AP Psychology (All Units)
1/774
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
775 Terms
memory
persistence of learning over time through encoding, storing, and retrieval of information
encoding
the processing of putting information into the memory system

storage
the retention of encoded material over time

retrieval
the process of getting information out of memory storage

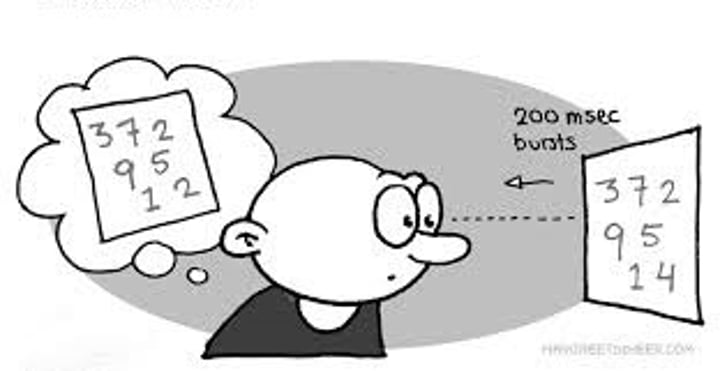
sensory memory
immediate, very brief recording of sensory information
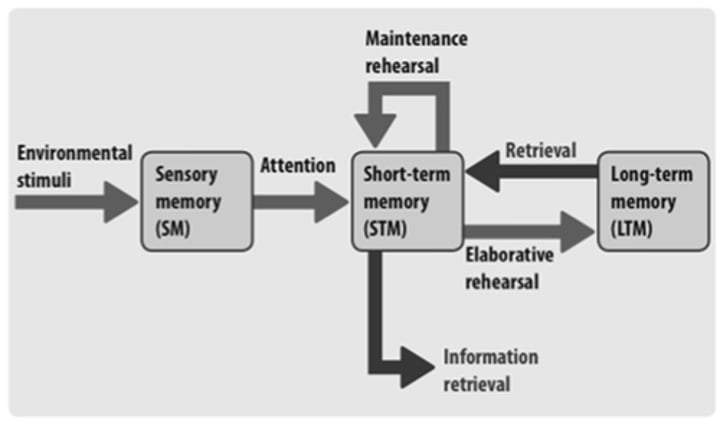
The Atkinson Schiffron 3-Stage Model (1968)
belief that information is processed from sensory memory, to short term memory, to long term memory
iconic memory
visual sensory memory (less than 1 second)
(you can glimpse an "icon")
echoic memory
auditory sensory memory (lasts a few seconds)

short term memory (STM)
few items (7 +/- 2 seconds) encoded briefly that lasts about 30 seconds. goes to LTM or is forgotten
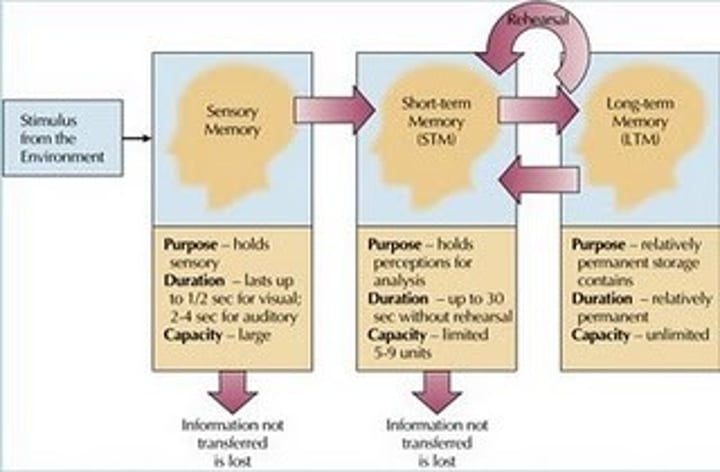
long term memory (LTM)
relatively permanent encoded information that is limitless
effortful processing
attention and conscious effort (rehearsal)

explicit memories
(declarative memories) memory or facts and experiences that one can consciously know and "declare"
automatic proccessing
unconscious encoding of incidental information (example: how many times a commercial is played and how often you notice)

implicit memory
(nondeclaritive memory) retention independent of conscious recall (impossible to explain)

chunking
organizing items into familiar, manageable units. often occurs automatically

mnemonics
memory aids, especially those using vivid imagery and organizational devices (example: guy cheating at the card game at the casino)

acronym
(type of chunking) typically 1st letter technique (example: remembering the solar systems)

peg-word system
pre-memorizing a list of words that are easy to associate with the numbers they represent (example: grocery list)
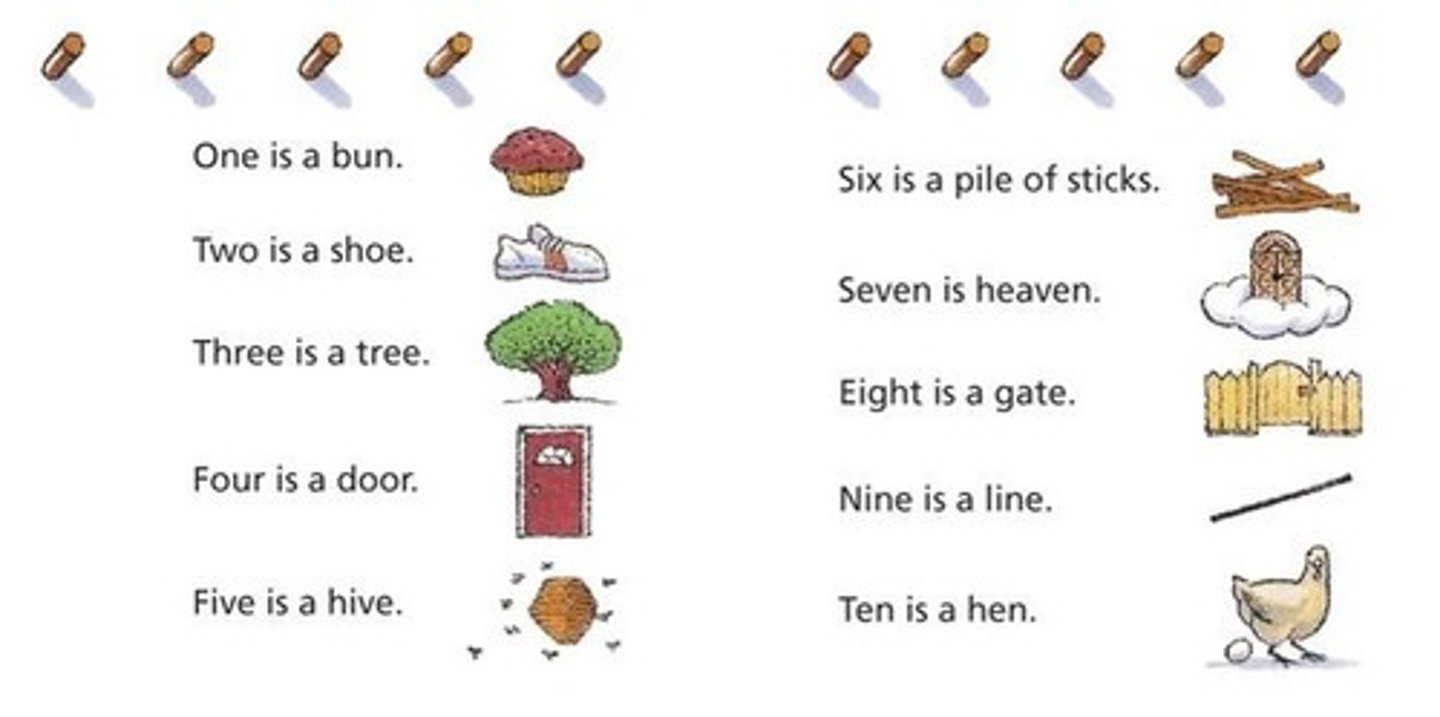
method of Loci
method of memorizing info by placing each item to be remembered at a point along an imaginary journey (example: cheating guy at the casino)

spacing effect
people encode more effectively when study is distributed evenly vs. a massive study session

testing effect
enhanced memory after retrieving, rather than simply rereading information

shallow proccessing
encoding on a basic level based on structure and appearance of words

deep processing
encoding based on the meaning of the words, tends to yield best retention

