Cytochemistry for Leukemias
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
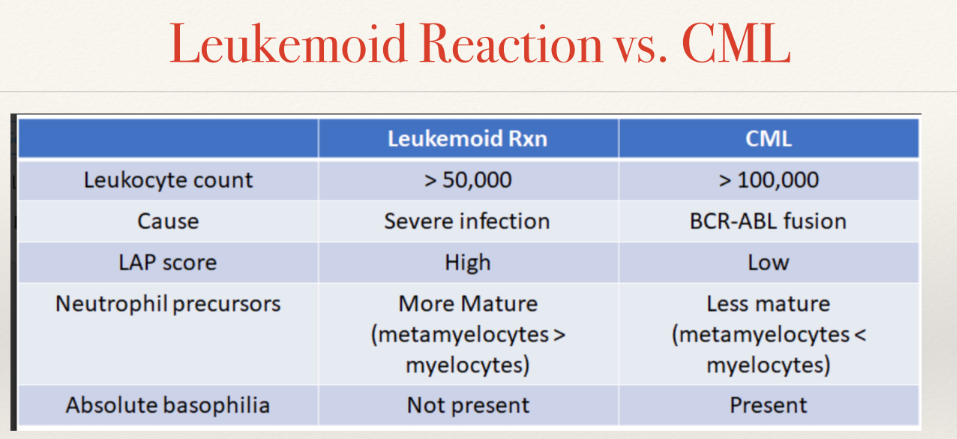
leukocyte alkaline phosphatase (LAP)
to: differentiate cells of CML from leukemoid rxn
LAP activity is present in varying degrees in secondary granules (after myelocyte stage) of maturing granulocytes (segs & bands)
LAP values
normal: 13-113
leukemoid LAP is high bc more mature granulocytes to fight infn
CML LAP is lower bc premature cells
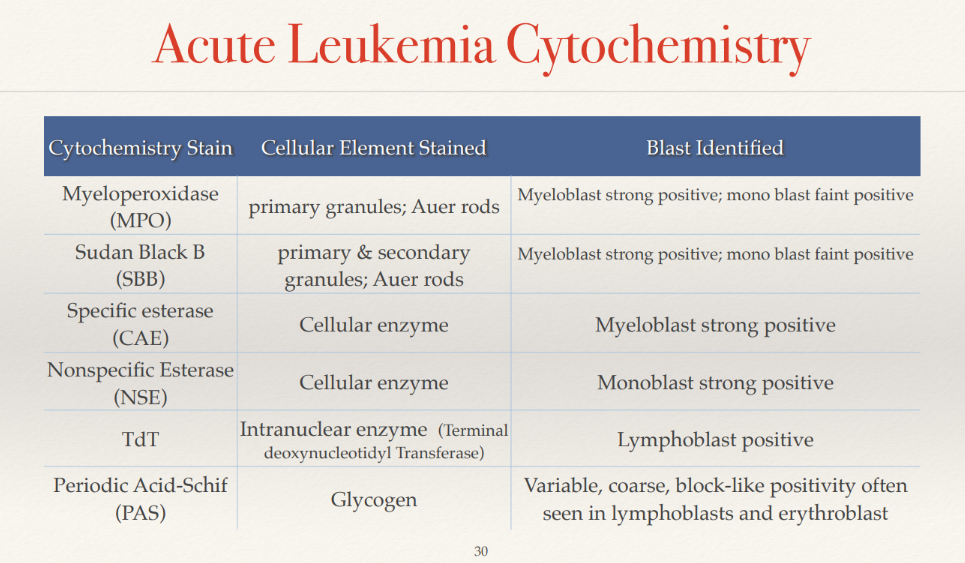
myeloperoxidase (MPO) P/P
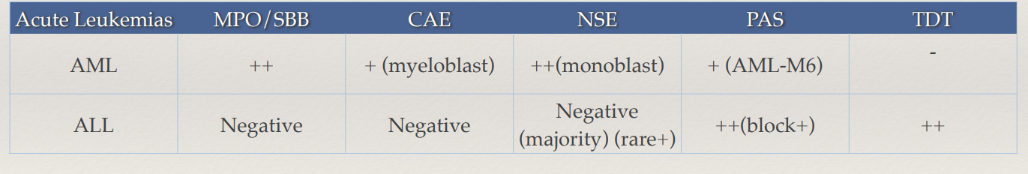
to differentiate acute myeloid leukemia from acute lymphocytic leukemia
MPO = enzyme in primary granules (azurophilic, appear at promyelocyte stage) of granulocytes, beginning at late myeloblast, promyelocyte stage and throughout myeloid maturation
low activity in monocyte
rbcs or lymphocytes = NEG MPO
MPO pos values
super MPO pos = promyelocytes & Auer rods
most leukemic myeloblasts are usually MPO pos in AML
MPO activity is limited in early myeloblast
neg for lymphs
Auer rods
abnormal fusion of primary granules in neoplastic myeloid blasts
possible to see AML-M1-3, super rare in M4, M5
m/c in M3 (APL)
Sudan Black B P/P
to distinguish AML from lymphocytic leukemia
dye stain phospholipid & other intracellular lipids found in primary & secondary granules of neutrophils, eosinophils, and in smaller qty in monocytes → more sensitive for early myeloid cells compared to MPO
Auer rods are SBB+
monocytic cells are neg (or W), lymphoblast are neg
SBB vs MPO: why is SBB better?
SBB is more sensitive to early myeloblasts
when fresh specimen isn’t available for MPO stain & when blast has MPO defic (in MDS)
specific esterase (chloracetate esterase)- CAE P/P
diff myelocytic & monocyclic leukemia
lysosomal enzymes, specific for granulocytic cells
CAE interpretations
POS = myeloid cells, Auer rods
neg-W = monocytes
neg = lymphocytes
can be used to ID granulocytes in formalin fixed tissues
