Chapter 10: Reaction Rates, Catalysts, and The Boltzmann Distribution
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
rate of reaction definition:
the change in concentration of a reactant / product in a given time
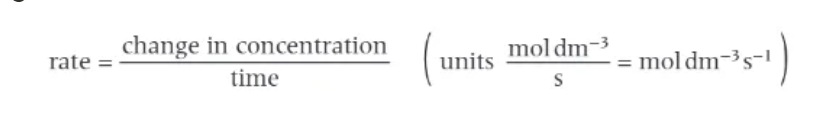
what shape does a typical concentration/time graph have?
curve:
steepest at start
becomes less steep
flattens off
4 factors that can change the rate of a reaction:
concentration (or pressure when reactants are gases)
temperature
use of a catalyst
surface area of solid contacts
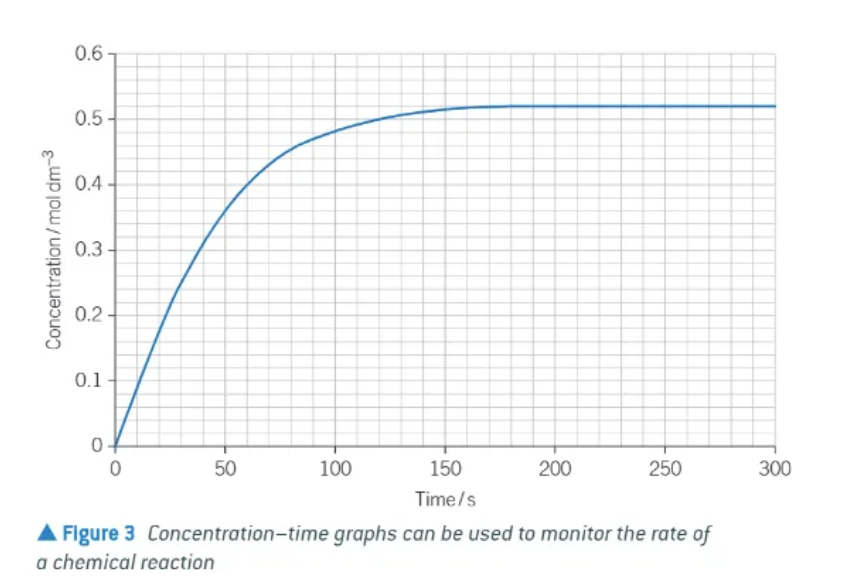
what does collision theory state?
2 particles must collide to react
why are some collisions effective, and some ineffective?
particles must collide with correct orientation.
particles must have sufficient energy to overcome the activation energy barrier of the reaction
how does increasing concentration affect the rate of reaction?
rate of reaction generally increases
increases the number of particles in the same volume
particles are closer together + collide more frequently
therefore → more frequency + successful collisions (correct orientation + sufficient energy) → increased rate of reaction
how does increasing the pressure of a gas affect the rate of reaction?
gas = compressed in a smaller volume → pressure of gas is increased → rate of reaction increases
concentration of gas molecules increases as the same number of gas molecules occupy a smaller volume
gas molecules = closer together + collide more frequently → leads to more effective collision in the same time
2 methods for following the progress of a reaction:
monitor removal (decrease in conc.) of reactant
monitor formation (increase in conc.) of product
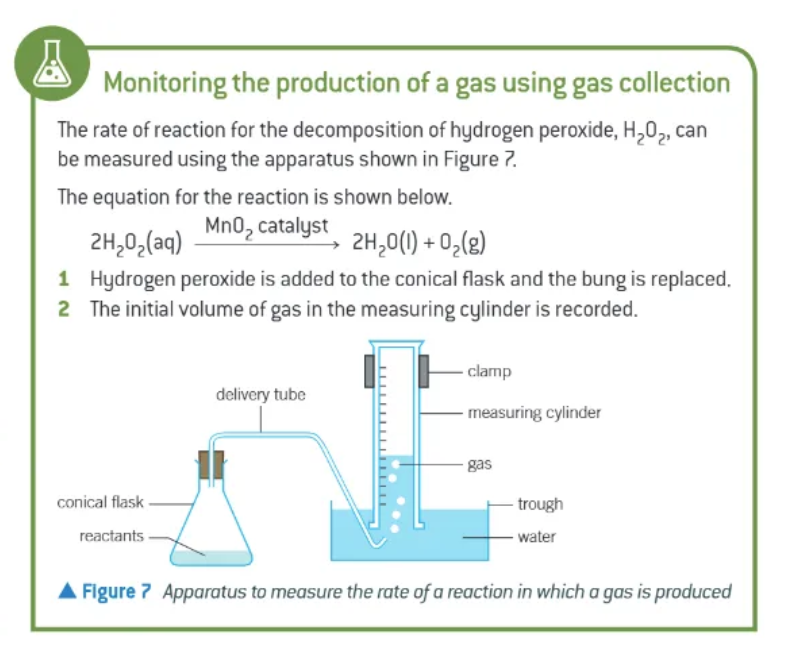
what 2 methods can be used for monitoring reactions that produce gas?
