3.4 Final accounts
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Final Accounts
keeps track of all the money in a business, whether it comes from owners, investors, or lenders. Final accounts make sure that every payment and receipt is properly recorded.
Since companies (especially those owned by shareholders) are required to provide these accounts, they prepare two main financial statements:
Profit and Loss Account – Shows how much money the business earned (revenue) and spent (expenses), and whether it made a profit or a loss.
Balance Sheet – Shows what the business owns (assets), what it owes (liabilities), and the total value of the company.
These accounts help businesses, investors, and lenders understand the company’s financial situation.
Purpose of Final Accounts (FA)
In some countries it is a legal requirment
purpose of FA to shareholders
they can asses business’s financial performance
purpose of FA to employees
assess the likelihood of pay increments and the degree of job security
purpose of FA to managers
target setting and strategic planning.
purpose of FA to competitors
make comparisons and make changes based on that
purpose of FA to goverment
ensure that they pay the correct amount of tax
purpose of FA to financers
they must know org.’s financial position before approving any funds
purpose of FA to suppliers
to decide the extent to which they will give trade credit
purpose of FA to potential investors
to assess whether an investment would be financially worthwhile.

ethics of accounting
ACCA regulates this
acca’s 5 code of ethics and conduct (picop)
professional behavior, integrity, confidentiality, objectivity, professional competence.
profit and loss account
•Also known as Income Statement
•P&L is a financial statement of a firm’s trading activities over a period of time, usually one year.
•Main purpose is to show the profit or loss of a business during a particular trading period.
•There are 3 sections of an income statement:
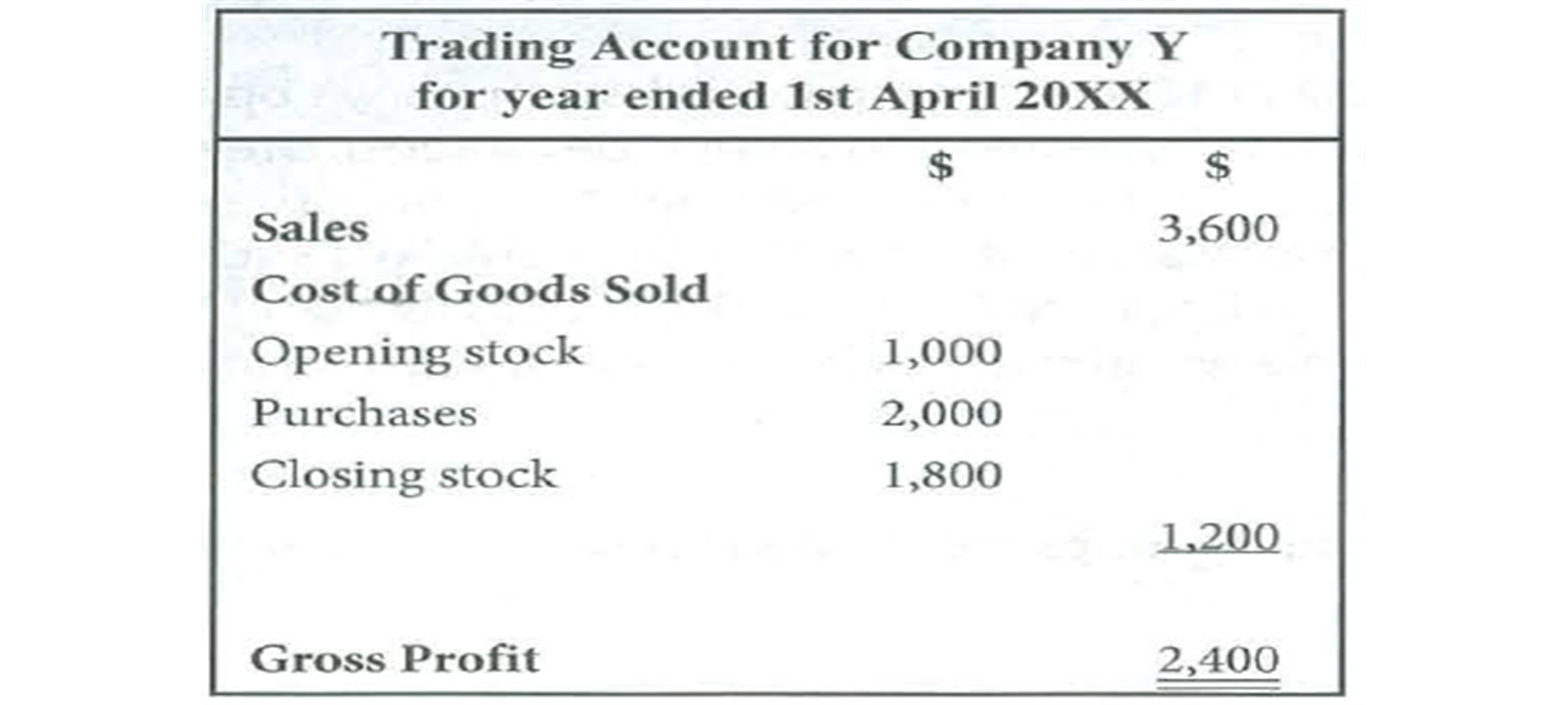
•The trading account
•The profit and loss account
