AP Comp Gov- UK
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Vexillology
Study of flags
UK's Regime
Constitutional/Parliamentary Monarchy (Democracy) – King/Queen doesn’t make decisions, decisions made by Parliament, has Democratic Consolidation (Advanced Democracy)
Head of State
King Charles III

Head of Government
Prime Minister – Keir Starmer

Head of Opposition
Kemi Badenoch

Political Culture
Multi-Nationalism
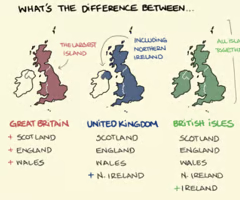
UK divided into England, Scotland, Wales, N. Ireland
Political Stability
Ability of a government and its institutions to function without major interruptions, violence, or sudden changes in leadership
Unitary State
Power in central government (London) with devolved powers to Scotland, Wales, N. Ireland – London can take powers back.
Devolution
Power to decide on education, health, and social services.
Magna Carta
Charter of Political Rights given to barons by King John in 1215.
Bill of Rights (UK) 1689
Limits monarch power; free elections; freedom of speech in Parliament; no taxation without Parliament’s agreement.
Parliamentary Act (1911)
Gave parliament power to pass acts without Lords’ approval

Parliamentary Act (1949)
Reduced the time Lords could delay bills
Uncodified Constitution
A country's system of government where the fundamental rules are not contained in a single, written document.
Parliamentary Sovereignty
What Parliament says is final.
Statutes
Written laws enacted by legislatures.
Common Law
Legal system based on custom and court rulings
Conventions
Accepted practices (like PM from majority party).
European Influence
European Convention on Human Rights, until Brexit, EU treaties shaped law.
Parliament
Lawmaking body of the British Gov -the UK's legislature.
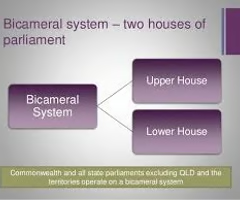
House of Commons
The first legislative body of Parliament whose members are elected. The lower house of parliament. Has more power then the house of Lords.
House of Lords
Members are appointed rather than chosen by voters. Members are usually bishops, hereditary peers, and life peers. The upper house of parliament. Has less power then the house of comons.
Elections
As a UK citizen, you cast one vote in a general election
You vote for one candidate to represent your local area (constituency)
There are 650 constituencies across the UK (based on population)
Constituency Result
Each elects one Member of Parliament. The candidate with the most votes wins – first-past-the-post system. That MP represents your area in the House of Commons
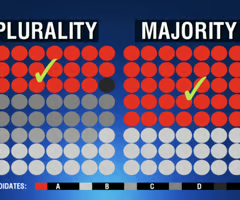
Plurality
Most votes but not a majority.
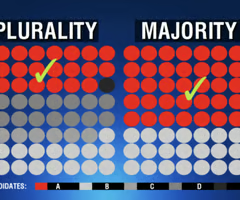
Majority
More than half.
Party Totals
After all constituencies vote, the party totals are added up. Party with most Members of Parliament usually governs
Who Governs?
If a party wins a majority of Members of Parliament (326 seats) → they form the government.
The leader of that party becomes Prime Minister
If no party wins a majority → parties may form a coalition or minority government
Party Selections
Candidates don’t have to be from district; leaders get safe seats
First-past-the-post
Candidate with most votes wins single-member district.
Hung Parliament
No party majority (326 seats); may form coalition or minority government.
Snap Elections
Early election called by Prime Minister (with Parliament approval)
Referendums
Citizen vote on single issue; rare in UK
Political Institutions
Structure of government: executive, legislature, judiciary
Bicameral
Two-house legislature
Hereditary Peers
House of Lords members with inherited titles
Life Peers
Appointed for life for distinguished service
Bishops
Heads of Church in major cities
The Government
Cabinet + Prime Minister + Civil Service under the Crown
The Crown
Symbolism, tradition, loyalty; politically neutral
Westminster
Neighborhood of government

Whitehall
Main British government offices

Downing Street 10
Prime Minister’s residence

Fusion of Powers
Executive and Legislative branches intertwined
Prime Minister
Leads Cabinet, directs policy, calls snap elections
Cabinet
Senior ministers leading departments; support PM publicly
Bureaucracy
Civil service – career officials implementing policy
Vote of No Confidence
Parliament votes on whether PM should stay in power
Opposition MPs
↓ calls for a no-confidence vote
↓House of Commons (all MPs) votes
↓ majority decides
→If government WINS
PM stays in power
→If government LOSES
Government must resign OR
New general election is called

Constitutional Monarch
Reigns but doesn’t rule; ceremonial role
Independent Judiciary
Separate from Parliament; UK Supreme Court (since 2009)
Code Law
Detailed legal codes; judges apply as written
Three Legal Jurisdictions
England & Wales, Scotland, N. Ireland
UK Supreme Court
Final court of appeal; decides devolution issues
Judges
Appointed by Judicial Appointments Commission. Appointments approved by the monarch on advice of the Prime Minister & Lord Chancellor.
Civil Liberties
Constitutional freedoms guaranteed to all citizens
European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR)
Lists basic rights: life, free speech, fair trial, no torture, etc.
Empire
Former colonies; immigration legacy
Immigration
Post-WWII waves shaped modern identity
Globalization
EU membership & Brexit – sovereignty vs integration
Cleavages
Political divisions among citizens
Consensus & Stability
Citizens accept democratic rules, gradual change
Pragmatism
Preference for practical, non-ideological solutions
Civic Culture
Voting, debate, trust in legitimate opposition
Respect for Tradition & Rule of Law
Pride in Parliament, monarchy, common law
Social Movements
Groups advocating for broad social change
Grassroots Movements
Hard to suppress, hard to organize
Interest Groups
Advocate for specific interests
Pluralism
Many interest groups competing for influence
Corporatism
Government co-opts groups for policy support
Quangos
Government-funded but independent organizations
Privatization
Selling public services to private companies
Welfare
Government programs for basic needs (e.g., NHS)
Austerity
Spending cuts to reduce debt
Insularity
Sense of separation from Europe
Brexit
British exit from the European Union
Conservative Party
Right-wing party favoring free markets and property ownership
Labour Party
Center-left party advocating reform and a peaceful transition to socialism, in time providing a viable alternative to the revolutionary emphasis of Marxism.
Liberal Democrats
Centrist-to-centre-left party supporting liberty, intervention for social and economic equality, environmental protection, and workers' rights.
Green Party
Focuses on environment and social justice.
Reform UK
Right-wing populist party

Scottish National Party
Campaigns for Scottish independence, most popular party in Scotland.

Plaid Cymru
Nationalist party in Wales, advocates more rights for the Welsh people, including use of the Welsh language.

Sinn Féin
Irish independence party, want to reunite Republic of Ireland and Northern Ireland.

Coalition government
two or more parties join together
Minority government
One party rules with fewer than 326 seats, but needs support from others to pass laws.