KAAP 220 Biology Terms & Definitions for Exam 1 Study
1/218
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
219 Terms
Seven Characteristics of Life
1. Composed of one or more cells
2. Energy use and metabolism
3. Response to stimuli
4. Maintain homeostasis
5. Growth and development
6. Reproduction
7. Are organized
four basic processes in humans
respiration, digestion, circulation, excretion
what is anatomy?
Study of the STRUCTURE of body parts and their relationship to one another
what is physiology?
the study of FUNCTION of the body - how the body parts work and carry out their life sustaining activities
The central principle of physiology is
homeostasis
3 tenants of cell theory
1. cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals
2. cells are produced by other cells
3. cells are the smallest living unit
organ system that defends against infection and disease
lymphatic
organ system that delivers air to sites where gas exchange occurs
respiratory
sensor that is sensitive to a particular environmental change
receptor
integration center that receives and processes the information supplied by the receptor and sends out commands
control center
area of homeostatic regulatory mechanism that responds to commands by opposing the stimulus
effector
when an effector activated by the control center opposes the original stimulus to minimize change
negative feedback
when an initial stimulus produces a response that exaggerates or enhances the change in original conditions rather than opposing it
positive feedback
9 anatomical regions
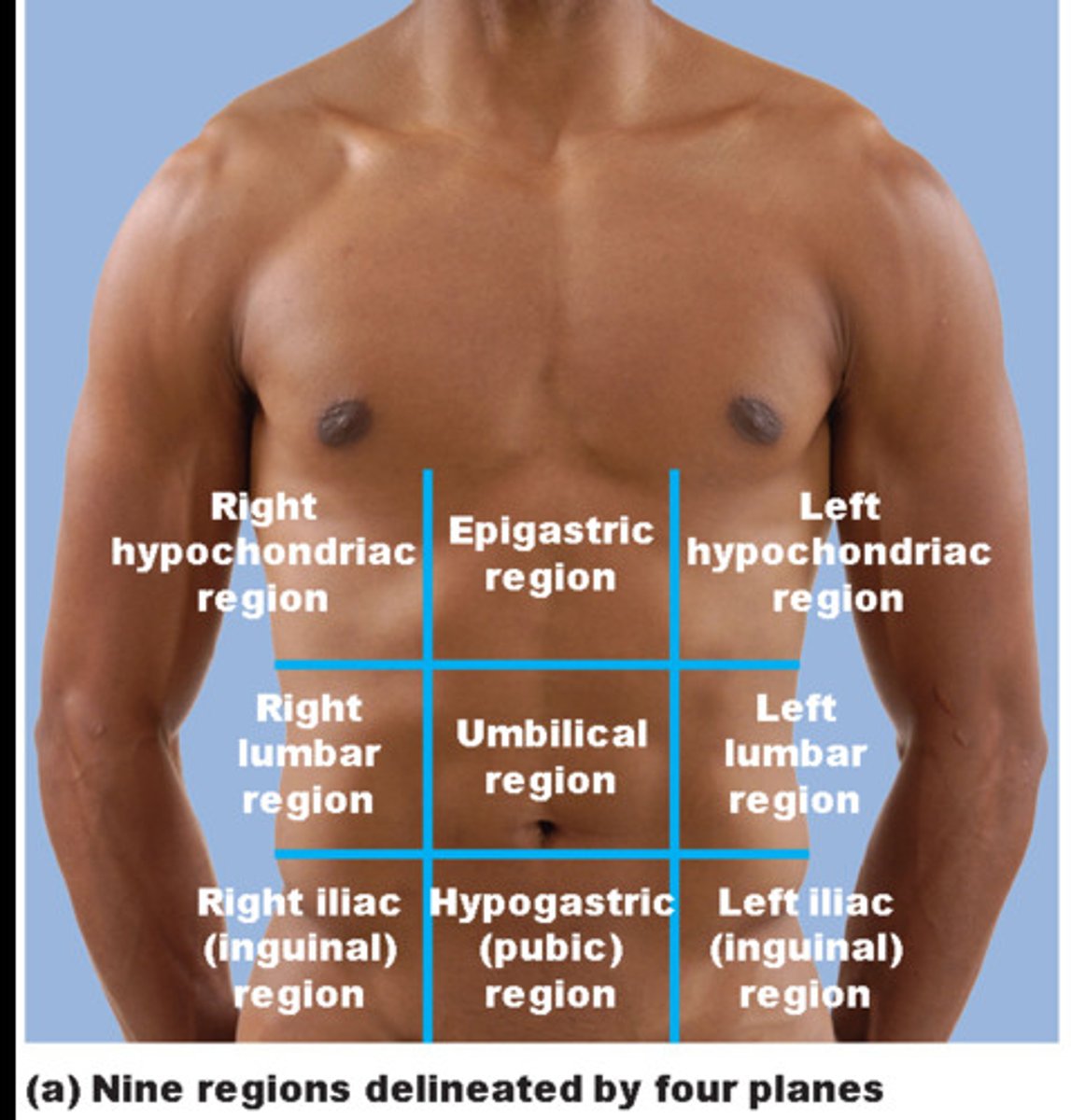
medial means...
toward the midline
lateral means...
away from the midline
proximal means...