monitor volume of gas produced at regular time intervals → gas collection
monitor loss of mass of reactants using a balance → mass removal
draw the equipment for gas collection:
on a concentration-time graph, what represents the rate?
the gradient
on a (gas collection or mass lost) / time graph, what represents the rate?
the gradient
3 rules for catalysts:
catalyst not used up in the reaction
may form an intermediate / provide a surface on which the reaction can take place
catalyst is regenerated at the end of reaction
Exo + Endothermic reaction enthalpy profile diagrams (with catalyst!)
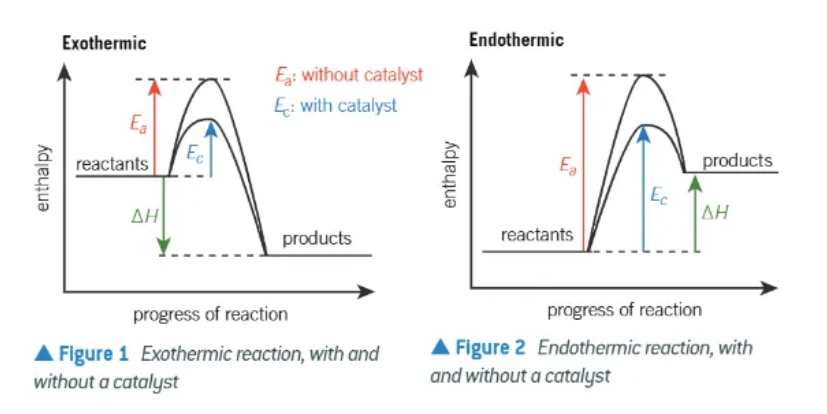
3 things to remember when drawing enthalpy profile diagrams?
reactants + products written out
∆H shown with an arrow pointing in correct direction
activation energy shown with upwards arrow
homogeneous catalysts:
same physical state as the reactants
forms an intermediate → breaks down to give catalyst + product
2 reactions that use homogeneous catalysis:
making esters (with sulphuric acid as a catalyst)
ozone depletion (Cl• catalyst)
heterogeneous catalyst:
different physical state from the reactants
usually solid → in contact with gaseous reactants/reactants in solution
reactant molecules are adsorbed (weakly bonded) → onto surface of catalyst → where the reaction takes place
product leaves surface of catalyst by desorption → at the end of the reaction
lower activation energy often means a lower…
temperature → this makes using catalysts more sustainable (less electricity etc.)
what does a Boltzmann distribution graph look like?
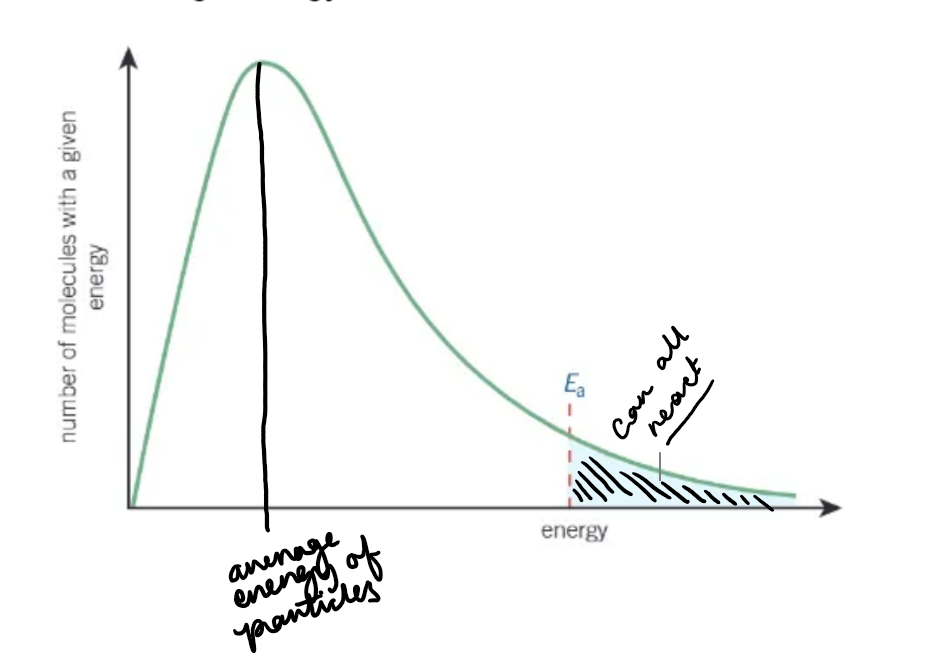
the curve should NEVER cross [which] axis on the Boltzmann distribution graph??
