1 antibacterials: protein synthesis inhibitors
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
bacteria ribosomes (70S) consist of:
30S & 50S subunits
what are the antibacterials that work on 30S subunit
"TAG"
- Tetracyclines
- Aminoglycosides
- Glycyclines
what are the Tetracyclines
- vibramycin (doxycycline)
- minocin (minocycline)
- tetracycline
spectrum of activity of Tetracyclines
- aerobic gram + (including MRSA)
- aerobic gram -
- spirochetes
- anaerobes
- atypical (ie chlamydia, mycoplasma, rickettsia_
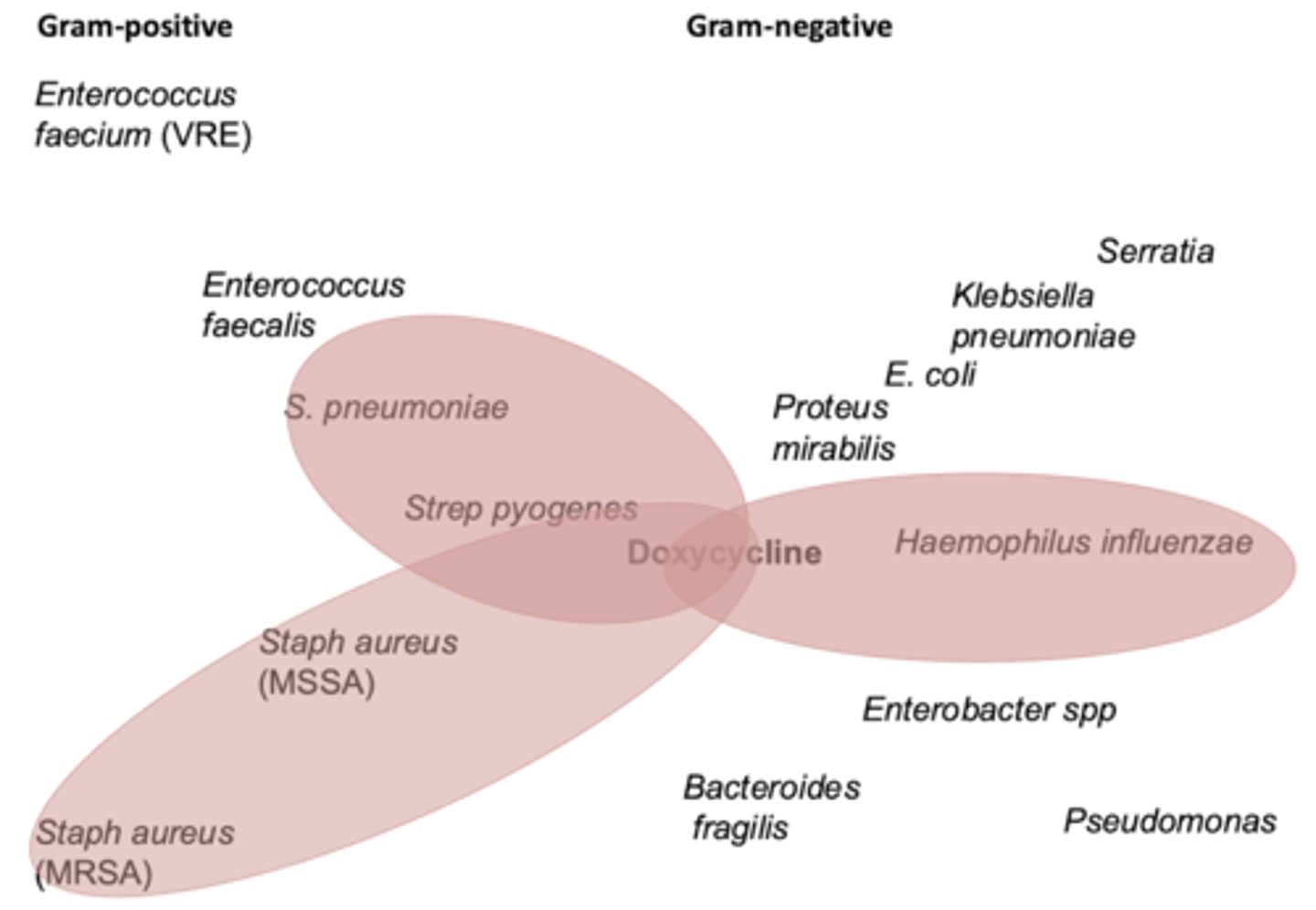
when do we use tetracyclines
primarily skin-skin, CAP, atypicals
- acne
- skin & soft tissue
- respiratory tract
- STDs
- lyme disease
- rocky mountain spotted fever
- leprosy (minocycline)
MOA of tetracyclines
- enter bacterial cell thru passive diffusion or energy-dependent transport
- 30S subunit binding
