Lecture 5 -- Food Prehension, Mastication and Salivation
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What are the principle organs involved in food prehension?
Lips, cheek, teeth and tongue.
How do horses adapt for food prehension?
Lips (Main prehensile structure) → Sensitive and mobile → Lips drawn back to sever grass with incisors during grazing
Vibrissae used to locate food (Have individual nerves going to the base of each vibrissae)
How do cattle adapt for food prehension?
Tongue (Main prehensile structure) → Long, rough and papillae → Tongue curves around grass → Draws it into the mouth and holds between the incisors and dental pad
Lips are less mobile and sensitive + Limited movement
How do sheep adapt for food prehension?
Similar to cattle
Upper lip is divided into left and right by cleft → For closer grass cropping
Tend NOT to swallow foreign objects
How do pigs adapt for food prehension?
Snout (Main prehensile structure) for rooting
Lower lip to transfer food into mouth
How do dogs and cats adapt for food prehension?
Tongue and teeth (Main prehensile structure) → Tongue: Lapping liquids
Lips are minimally important
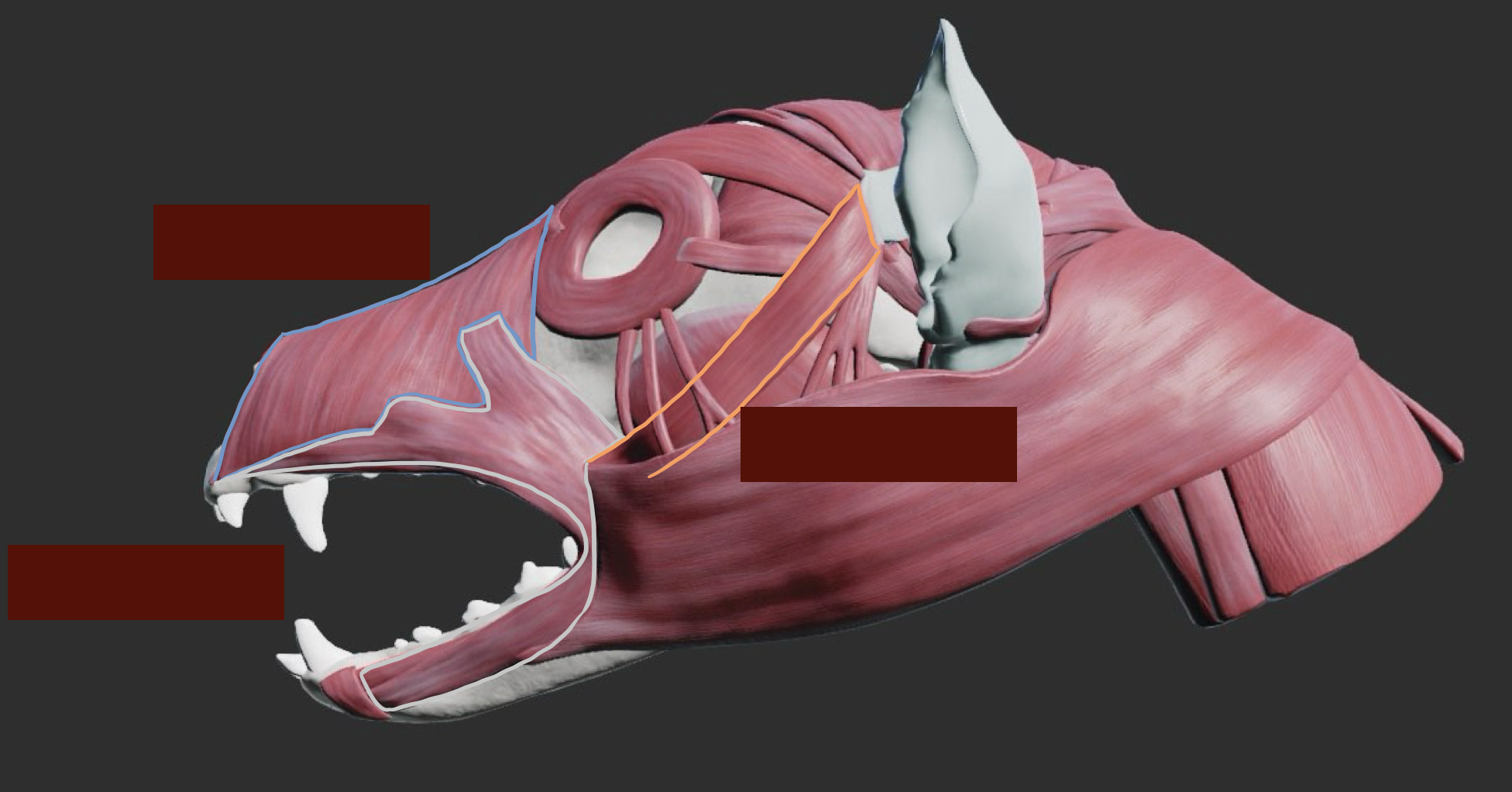
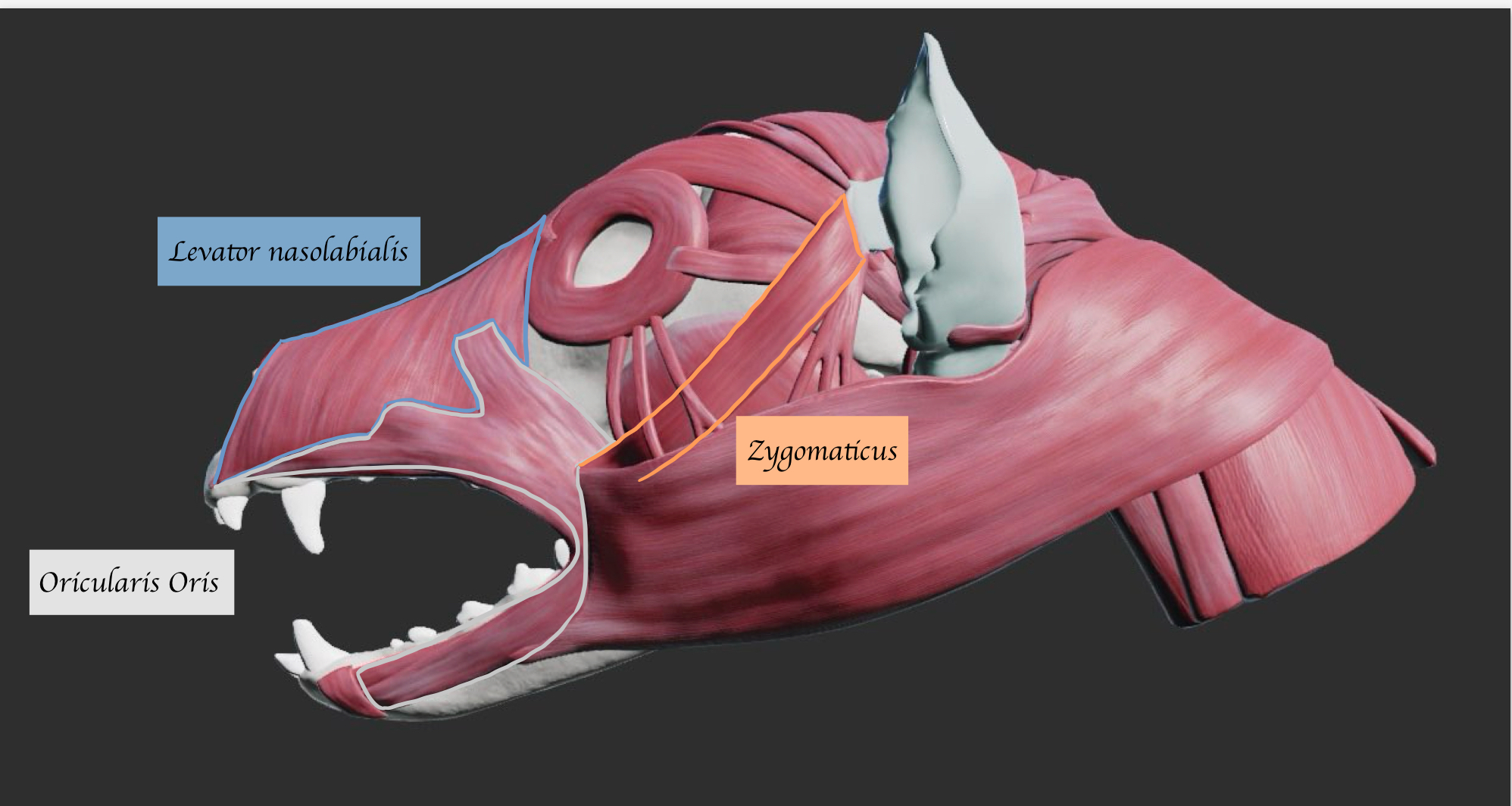
List all the muscles of the lips and their functions. Which nerves innervate these muscles (Motor and sensory) ?
