#1 Introduction and wetland types
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What types of plants were present during the Carboniferous period?
Coal bearing
Wetlands are good at sustaining and storing materials
Majority of fossilized material is plants that comes from wetlands
Releases a vast amount of carbon
What was the significance of the Carboniferous period?
The formation of enormous wetlands in tropical regions led to massive deposition of peat, which over geological time was compressed into much of the Earth's coal
Wetland
a transitional area where the water table is at or near the surface, resulting in saturated soils and the presence of plants (hydrophytes) specifically adapted to those waterlogged conditions
What were some early human practices that relied on wetlands?
Agriculture
Some cultures
What were some early agricultural practices that relied on wetlands?
Banks of wetlands periodically floods = good spot for agriculture
Like rice fields
Littoral wetlands-> wetlands close to a lake
What were some early cultural practices that relied on wetlands?
Ahwaris of Iraq
Marsh Arabs
Mudhif houses
Makes their entire livelihoods in wetlands
Why are wetlands considered an endangered ecosystem?
More than 90% in Europe are gone
South America also has massive loss of wetlands
In the US->
In 22 states at least 50% of original wetlands have been lost
7 have lost over 80%
Massive lost, more than any other (prairie/grasslands) types in the US
What are some reasons that have made wetlands an endangered ecosystem?
Land creation
Agriculture
Water, irrigation, and flood control
Disease mitigation
destroy wetlands = destroy disease hotspot
Unintentional destruction
Dams, agriculture run-off
What makes up a wetland?
Vegetation
Hydric soil/ soil biochemistry
Anoxic (redox reaction)
Fluctuating water levels
What specific vegetation is found in wetlands?
hydrophytes/aquatic plants
Plant communities that are adapted to a wetland system
What are some key points to define wetlands? (first 3)
Water at or near the surface
Soils that are physically and chemically distinct from uplands due to waterlogging (hydric soils)
Vegetation adapted to wet conditions (hydrophytes)
What are some key points to define wetlands? (last 3)
Slow rates of decompositions usually due to anoxic conditions
Lack of flood-intolerant organisms
Lead to adaptations
in animals→ Hooves
Fish→ being flat to not get stranded
What are the 6 major wetland types?
Marsh
Swamp
Fens
Bogs
Wet meadow
Shallow lakes
What type of vegetation typically dominates marshes?
Herbaceous plants
Trees are generally absent
What is the general productivity level in a marsh, and what does productivity mean in this context?
High end of productivity
increase Productivity = increase production of biomass
What is biomass?
organic material from living or recently living organisms
How is water availability characterized in marshes?
Periodic or long-term inundation
Frequent drenches
No dry periods, at least for a long period of time
Lot of water flow
Is peat typically present in marshes?
No, peat is not present
How are marshes commonly categorized?
Tidal Marshes
Inland Marshes
Tidal Marshes
both fresh and saltwater influences
EX: estuaries
Inland Marshes
dependent on rainfall, runoff, etc
EX: edge of a river
What is 3 examples of Marshes?
Estuaries
Wet meadows
Prairie potholes
Isolated marsh sections
What type of vegetation typically dominates swamps?
trees (mainly large trees) or shrubs
woody vegetation
How do swamps differ from marshes in terms of dominant vegetation?
Swamps are dominated by trees and shrubs
marshes are dominated by herbaceous (non-woody) plants
What is the primary water source for swamps?
Usually by surface water
Is peat typically found in swamps?
No presence of peat
What are 2 examples of swamps?
Southern hardwood swamps
Mangrove swamps
What type of vegetation typically dominates fens?
Herbaceous plants
Maybe some dwarf trees
How do fens compare to bogs in terms of peat accumulation?
Fens typically have more peat accumulation and contain an extensive peat layer than bogs
How does the acidity of fens compare to that of bogs?
Less acidic than bogs
contributes to greater plant and microbial diversity
What is the primary water source for fens?
soil drainage or groundwater movement
Are fens more or less diverse than bogs? Why?
more diverse
This is due to their higher nutrient levels, less acidic conditions, and greater water movement.
What is an example of a fen?
Great Lakes fens
What types of plants typically dominate bogs?
herbaceous plants
beds of sphagnum moss and/or peat moss
What is the primary water source for bogs?
primarily fed by rainfall (precipitation)
Fairly stagnant = very little exchange with groundwater or surface water systems.
What does limited water flow in bogs mean?
low oxygen levels and minimal nutrient input
What is the typical pH or acidity level of bogs?
highly acidic
accumulation of sphagnum moss
lack of flushing or water exchange
Why is decomposition slower in bogs compared to other wetlands?
Because bogs are acidic, stagnant, and low in oxygen, decomposition is very slow
leads to the accumulation of peat
What results from the slow decomposition in bogs?
organic matter accumulates and forms an extensive peat layer
making bogs important carbon sinks
Are bogs highly biodiverse ecosystems? Why or why not?
No, bogs are typically less diverse than other wetland types due to:
Low nutrient availability
High acidity
Harsh growing conditions
Only specialized organisms can survive in bogs
What are 2 examples of bogs?
Northern bogs
In Canada
Pocosins
How do bogs relate to fens?
Both can exist on a spectrum
fens are less acidic, more nutrient-rich, and more biodiverse than bogs
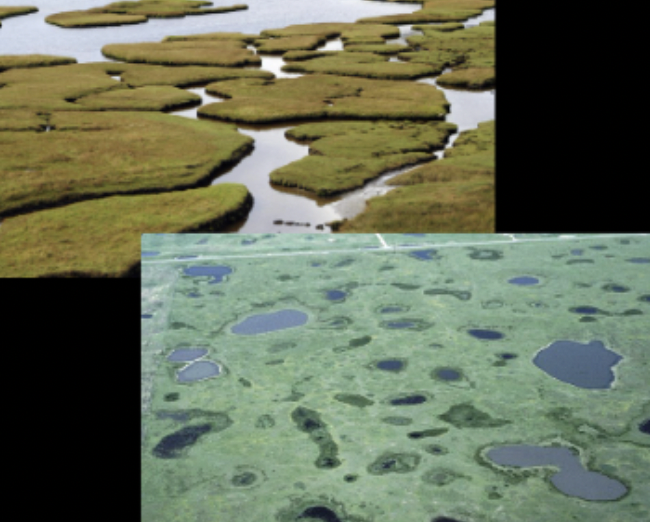
What type of wetland is this?
Marsh
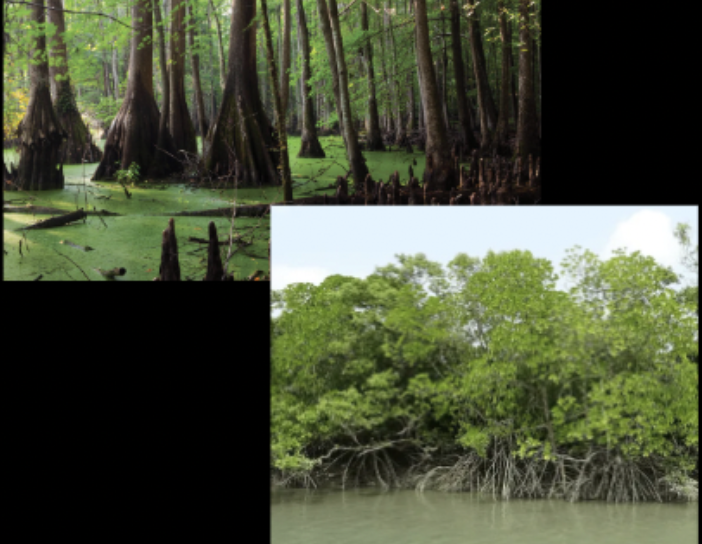