- prevents tRNA binding to mRNA-ribosome complex --> inhibition of protein synthesis
bacteriostatic
bioavailability of tetracyclines
~ 100%
- administer 1 hr before or 4 hrs after dairy products & antacids (co-admin decreases abx absorption)
metabolism of tetracyclines
- doxy: eliminated via bile in feces (no hepatic/renal)
- tetra: eliminated unchanged in urine (renal adjust)
- minocycline: hepatic & lesser extent kidneys
adverse effects of tetracyclines
- GI disturbance most common
- phototoxic: wear sun protection
- NOT in preg or breastfeeding women, or kids <8 yo (causes tooth discolor & stunt bone growth)
more rare but severe effects of tetracyclines
- assc w pseudotumor cerebri (intracranial htn)
- dizziness, vertigo, tinnitus (esp minocycline)
- blue-black hyperpigmentation of skin & mucosal membr w minocycline
what are the glycylcyclines
tygacil (tigecycline), IV
spectrum of activity of glycylcyclines
- gram + (including MRSA, MSR Streptococci, VRE)
- gram - (including ESBL enterobacteriaceae)
- acinebacter
- many anaerobes like Bacteroides
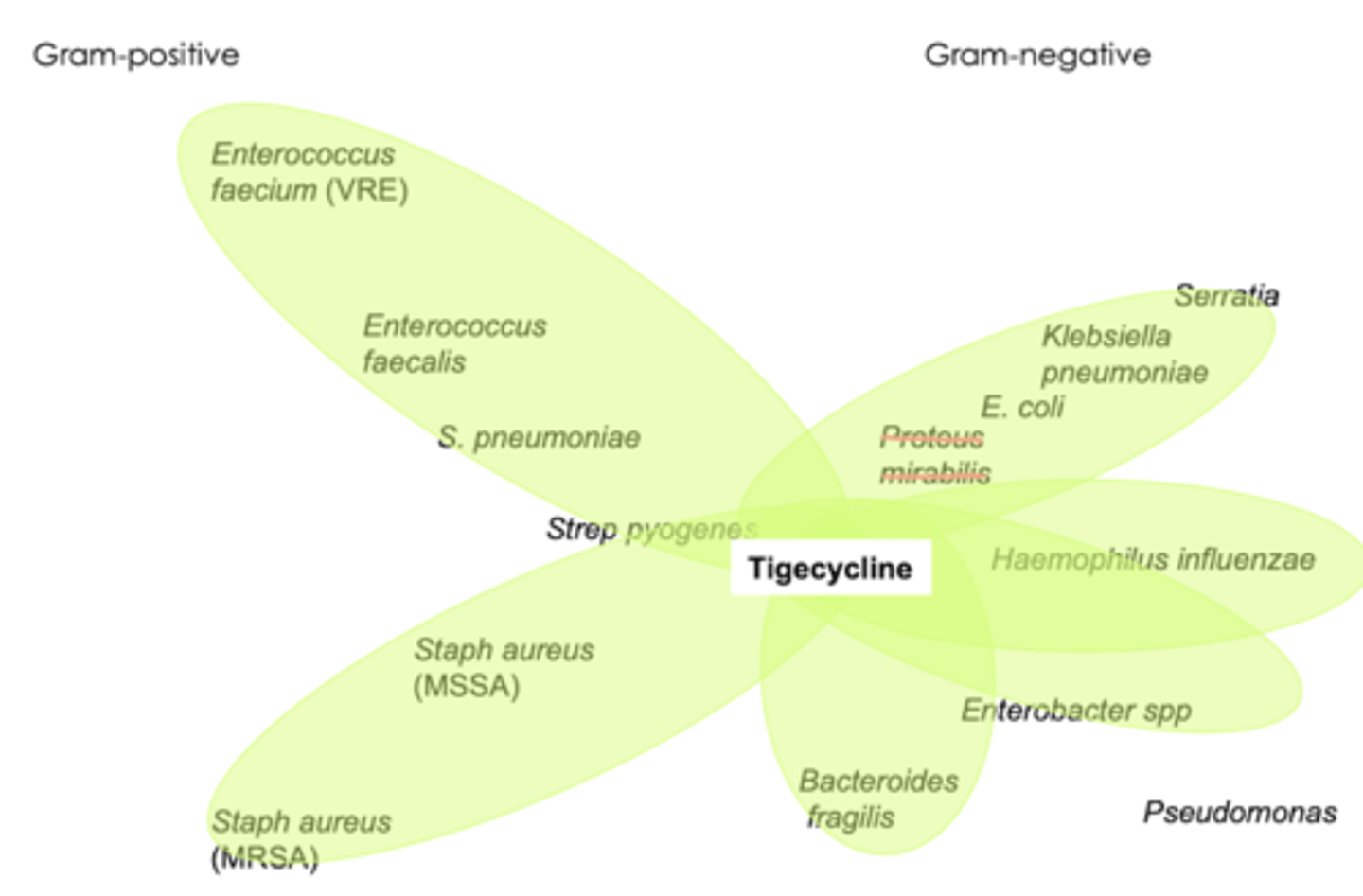
when do we use glycylcyclines
- complicated skin & soft tissue infections
- complicated intra-abdominal infections
- BBW: higher treatment mortality (use as last line)
MOA of glycylcyclines
same as tetracyclines!
D--D w glycylcyclines
warfarin
adverse effects of glycylcyclines
- N/V (cannot be relieved w Ondansetron)
- risk for hepatotoxicity
- same concerns as tetracycline
what are the aminoglycosides
- amkin (amikacin)
- garamycin (gentamicin)
- neomycin
- zemdri (plazomicin)
- streptomycin
- tobrex, tobi (tobramycin)
spectrum of activity for aminoglycosides
- monotherapy: gram - only
- combo (gentamycin): w Beta lactam (Vanc or Ampicillin) for enterococcus endocarditis
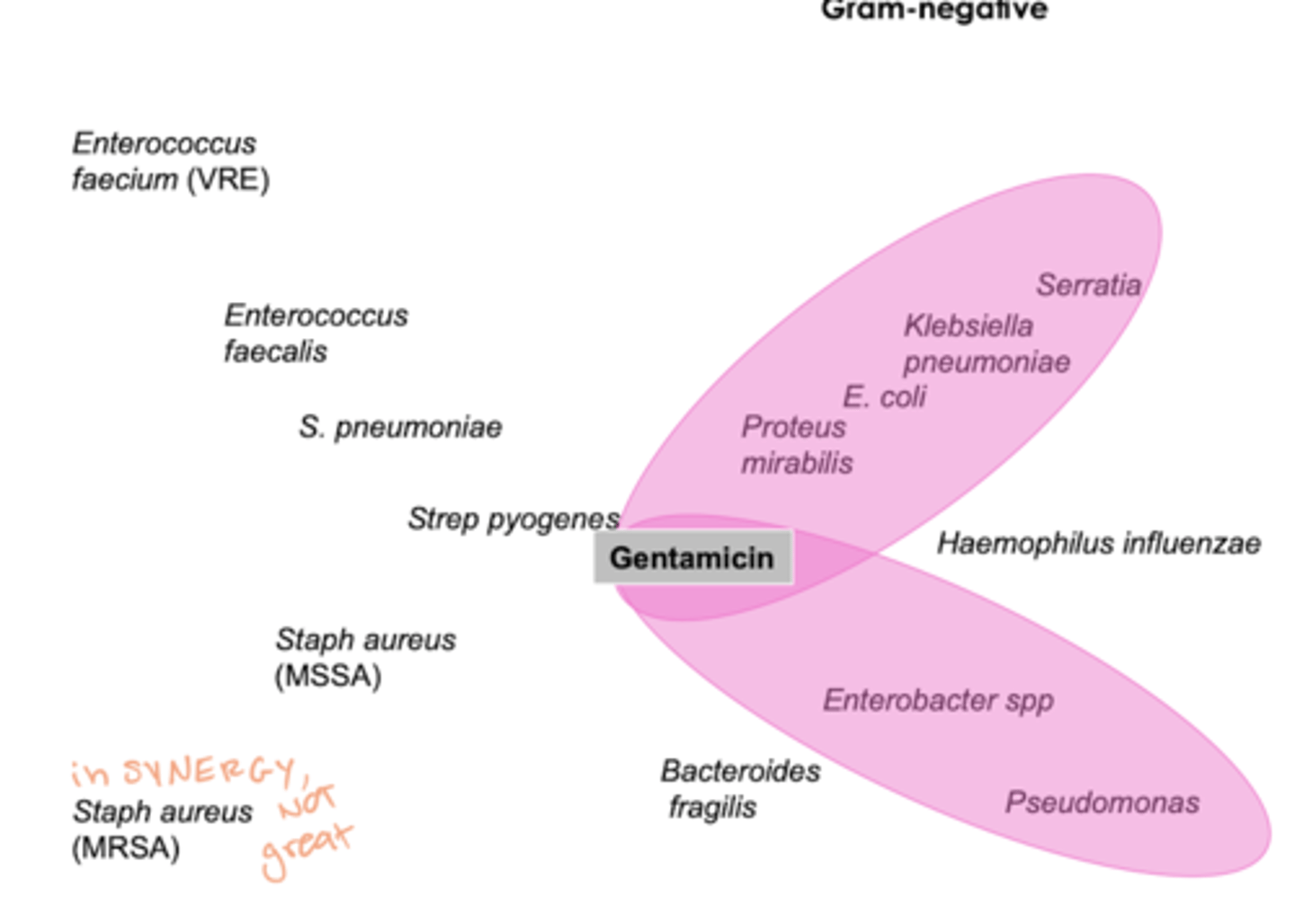
when do we use aminoglycosides
concern for resistant gram neg infections
- usu in synergy
- only monotherapy ijn UTIs!
MOA of aminoglycosides
- bind to 30S ribosomal subunit: interfere w assembly of ribosomal apparatus --> misread genetic code
batericidal
2 dosing schemes of aminoglycosides
traditional dosing
- multiple, lower doses per day
- will order peaks & troughs
extended interval
- larger doses Q12h or > (usu Q24hr- shortest_
- relies on antibiotic effect
- less nephro/ototoxicity
- easier drug monitoring (w random level)
steps for dosing aminoglycosides
step 1: indication, decide on strategy to dose
step 2: calculate CrCl, identify weight
step 3: calc maintenance dose & frequency
step 4: schedule monitoring- peaks/troughs (traditional) vs random level (extended)
what weight do you use for traditional dosing?
ideal body weight
traditional dosing frequency is determined by...