Orbicularis oris (Ring of muscle around the mouth) - Sucking/ howling
Levator labii superioris - Lift the upper lip
Levator nasolabialis - Lift the upper lip and nostril
Depressor labii inferioris - Depress the lower lip
Caninus - Retractor 向後 of upper lip and nostril
Zygomaticus - Retractor of caudal commissure (corner of mouth) of lip → Help animals get food inside of their mouth + indicate the act of aggression
Innervated by
Motor: facial nerve
Sensory: Maxillary division of trigeminal nerve (Upper lip)/ Mandibular division of trigeminal nerve (Lower lip)
Identify the muscles of facial expression and prehension
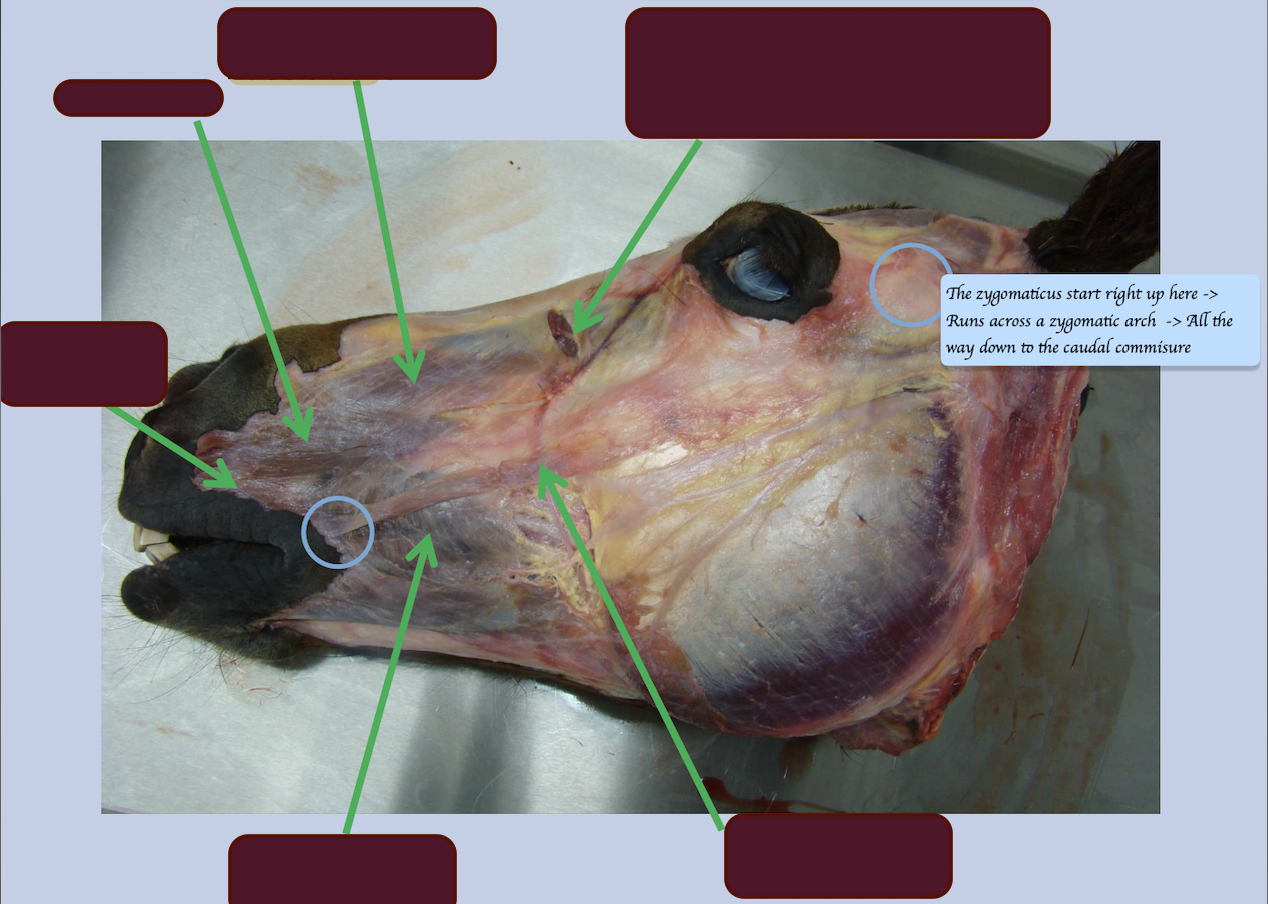
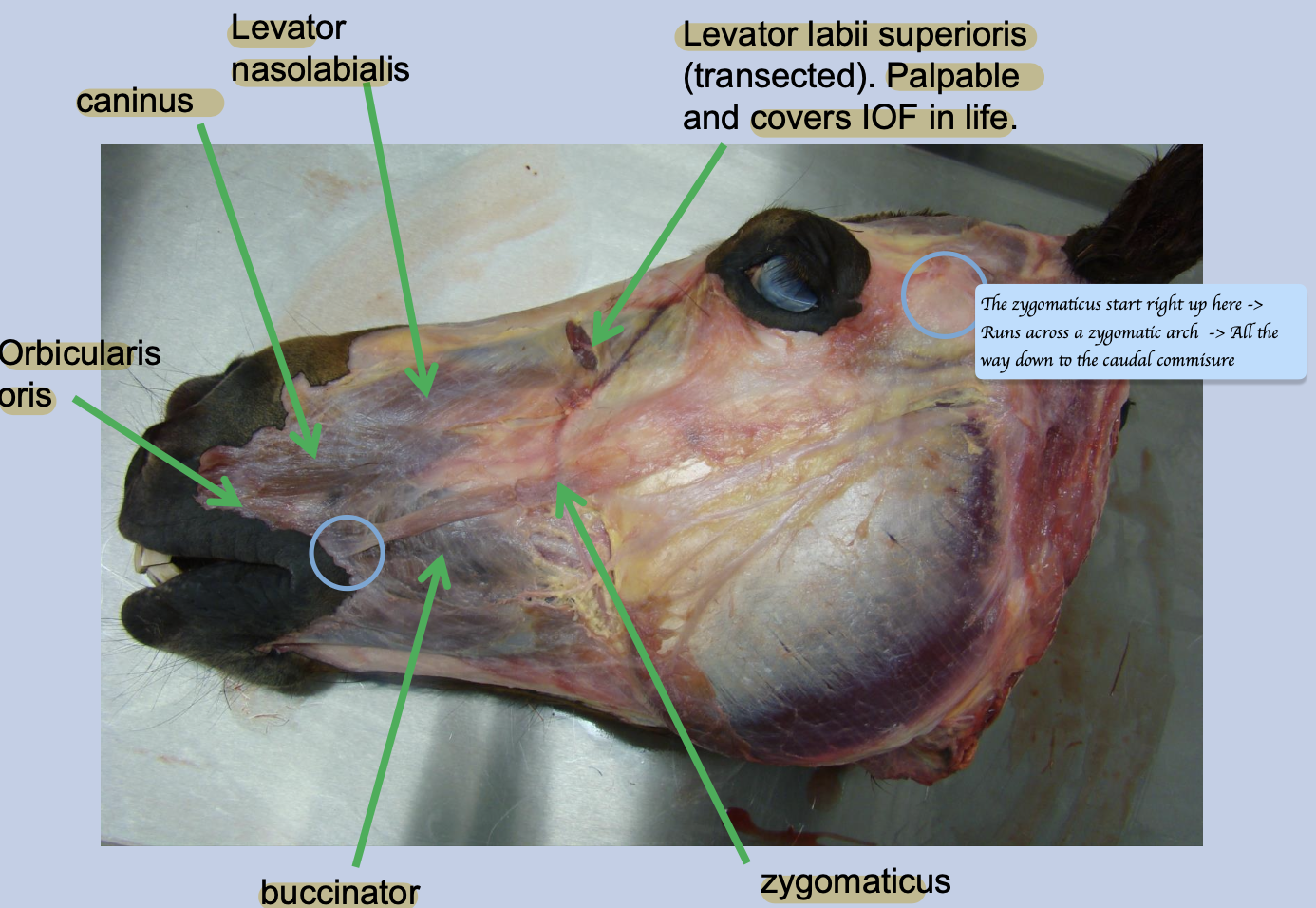
In carnivores, which muscles of the lip are absent?