What type of wetland is this?
Swamp

What type of wetland is this?
Fen

What type of wetland is this?
Bog
Wet meadow
Mostly dry, occasionally flooded
Shallow lakes
Mostly flooded, occasionally dry to allow some terrestrial plants to grow there
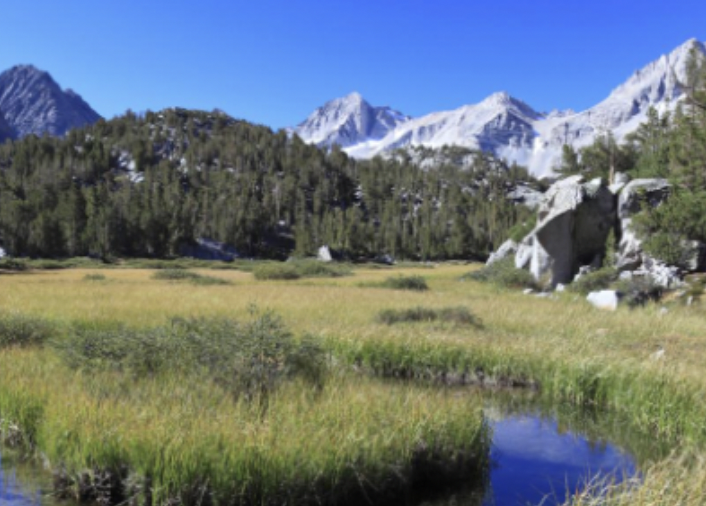

Which type of wetland is this?
Wet meadow
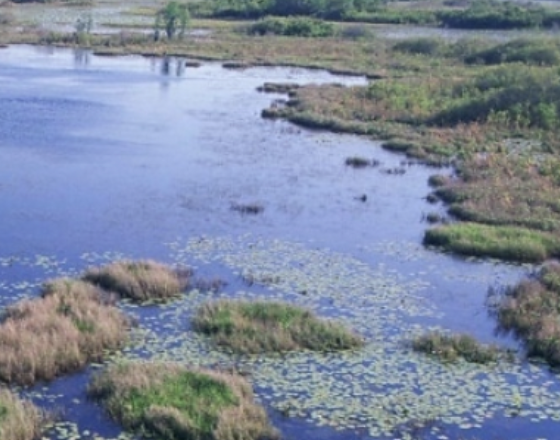

Which type of wetland is this?
Shallow lakes
What is Peat?
Partially decomposed organic matter
Formed mostly from plant matter (often from mosses in bogs and fens)
What is Peat a consequence of?
Waterlogged soils with high acidity and low oxygen and nutrient levels
Slows down aerobic decomposition