•The appropriation account
gross profit
= sales revenue - cost of goods sold→ accountants term for the direct costs of the goods that are actually sold such as raw material costs
cost of goods sold
=opening stock + purchases - closing stock
ways to improve gross profit
use cheaper supplies: this reduces COGS and likely the quality as well.
increase selling price
promotion etc
p&l account
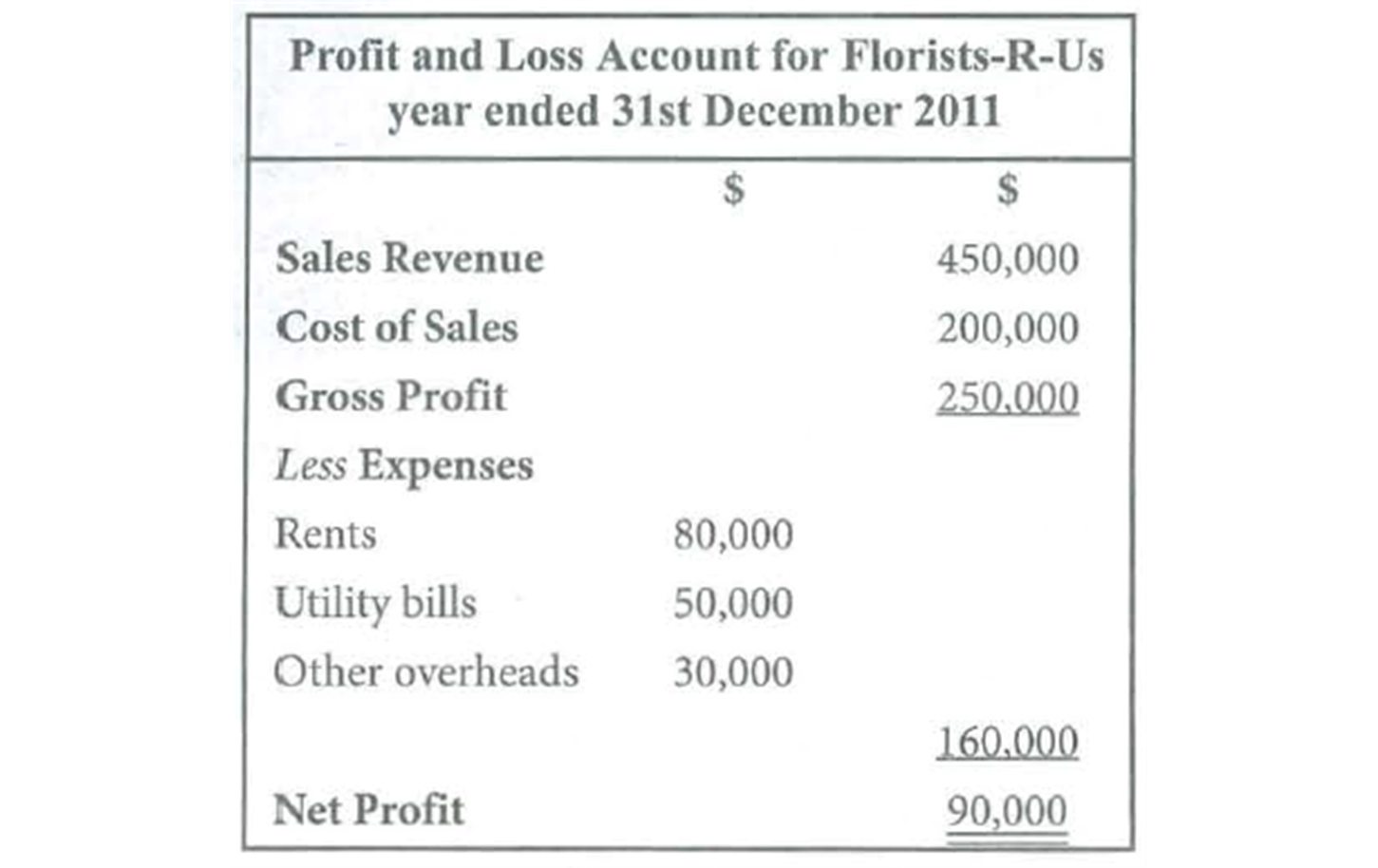
trade account
p&l shows
shows net profit or loss in certain period of time
Appropriation Account
•Final section of the P&L account
•2 parts:
•Dividends
•Retained profit
DIVIDENDS
•This shows the amount of net profit after interest and tax that is distributed to the owners (shareholders) of the company.
RETAINED PROFIT
This shows how much of the net profit after interest and tax is kept by the business for its own use, such as investing it in the company or to expand the business.
Limitations to the P&L account
•P&L shows historical performance of a business. There is no guarantee that future performance is linked to past performance or success.
•Window dressing can occur (the legal manipulation of FA to make them look financially more attractive. This disguises the underlying financial position of the company.
•As there is no internationally standardized format for producing a P&L account
The Balance Sheet
•Companies are required to produce for auditing purposes
•Contains information on the value of an organization’s assets, liabilities and the capital invested by the owners
•As it shows the financial position of a business on one day only (usually the last day of the accounting year), it is often described as a ‘snapshot’ of a firm’s financial situation.
•Helps ensure that all monies within the organization are properly accounted for
3 Parts of the Balance Sheet:
•Assets
•Items of monetary value that are owned by a business
•Liabilities
•Legal obligation of a business to repay its lenders or suppliers at a later date (amount of money owed by the business)
•Equity (capital and reserves)
