AP Unit 7 Lesson 2: Female Reproductive System
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
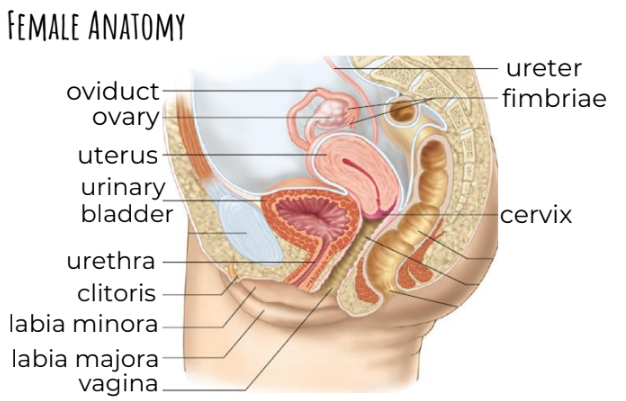
Female Anatomy Diagram
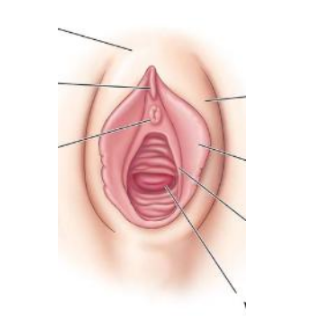
Vagina Diagram
Female Reproductive System - Functions (What do Ovaries do?)
Ovaries: paired gonads hat produce eggs, estrogen and progesterone
A female is born with 2 million follicles, reducing to 350000 - 400000 at puberty
Female Reproductive System - Functions pt. 2 (What do the Oviducts do?)
Oviducts (fallopian tubes): tubes from ovaries to uterus
The egg leaves the ovary and is moved into the oviduct by the fimbriae, muscle contractions, and cilia
Female Reproductive System - Functions pt. 3 (What does the Uterus and Endometrium do?)
Uterus: a muscular sac that nurtures embryo / developing fetus
Endometrium: lining of uterus - is made of connective tissue, glands and blood vessels
forms a placenta during pregnancy
Female Reproductive System - Functions pt. 4 (What does the Cervix and Vagina do?)
Cervix: opening to the uterus at the back of the vaginal canal
Vagina: muscular tube with mucosal lining
Female Reproductive System - Functions pt. 5 (What does the Labia Majora / Minora and Clitoris do?)
Labia Majora/Minora: outer / inner part of fat padded skin folds that extend from the vaginal opening to the clitoris
Clitoris: shaft of erectile tissue capped by the glans
houses sensory receptors
Ovarian Cycle: Menstruation
Menstruation: Decreased levels of female hormones of estrogen, progesterone, FSH, LH, and GnRH causes menstruation
The endometrium is at its thinnest during this
Ovarian Cycle: Follicular Phase
Follicular Phase: endometrial thickening
Increased levels of estrogen thicken the endometrium via proliferation of blood vessels and mucus glands
Ovarian Cycle: Ovulation
Ovulation: egg release
LH surge causes mature follicles to rupture, which releases the egg
Ovarian Cycle: Luteal Phase
Luteal Phase: corpus luteum produces increased amounts of progesterone and moderate amounts of estrogen
This causes the endometrium to thicken x2
What is the Uterine Cycle?
Describes the fluctuation in thickness of the endometrium
Uterine Cycle: Menstruation + Proliferative Phase
1) Menstruation: breakdown of endometrium due to low hormone levels
2) Proliferative Phase: endometgrium gets thicker due to increased estrogen levels
Uterine Cycle: Secretory Phase
3) Secretory Phase: Endometrrium continues to thicken + mature mucus (uterine) glands secrete mucus due to increased progesterone levels