nonspecific esterase (NSE) p/p
diff myelocytic & monocyclic leukemia
lysosomal enzymes specific for monocytes lineage
substrates: a-Napthyl acetate & a-napthyl butyrate
NSE interpretation
NSE exhibits strong activity in monocytic cells but v weak in granulocytes, megakaryocytes & lymphocytes
POS = bright red-brick color on monocytic cells
NSE w/fluoride inhibition
if fluoride added, only monocyte NSE will be inhibited
dual esterase stains
useful in ID monoblast & promonoblast populations in acute monoblastic leukemia & acute myelomonocytic leukemia
periodic acid Schiff (PAS) reaction
dx of erythroleukemia, erythroblasts ie subtype of AML-M6
AND dx of some acute lymphocytic leukemia
the stain indicates intracellular glycogen & related mucopolysaccharides
PAS interpretations
diffuse staining POS = erythroid popn in erythroblastic leukemias
and
block/coarse POS = lymphoblasts
neg = myeloid or monocytic blasts
tartrate resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) p/p
dx of hairy cell leukemia (old gold standard)
acid phosphatase is in myelocytes, lymphocytes, monocytes, plasma cells, and plts
→ AP is inhibited in presence of L-tartrate → no color
→ AP in hairy cell will not be inhibited → POS stain
iron stain (Prussian Blue rxn) p/p
to detect Fe-contain granules (siderotic granules) found in CP of developing cells in BM/tissue
rxn occurs w treatment of sections in acid solutions of ferrocyanides (Perl’s rgt) → siderotic granules found in nRBCs and some retics
any ferric ion in tissue reacts w ferricyanide → Prussian blue → used to assess BM iron reserves → useful in evaluating pt w anemia, iron overload & myelodysplasia (MDS) + Pappenheimer bodies!
terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)
TdT = intra-nuclear enzyme in stem cell & immature lymphoid cells w/in BM
90% present in ALLs, but only 5-10% in AML
acute leukemia cytochemistry table
AML vs ALL cytochem tests