IT-341 Module-12 Chapter-16 (Cisco)
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
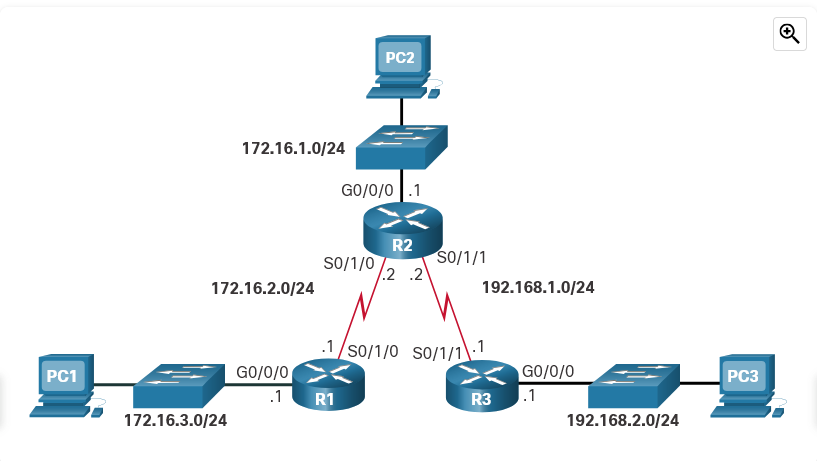
Refer to the exhibit. True or False? R1 must encapsulate received packets into new frames before forwarding them to R2.
True
False
True
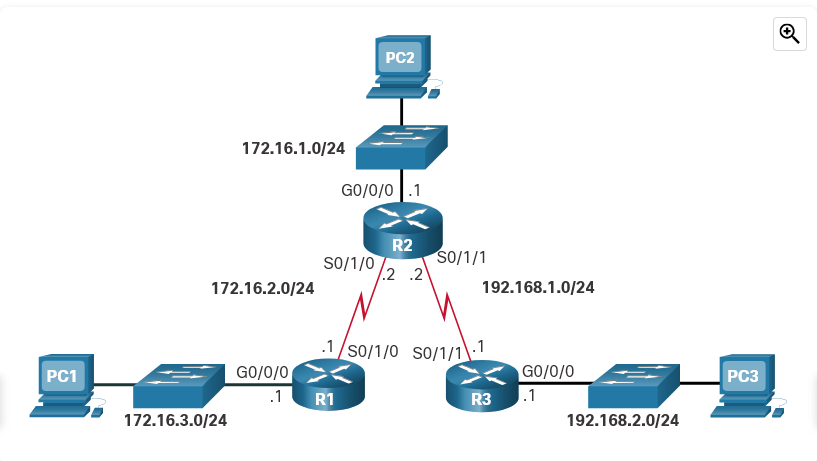
Refer to the exhibit. True or False? R2 will forward frames to R3 with an all 1s Layer 2 address.
True
False
True
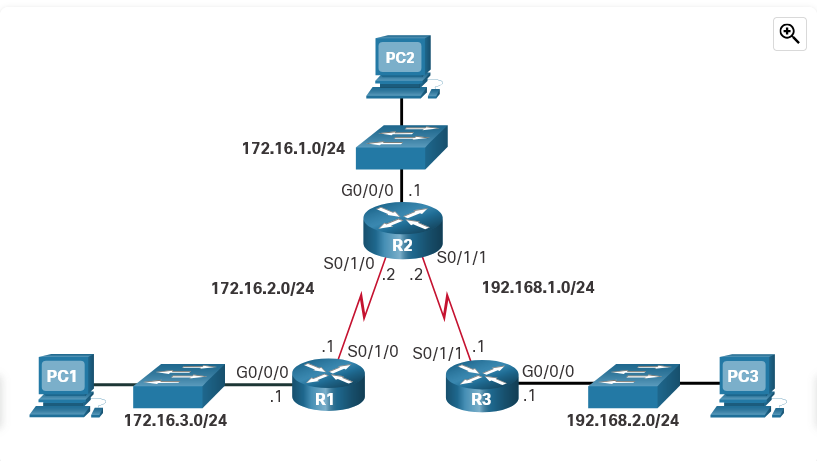
Refer to the exhibit. What action will R3 take to forward a frame if it does not have an entry in the ARP table to resolve a destination MAC address?
a. Sends a DNS request
b. Drops the frame
c. Sends an ARP request
d. Sends frame to the default gateway
c. Sends an ARP request
Which sequence correctly identifies the order of the steps that a router will perform when it receives a packet on an Ethernet interface?
a.