Closer to the point of attachment to the trunk
distal means...
farthest from the point of attachment from the trunk
caudal means...
toward the tail
anterior or ventral means...
Front of body/body part
posterior or dorsal means...
Back of body/ body part
what plane separates anterior and posterior
frontal plane
what plane separates right and left
sagittal plane
what plane separates superior and inferior
transverse plane
What does the thoracic cavity contain?
The heart and lungs which are protected by the bony rib cage.
what kind of cavities house the lungs
pleural cavities ; separated by the mediastinum
What does the pelvic cavity contain?
reproductive organs, bladder, rectum
what kind of serous membrane lines the pelvic cavity
peritoneum
internal organs that are completely enclosed by body cavities
viscera
functions of serous membrane
protects organs from shocks and impacts; permits changes in size and shape of organs
smallest units of matter
atoms
what determines the mass number
number of protons and neutrons
what determines atomic number
number of protons
elements present in the body in very small amounts are called...
trace elements
elements that do not readily participate in chemical processes are said to be....
inert
movement of an object or change in the physical structure of matter is known as...
work
energy of motion
kinetic energy
stored energy is also known as
potential energy
quantity with a weight in grams = to the atomic weight
mole
enzymes proceed until...
equilibrium is reached
reactions that release energy
exergonic reactions
reactions where more energy is required than is released
endergonic
sheath of water molecules around an ion in a solution
hydration sphere
soluble inorganic substances whose ions conduct an electrical current in solution
electrolytes
a solution containing dispersed proteins or other large molecules
colloid
A ___ contains large particles in solution that will settle out due to gravity
suspension
low blood pH
acidosis
high blood pH
alkalosis
ionic compound consisting of any cation that is not H+ and any anion that is not OH-
salt
what functional group is NH2
amino
what functional group is COOH (double bone)
carboxyl
what functional group is OH
hydroxyl
what functional group is PO4 2-
phosphate
most important molecule for metabolic fuel in the body
glucose
molecules with the same molecular formula but different 3D structures
isomers
polysaccharide that is used for storage in human muscle cells; breaks down when there is a high demand for glucose
glycogen
macromolecule that forms essential components of all cells and acts as energy reserves
lipids
lipids derived from arachidonic acid
eicosanoids
lipids produced primarily by cells involved with coordinating the responses to injury or disease
leukotrienes
short fatty aid chains with 5 carbon ring; directs local cellular activities
prostaglandins
molecules found in the membrane of all animal cells; needed for cell growth and division; steroid
cholesterol
amino acids are transferred to the ribosome by...
tRNA
what part of the phospholipid is hydrophobic
fatty acid tails
what part of the phospholipid is hydrophilic
phosphate head
what structure of proteins form alpha helices and beta sheets
secondary structure
reactants in enzymatic reactions
substrates
what are all cells the descendant of
fertilized ovum
when daughter cells begin to develop specialized structural and functional characteristics
cellular differentiation
a molecule of ___ contains all the necessary codons to build a particular polypeptide
mRNA
during mitosis, chromatids separate into daughter chromosomes during...
anaphase
organelle that breaks down organic compounds and neutralized toxins
peroxisome
organelle that destroys foreign material, removes damaged organelles, and performs autolysis
lysosome
golgi apparatus function and structure
stack of flattened membranes (cisternae); store, alter, and packed synthesized products
organelle that stores genetic information, controls metabolism and protein synthesis
nucleus
smooth er structure and function
no ribosomes; synthesizes lipids and carbs
rough er structure and function
has ribosomes, protein modification and packaging
function of ribosomes
protein synthesis
organelle that produces ATP
mitochondria
organizing center containing pair of centrioles
centrosome
what organelles strengthen and support the cell, move materials
cytoskeleton
functions of the plasma membrane
physical isolation, regulation of exchange with the environment, sensitivity, structure
proteins that stabilize the membrane position
anchoring proteins
proteins that are detected by cells of the immune system
recognition proteins
proteins that bind to specific extracellular molecules (ligands)
receptor proteins
what do receptor proteins bind to
ligands
proteins that transport solutes across the membrane
carrier proteins
proteins that form a passageway completely through the plasma membrane
channels
something with hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts is known as...
amphipathic
layer of the plasma membrane formed by superficial membrane carbohydrates
glycocalyx
finger-like extensions of the plasma membrane
microvilli
layer of microfilaments just inside the plasma membrane that forms a lining
terminal web
strongest and most durable cytoskeleton elements
intermediate filaments
largest components of the cytoskeleton; built from tubulin
microtubules
cylindrical structures composed of short microtubules
centrioles
what side of the golgi is the receiving side
cis
what side of the golgi is the shipping side
trans
folds of the mitochondria are called
cristae
hollow tubes within the ER
cisternae
What does glycolysis do?
breaks down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate
What does the citric acid cycle (TCA) do?
completes the breakdown of pyruvate into carbon and hydrogen