the x axis
why does the curve of a Boltzmann distribution graph start at the origin?
no molecules have 0 energy
what is the area underneath the curve of a Boltzmann distribution graph equal to?
the total number of molecules
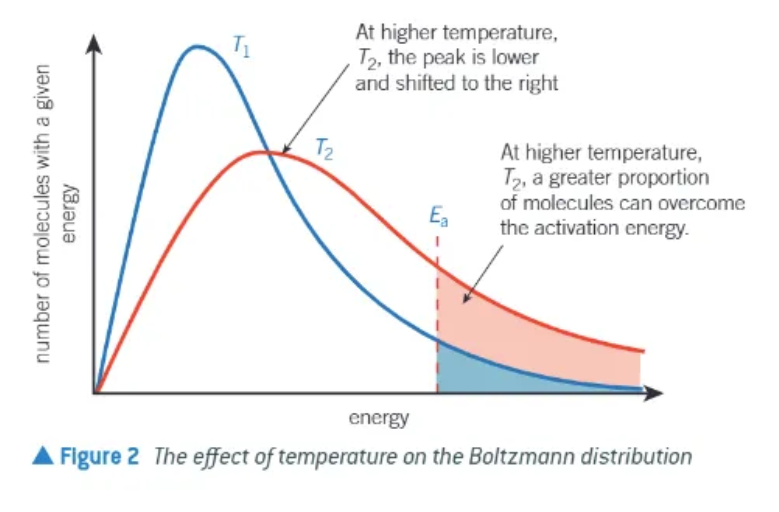
what happens to a Boltzmann distribution in changing temperature?
temperature increases ⬆average energy of molecules increases ⬆
more molecules have higher energy
graph is now stretched over a greater range of energy values
peak of the graph is now lower ⬇ on the y-axis and further along the x-axis → the peak of average energy is now higher (further towards the right!)
number of molecules = the same → area under the curve is the same
how does a higher temperature increase reaction rate?
more molecules surpass the activation energy
greater proportion of collisions → will lead to reaction
reaction rate is increased
collisions = more frequent as molecules are moving faster → increased energy of molecules is much more important than increased frequency of collisions!
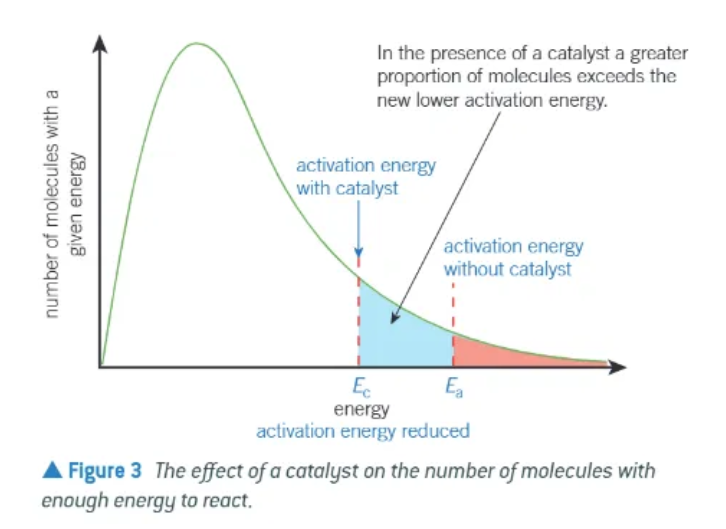
effect of a catalyst on a Boltzmann distribution:
alternative route → lower activation energy
compared to Ea, a greater proportion of molecules now have an energy equal to, or greater than the lower activation energy, Ec. On collision, more molecules will reacts to form products → increase in rate of reaction
the Haber process is an example of a [what] reaction?
reversible
dynamic equilibrium definition:
the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction
the concentrations of reactants and products do not change
in a closed system
le Chatelier’s principle:
when a system in equilibrium is subjected to an external change, the system adjusts itself to minimise the effect of that change
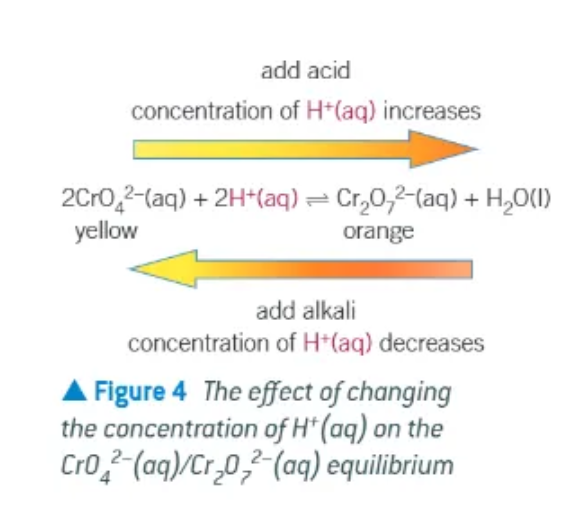
Which experiment can be used to investigate the changes to position of equilibrium with concentration?