self-reference effect
people more easily remember material that is personally meaningful
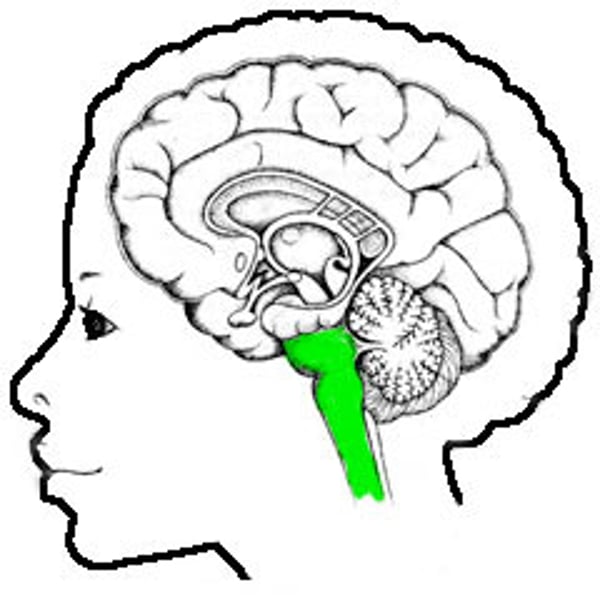
hippocampus
associated with declarative memory
flashbulb memory
clear moment, emotionally significant moment or event (associated with the amygdala)

infantile amnesia
conscious memories of first three years are blank

cerebellum
associated with nondeclararitive memory
procedural memories
motor and cognitive skills

semantic memories
general facts and knowledge of the world
long term potentiation
increase in a cell's firing potential after brief, rapid stimulation

recall
retrieving information from memory

recognition
identifying the target from possible targets (example: multiple choice quiz)

retrieval cues
stimuli that help retrieve a certain memory

Priming
the activation, often unconsciously, of a particular association with a memory

state-dependent memory
what we learn in one state (drunk or sober) may be more easily recalled in that state

mood-congruent memory
tendency to recall experiences that are consistent with one's current mood (sad or happy)

serial position effect
our tendency to recall best the first and last items in a list
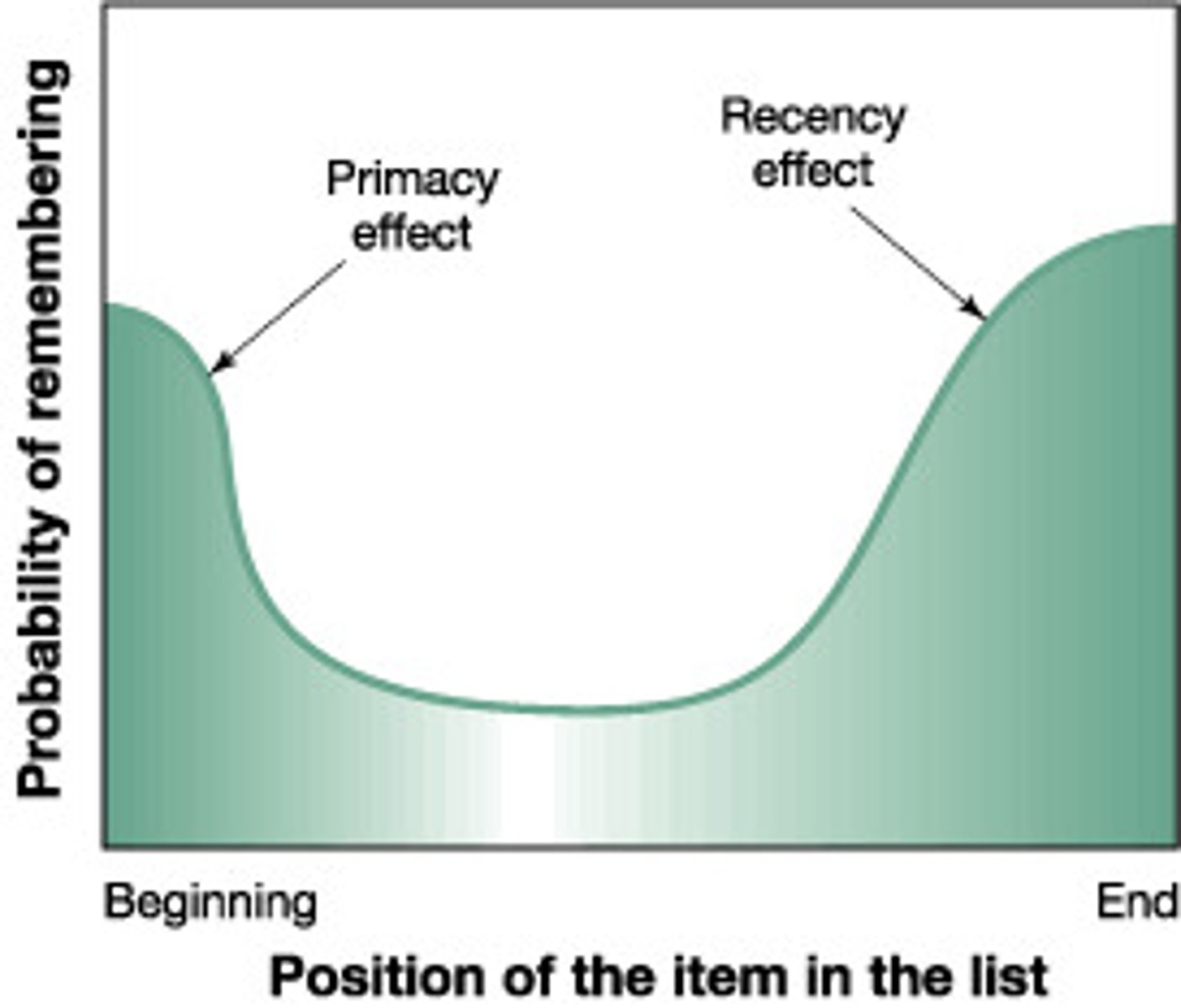
anterograde amnesia
inability to form new memories (explicit memories)

retrograde amnesia
inability to retrieve information from the past (explicit memories)