Depressor labii inferioris → Action of depressing the lower lip is replaced by buccinator muscle
Name the muscles below.
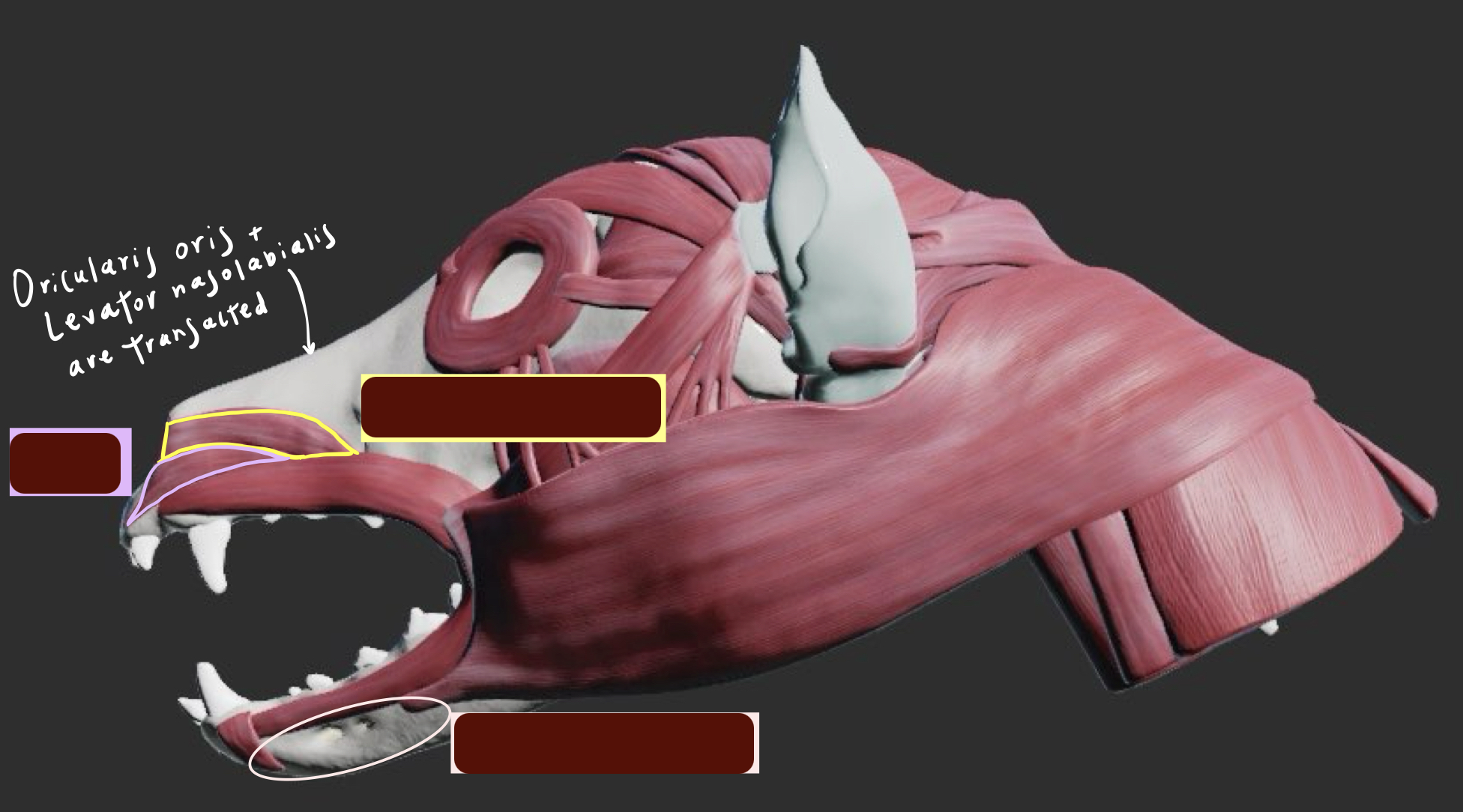
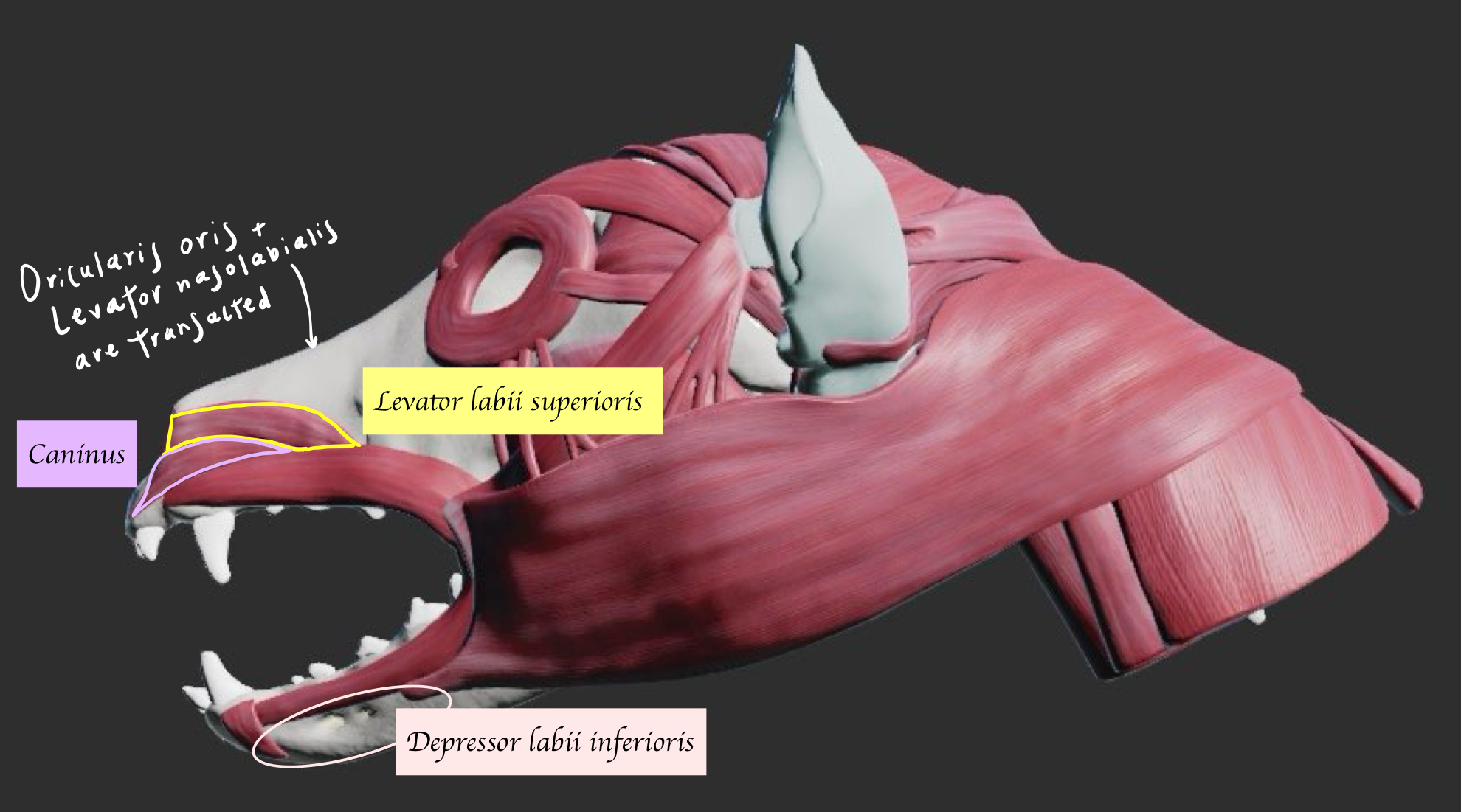
List out the cheek muscle. Which nerves innervate these muscles (Motor and sensory) ?
