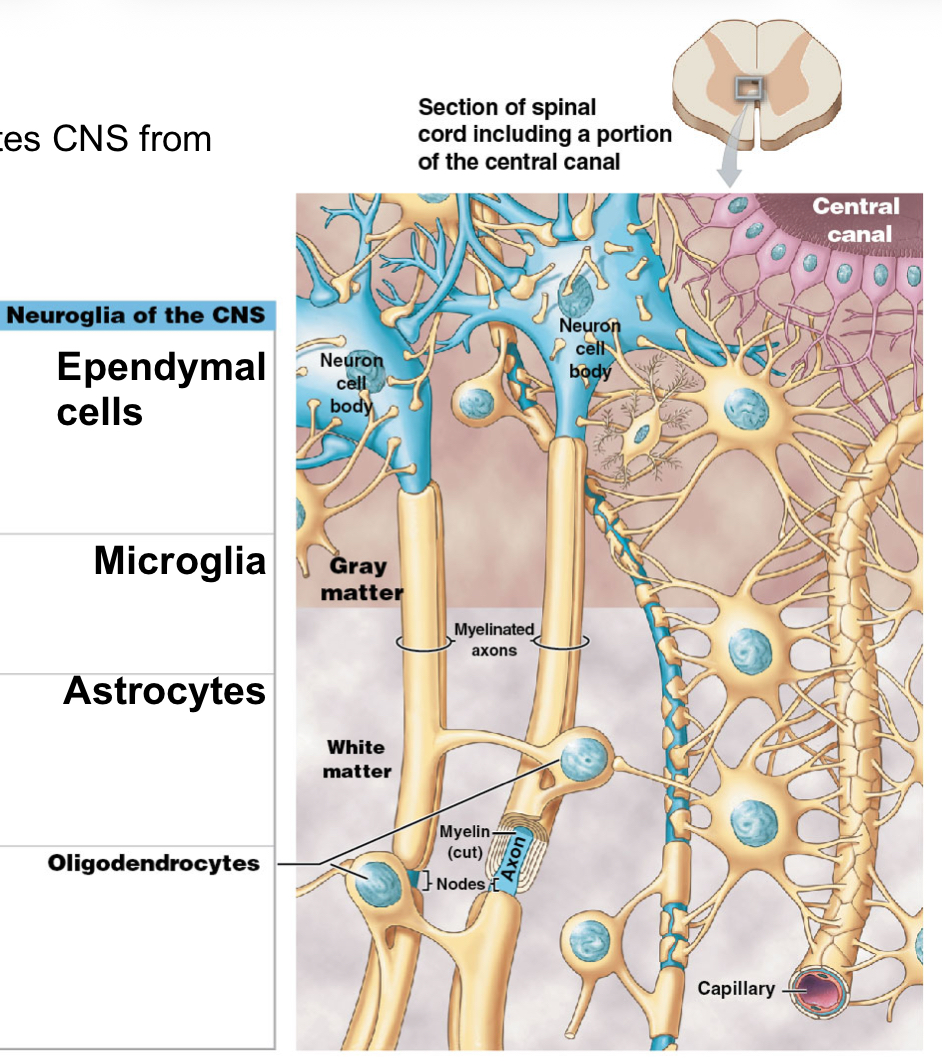
What is the function of the ependymal cells?
Create cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
What do ependymal cells form? Where are they found?
Form; Ependyma
Found; central canal (SC) and ventrioles (brain)
What is the function of the microglia?
Phagocytic cells that remove debris, wastes, pathogens
What is the main function of the astrocytes?
Maintain Blood Brain Barrier (BBB); isolates CNS from chemicals and hormones in blood
What do the astrocytes and BBB regulate?
Regulate; ion, nutrient, gas concentration in interstitial fluid
shared fluid of neurons
What do astrocytes do with the neurotransmitters?
Absorbs/recycles neurotransmitters (after being used)
What is the function of oligodendrocytes?
Provide CNS framework and produce myelin
What do the oligodendrocytes do to the axon?
