AP Bio unit 2
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
UNIT 2
Cell Structure and Function
Organelles to remember
1. plasma membrane
2. cell wall
3. nucleus
4. nuclear envelope
5. chromatin
6. ribosomes
7. smooth endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
8. rough endoplasmic reticulum
9. golgi apparatus
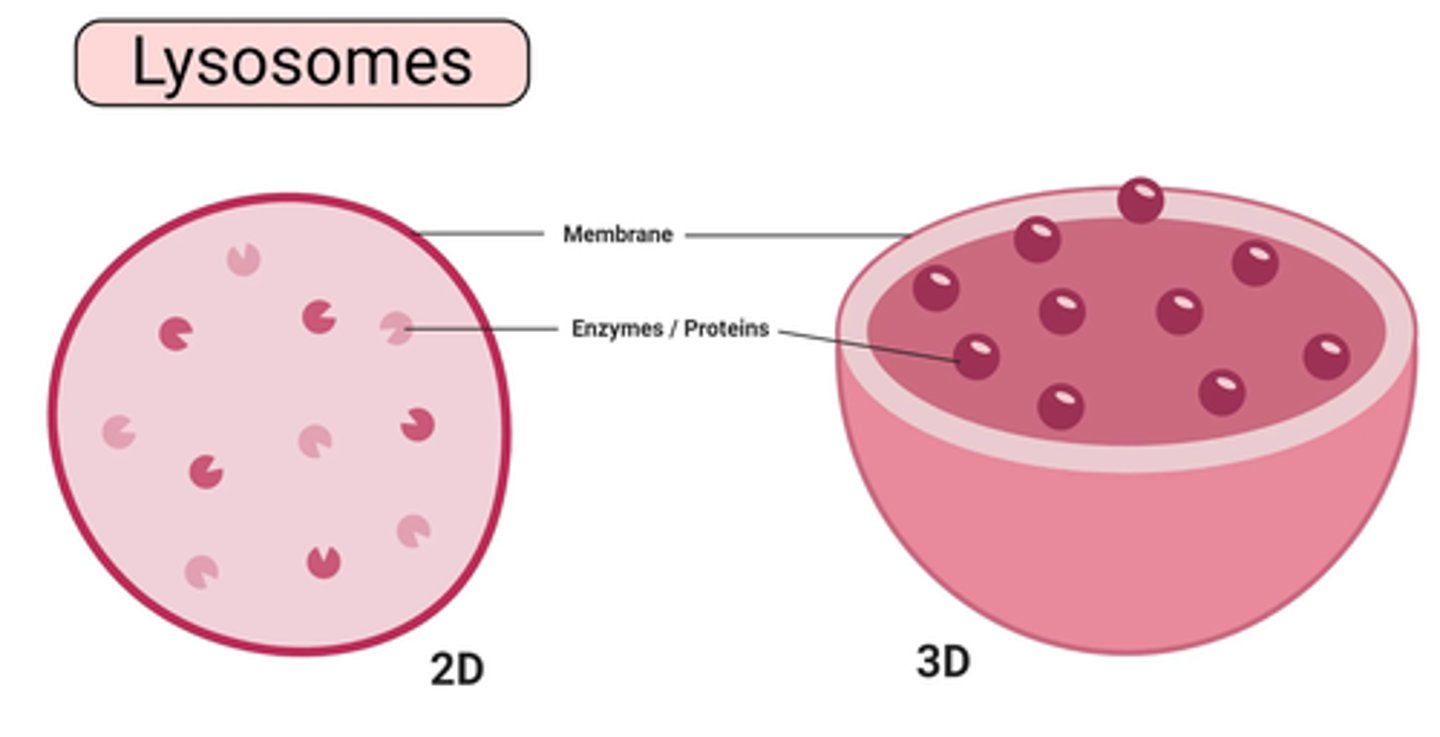