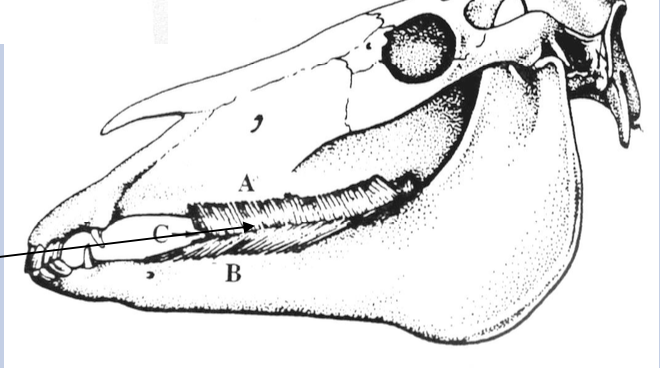
Buccinator
Function: Help move the food inside the mouth
Innervated by
Motor: facial nerve
Sensory supply for both internal (mucosa) + external (skin): Buccinator nerve of mandibular division of trigeminal nerve (Located on top of the pterygoid muscle)
Which nerve innervates the upper and lower teeth?
Upper - Maxillary division of trigeminal nerve
Lower - Mandibular division of trigeminal nerve
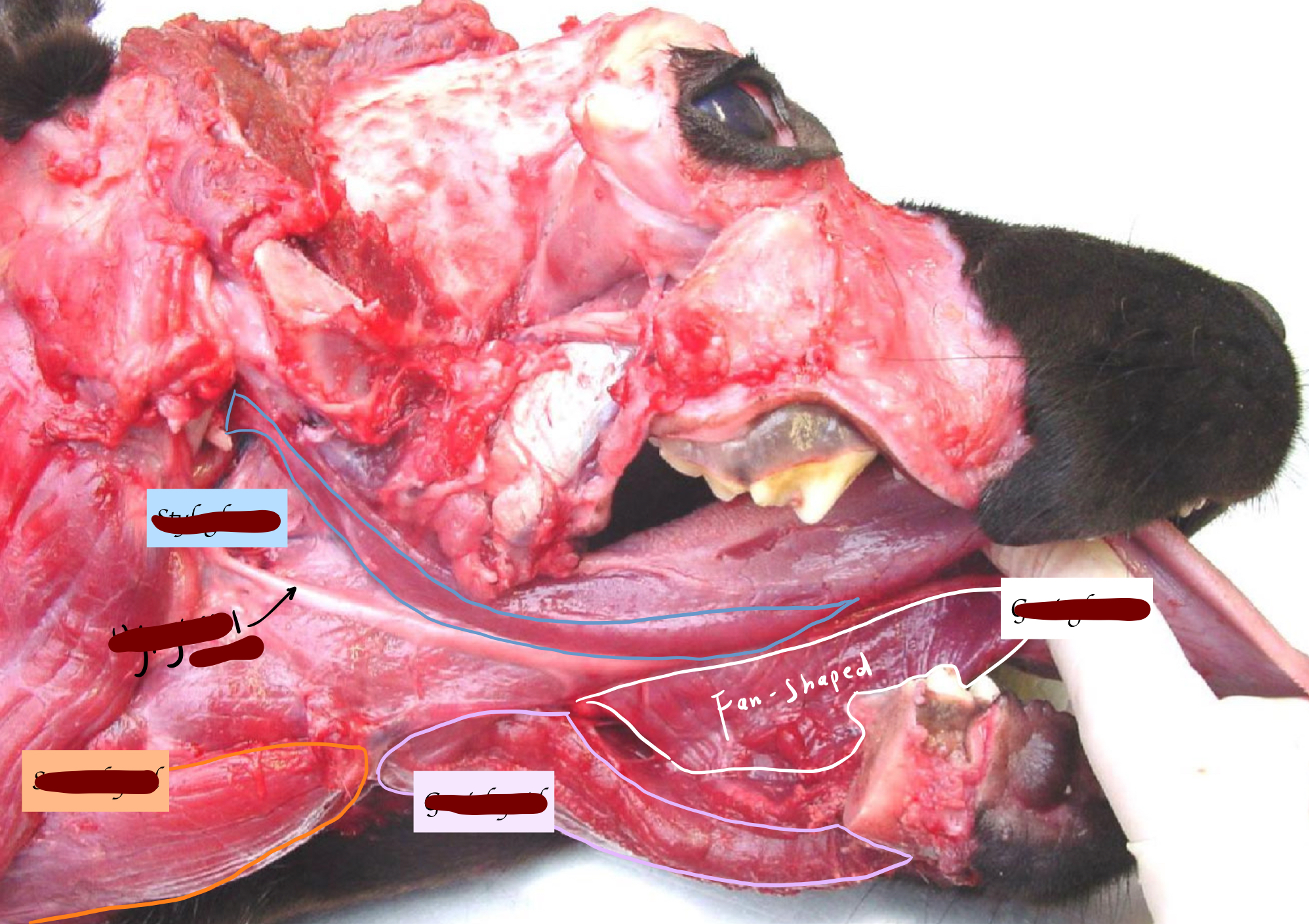
Name the extrinsic muscles of the tongue and their function.