Wraps axon with layers of myelin and plasma membrane: myelin sheath
What is the difference between oligodendrocytes (CNS) and schwann cells (PNS)?
Oligodendrocytes; one cell product myelin for multiple internodes (areas of axon)
Schwann cells; singe cell wraps around internode
What are myelinated axons?
Axons with myelin sheaths (appear white)
What is CNS white matter?
Many myelinated axons
What are internodes?
Internodes: myelin wrapped areas
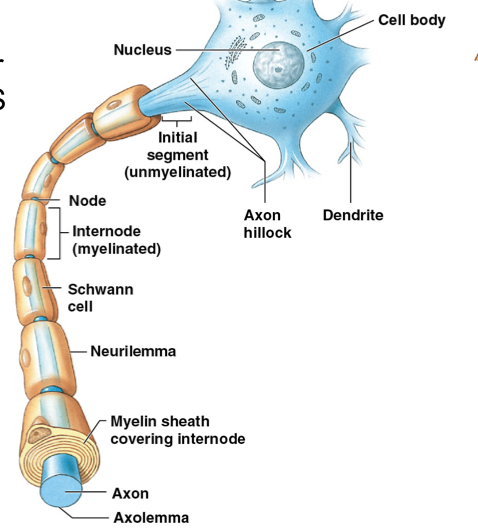
What are nodes?
Nodes: gaps between internodes (nodes of Ranvier)
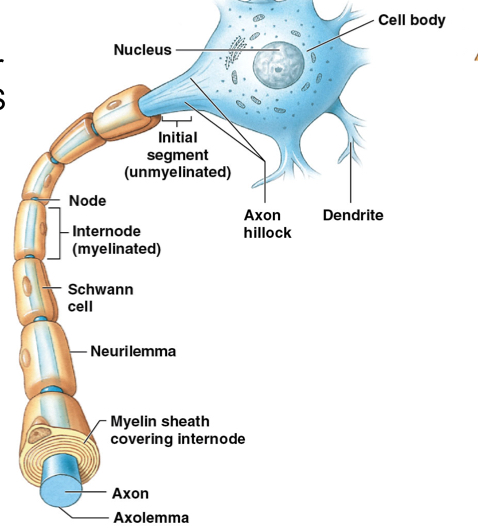
What are unmyelinated axons?
Unmyelinated axons: axons without myelin sheath
What is CNS gray matter?
Most cell bodies and unmyelineated axons
What are the two types of Neuroglia in the PNS?
Schwann cells
Satellite cells
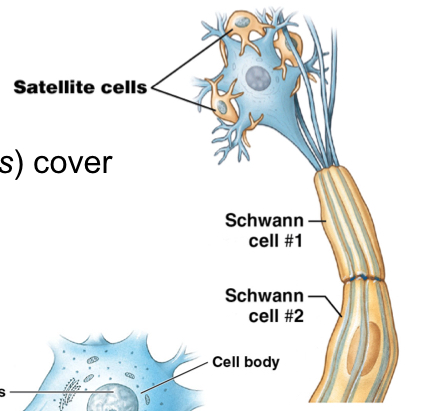
What is the function of schwann cells? Found?
Axon repair and forms myelin sheath of axon
Found; cover peripheral axons
What is neurilemma?
Plasma membrane of schwann cells in PNS
What is membrane potential?
Unequal charge distribution across a membrane
inside of cell; negative
outside of cell; positive
What is the charge inside of a cell?
- 70 mV
What is resting membrane potential?
Undisturbed, starting point
has energy, holding back
What is the graded potential?
Temporary, localized change in resting potential
determine if stimulus is enough (“grades”); Na+ moving in
What is action potential? What is it triggered by?
Electric impulse spreading from axon surface to axon terminals
Triggered by sufficiently large graded potential; enough Na+ entering
What is an example of a cell that has reached synaptic acitivity?
Neuromuscular junction
simplest form of information processing
What the general steps of synaptic activity?