1. The router examines the destination IP address.
2. The router examines the destination MAC address.
3. The router identifies the Ethernet Type field.
4. The router de-encapsulates the Ethernet frame.
b.
1. The router examines the destination MAC address.
2. The router identifies the Ethernet Type field.
3. The router de-encapsulates the Ethernet frame.
4. The router examines the destination IP address.
c.
1. The router examines the destination IP address.
2. The router examines the destination MAC address.
3. The router de-encapsulates the Ethernet frame.
4. The router identifies the Ethernet Type field.
d.
1. The router de-encapsulates the Ethernet frame.
2. The router examines the destination MAC address.
3. The router identifies the Ethernet Type field.
4. The router examines the destination IP address.
e.
1. The router examines the destination MAC address.
2. The router identifies the Ethernet Type field.
3. The router examines the destination IP address.
4. The router de-encapsulates the Ethernet frame.
b.
1. The router examines the destination MAC address.
2. The router identifies the Ethernet Type field.
3. The router de-encapsulates the Ethernet frame.
4. The router examines the destination IP address.
Which three IOS troubleshooting commands can help to isolate problems with a static route? (Choose three.)
a. show version
b. ping
c. tracert
d. show ip route
e. show ip interface brief
f. show arp
b. ping
d. show ip route
e. show ip interface brief
A network administrator has entered a static route to an Ethernet LAN that is connected to an adjacent router. However, the route is not shown in the routing table. Which command would the administrator use to verify that the exit interface is up?
a. show ip interface brief
b. show ip protocols
c. show ip route
d. tracert
a. show ip interface brief
A static route has been configured on a router. However, the destination network no longer exists. What should an administrator do to remove the static route from the routing table?
a. Change the routing metric for that route.
b. Nothing. The static route will go away on its own
c. Change the administrative distance for that route.
d. Remove the route using the no ip route command.
d. Remove the route using the no ip route command.
Which statement describes the sequence of processes executed by a router when it receives a packet from a host to be delivered to a host on another network?
a. It receives the packet and forwards it directly to the destination host.
b. It de-encapsulates the packet, selects the appropriate path, and encapsulates the packet to forward it toward the destination host.
c. It de-encapsulates the packet and forwards it toward the destination host.
d. It selects the path and forwards it toward the destination host.
b. It de-encapsulates the packet, selects the appropriate path, and encapsulates the packet to forward it toward the destination host.
A network engineer issues the show cdp neighbor command on several network devices during the process of network documentation. What is the purpose of performing this command?
a. To obtain information about directly connected Cisco devices
b. To check the networks that are advertised by the neighboring routers
c. To verify the network addresses that are attached to the network devices
d. To check the connectivity of PCs that are connected to the network devices
a. To obtain information about directly connected Cisco devices
A network administrator notices that a correctly entered static route is not in the routing table. What two router commands would an administrator use to determine if the exit interface was up and the next hop address is available? (Choose two.)
a. ping
b. show ip protocols
c. show ip interface brief
d. show ip route
e. tracert
a. ping
c. show ip interface brief
A network administrator has entered the following command:
ip route 192.168.10.64 255.255.255.192 serial0/0/1
When the network administrator enters the command show ip route, the route is not in the routing table. What should the administrator do next?
a. Re-enter the command using the correct mask.
b. Verify that the serial 0/0/1 interface is active and available.
c. Verify that the 192.168.10.64 network is active within the network infrastructure.
d. Re-enter the command using a network number rather than a usable IP address.
b. Verify that the serial 0/0/1 interface is active and available.
What will a router do if it does not have a default route configured and a packet needs to be forwarded to a destination network that is not listed in the routing table?
a. Forward it to another router
b. Drop it
c. Send it back to the source
b. Drop it
What does the letter C mean next to an entry in the output of the show ip route command?
a. It identifies a network that is a static route.
b. It identifies a network that is learned through OSPF.
c. It identifies a network that is learned through EIGRP.
d. It identifies a network that is directly connected to the router.
d. It identifies a network that is directly connected to the router.