CrCl
traditional dosing: efficacy
for the kill
- 6-8 for gram - (Tobramycin)
- 3-5 for gram + (Gentamycin)
traditional dosing: troughs
nephrotoxicity
irreversible ____ has been assc with HIGH PEAKS
ototoxicuty
if peaks & troughs are both low:
increase dose
if peaks & troughs are both high:
decrease dose
if peak cannot proportion:
must recalculate
advantages to extended interval dosing of aminoglycosides
larger doses, less frequently (post antibiotic effect)
advantages:
- as efficacious
- less nephrotoxicity/ ototoxicity
- convenient & easy
- reduced cost
when to avoid extended interval dosing of aminoglycosides
- renal dysfunction (CrCl < 30 ml/min or dialysis)
- burns > 20%
- cirrhosis/ ascites
- pregnancy
monitoring extended interval dosing of aminoglycosides
- evaluate a RANDOM level at 10 hours after first dose
urban & craig nomogram is used in ____
obstetrics
- 5 mg/kg
adverse effects of aminoglycosides
- monitor for nephro & ototoxicity (deafness can be irreversible)
- risk of neuromuscular paralysis when given w neuromuscular blockers or when high doses given too quick
- renal dose adjust
what are the drugs that work on the 50S subunit
"CLEan"
- clindamycin
- linezolid
- erythromycin
what are the macrolides
- zithromax, zpak (azithromycin); PO, IV, opthalmic
- biaxin (clarithromycin), PO
- E.E.S, ery-tab (erythromycin); PO, IV, opthalmic, topical