10. lysosomes
11. vacuoles
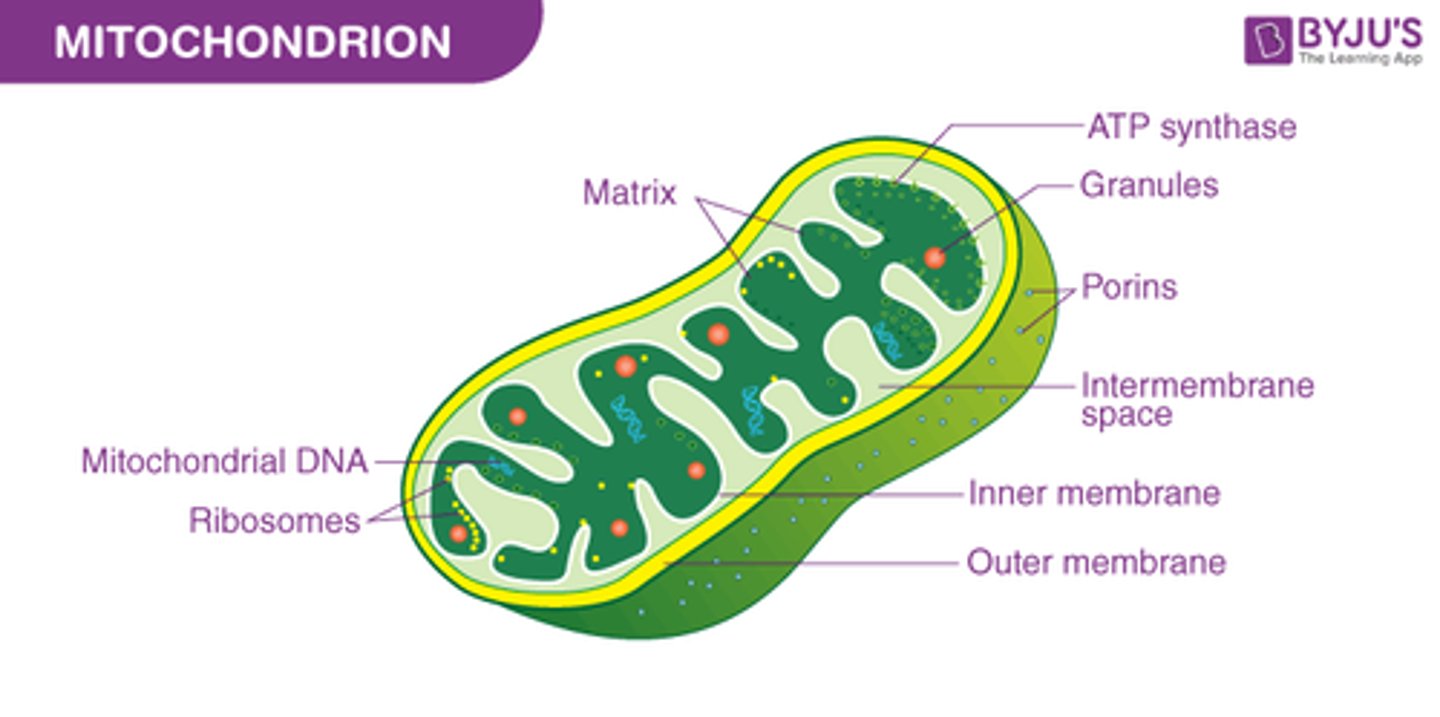
12. mitochondria
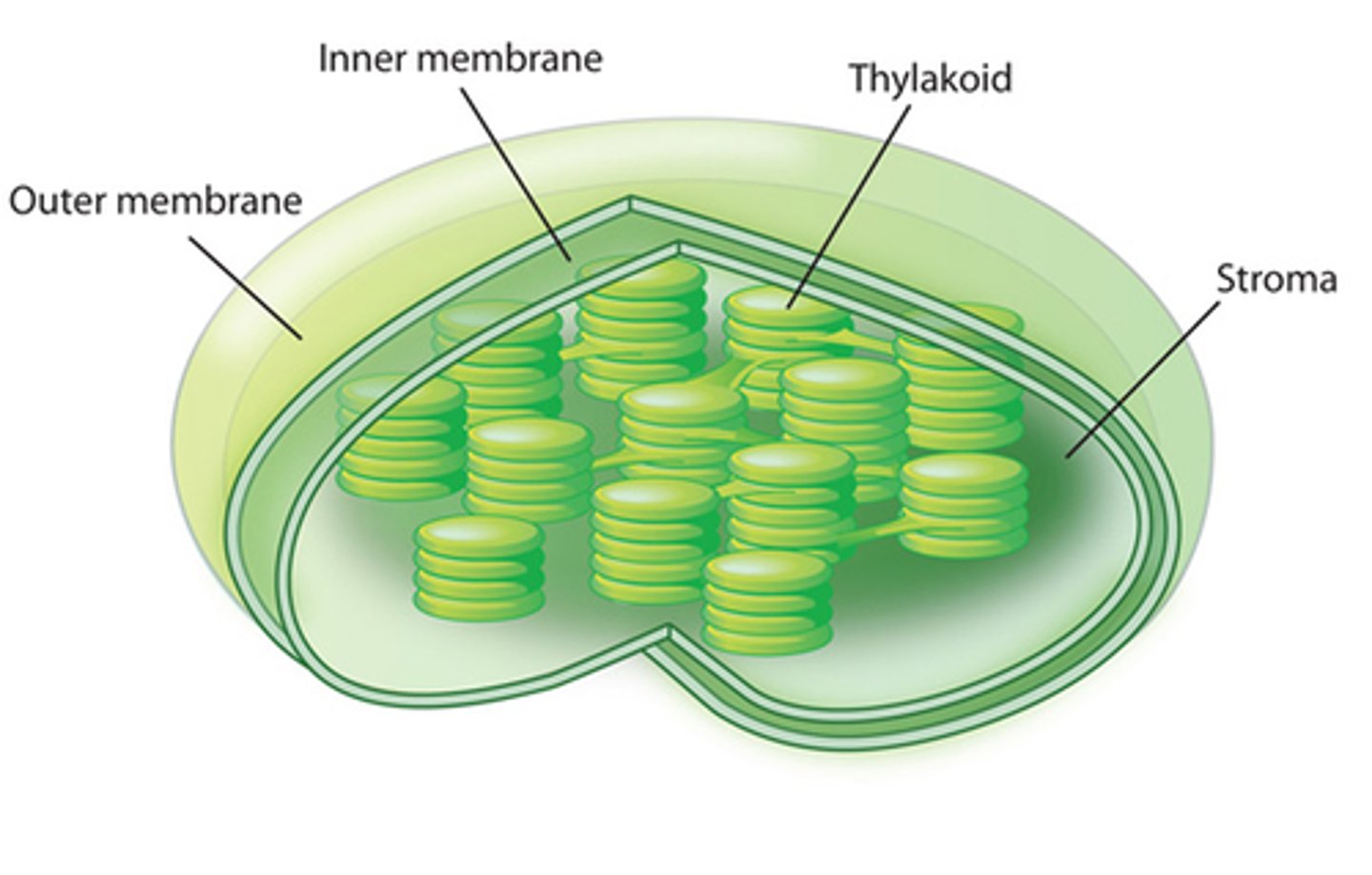
13. chloroplasts
14. peroxisomes
15. cytoskeleton
16. microtubules
17. centrosomes & centrioles
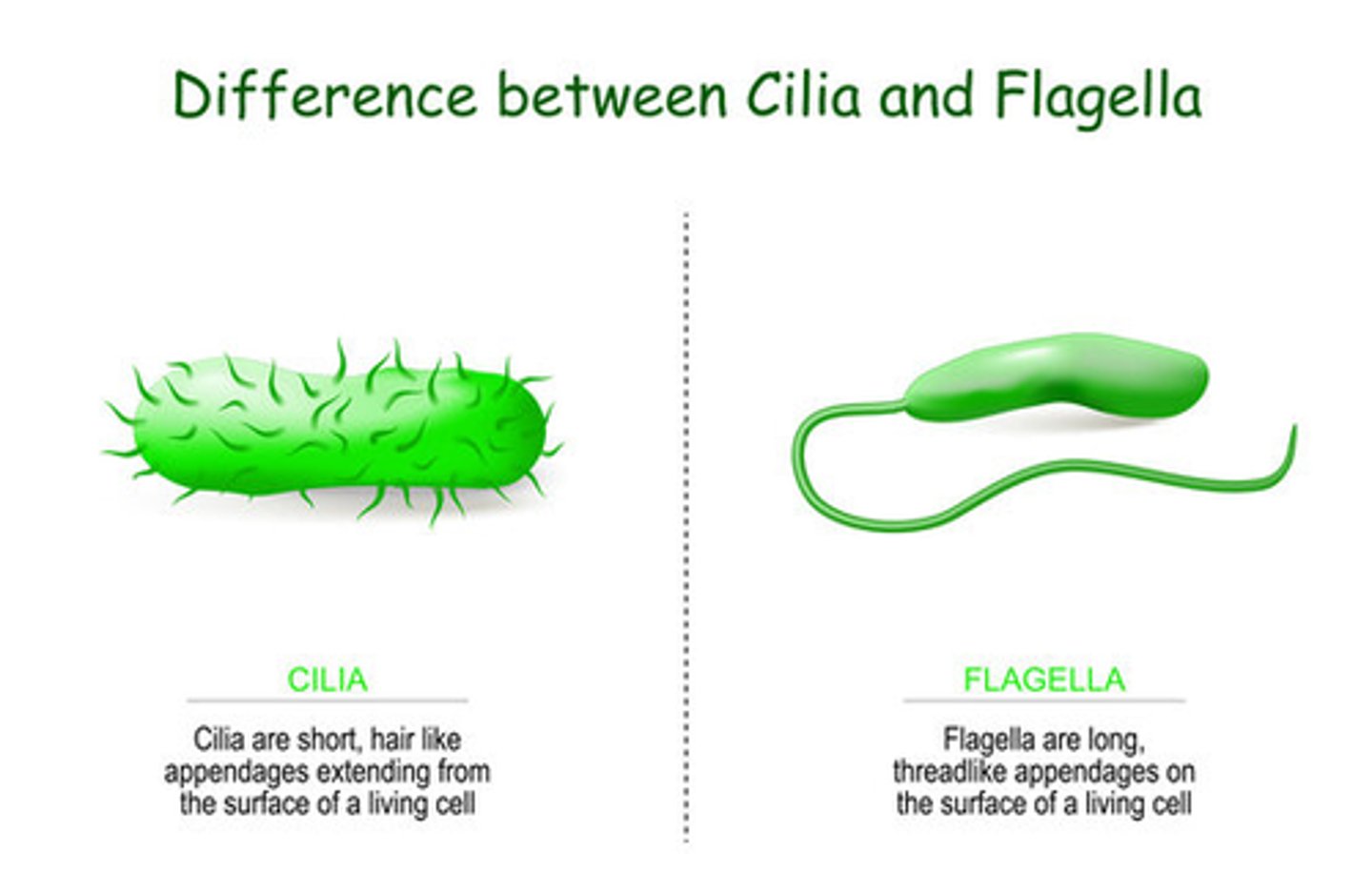
18. Cilia & flagella
19. nucleolus
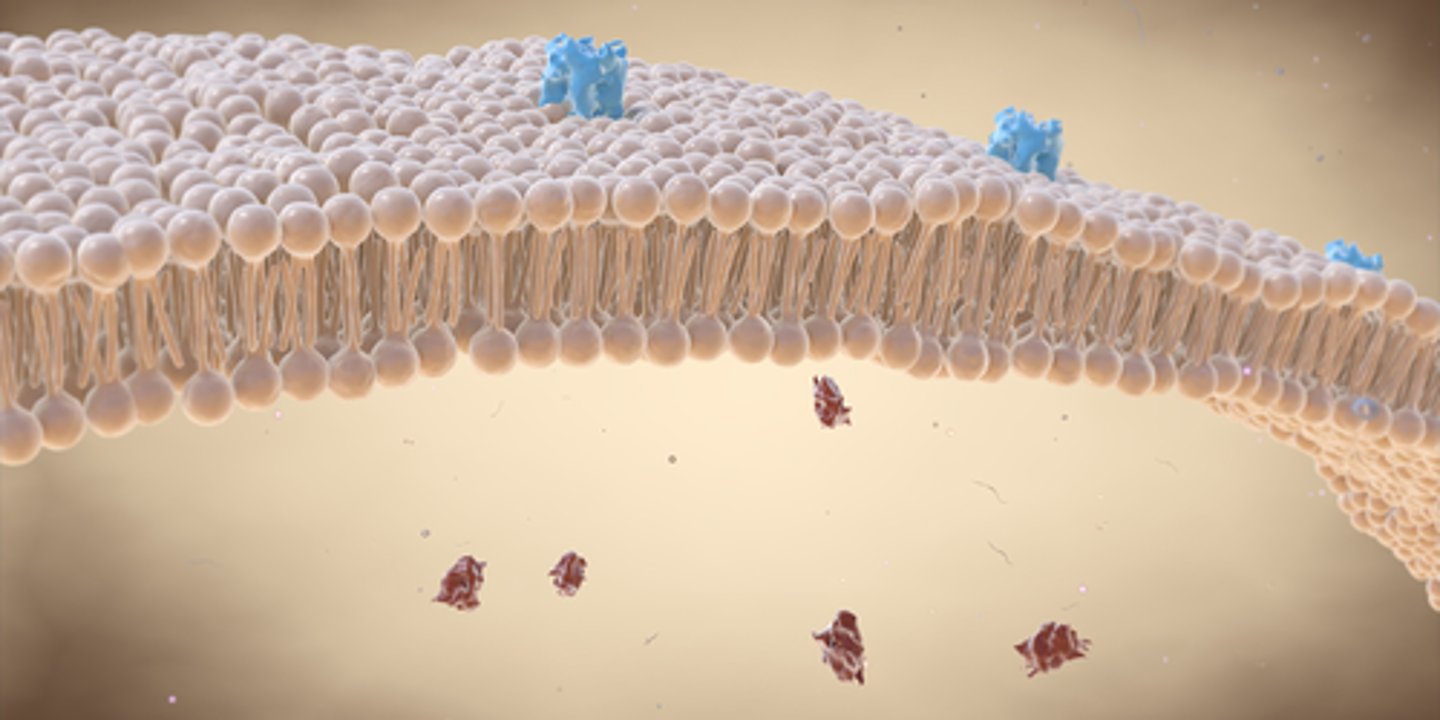
what does the plasma membrane do?
