MRI
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
MRI stands for...
magnetic resonance imaging
MRIs use _______ to create images.
radiofrequency waves applied to a strong magnetic field
do MRIs use ionizing radiation?
no, they use radiofrequency waves + magnetic field
what is completely contraindicated in an MRI?
any metal within the animal (even a microchip)
how does an MRI work?
strong magnets line up the hydrogen atoms in the animal's body, and then we send radiofrequency waves and deactivate the magnet to release the energy from the atoms. this energy creates the image
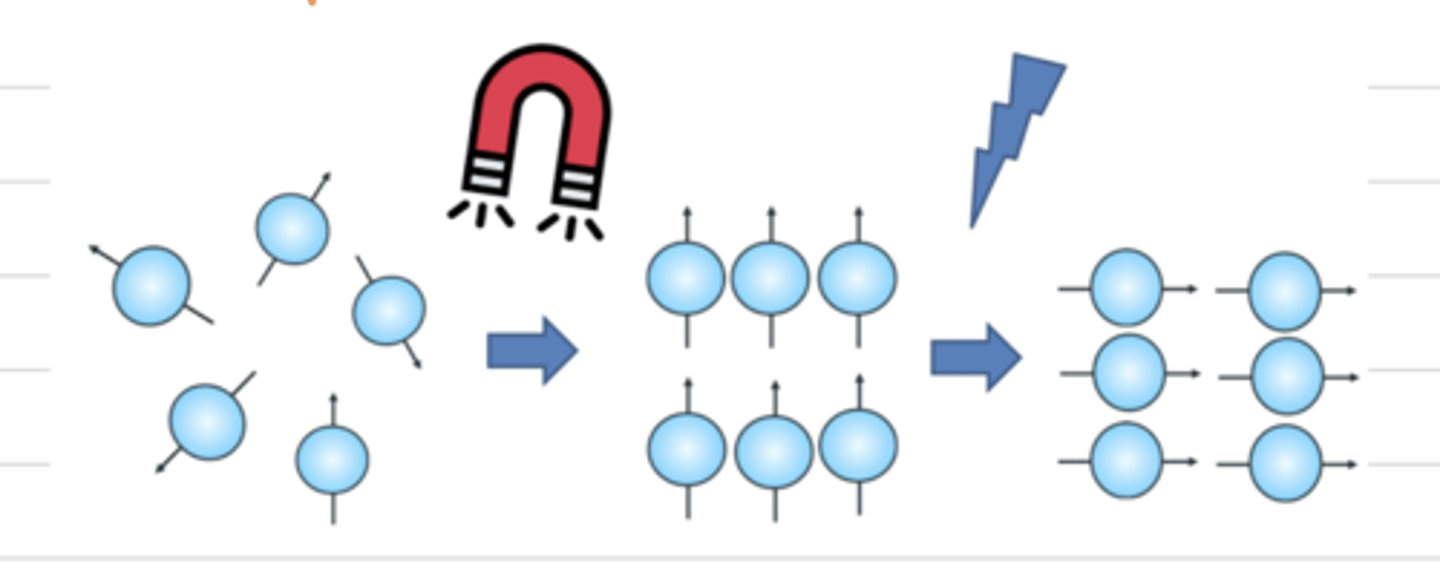
what is the difference between a low field and high field MRI?
low: open power of less than 1 T
high: power of more than 1 T
what is the difference between T1 and T2?