spectrum of activity of macrolides
"Jack of all trades but master of NONE"
- gram +
- gram -
- atypicals
- mycobacteria
- spirochetes
NO MRSA. enterococcus, psedomonas, bactereoides
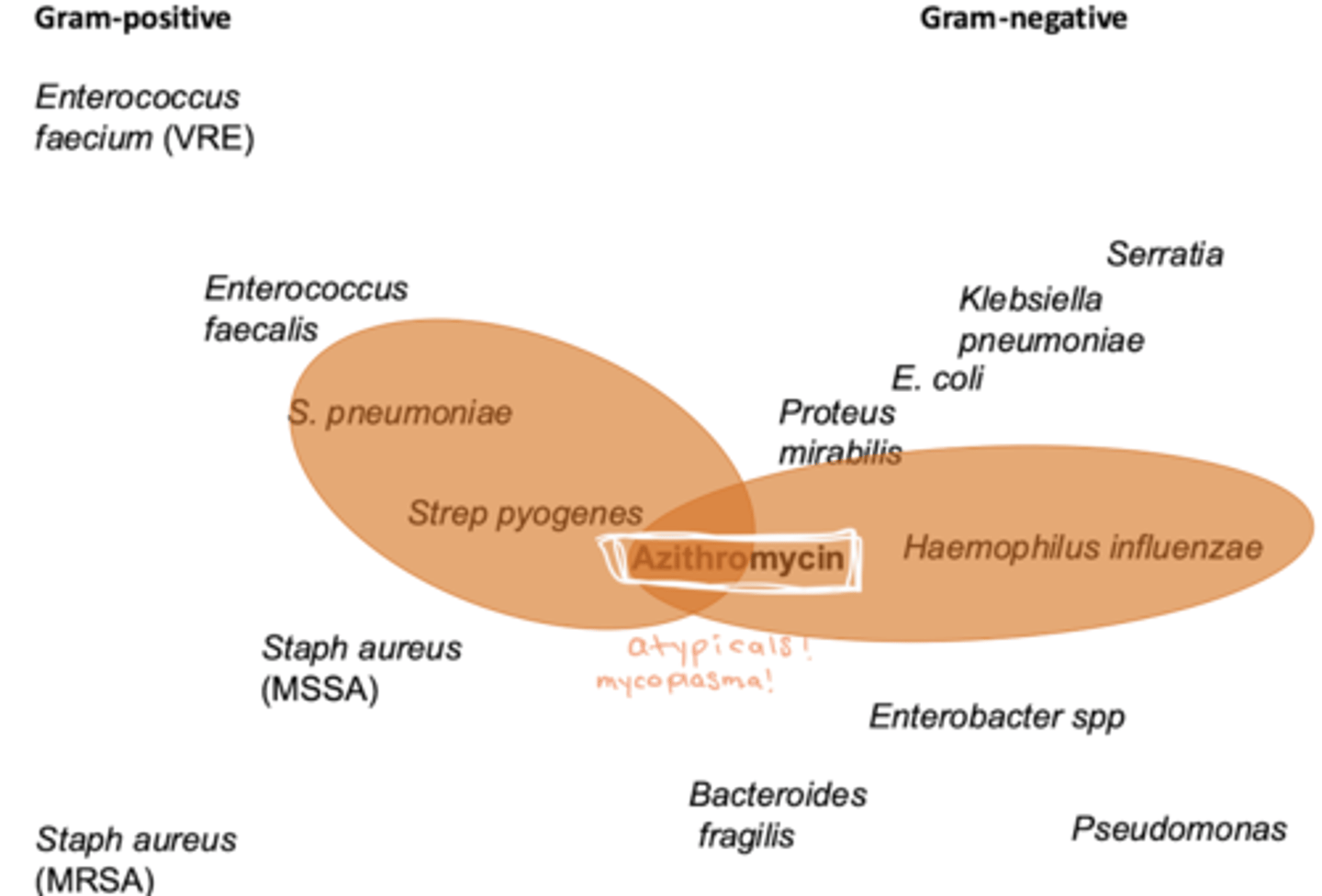
when do we use macrolides
- AECOPD
- mycobacterium avium complex (opportunistic infection prophylaxis)
- STDs
- whooping cough (not as much URI)
- usu: CAP to cover atypicals (Mycoplasma, PNA)
MOA of macrolides
- irreversibly binds to 50S subunit
- inhibits translocation steps of protein synthesis
- bacteriostatic
D--D with macrolides
- with erythromycin: some interaction w other CYP P450 drugs
- QT prolonging agents (also mainly erythromycin)
adverse effects w macrolides
- GI absorption: diarrhea
- some QT prolongation
- azithromycin hepatically eliminated
what macrolide has the longest half life
- azithromycin, due to tissue accumulation (large volume of distrubution)
discuss opthalmic use of macrolides
- prophylaxis of opthalmia neonatorum (gonorrhea & chlamydia)
what are the oxazolidinones
zyvox (linezolid)
spectrum of activity of oxazolidinones
- gram + including MRSA, VRE !!, & mycobacterium TB
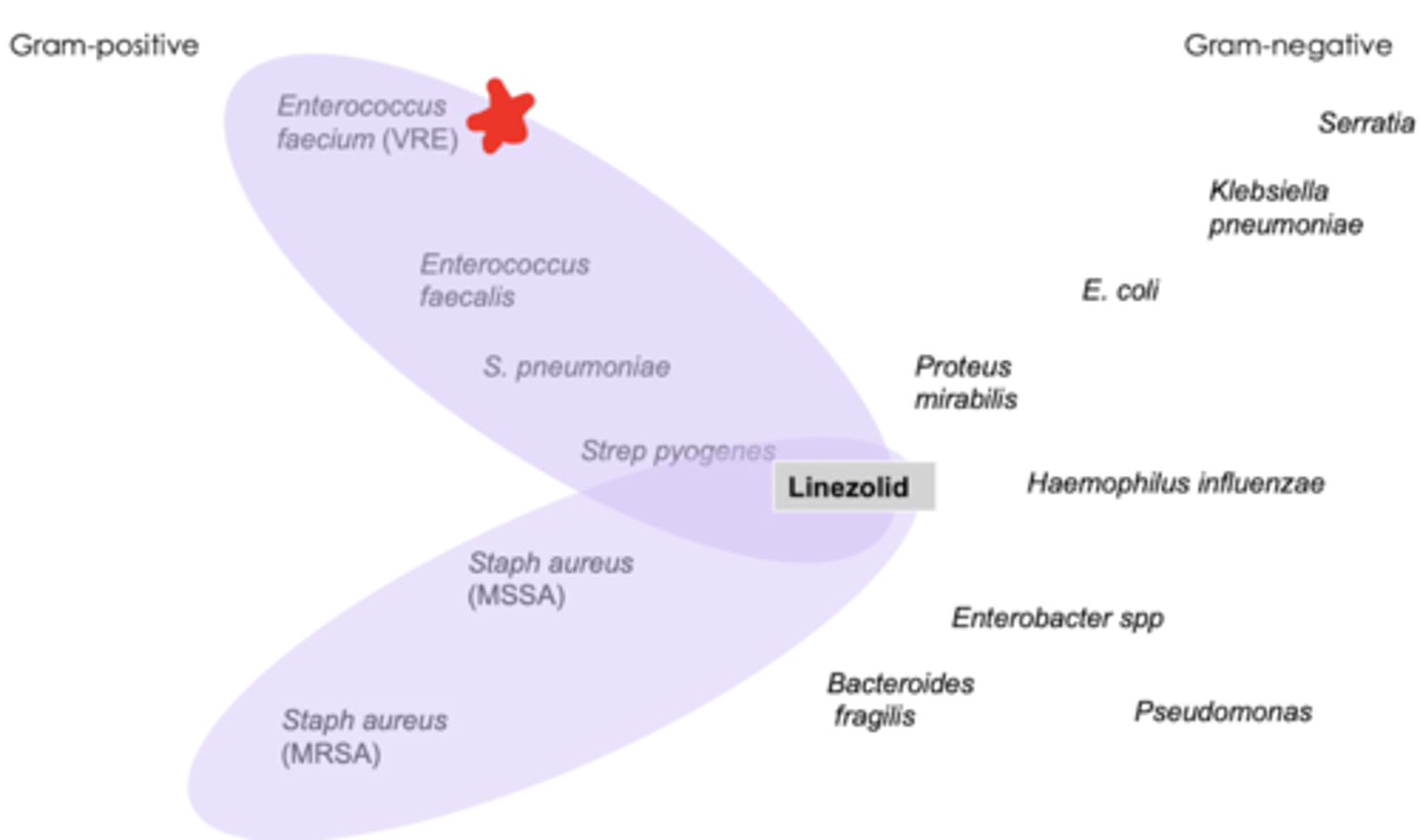
when do we use oxazolidinones
- needing coverage for resistant gram + organisms
- avoid for MRSA bacteremia
MOA of oxazolidinones
- 50S subunit, blocks formatino of 70S initiation complex
- bacteriostatic but bactericidal against Strep spp.