controls what goes in/out of the cell
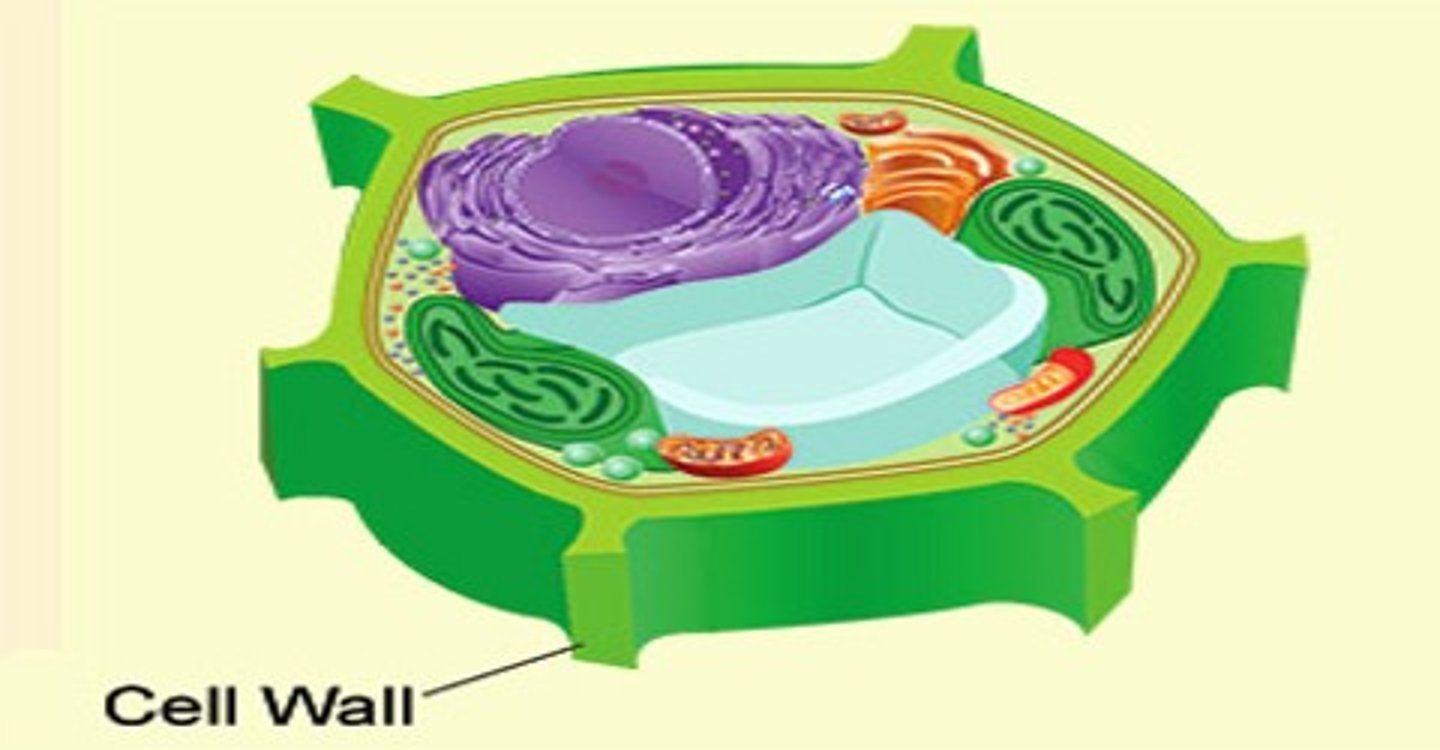
Cell wall (plants)
maintains structure. usually made of cellulose
nucleus
contains DNA
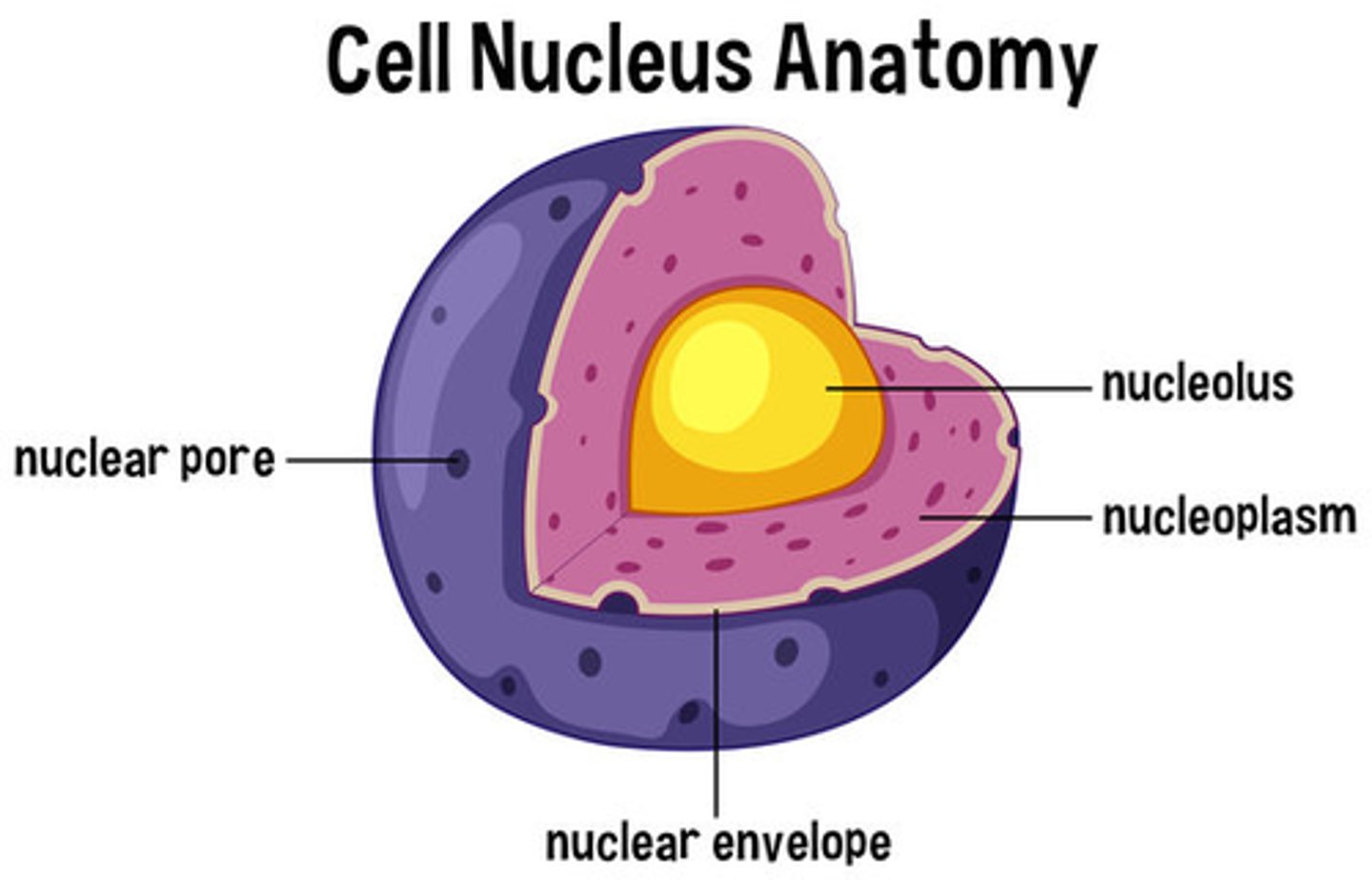
nuclear envelope
surrounds DNA
nucleolus
makes DNA
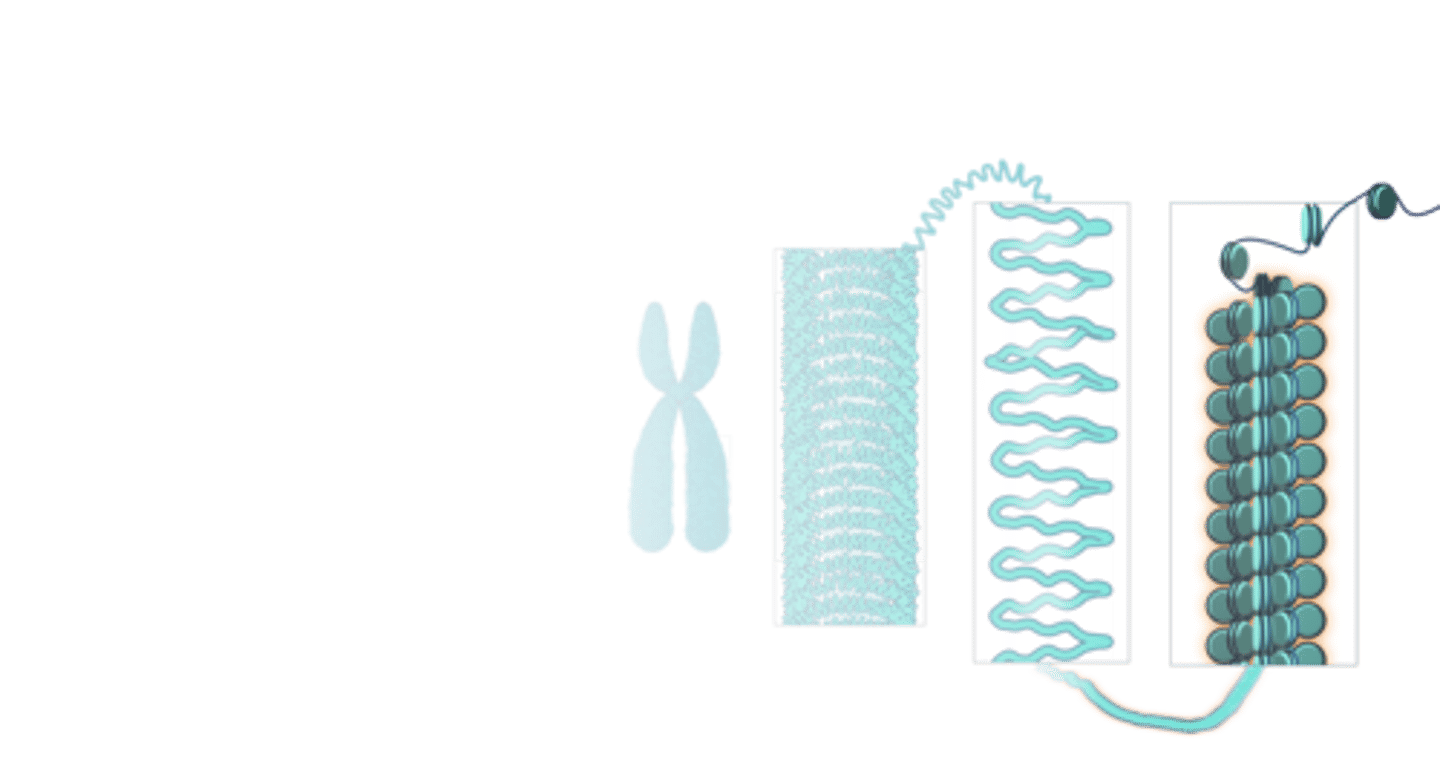
Chromatin
the actual thread of DNA
ribosomes
make protein
Smooth ER
makes lipids
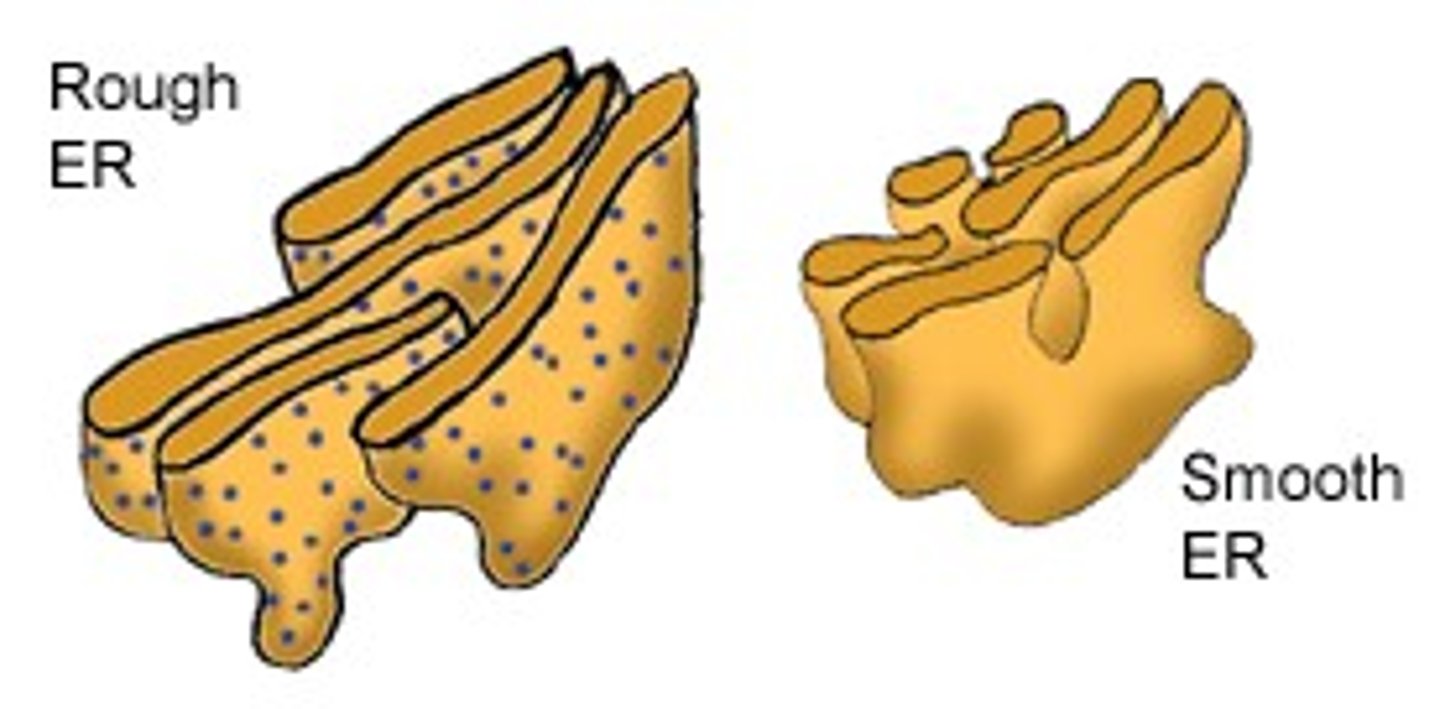
Rough ER
folds proteins
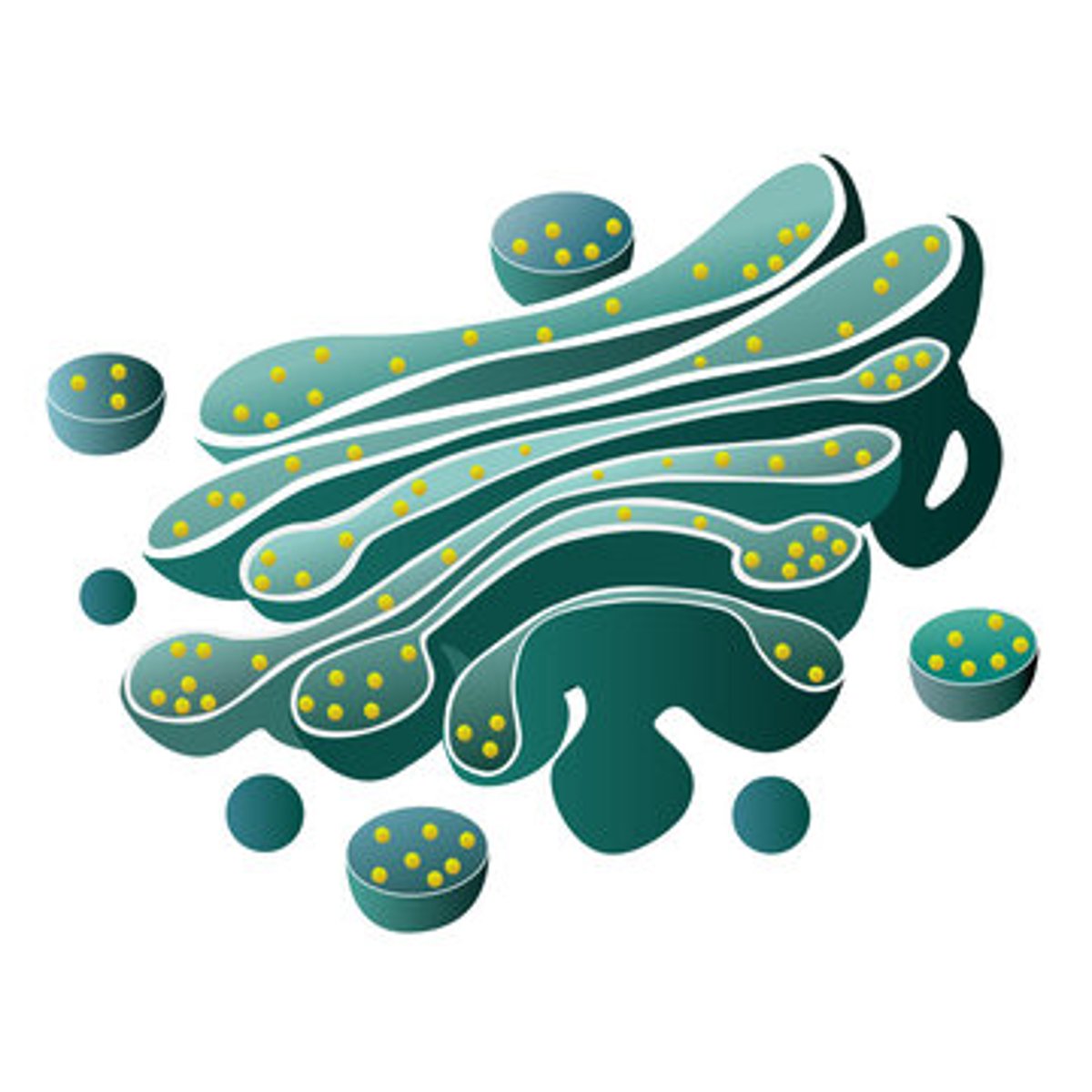
golgi apparatus
packages and transports materials (typically proteins)

lysosomes
splits things apart/breaks things down
vacuoles
storage (ex: stores water in plants)
mitochondria
makes ATP (energy currency) by breaking down glucose
chloroplasts
makes sugar, they're only in plants
peroxisomes
detoxify alcahol
cytoskeleton
internal structure
microtubules
smaller component of cytoskeleton
centrosomes
helps with cell division (mitosis/meiosis)
cilia/flagella
movement of cell
What is the process in which energy is made in the mitochondria?