the equilibrium between yellow aqueous chromate ions and orange aqueous dichromate ions
add yellow potassium chromate ions to a beaker → K2CrO4 to a beaker
add dilute sulphuric acid, H2SO4 dropwise until there is no further change → solution turns an orange colour
add aqueous sodium hydroxide, NaOH, until there is no further colour change. The solution turns back to a yellow colour
adding H2SO4 increases the concentration of H+ ions → increases the rate of the forwards reaction, causing the position of equilibrium to shift to minimise the change in H+ concentration
position of equilibrium shifts to the right → making more products
adding NaOH increases the number of OH- ions. position of equilibrium shifts to the left, making more the H+ reactant → a new position of equilibrium is established.
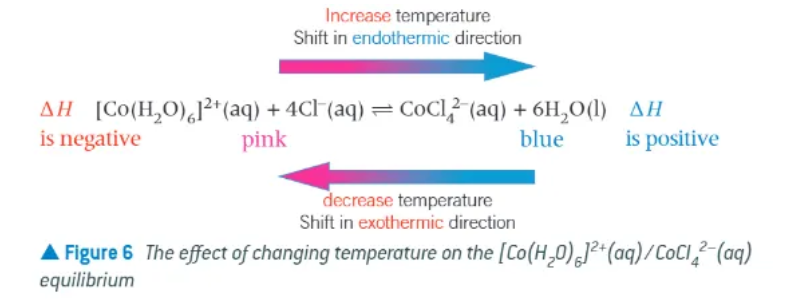
how can we investigate changes to the position of equilibrium with temperature?
dissolve cobalt chloride in water in a boiling tube
add a small quantity of HCl
place the boiling tube in some iced water → solution colour is pink
set up a boiling water bath and transfer the boiling tube into the boiling water → solution turns a blue colour
transfer the boiling tube back to the iced water → solution turns pink again
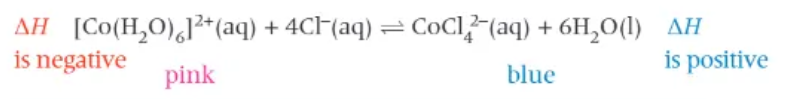
what can be added to help in the colour change of dissolving Cobalt Chloride in a dynamic equilibrium?
Hydrochloric acid → eq. shifts to the right!
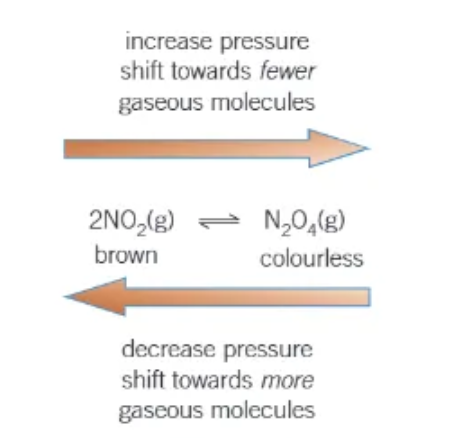
does a change in pressure affect equilibrium?
changing the pressure of a system containing gases in equilibrium may result in the position of equilibrium changing → only if there are more gaseous molecules on one side of the equation that the other!
the pressure of a gas is proportional to its…
concentration → two moles of 2NO2 (g) will have 2x the concentration and 2x the pressure of 1 mole of N2O4 (g)
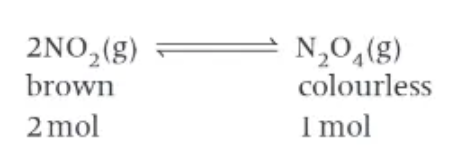
effect of changing pressure on 2NO2(g) ⇌ N2O4 (g)
does adding a catalyst have an effect on equilibrium?
no → merely speeds up the rates of the forward and reverse reactions equally. A catalyst will, however, increase the rate at which an equilibrium is established
Kc formula:
using the EQUILIBRIUM concentrations!
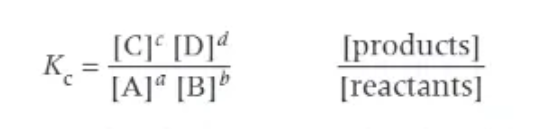
what does the Kc value tell us?
→ Kc = 1 → equilibrium is halfway between reactants + products
→ Kc > 1 → equilibrium sits towards the products
→ Kc < 1 → equilibrium sits towards the reactants