T1: used to see normal anatomy, white matter is light and grey matter is dark grey, liquid is dark
T2: used to see abnormal structures, white matter is dark grey and grey matter is light, liquid is bright
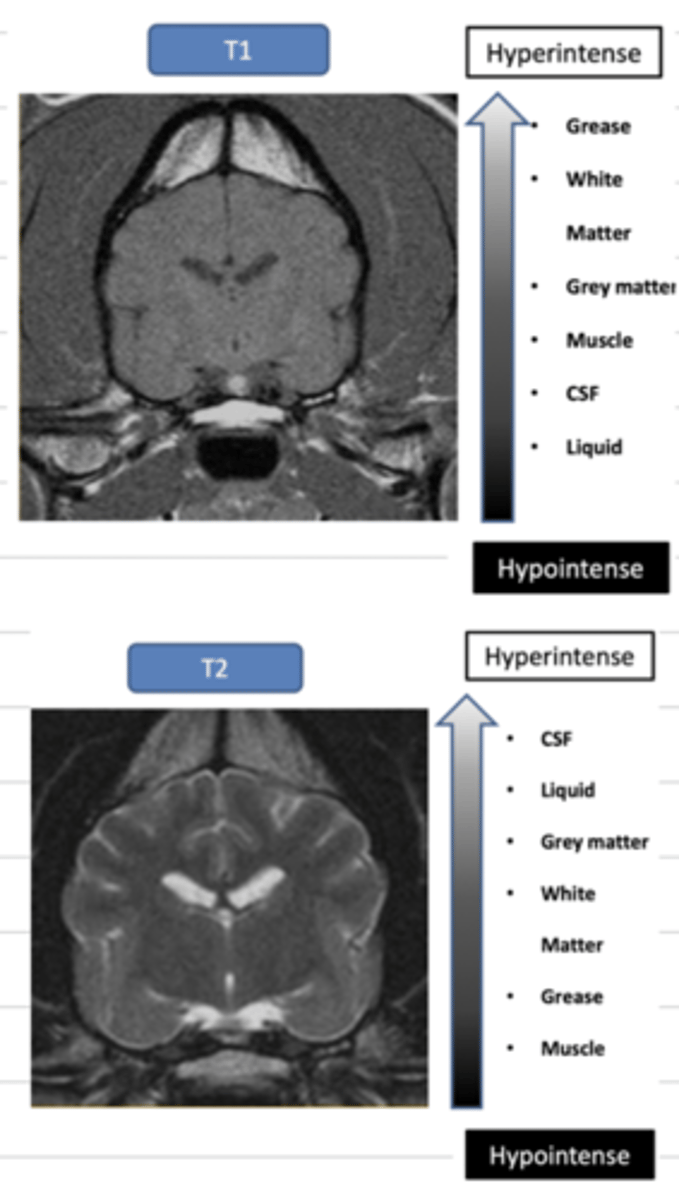
with which- T1 or T2- is contrast used?
T1
with which- T1 or T2- is white matter dark grey and grey matter is white?
T2
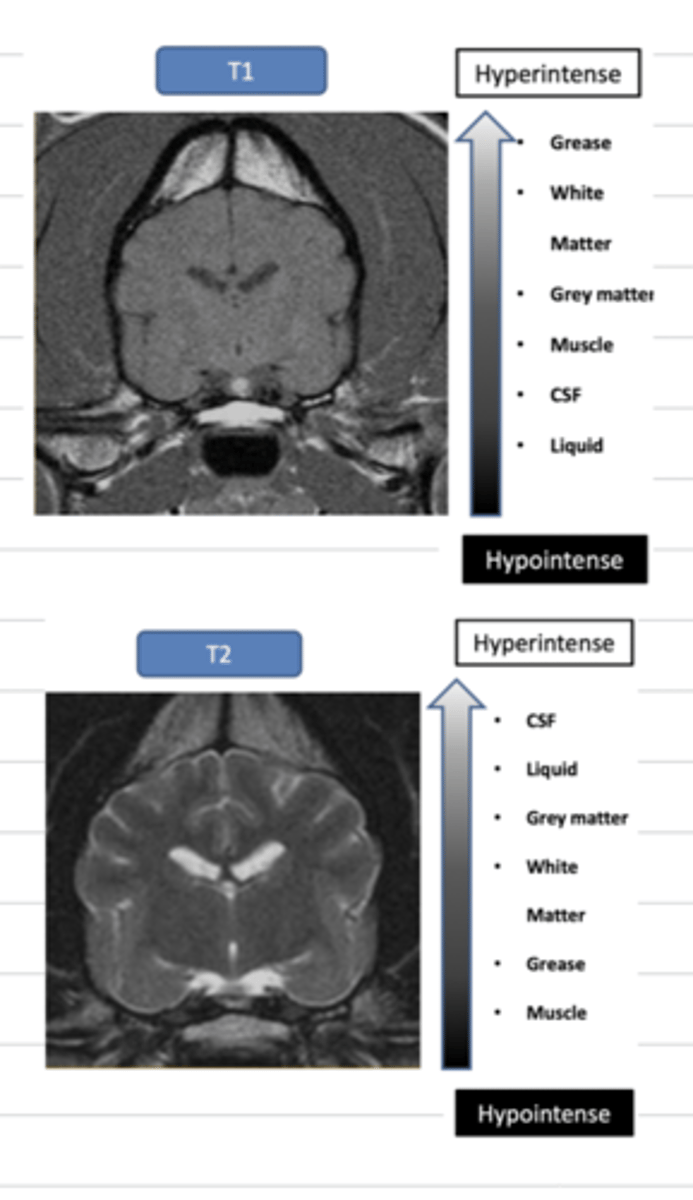
what is gadolinium?
a paramagnetic contrast used with T1
MRIs are best for what type of tissue?
soft tissue
(brain, spinal cord, ligaments, tendons)
what are the advantages and disadvantages of MRI?
advantages: no radiation used (staff can be in the room, and there are no biological effects), non invasive, no overlapping, high resolution
disadvantages: no metal, needs anesthesia, very expensive, takes a long time