cellular respiration
What are the steps of cellular respiration?
1. Glycolysis: glucose is broken down in the cytoplasm
2. Krebs cycle: more detail later
3. electron transport chain: more later
4.Formula: C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2 --> 6CO2 +6H2O
Energy = ATP
What is the process in which chloroplasts capture light to make sugars?
photosynthesis
What are the two phases of photosynthesis?
1. light dependent reactions. (electron transport chain)
2. Light independent reactions (Calvin cycle)
3. Formula: 6CO2 + 6H2O --> C6H12O6 + 6O2 (opposite of cellular respiration)
The endosymbiotic theory states...
Mitochondria and chloroplasts were once free living bacteria. they were engulfed by another cell and evolved to stay that way.
What organelles are involved in making proteins?
1. Nucleus: DNA --> RNA
2. Ribosomes: RNA --> protein
3. Rough ER: Folds proteins (structure/function)
4. golgi apparatus: packages proteins
What are the two types of cells?
1. Prokaryotes: have no organelles except for ribosomes and membrane. smaller
2. Eukaryotes: have organelles
To remember which is which:
Pro rhymes with no (no organelles)
Eu rhymes with do (do have organelles)
How does size relate to the efficiency of a cell?
1. smaller cells have a higher surface area to volume ratio (look up examples if this doesn't make sense)
2. a higher SA:V ratio is better because it is less distance traveled to move things in and out of a cell
3. cells will fold, project, or elongate to increase their SA:V ratio (Ex: o --> 0)
Three things that are usually in the plasma membrane
1. Phospholipids: make up the majority of the cell membrane. A hydrophilic head with two hydrophobic tails.
2. Proteins: channel proteins and receptor proteins exist on/in the plasma membrane. Channel proteins allow big/polar things through that cannot pass through the membrane. Receptor proteins receive signals.
3. Cholesterol (mainly animal cells): A lipid steroid that regulates membrane fluidity, keeps from freezing at low temps, and keeps from melting at high temps.
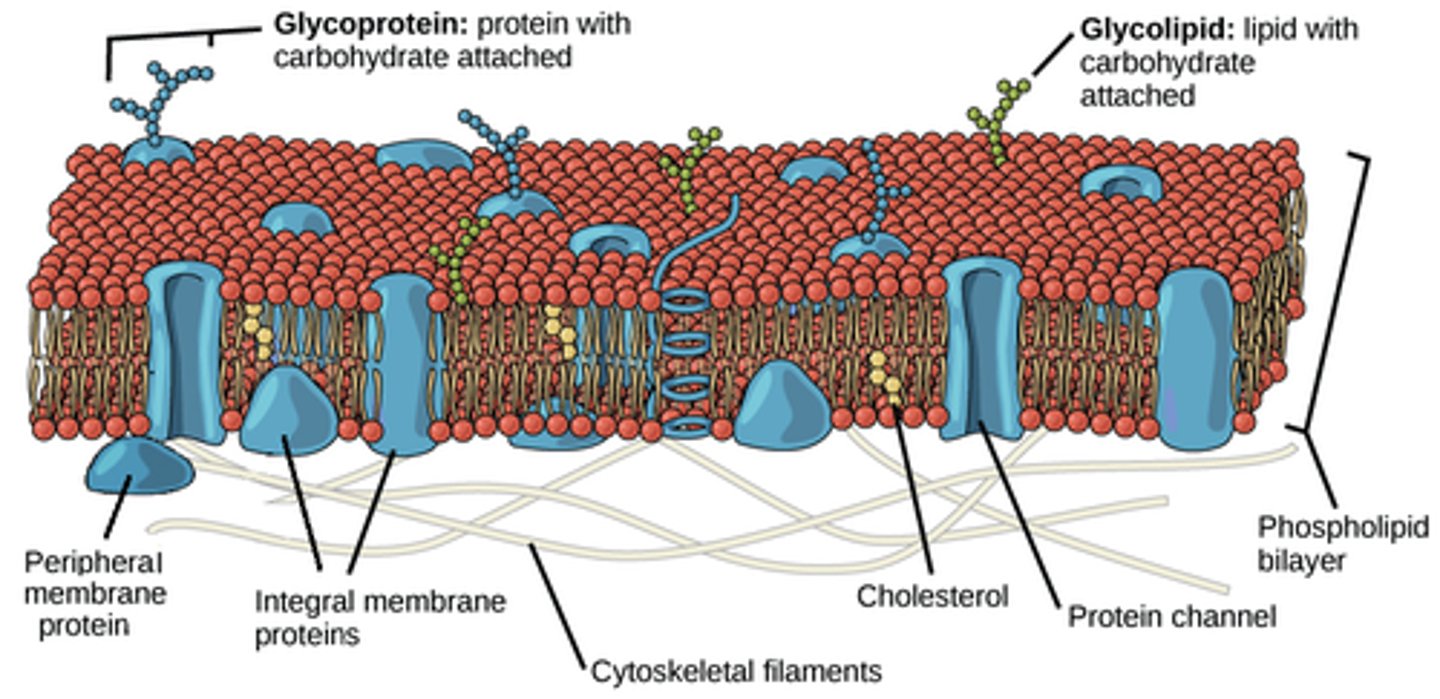
What is selective permeability?
The cell lets some stuff in and keeps other stuff out.
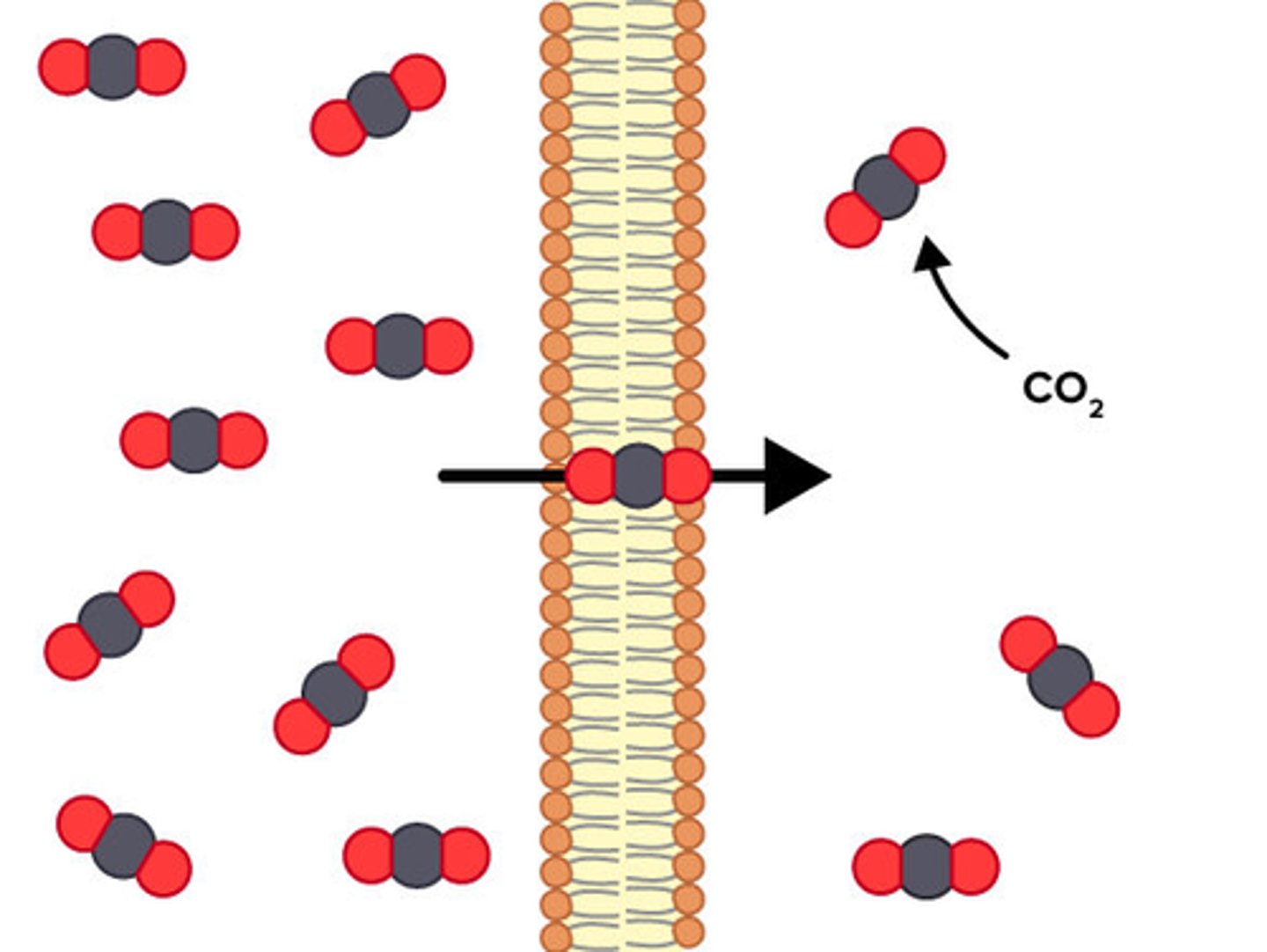
What types of molecules can pass through the phospholipid bilayer of the plasma membrane?