Genioglossus (From genu to the tongue) - Pulls tongue out
Styloglossus (From stylohyoid to the tongue) - Retracts tongue
Hyoglossus (From basihyoid to the tongue) - Depress and retract tongue
Below the tongue
Geniohyoid (From genu to hyoid) - Pull the hyoid → Tongue move forward
Sternohyoid (From the sternum to hyoid) - Pull the hyoid caudally → Tongue move caudally
Name the muscles
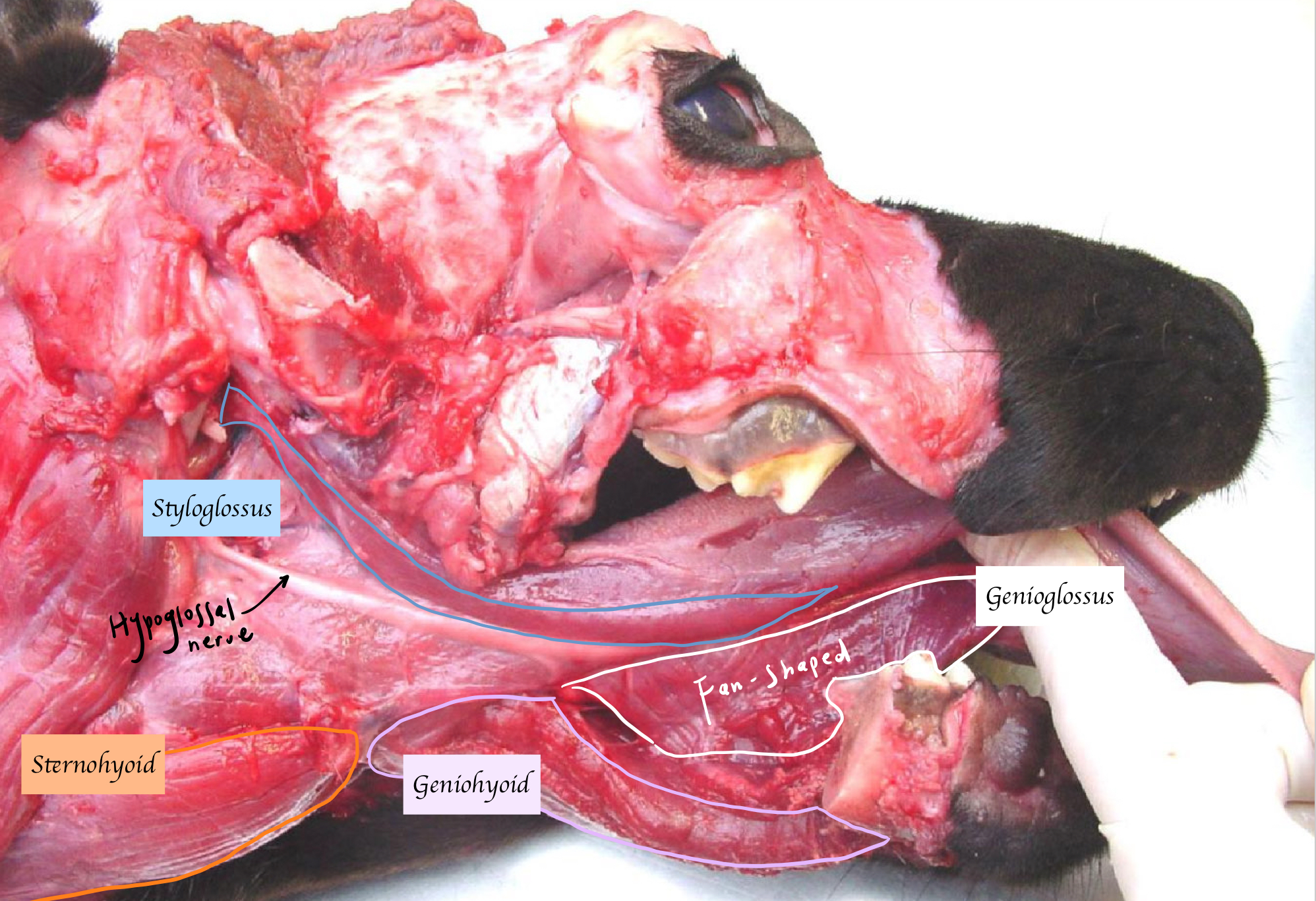
What nerve innervates the extrinsic muscles of the tongue?
Motor:
Hypoglossal nerve XII (SE)
→ Except sternohyoid (Innervated by cervical nerve)
Sensory:
Rostral 2/3 tongue: Lingual nerve of mandibular branch of trigeminal nerve (SA)
Caudal 1/3 tongue: Glossopharyngeal and vagus nerve (AA)
Taste:
Rostral 2/3 tongue: Chorda tympani branch of facial nerve (AA)
Caudal 1/3: Glossopharyngeal and vagus nerve (AA)
What is the type of epithelium the tongue lined?
Stratified squamous keratinised epithelium
The dorsal surface of the tongue is covered by the projections of mucosa. What is it named? What is its function?
Papillae
Function: Hose taste buds/ Give a rough surface for feeding and grooming
What marks the division between the rostral two thirds and caudal one third of the tongue?
Vallate papillae.
Which two joints involve in mastication?
Temporomandibular joint + Symphysial joint
The joint capsule of temporomandibular joint is subdivided into two compartments. What are those two compartments?
Are divided into meniscotemporal (upper) and meniscomandibular (lower) compartment by fibrocartilaginous articular disc
Which movement occur between the mandible and the disc?
Hinge Movements
Which movement occur between the disc and the temporal bone?
lateral movements (translations)
What are the different adaptations between dogs and herbivores for jaw movement?
Dogs: There is retroglenoid process → Prevent backwards movement of jaw → Allows for efficient hinge movements
Herbivores: Mandibular head is larger + Temporal surface is large and flat + No retroglenoid process → Able to grind their food
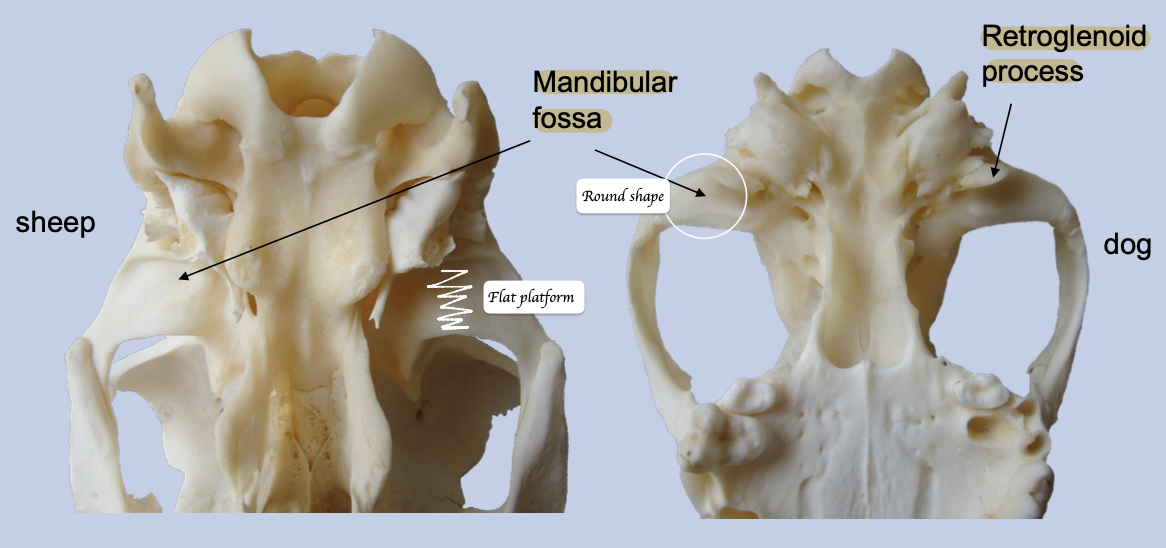
What are the differences between the symphysial joint
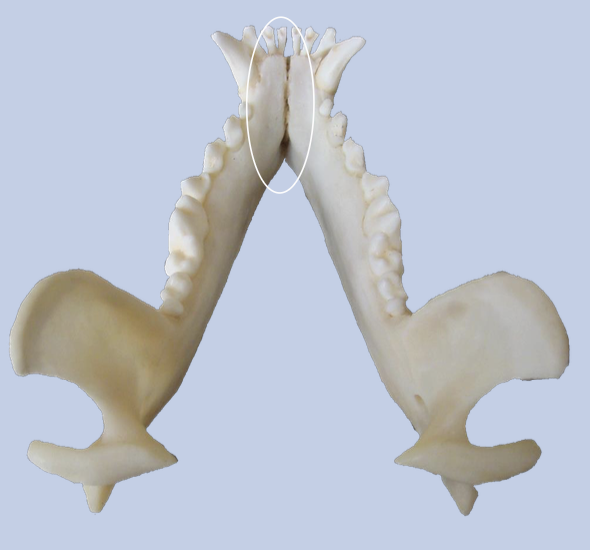
Unfused in carnivores; Most fused in horses
What is the function of symphysial joint?