encoding failure
we cannot remember what we do not encode

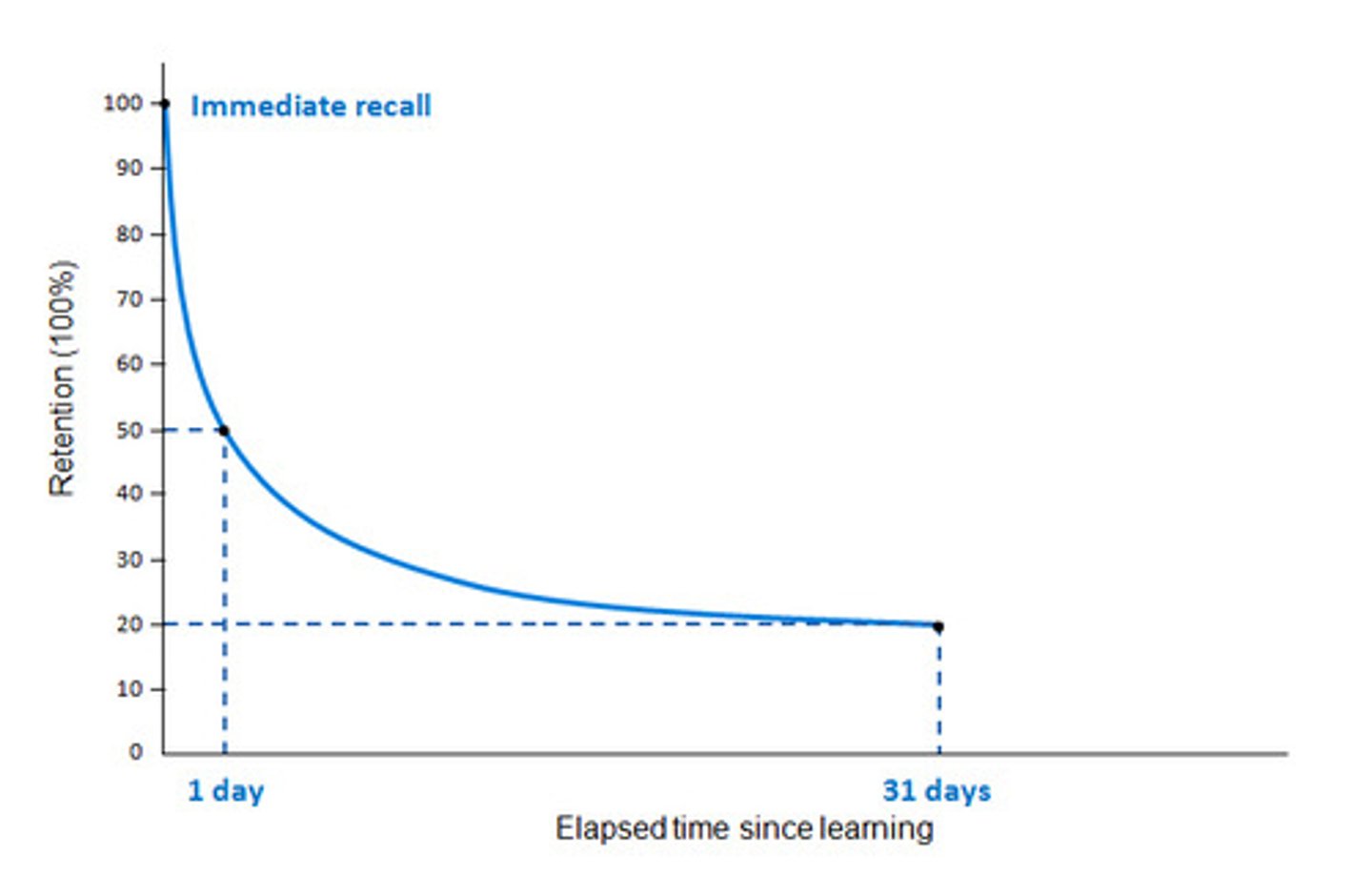
storage decay
(Ebbinghaus Forgetting Curve) forgetting initially rapid then levels off
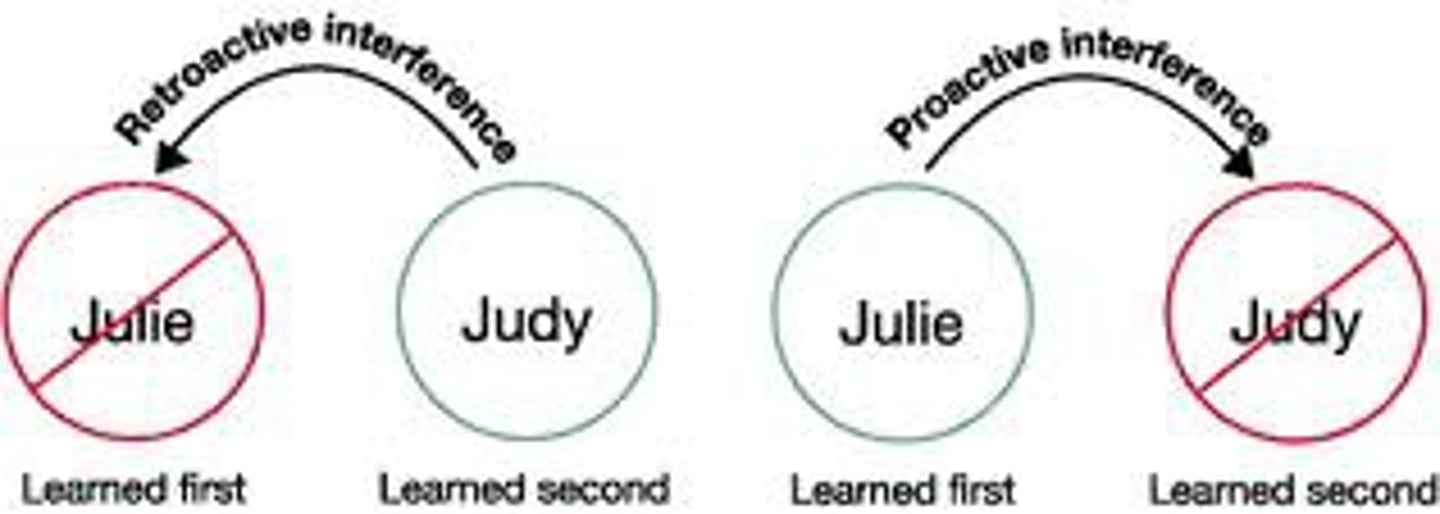
proactive interference
the disruptive effect of prior learning on the recall of NEW information
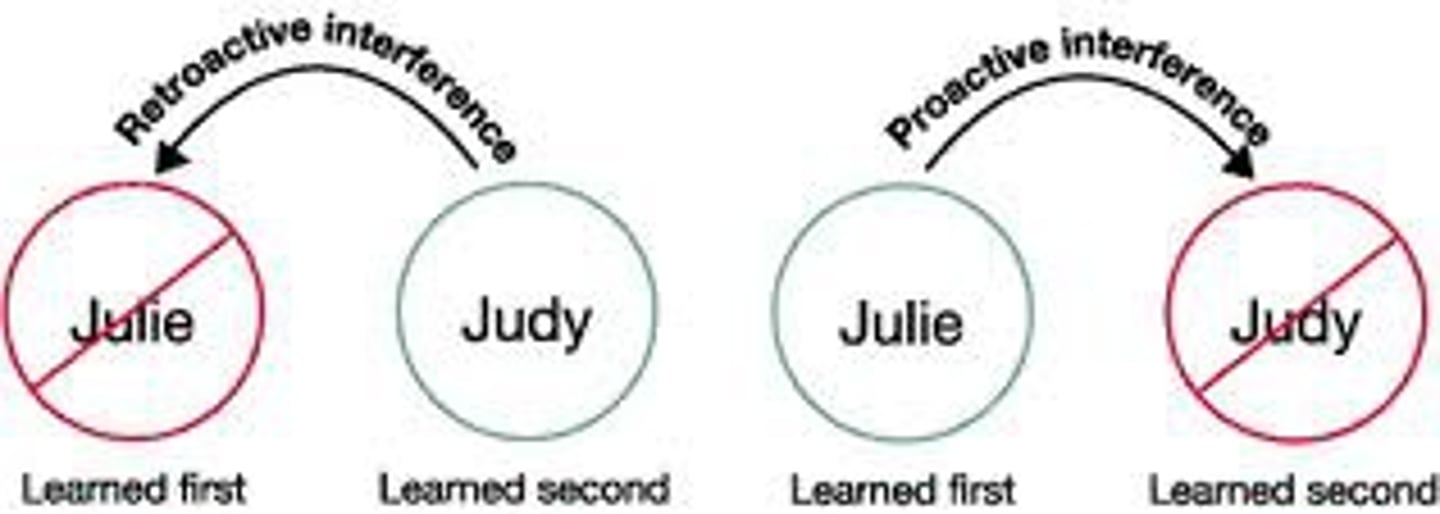
retroactive interference
the disruptive effect of new learning on the recall of OLD information
repression
Freud theory
unconsciously banishes from consciousness anxiety-arousing thoughts, feelings, and memories

misinformation effect
incorporating misleading information into one's memory of an event

source amnesia
source misattribution

deja vu
"I've experienced this before"

concepts
a mental grouping of similar objects, events, ideas, or people

prototypes
a mental image or best example of a category (your personal representation)