drug--food interactions with oxazolidinones
- combined w high tyramine-containing foods, serotogenic agents, and/or monoamine oxidase inhibitors --> serotonin syndrome
adverse effects of oxazolidinones
- GI upset, diarrhea, nausea
- HA
- rash
- myelosuppression when given extended durations (>2 weeks): monitor CBC weekly
- peripheral & optic neuropathy: when used >28 days; monitor for visual disturbances --> perm blindess
what are the lincosamides
- cleocin (clindamycin); PO, IV, topical
spectrum of activity for lincosamides
- aerobic gram + including MRSA & anaerobes
"clinda ABOVE (gram + anaerobes), metronidazole BELOW (gram - anaerobes)
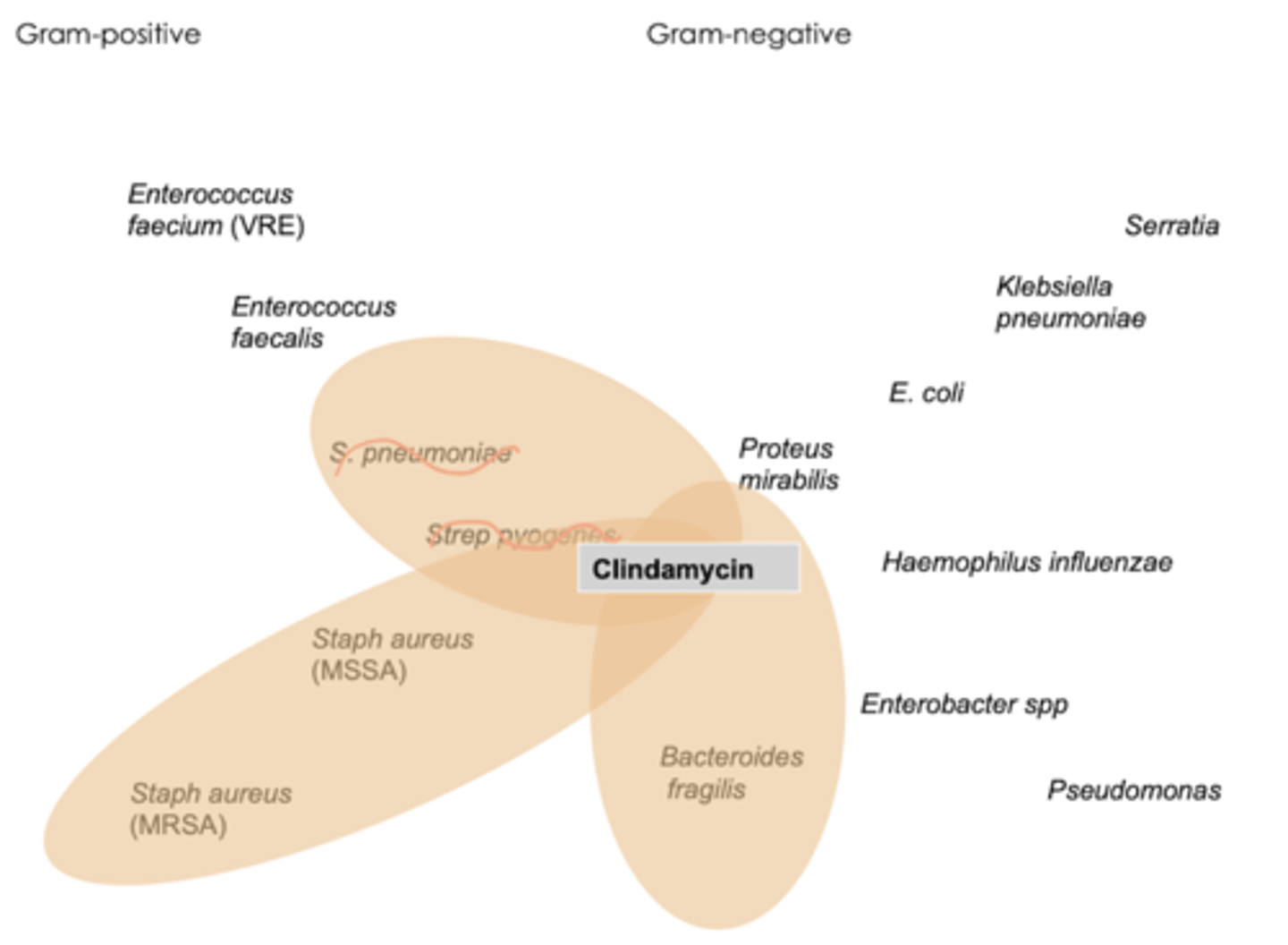
when do we use lincosamides
- skin & soft tissue infections
- acne
MOA of lincosamides
similar to macrolides!
whats important to test when giving lincosamides/ clindamycin
detest!
- erythromycin can induce resistance to clindamycin
- if + detest... we avoid clindamycin
ADME considerations for lincosamides/clindamycin
- good distribution into bone but poor concentration in CSF
- primarily excreted in bile
- low urinary elimination --> do NOT Use this for UTIs
adverse effects of lincosamides/clindamycin
- diarrhea & pseudomembranous colitis
- take w full glass of water to avoid esophageal irritation
- BBW: common cause of C.diff
- assc w severe skin rxns
what are the chloramphenicol drugs