Allows small changes in angulation of lower teeth → Aid food prehension
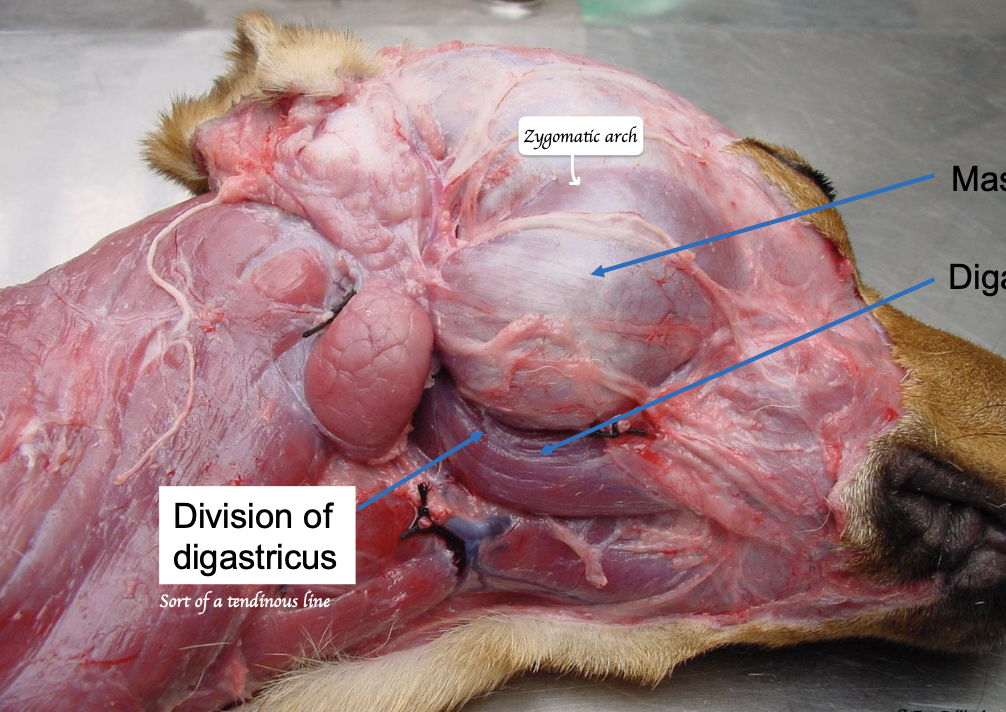
Name the jaw closing muscles.
Temporalis, Masseter, Pterygoids.
Where do the temporalis originate from and insert to? What is its function?
O: Lateral cranium
I: Coronoid process of mandible
Function: Move jaw upward
Where does the masseter lie? What is its function?
Lies lateral to the mandible and ventral to zygomatic arch
Function: Move jaw upward BUT move jaw laterally in herbivores
Where do the pterygoid originate from and insert to?
O: Pterygopalatine region
I: Medial aspect of mandible
Function: Move mandible upwards, medially and forward
Which nerve innervates the jaw closing muscle?
Mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve (SVE)
How many pterygoids in carnivores and herbivores?
Large medial pterygoid + Small lateral pterygoid
Carnivores: Regards as one structure
Herbivores: Two distinct muscles
Name the jaw opening muscle.
Digastricus
Where does the digastrics orginate from and insert to? Which nerve innervate the digastrics?
O: Jugular process of exoccipital bone
I: Ventral border of the mandible
N: Rostral part - Mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve (SVE); Caudal part - Facial nerve (SVE)
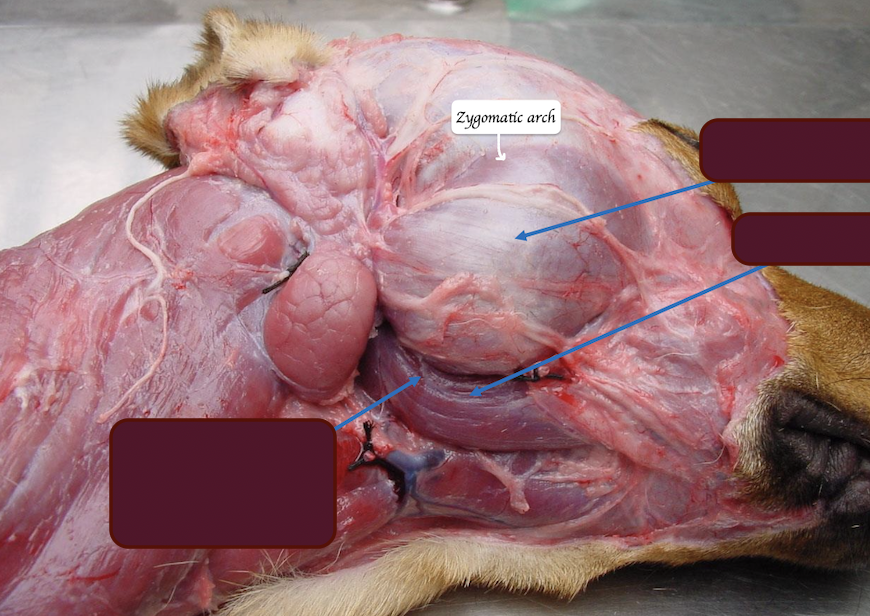
Name the muscles above
How the translational jaw movements perform?
Masseters and pterygoid work together
Right masseter contract + Left pterygoid contract → Jaw moves right
What are the differences between carnivore and herbivore regarding to the muscle for mastication?
Carnivore: Large area of origin for temporals + Small areas of insertion for masseter + Digastricus
Herbivore: Small area of origin for temporals + Large areas of insertion for masseter + digastrics
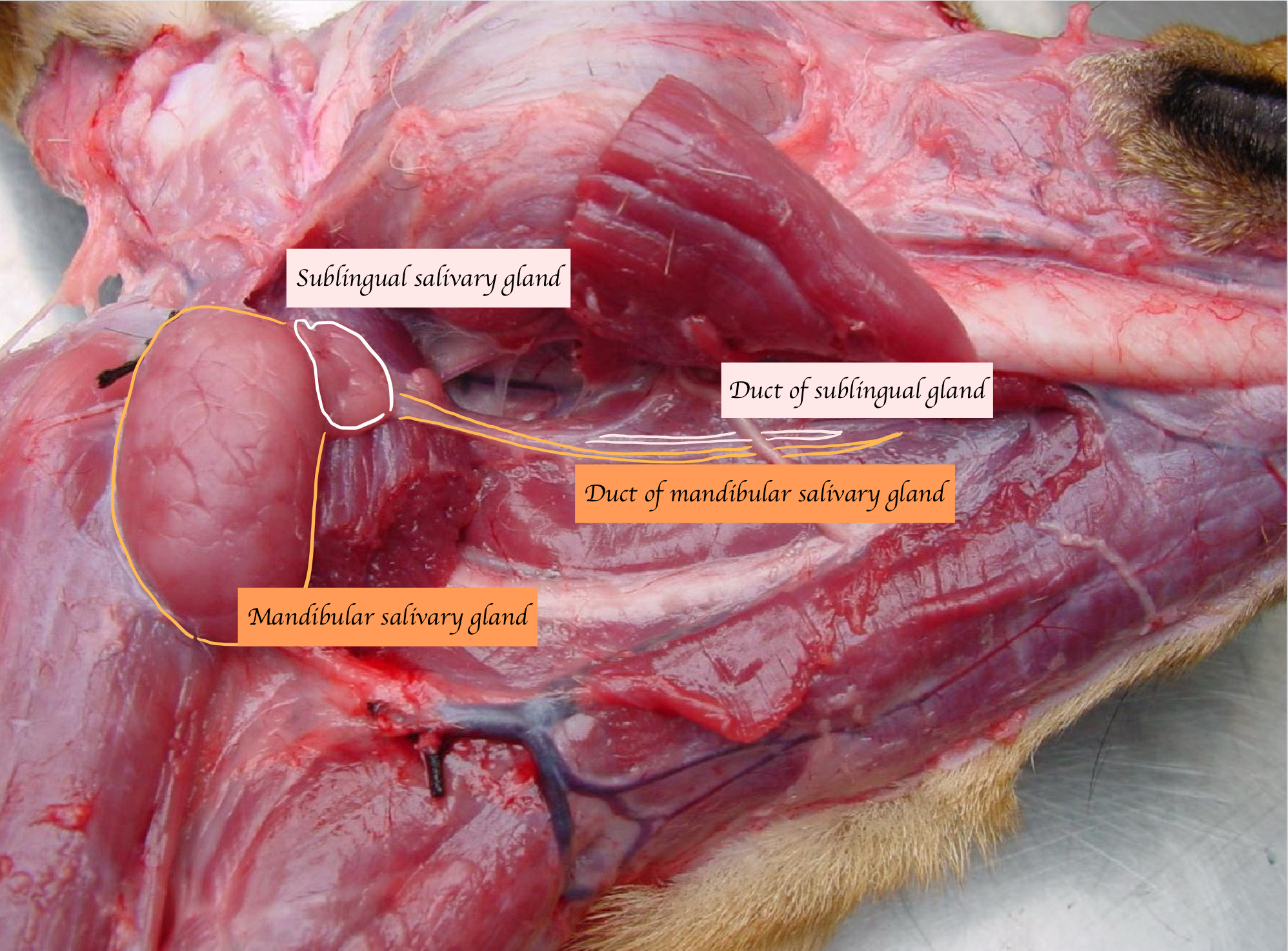
Name the large salivary glands. What types of saliva do they secrete?