creativity
the ability to produce new, unusual, or valuable ideas

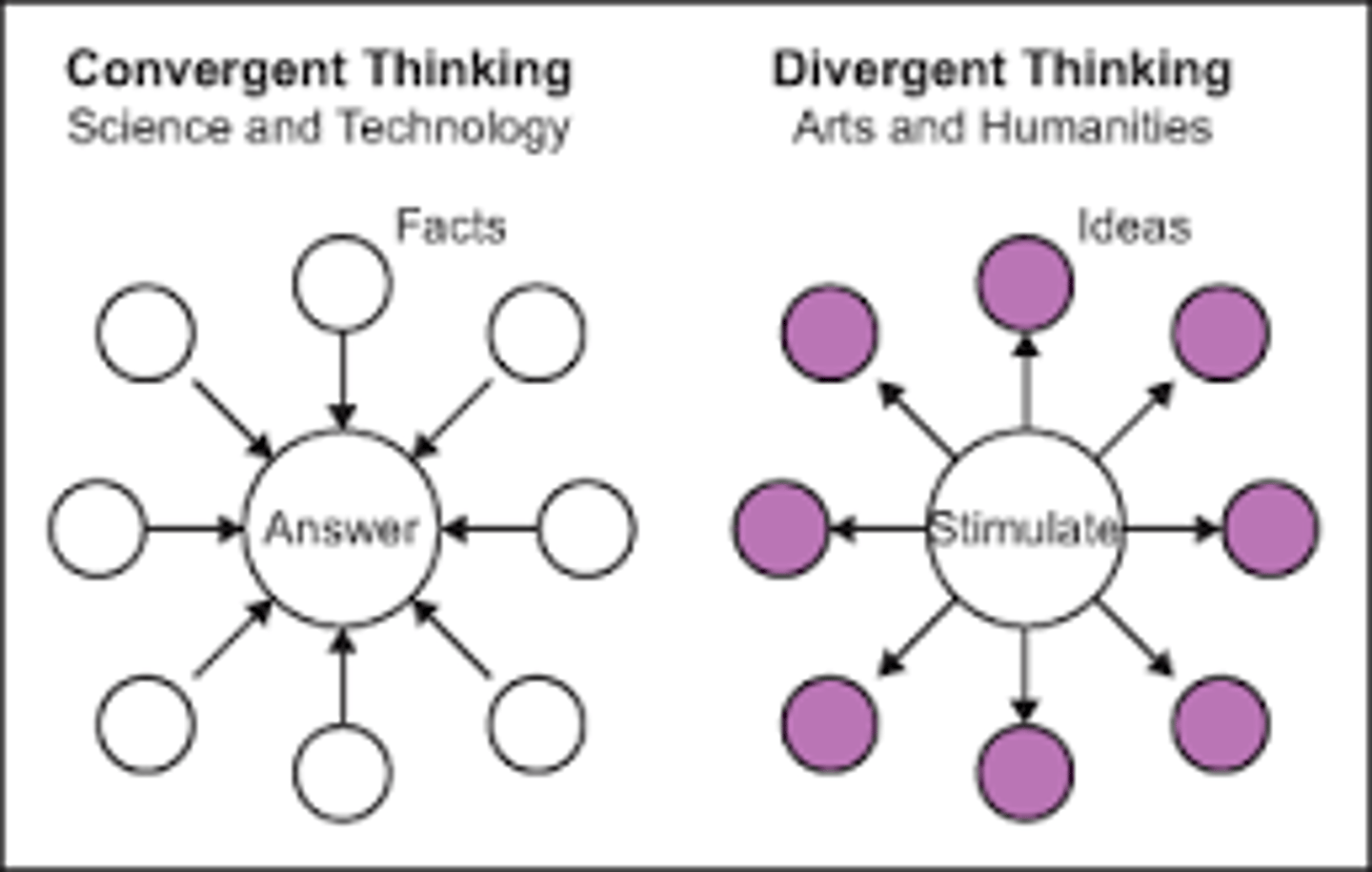
convergent thinking
narrows available problem solutions to determine the SINGLE BEST solution (example: intelligence tests)
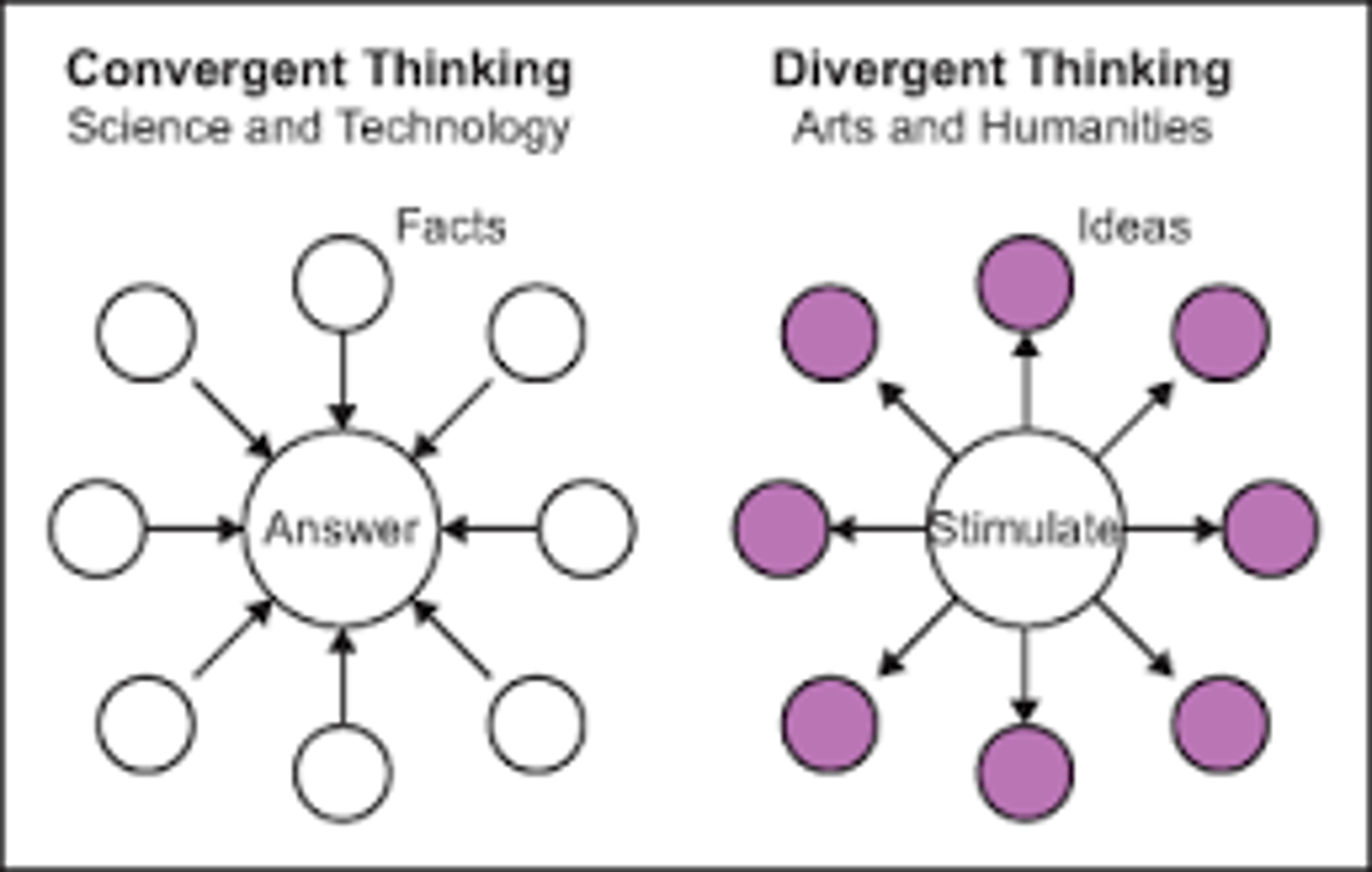
divergent thinking
expands number of possible problem solutions (example: creativity tests)
trial and error
repeated and varied attempts which are continued until success

algorithm
a methodical, logical rule or procedure
grantees solving, is time consuming, and exhausts all possibilities

heuristic
rule-of-thumb strategy, make judgement and solve problems efficiently, a short cut

insight
a sudden realization of a problems solution

confirmation bias
a tendency to search for information that confirms ones perceptions

fixation
an inability to see a problem from a fresh perspective (this impedes problem solving)
mental set
a tendency to approach a problem in a particular way, especially if it has worked in the past

functional fixedness
the tendency to think of things only in terms of their usual functions (example: brick)

repressentativeness heuristics
judging the likelihood of things in terms of how well they match our prototypes

availability heuristics
estimating the likelihood of events based on their availability in our memory. If it comes to mind easily we presume it is common

overconfidence effect
overestimate the accuracy of your belief or judgments

framing
the way an issue is posed significantly affected depending upon how an issue is framed

belief perseverance
clinging to your initial conceptions after the basis on which they were formed has been discredited (example: supporting a losing team)

phonemes
smallest distinctive sound unit (l, y, ch)

morphemes
smallest unit of meaning in a language (a, i, cat)

grammer
system of rules in a language

semantics
set of rules by which we derive meaning in language
syntax
rules for combining words into grammatically sensible sentences