1. Small non-polar molecules (O2, CO2, N2)
2. Small polar uncharged molecules: water
(water cannot efficiently go through the membrane quickly)
If a molecule cannot pass through the bilayer, what is needed?
Channel proteins or carrier proteins
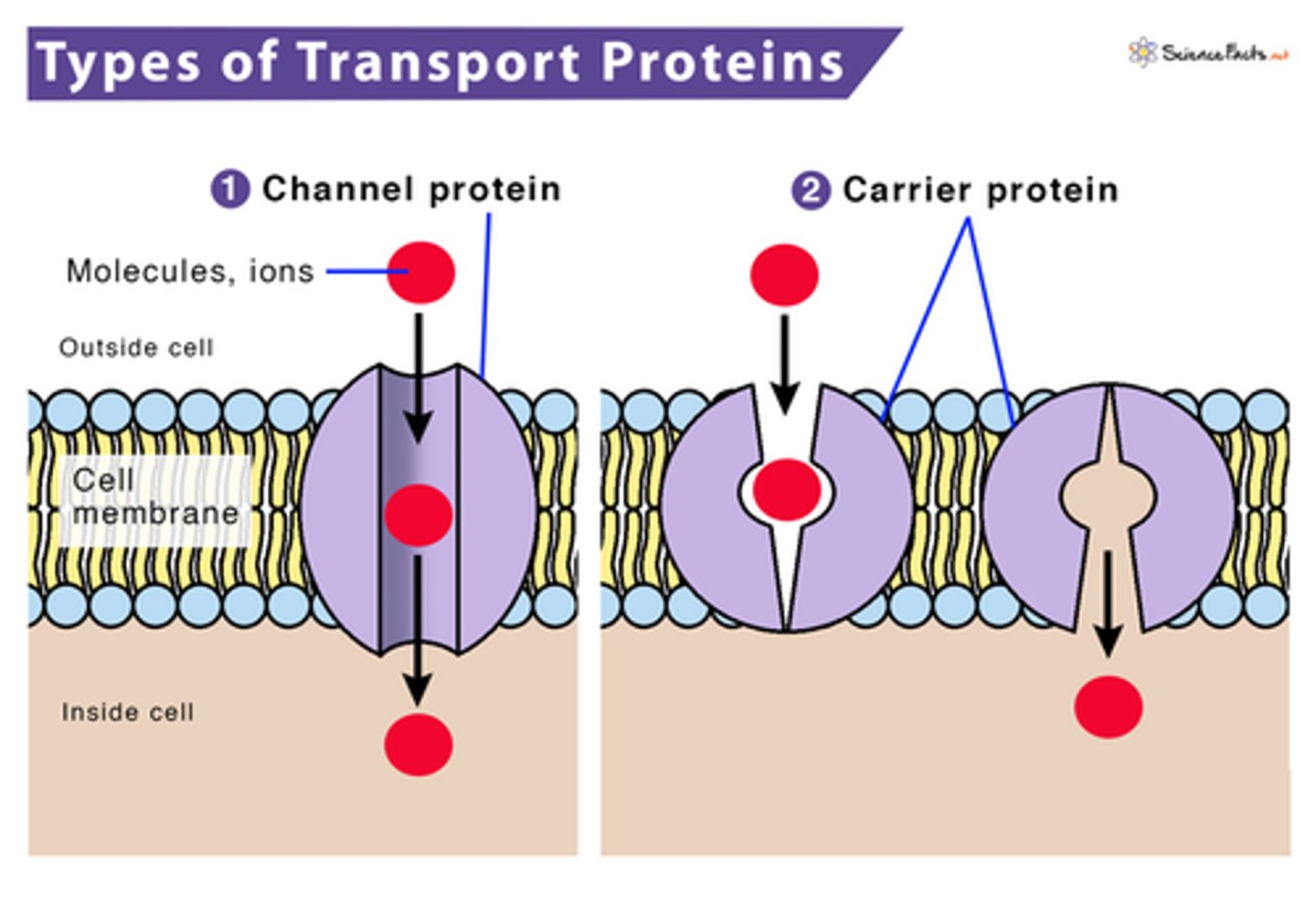
What types of molecules use proteins pass the membrane
1. Polar charged molecules
2. Big molecules
Ex: glucose is big and polar
Although water (polar uncharged) can pass through the bilayer, it can go through the membrane more efficiently through proteins called aquaporins.
What is passive transport?
1. Uses no energy
2. Things are moved from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration (diffusion)
3. usually membrane facilitated (passes through bilayer)
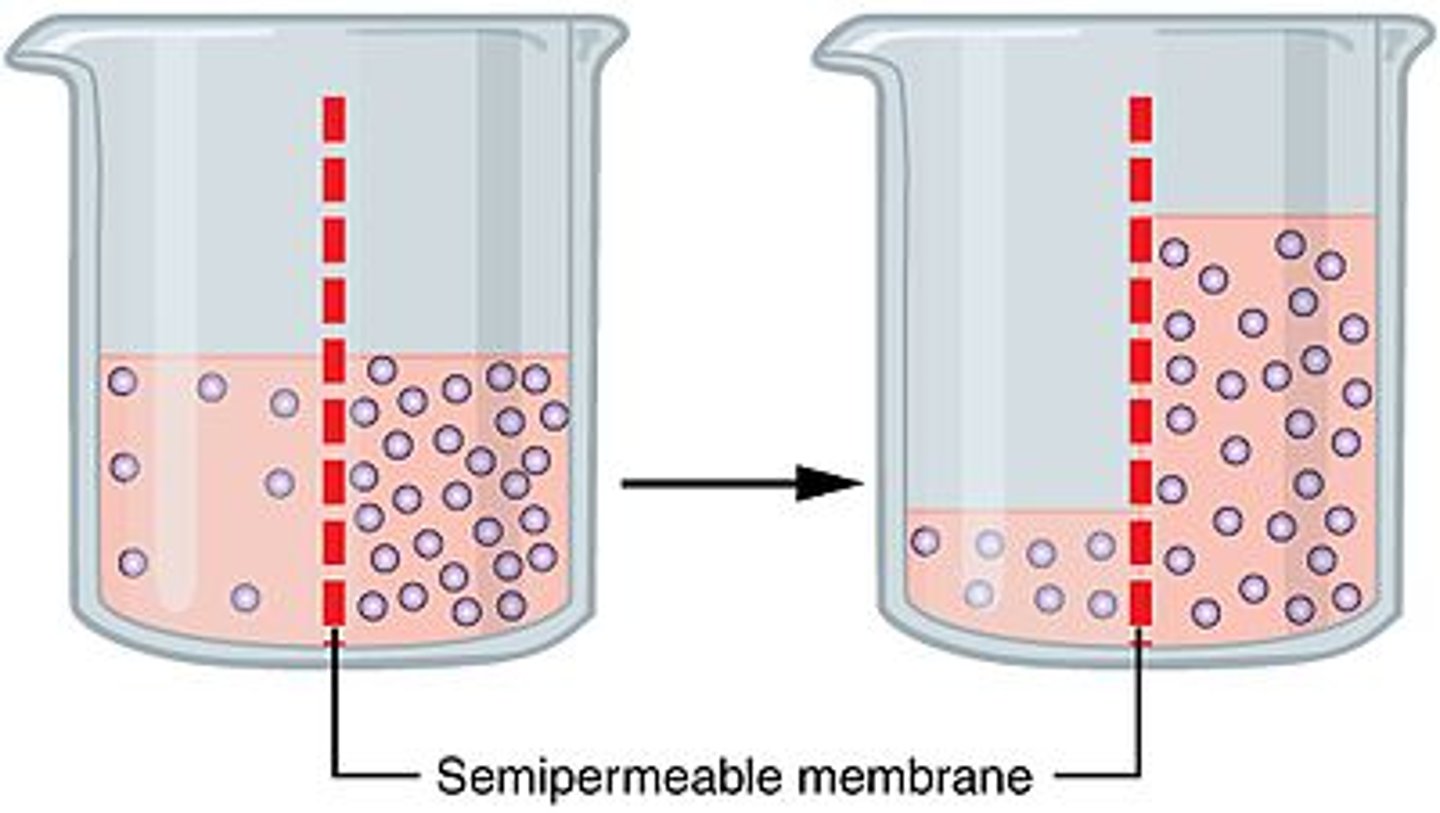
What is osmosis?