Parotid: Serous
Mandibular: Mucous (Carnivores)/ Mixed
Sublingual: Mixed
Zygomatic (carnivores) or buccal (herbivores): Mixed
What are the function of saliva, regrading to different species?
Carnivores: Lubrication
Herbivores and omnivores: Contain amylase (Digestion of starch) + HCO3 and NaCl (Buffer to fatty acids)
Ruminant: Fluid for fermentation
What innervates the salivary gland?
Sympathetic: Cranial cervical ganglion
Parasympathetic: Salivatory nuclei in brainstem → Facial + Glossopharyngeal nerves → Trigeminal nerve
Where is the parotid salivary gland located, and where does it open?
Nestles around the bottom of ear cartilage
Open near upper premolar 4
Where do the mandibular and sublingual duct open?
Open on sublingual caruncle
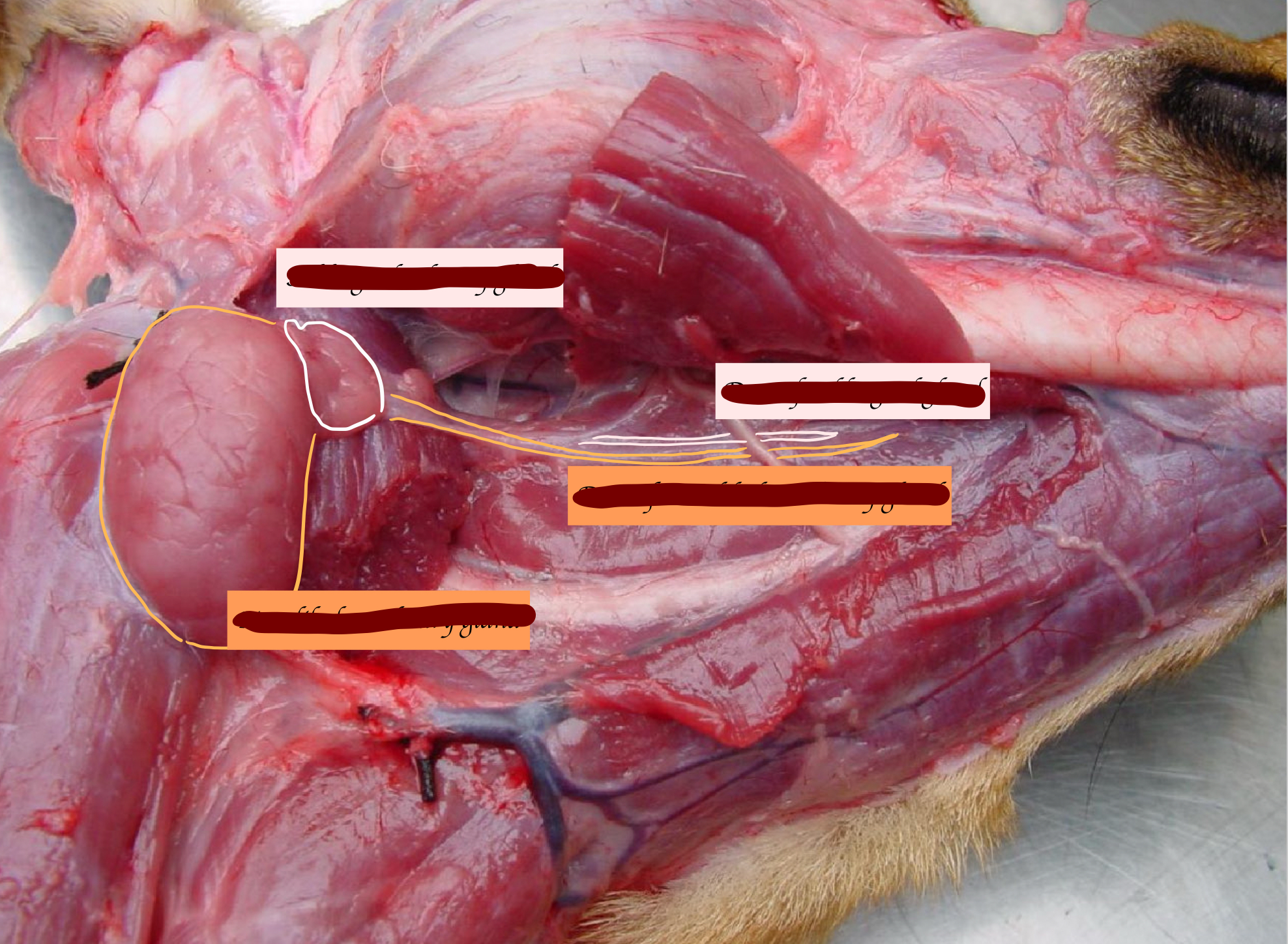
Where is the zygomatic salivary gland located, and where does it open?
Located near the rostral end of zygomatic arch + Ventral to the eyes
Opens near the last upper molar
Which salivary gland is the largest in horses?
Parotid salivary gland
Which salivary gland is the largest in pigs?
Mandibular salivary gland
Name the salivary gland in the below picture.