babbling stage
spontaneously utter various sounds

one-word stage
say one word at a time

two-word stage
telegraphic speech, typically 2 words

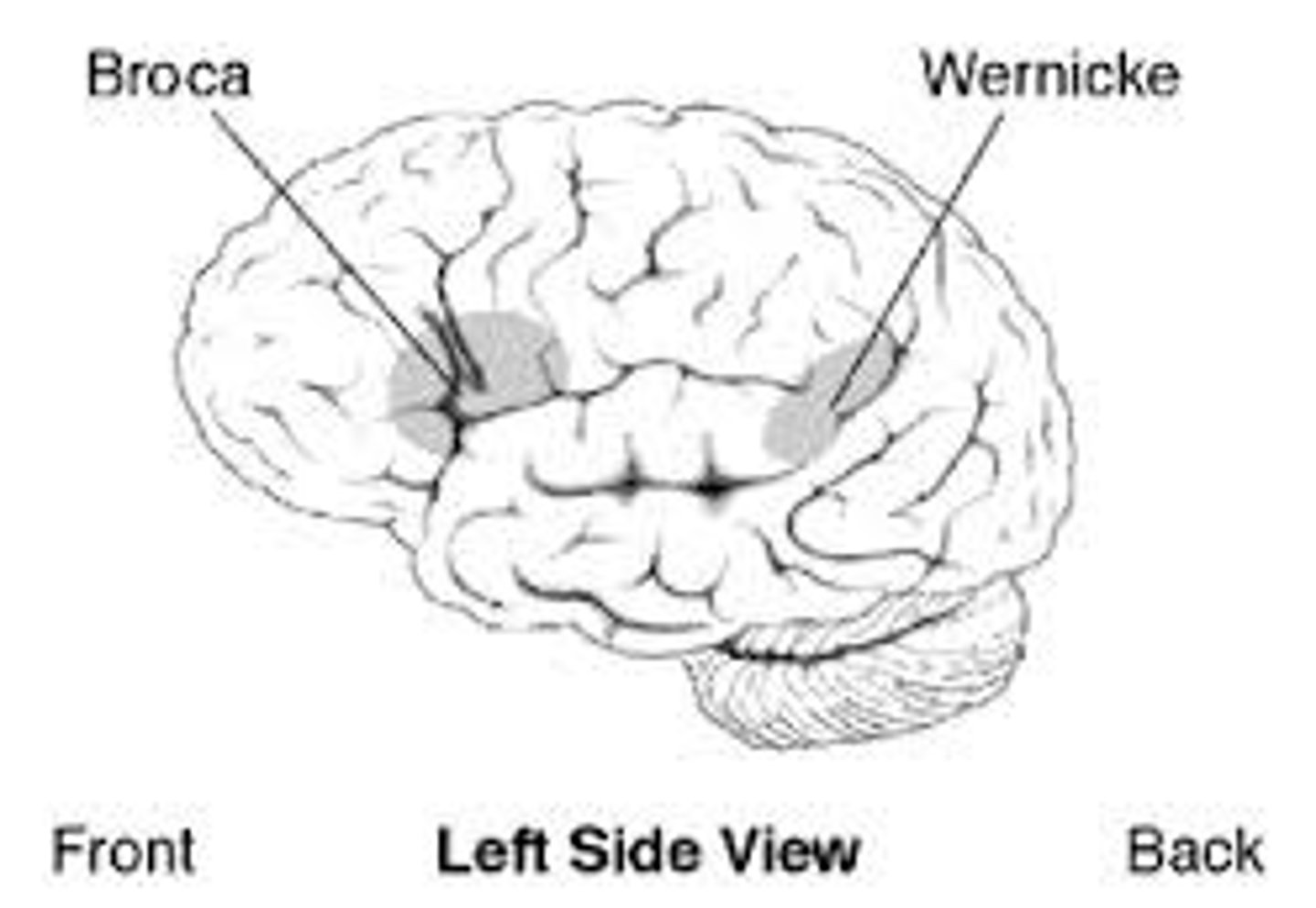
brocas area
controls language expression
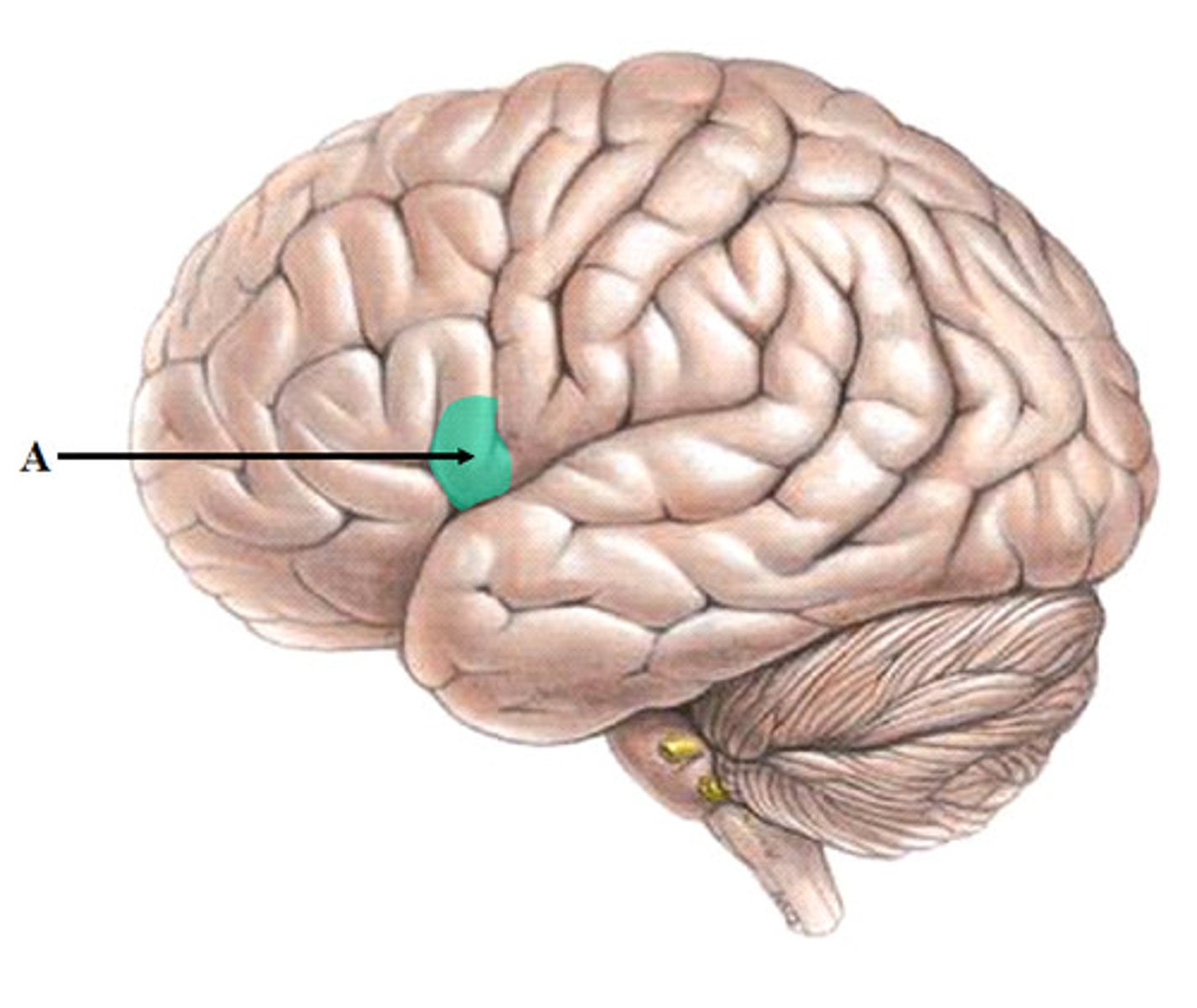
wernickes area
comprehends language and controls reception
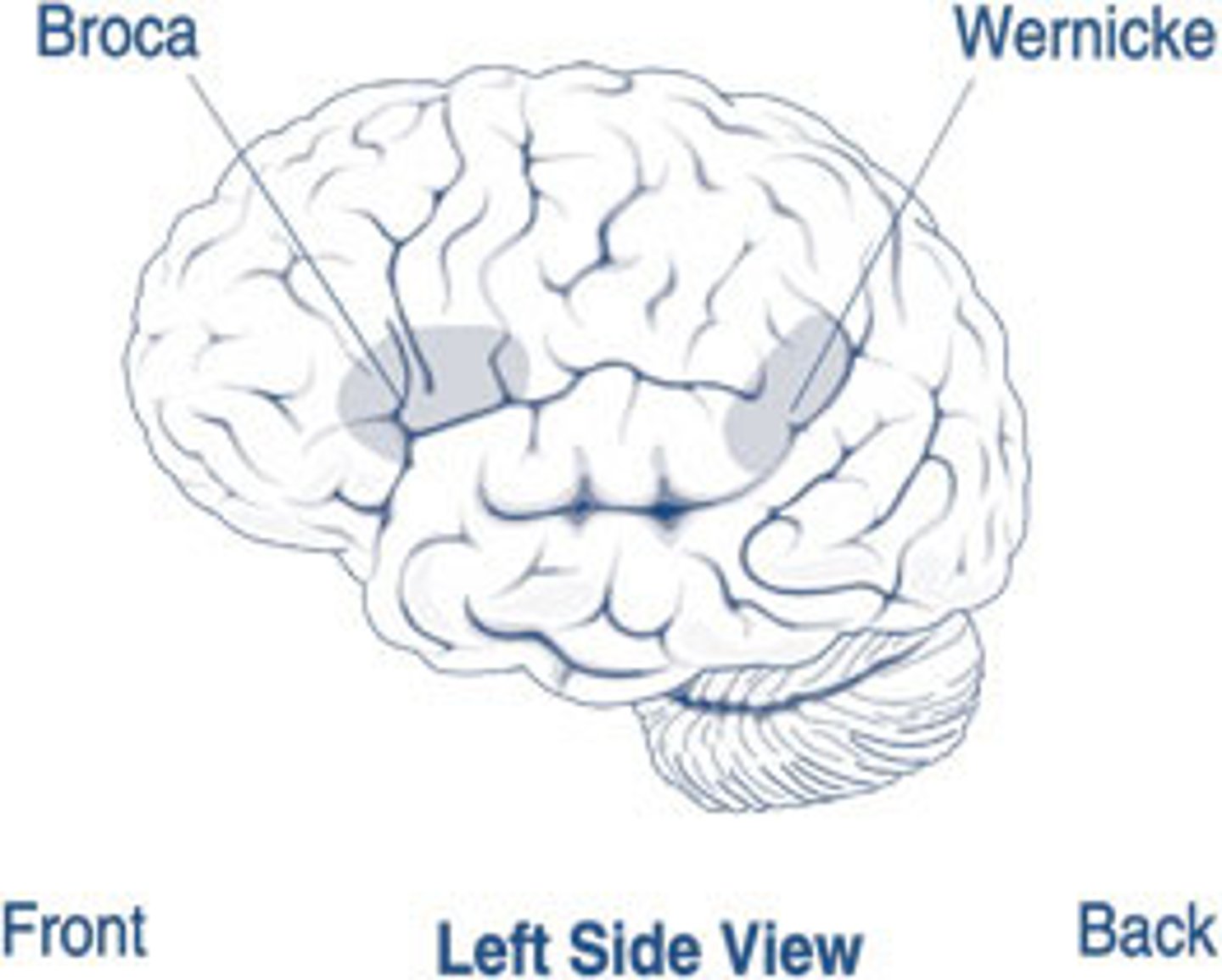
aphasia
impairment of language (typically left hemisphere)
inborn universal grammer
(Noam Chomsky) acquisition so fast that it cannot be explained. most of it is unborn (language acquisition device)