1. Water with a solute (something dissolved into the water, like salt) will move across the membrane if the other side of the membrane has more solute.
2. This will occur until the water on both sides of the membrane has the same concentration of solute.
3. This is a form of passive transport
The solute does not pass through the membrane, the water does
A good way to think about it:
If there is more solute in the water, the water molecules have more stuff blocking them from moving through the membrane. If there is less solute in the water, more water molecules will pass through because there is less stuff blocking them. This balances out so the sides have the same solute per water.
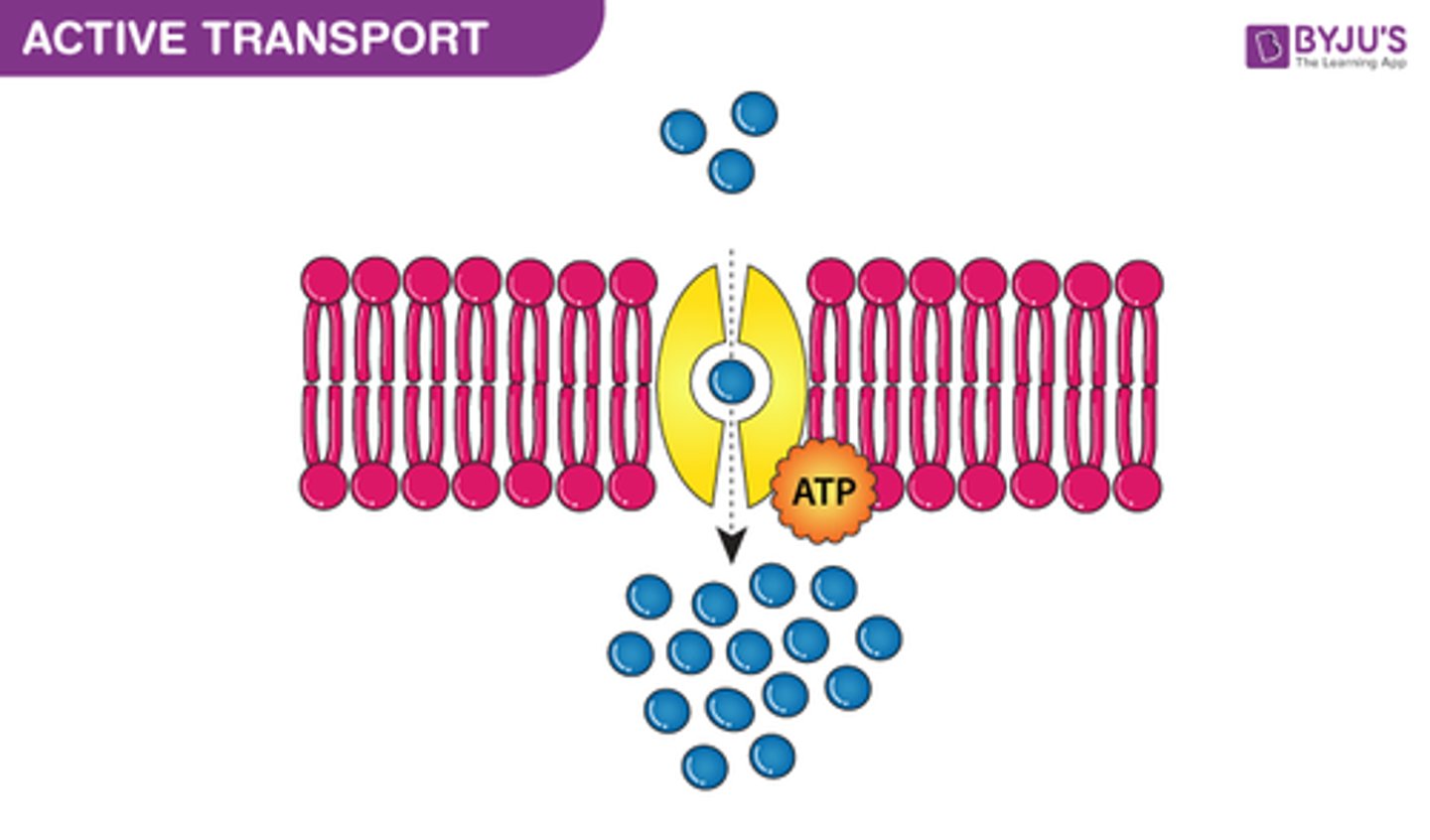
What is active transport?
1. uses energy (ATP)
2. Stuff goes from an area of low concentration to high concentration
3. Proteins are used usually
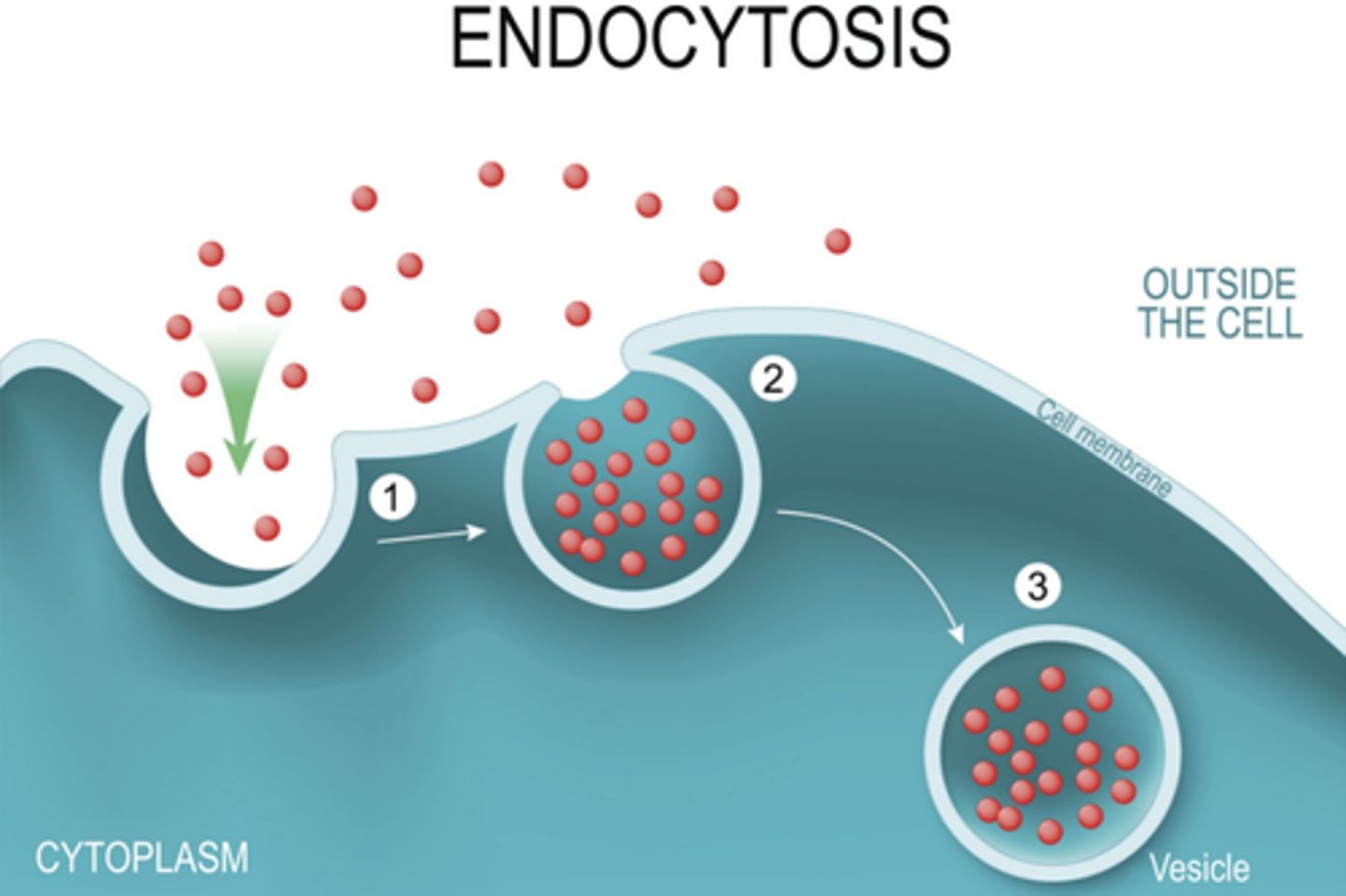
what is endocytosis?