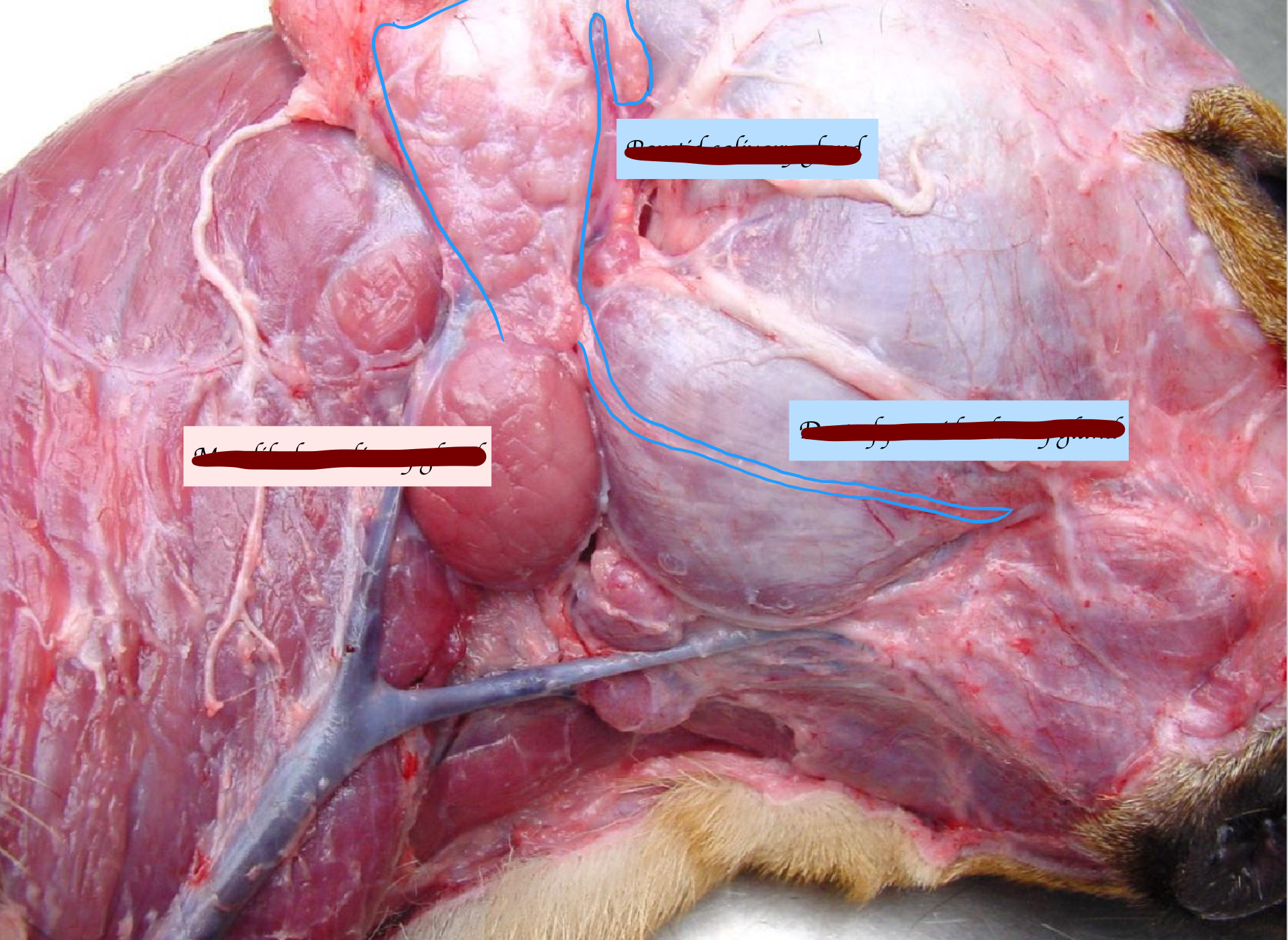
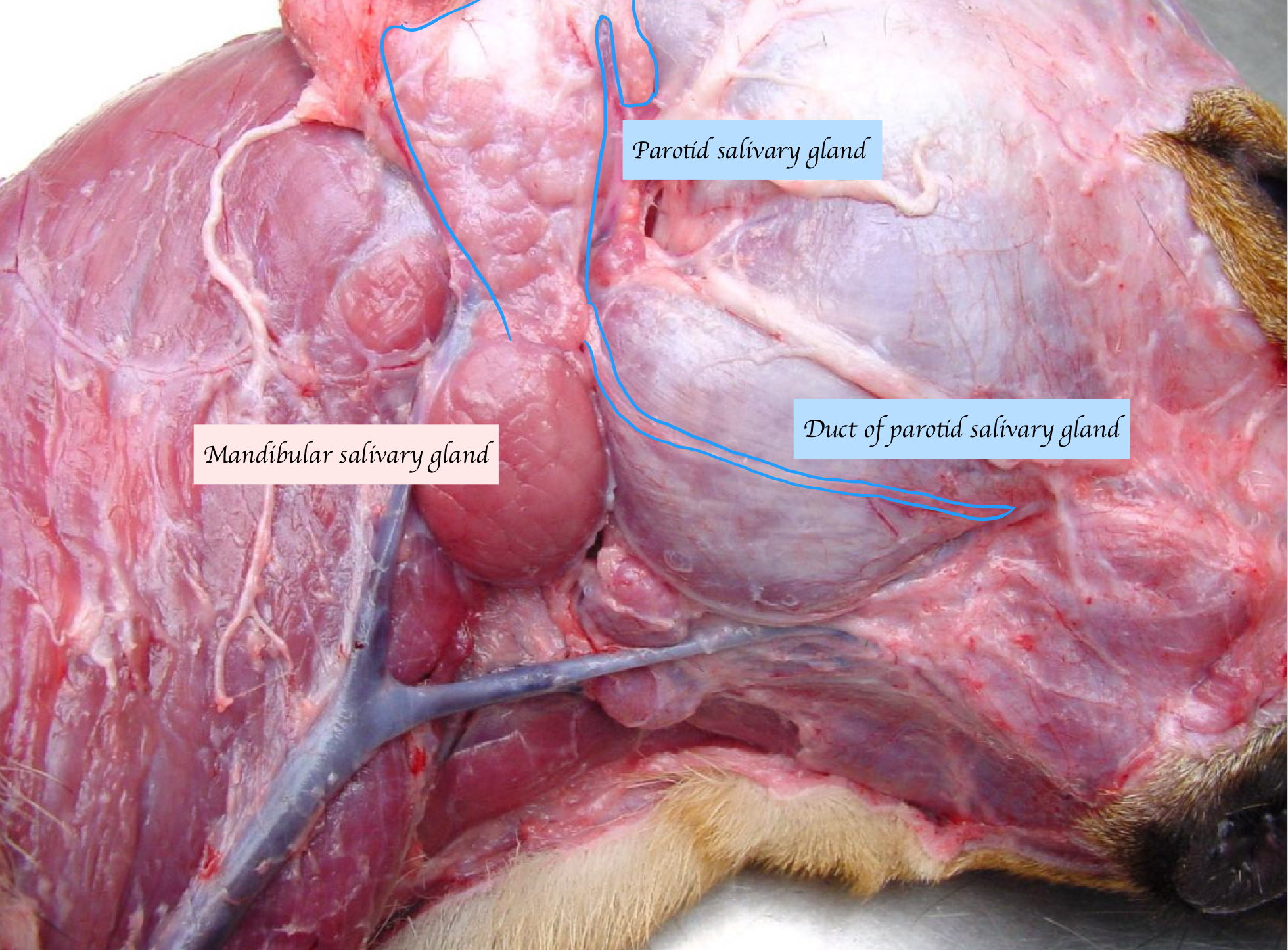
Name the salivary gland in the below picture.
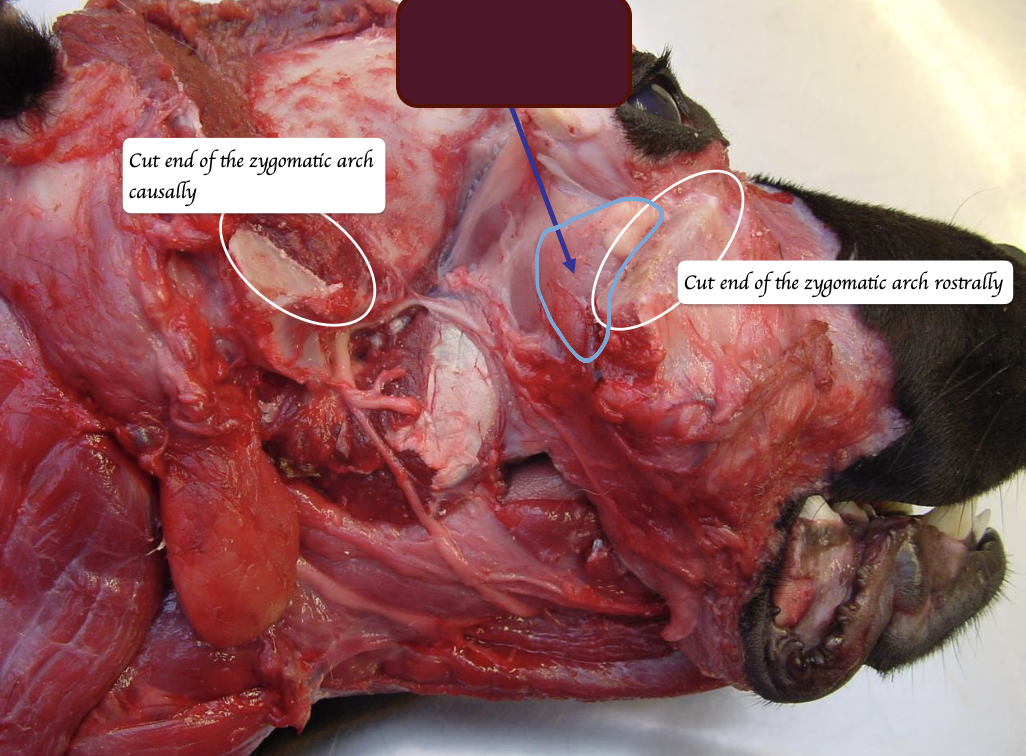
What is this?
Zygomatic salivary gland