Whorf's Linguistic Relativity (Determinism)
idea that language determines the way we think

motivation
need or desire that energizes and directs behavior
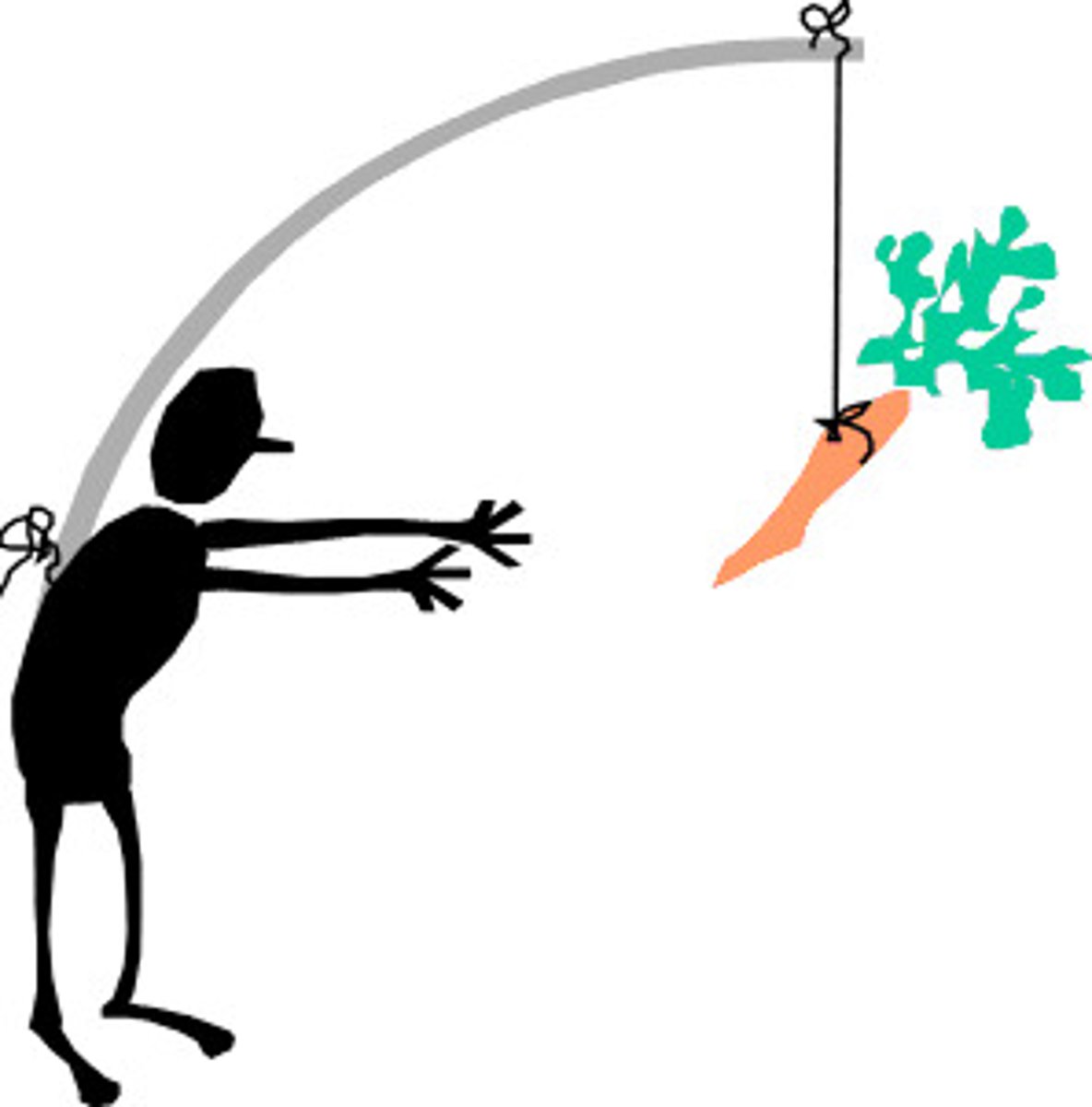
instinct
a complex, unlearned behavior that is rigidly patterned throughout a species

drive reduction theory
physiological need creates an aroused tension state (drive) that motivates an organism to satisfy the need (aim is to achieve homeostasis)

incentives
positive or negative stimuli that lure or repel us

optimum arousal theory
people are driven to perform actions in order to maintain an optimum level of physiological arousal

Yerkes-Dodson Law
performance increases with arousal only up to a point, beyond which performance decreases

Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
pyramid of human needs
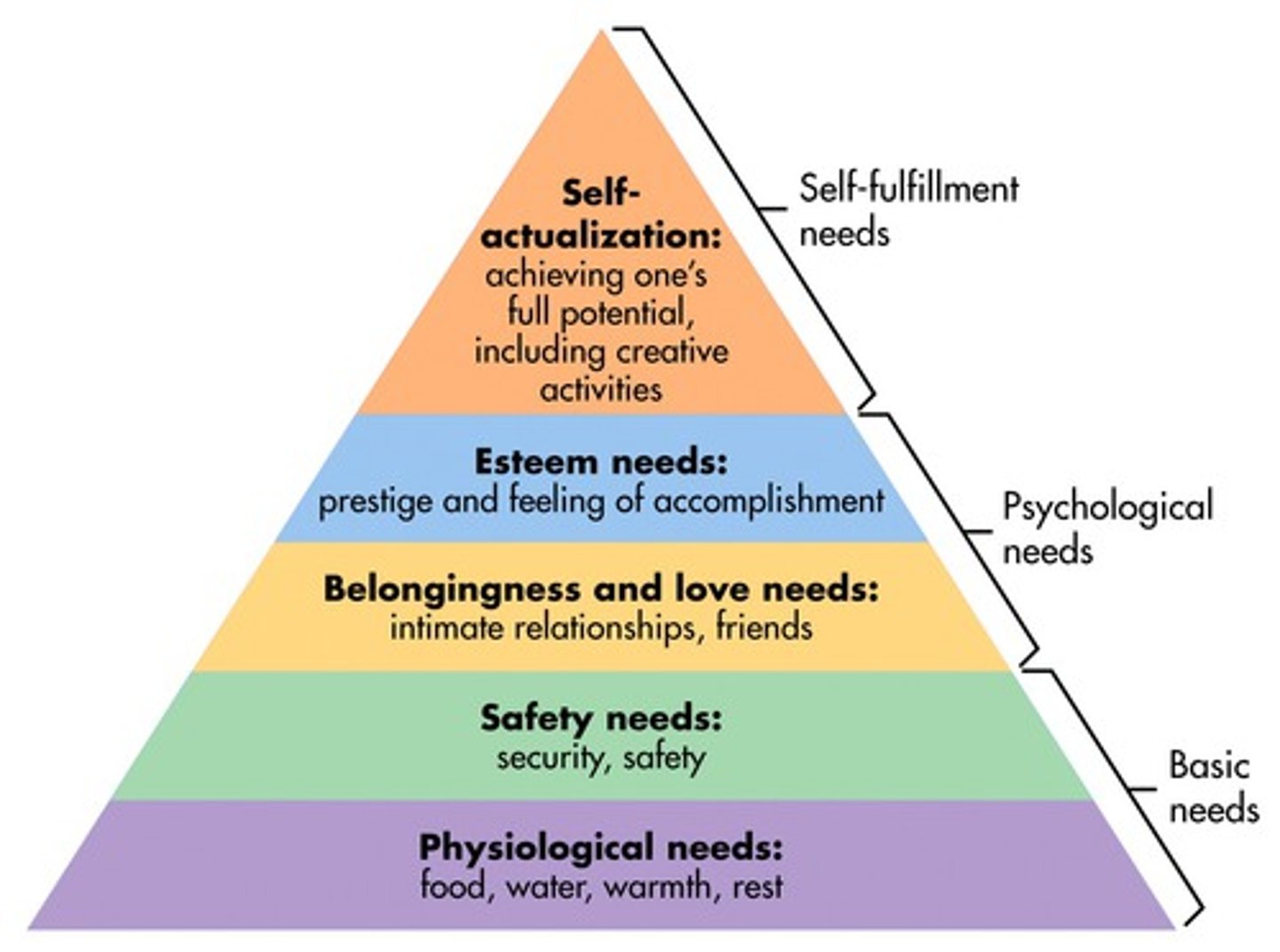
self-actualism
living up to your fullest, most unique potential