chloromycetin (chloramphenicol), IV
spectrum of activity of chloramphenicol
- broat spectrum
- gram + including MRSA, enterococcus, gram -, bacteroides, atypicals
when do we use chloramphenicol
rarely used due to toxicity profile
- serious infections when nothing else available
MOA of chloramphenicol
- 50S, peptidyl transferase rxn occurs --> protein synthesis inhibition
- bacteriostatic, but depending on organism can be bacteriocidal
adverse effects of chloramphenicol
- BBW: bone marrow toxicity; do NOT use in pt w G6PD deficiency --> hemolytic anemia
- avoid use in breastfeeding females & neonates
what are the streptogramins
synercid (quinupristin/dalfopristin), IV
spectrum of activity for streptogramins
- gram + including enterococcus faecium (including VRE)
what pathogen is covered by synercid?
- pseudomonas
- Enterococcus fatalis
- proteus
- enterococcus faecium!
MOA of streptogramins
- dalfopristin: interferes w addition of amino acids to peptide chain
- quinupristin: incomplete peptide chains being released
combo is bactericidal
pearls: streptogramins
- must be infused via central line
- 1/4 will experience hyperbilirubinemia (competes w bilirubin excretion)
- 50% experience reversible arthralgias & myalgias
which covers pseudomonas
aminoglycosides
which do NOT cover MRSA
macrolides
aminoglycosides
which are bactericidal
aminoglycosides
streptogramins