A cell engulfs something big, active transport.
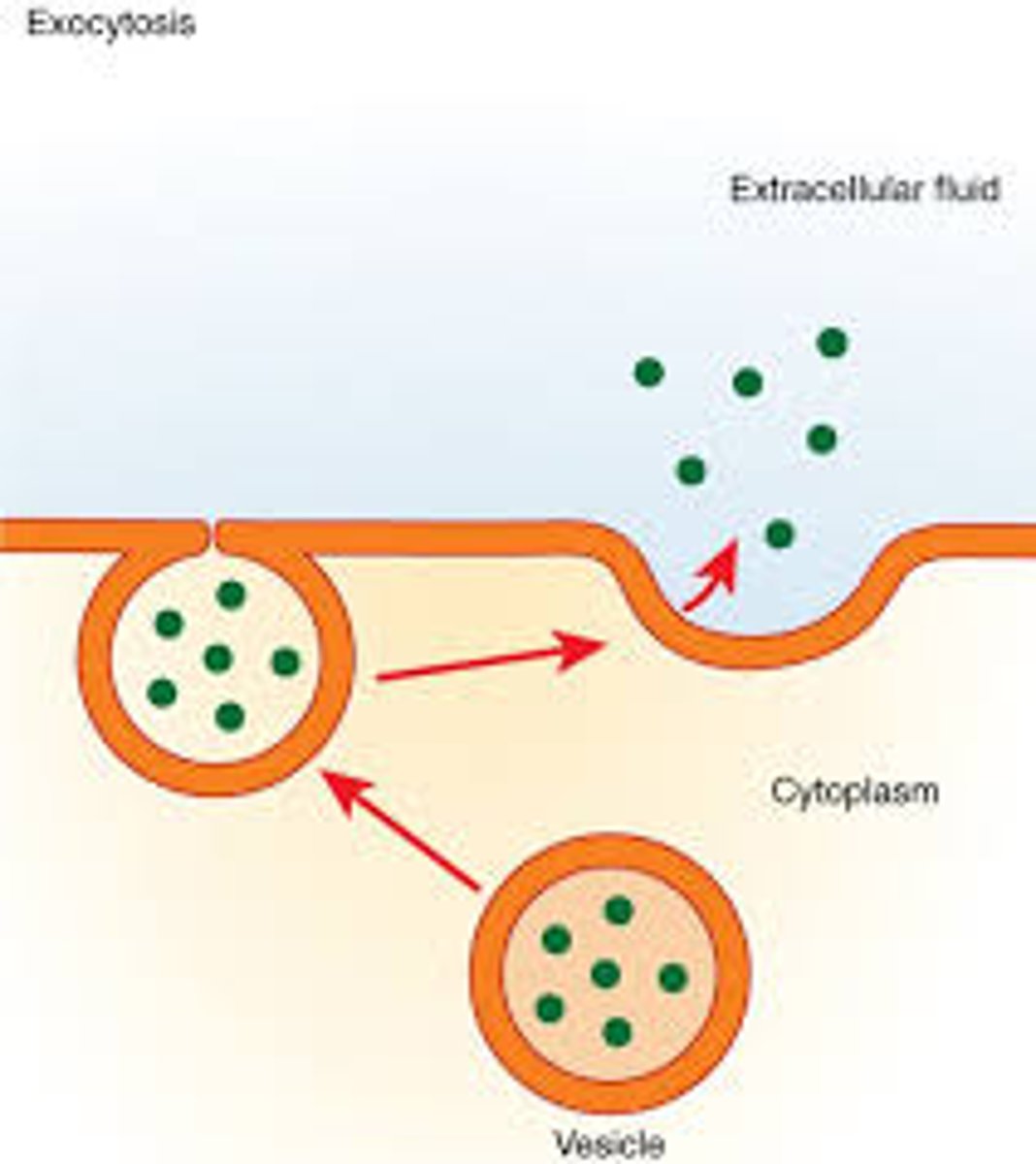
What is exocytosis
A cell expels a something big, active transport.
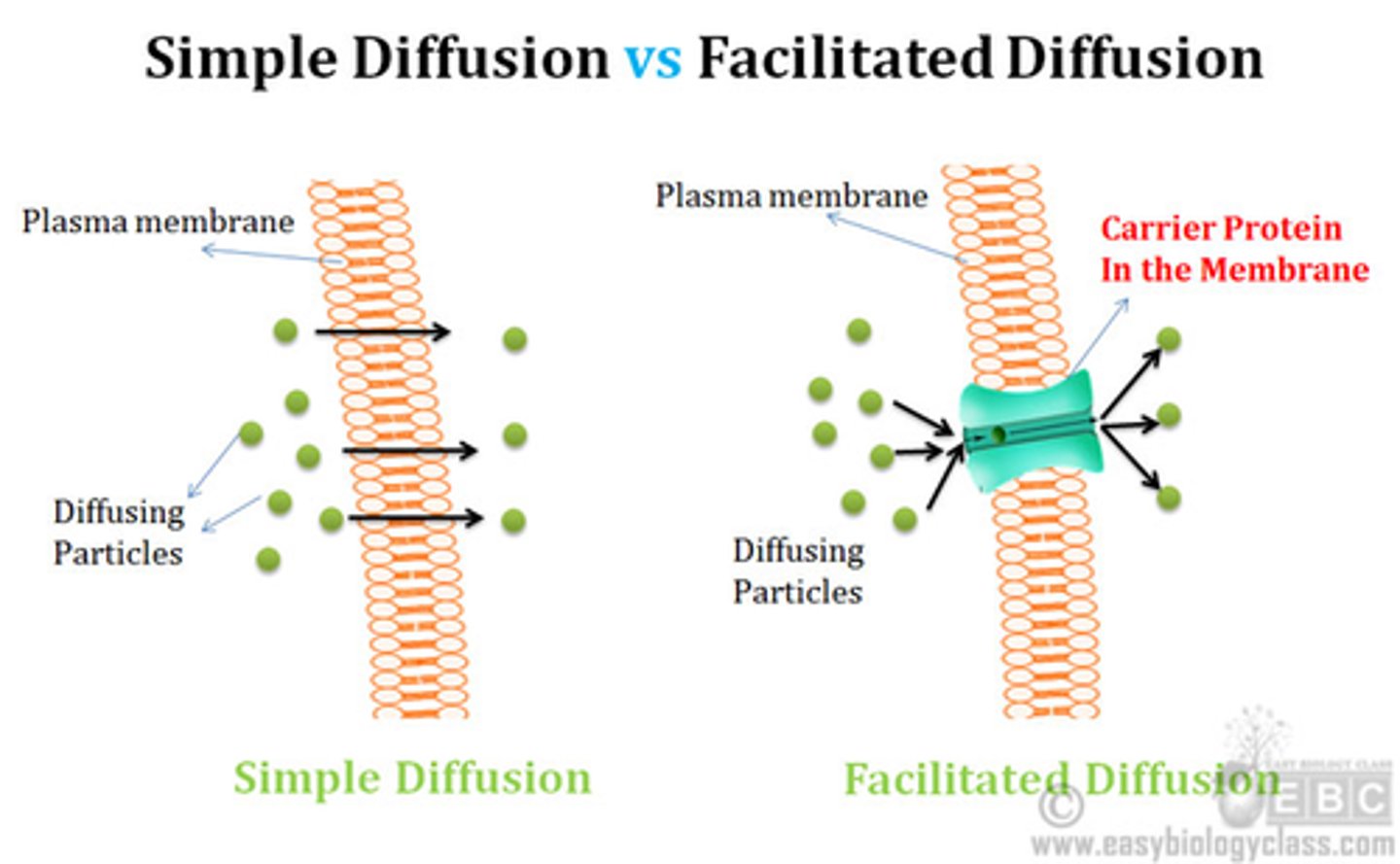
Facilitated diffusion vs. simple diffusion
1. Facilitated diffusion uses a transport protein
2. simple diffusion goes right through the membrane
What is osmoregulation and tonicity?
1. Osmoregulation: Cells use osmosis (remember 5 cards ago?) to regulate how much water is in them
2. Tonicity: determines if water will exit or enter the cell based on how much solute is in/around the cell.
Three types of tonicity:
1. Hypotonic: more solute is in the cell, so water will enter the cell and the cell will grow. (you can remember that hypo rhymes with grow)
2. Isotonic: the solute in the cell is equal to the solute outside the cell. Size stays the same
3. Hypertonic: more solute is outside the cell, so water will exit the cell and the cell will shrivel up.
This is why saline solution is used in I.V.s; if water was used, the solute around you cells would decrease in concentration and your cells would gain water and possible burst. This is also why you shouldn't drink soy sauce, your brain cells will shrivel up because you are putting more solute around them.