glucose
form of sugar- major source of energy for body tissues
(low levels=hunger)

lateral hypothalamus
brings on hunger
stimulate= animal will begin to eat
lesion= animal will have no interest in food

ventromedial hypothalamus
depresses hunger
stimulate= animal will stop eating
lesion=animal will continuously want to eat

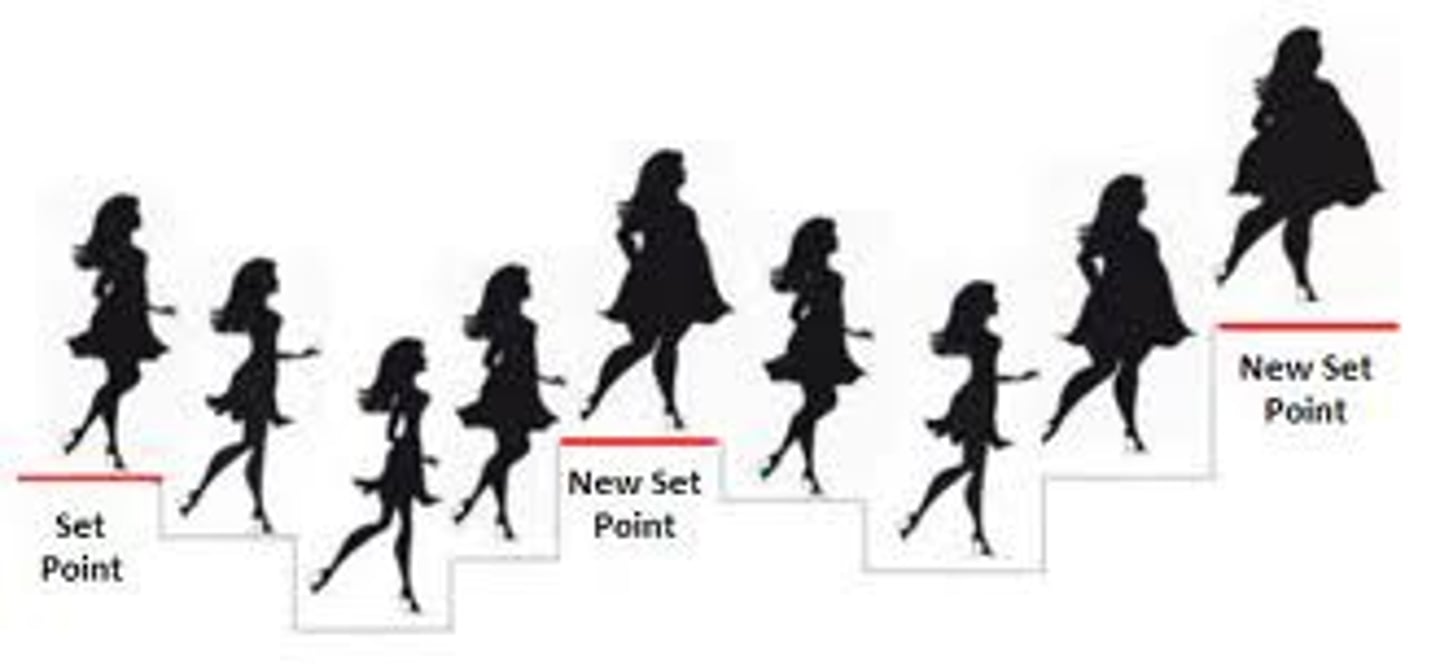
set point theory
hypothalamus= "thermostar" general stable weight
body below weight -> increased hunger, lower metabolism
basal metabolic rate
body's resting rate of energy expenditure
William Masters & Virginia Johnson
sexual response cycle (4 stages)