Presynaptic cell releasing neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters binds to receptors on postsynaptic cell membrane changing permeambility
Produces graded potentials in postsynaptic membrane; depends on action
What is the sodium potassium pump?
Pumps 3 Na+ OUT of cell to ECF
Pumps 2 K+ INSIDE of cell
active transport; requires ATP
What is the function of the sodium potassium pump?
Maintain stable resting potential (-70 mV)
occurring at resting potential
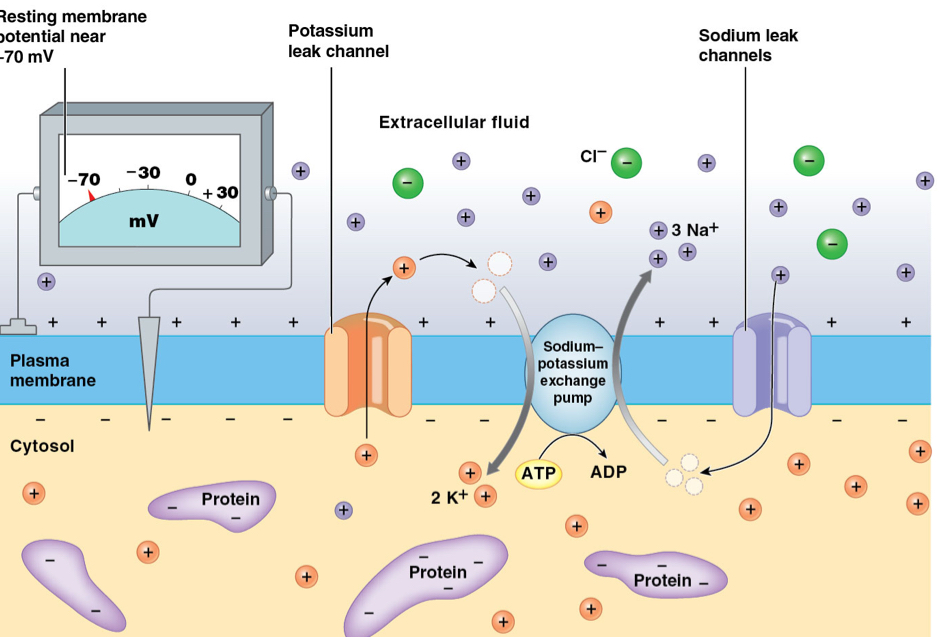
What are the leaky channels?
Passive membrane channels always open
create membrane potential (-70 mV)
What are the potassium leak channels? Their purpose?
K+ leak channels; K+ LEAVING cell
rush out when cell is too positive
What are the sodium leak channels? Their purpose?
Na+ leak channels; Na+ ENTERING cell
rush in when cell is too negative
How does the ECF and cytosol contribute to resting membrane potential?
ECF; high conc. of Na+ and Cl- (pos.)
Cytosol (inside of cell); high conc. of K+ and negatively charged proteins (neg.)
What is essentially a nerve impulse?
Contributors of Resting Membrane Potential
Nerve (AP): movement of Na+ and K+ going in and out
What do proteins and ions have to use to move?
Contributors of Resting Membrane Potential
Proteins/Ions; CANNOT move freely, have to use active transport or passive membrane channels
What are the general steps of the changes in membrane potential?
Stimulus
Depolarization; Na+ ions in
Repolarization; K+ ions OUT
Hyperpolarization
Resting state
What is the first step of a change in membrane potential?
Graded potential; enough of a stimulus reaches threshold (-55 mV)
What is the second step of a change in membrane potential?
Triggers AP/depolarization; rushing in Na+ ions to cells
What is the third step of a change in membrane potential?
Hits +40; Repolarization: rushing K+ OUT of cell
to restore/repolarize to negative cell
What is the fourth step of a change in membrane potential?
Hyperpolarization; overshoot of K+ ions out of cell activates sodium potassium pump
What is the fifth step of a change in membrane potential?
Sodium potassium pump restores resting state