•Shows the value of the business belonging to the owners
Formula:
Total Assets – Total Liabilities = Owner’s Equity
asset
•Assets
•Items of monetary value that are owned by a business
•Liabilities
•Legal obligation of a business to repay its lenders or suppliers at a later date (amount of money owed by the business)
•Equity (capital and reserves)
•Shows the value of the business belonging to the owners
Formula:
Total Assets – Total Liabilities = Owner’s Equity
liabilities
•Current Liabilities
•Debts that must be settled within one year of the balance sheet date
•Ex. Taxes owed to the government, dividends to shareholders and bank overdrafts
•Long-term liabilities
•Debts that are due to be repaid after 12 months
•Ex. They are sources of LT borrowing
•Debentures, mortgages and bank loans
EQUITY (Capital and Reserves)
value of the business belonging to the owners. It can appear in 2 ways:
•Shareholder’s Equity
•For limited liability companies
•Owner’s Equity
•Businesses other than limited companies
Two main sections:
•Share Capital
•Refers to the amount of money raised through the sale of shares
•It shows the value when the shares were first sold, rather than the market value
•
•Retained Profit
•Amount of net profit after interest, tax and dividends have been paid
•Reinvested in the business for its own use
•Money belongs to the owners
•The figure comes from the firm’s P&L account
Balance Sheet
•Total assets – Total Liabilities = Equity
•Review Page 261
Limitations of Balance Sheet
•Static documents – financial position of a business may be different in subsequent periods
•Figures are only estimates of the values of assets and liabilities
•Different businesses will produce accounts in varying formats and include different assets and liabilities which makes difficult to compare financial positions of different firms
•Not all assets are included esp. intangible assets and the value of human capital
Intangible Assets
non-physical fixed assets that have the ability to earn revenue for a business
•brand names, goodwill, trademarks, copyrights and patents