Chapter 25 - Analyzing the Latent Radiographic Image
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Week 9
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is a latent image?
The image before it is developed
The smallest absolutely object size that can be reproduced is ____ proportional to _______ the spatial frequency.
inversely, one-half
Spatial Resolution: Spatial Frequency

Which side has a hotter technique?
Left side

Which side has a thicker wire?
Left side

Which side has a smaller FS?
Right side

Which side has more detail?
Right side (smaller FS)
More line pairs = ___ resolution
more
What are the lead foil line-pair templates measured in?
Line-pairs per millimeter
What does spatial resolution: spatial frequency mean?
The smallest object that can be measured is the width of one line at the smallest resolved line-pair (as opposed to a pair of lines)
What is minimum object size?
Smallest object that can be measured before disappearing into penumbra or obliterated
What is the equation for minimum object size?
½ (1/SF)
So if our smallest visible line-pair was 3 line-pairs per mm, our minimum object size would be?
SF = 3 so…
Minimum object size = ½ (1/3)
1/6 or 0.17mm
What is important to note about the resolution of the final image?
It is dependent upon many additional processing and display factors
No object ____ than a single pixel can be recorded.
smaller
Limited by the size of the individual electronic detector elements
Pixel size is a THEORETICAL limiting factor
Resolution of final image
Objects ____ than the FS cannot be recorded because the penumbra will ___ them.
smaller, absorb
Today, pixel size (0.1mm) is much smaller than the typical FS used (0.5-1.2 mm)
Resolution on final image
Focal spot is still considered the ____ limiting factor for spatial resoltion.
primary
What does MTF stand for?
Modulation Transfer Function
What is MTF?
The ratio of the recorded contrast of an image to the real object’s subject contrast.
What is a perfect MTF?
1.0
Meaning that the contrast of the real object is recorded with 100% accuracy in the image.. think of each line pair as pure white of the lead strip and pure black
Is a MTF of 1.0 realistic?
No
Doesn’t happen because of penumbra
rounds off edges of image which affects subject contrast
Imaging equipment is not a perfect system
Where do numbers fall normally for MTF?
0-1.0
MTF of 0.5 means that the image has ½ of the contrast of the real anatomy
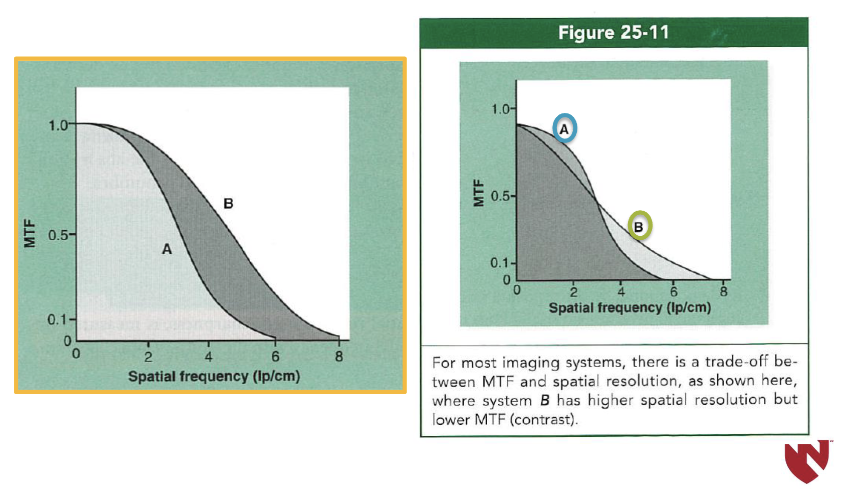
Spatial Resolution and MTF are ____ related.
inversely
trade-off occurs where higher spatial resolution is obtained at the expense of the contrast resolution & vice versa