excitement stage
body is preparing for sex
plateau phase
excitement peaks (breathing quickens, pulse rises, blood pressure rises)
orgasm
muscle contractions
sympathetic nervous system triggered
helps facilitate conception
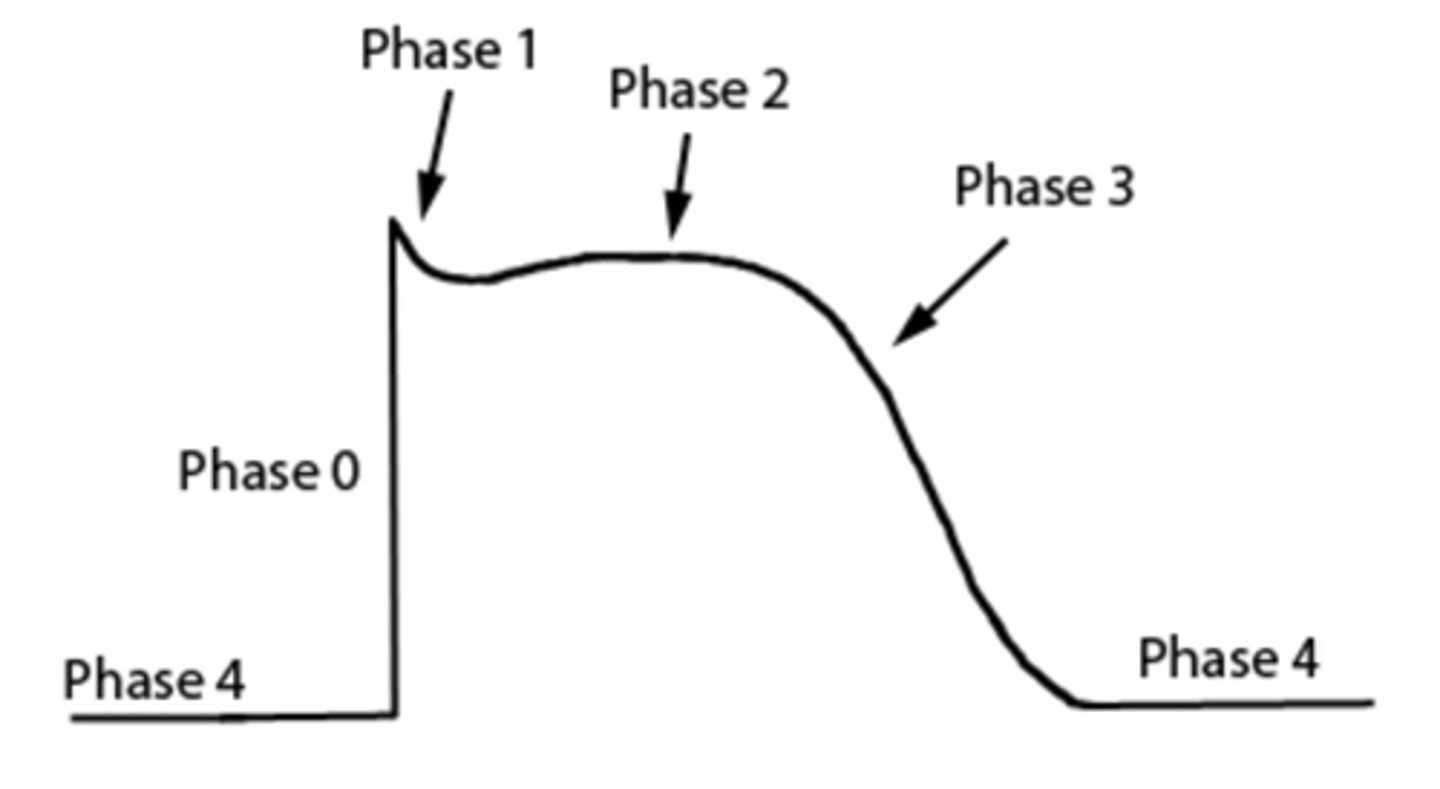
resolution phase
body returns to unaroused state
parasympathetic nervous system
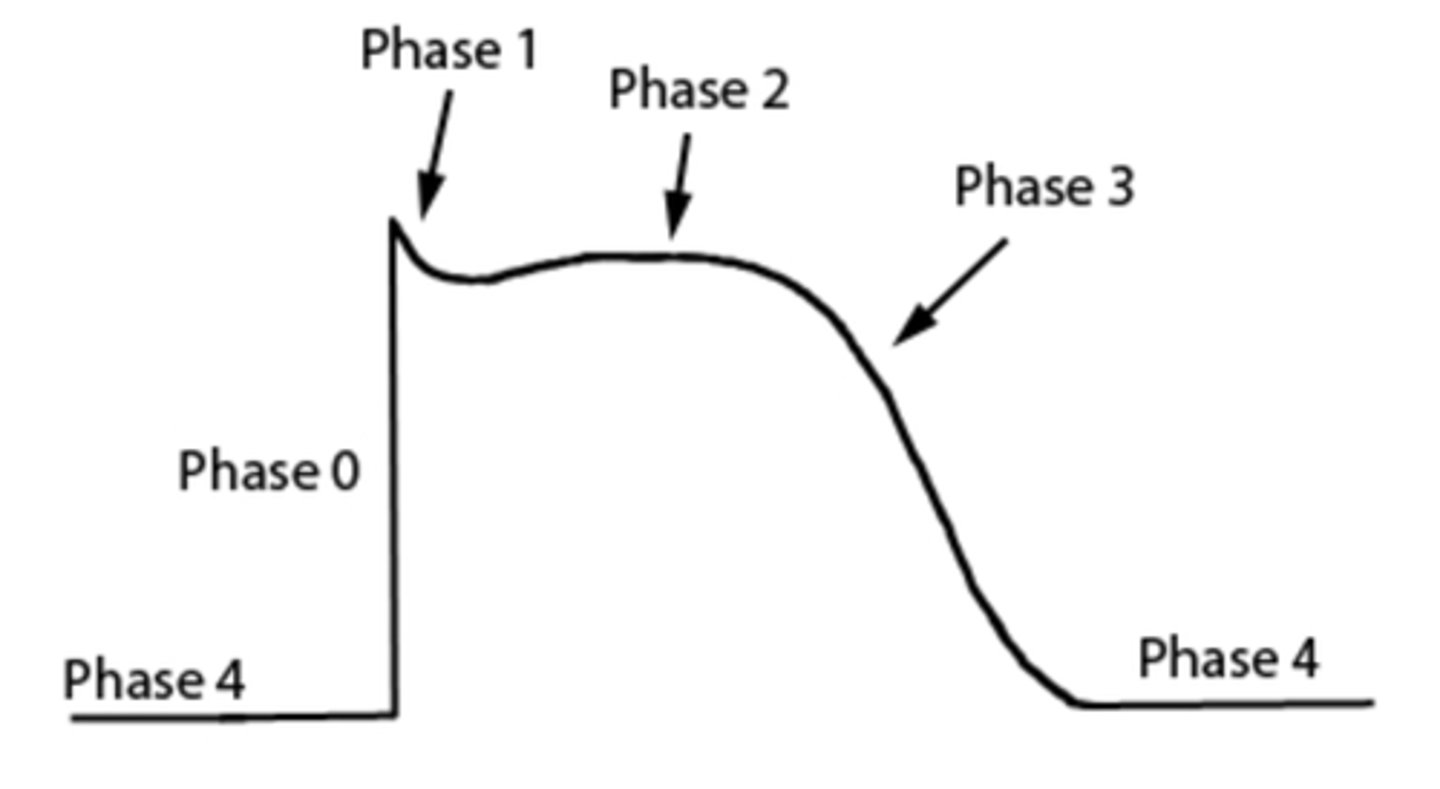
refractory period
(only in men) resting period after orgasm, during which he cannot achieve another orgasm
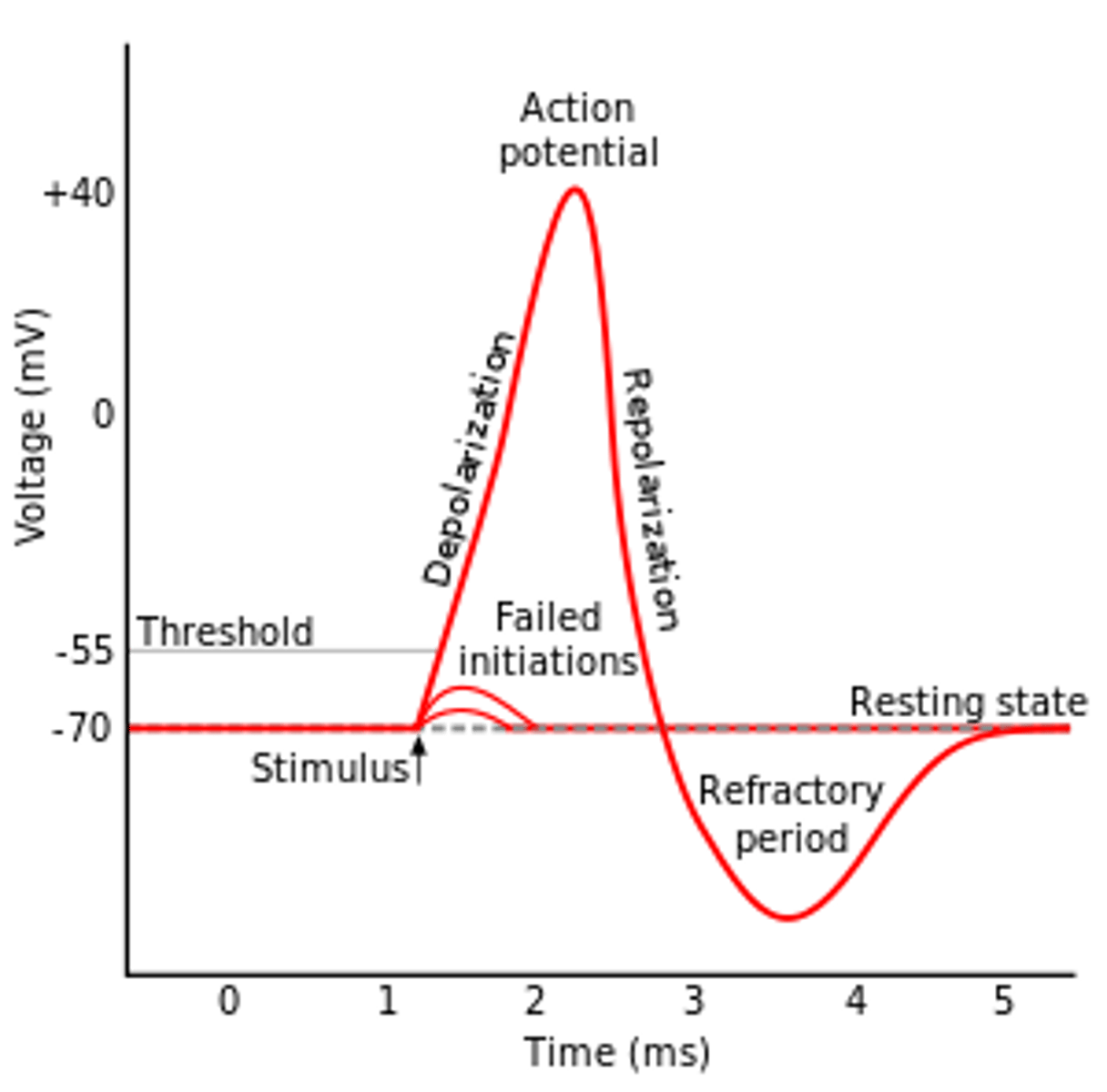
testosterone
constant in males
activates sexual behavior
stimulate growth of male sex organs in the fetus and sex characteristic during puberty

estrogen
contributes to female sex characteristics
levels peak during ovulation
